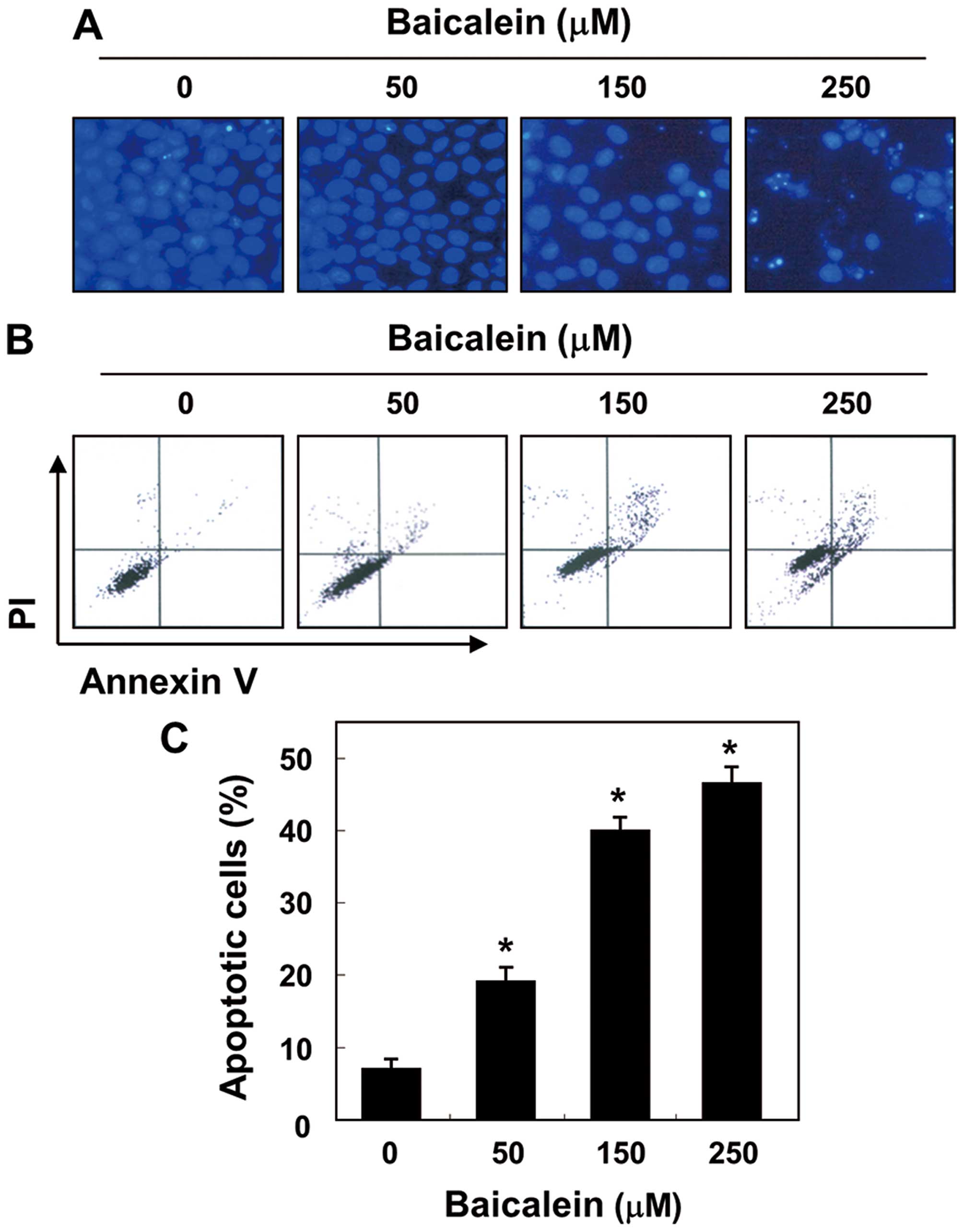
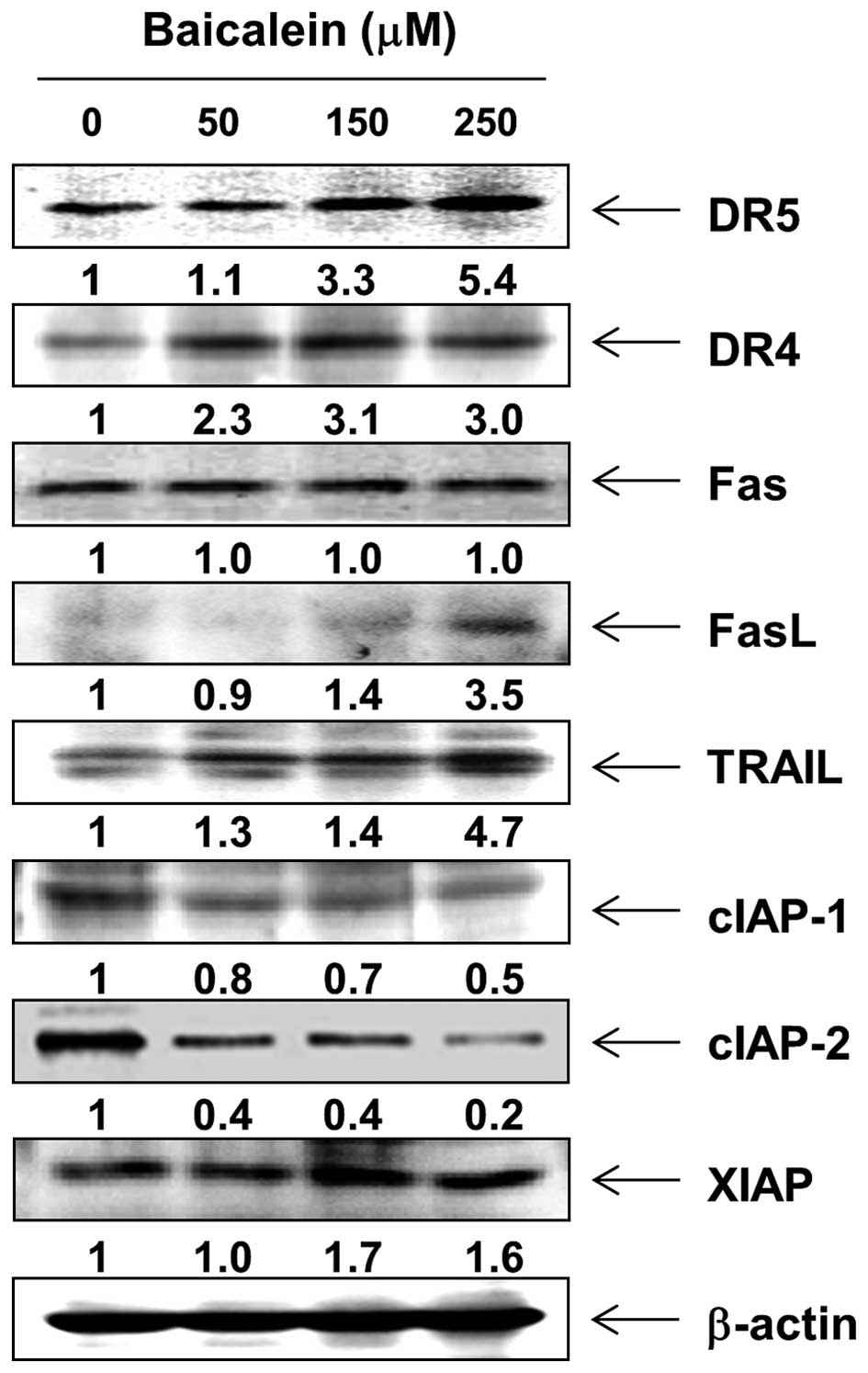
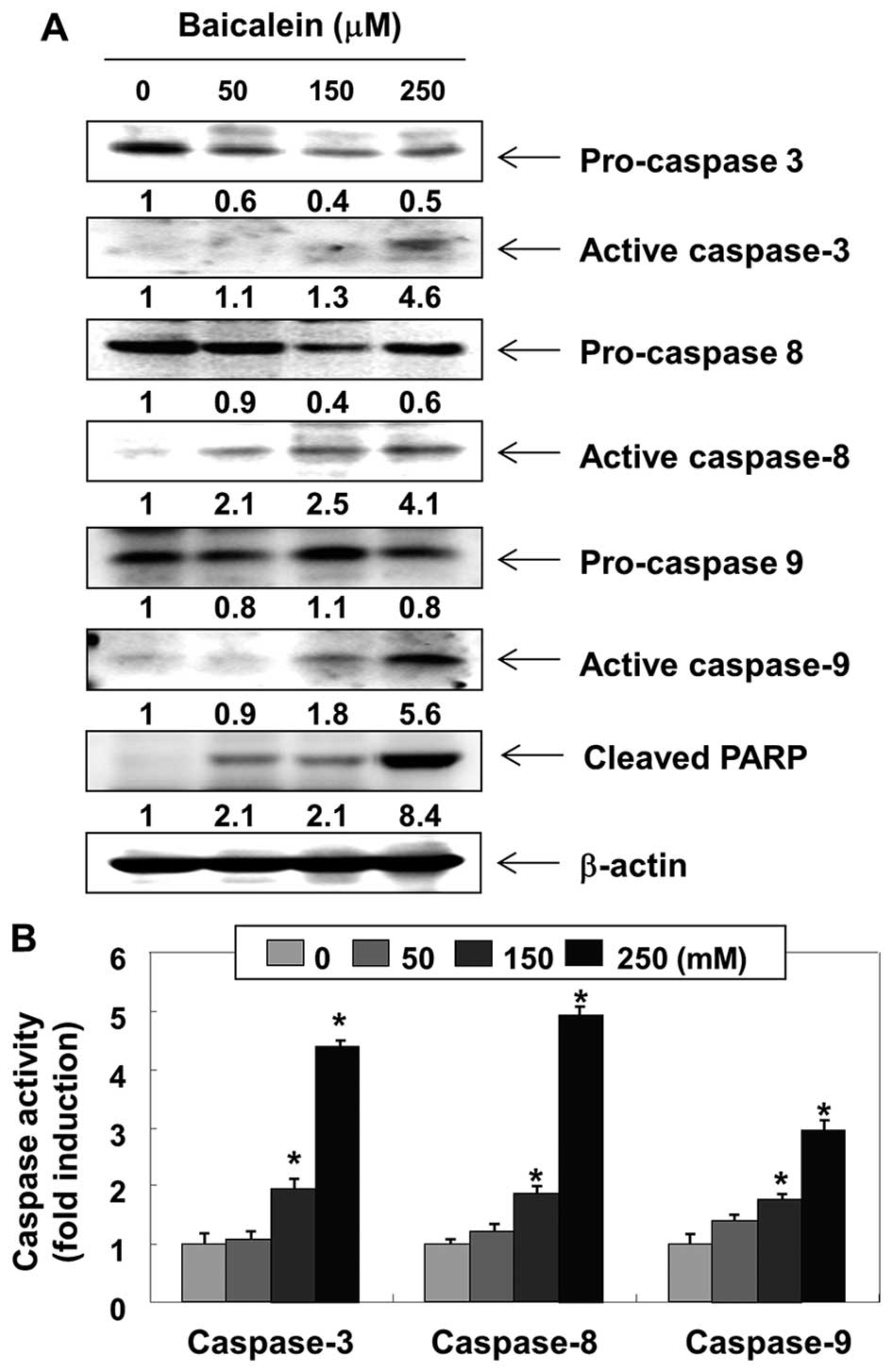
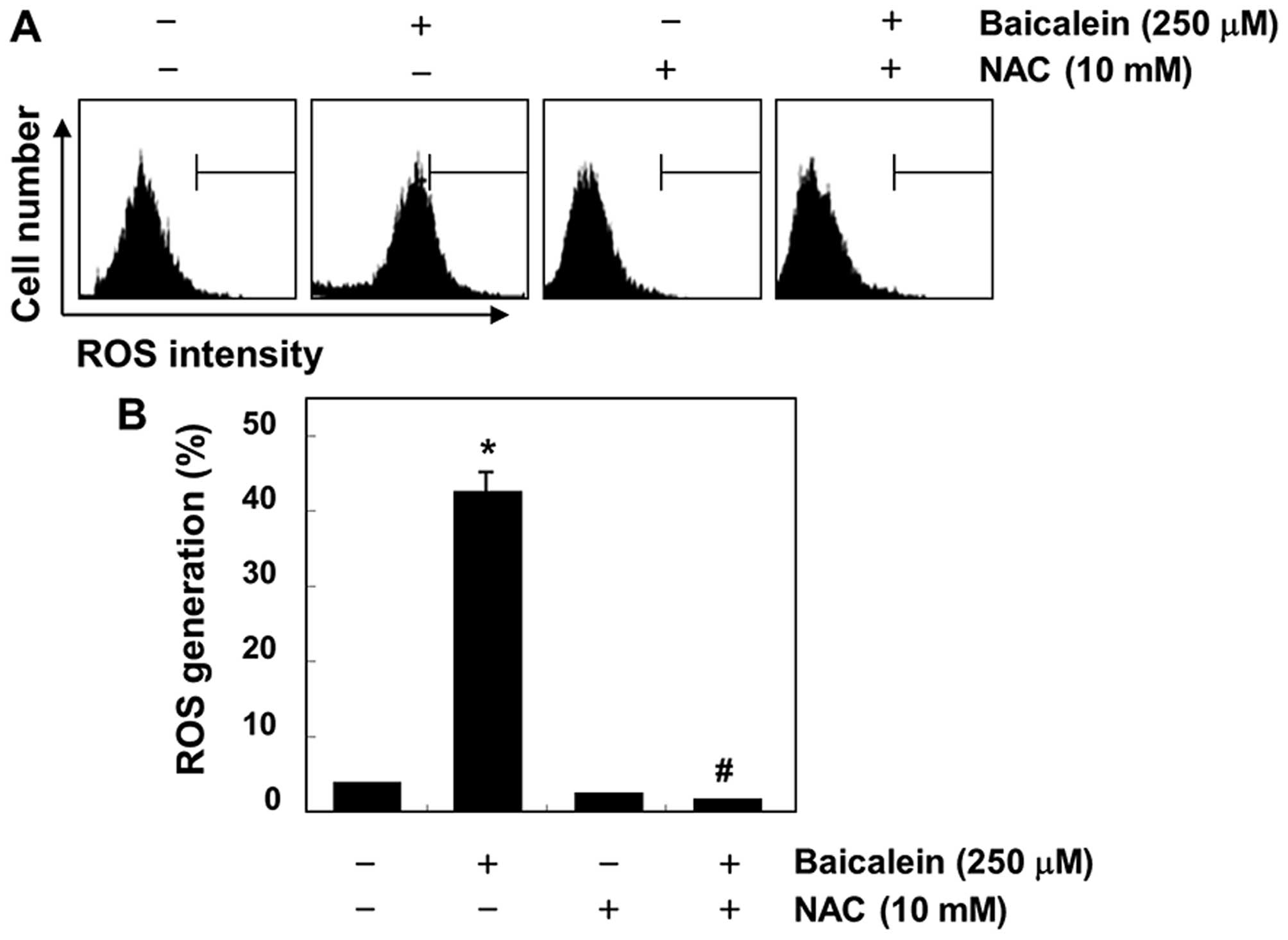
|
1
|
Lei AQ, Cheng L and Pan C-X: Current
treatment of metastatic bladder cancer and future directions.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:1851–1862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Kessel KE, Zuiverloon TC, Alberts AR,
Boormans JL and Zwarthoff EC: Targeted therapies in bladder cancer:
An overview of in vivo research. Nat Rev Urol. 12:681–694. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Donato F, Boffetta P, Fazioli R, Aulenti
V, Gelatti U and Porru S: Bladder cancer, tobacco smoking, coffee
and alcohol drinking in Brescia, northern Italy. Eur J Epidemiol.
13:795–800. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu X, Ros MM, Gu J and Kiemeney L:
Epidemiology and genetic susceptibility to bladder cancer. BJU Int.
102B:1207–1215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pal SK, Milowsky MI and Plimack ER:
Optimizing systemic therapy for bladder cancer. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 11:793–804. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Feuerstein MA and Goenka A: Quality of
life outcomes for bladder cancer patients undergoing bladder
preservation with radiotherapy. Curr Urol Rep. 16:752015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fridlender M, Kapulnik Y and Koltai H:
Plant derived substances with anti-cancer activity: From folklore
to practice. Front Plant Sci. 6:7992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Plants as a source
of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:72–79. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagai T, Yamada H and Otsuka Y: Inhibition
of mouse liver sialidase by the root of Scutellaria baicalensis.
Planta Med. 55:27–29. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li-Weber M: New therapeutic aspects of
flavones: The anti-cancer properties of Scutellaria and its main
active constituents Wogonin, Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat
Rev. 35:57–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang Y, Tsang SY, Yao X and Chen ZY:
Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system. Curr
Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 5:177–184. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li C, Lin G and Zuo Z: Pharmacological
effects and pharmacokinetics properties of Radix Scutellariae and
its bioactive flavones. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 32:427–445. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Firuzi O, Miri R, Tavakkoli M and Saso L:
Antioxidant therapy: Current status and future prospects. Curr Med
Chem. 18:3871–3888. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He X, Wei Z, Zhou E, Chen L, Kou J, Wang J
and Yang Z: Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by
suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in
LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:470–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao JR, Do CW and To CH: Potential
therapeutic effects of baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin in ocular
disorders. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 30:605–614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng YH, Li LA, Lin P, Cheng LC, Hung CH,
Chang NW and Lin C: Baicalein induces G1 arrest in oral cancer
cells by enhancing the degradation of cyclin D1 and activating AhR
to decrease Rb phosphorylation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
263:360–367. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng YH, Yin LH, Grahn TH, Ye AF, Zhao YR
and Zhang QY: Anticancer effects of baicalein on hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 28:1342–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee HZ, Leung HW, Lai MY and Wu CH:
Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung
squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Res. 25A:959–964.
2005.
|
|
19
|
Aryal P, Kim K, Park PH, Ham S, Cho J and
Song K: Baicalein induces autophagic cell death through AMPK/ULK1
activation and downregulation of mTORC1 complex components in human
cancer cells. FEBS J. 281:4644–4658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim DH, Hossain MA, Kang YJ, Jang JY, Lee
YJ, Im E, Yoon JH, Kim HS, Chung HY and Kim ND: Baicalein, an
active component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, induces
apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and prevents AOM/DSS-induced
colon cancer in mice. Int J Oncol. 43:1652–1658. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chung H, Choi HS, Seo EK, Kang DH and Oh
ES: Baicalin and baicalein inhibit transforming growth
factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
breast epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:707–713.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Li Z, Chen AY, Ye X, Luo H, Rankin
GO and Chen YC: Inhibitory effect of baicalin and baicalein on
ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:6012–6025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rushworth SA and Micheau O: Molecular
crosstalk between TRAIL and natural antioxidants in the treatment
of cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 157:1186–1188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HJ, Park C, Han MH, Hong SH, Kim GY,
Hoon Hong S, Deuk Kim N and Choi YH: Baicalein induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis associated with the generation of ROS
and the activation of AMPK in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Drug
Dev Res. 77:73–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park MH and Han JS: Padina arborescens
extract protects high glucose-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β
cells by reducing oxidative stress. Nutr Res Pract. 8:494–500.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim SJ, Ho Hur J, Park C, Kim HJ, Oh GS,
Lee JN, Yoo SJ, Choe SK, So HS, Lim DJ, et al: Bucillamine prevents
cisplatin-induced ototoxicity through induction of glutathione and
antioxidant genes. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim YS, Li XF, Kang KH, Ryu B and Kim SK:
Stigmasterol isolated from marine microalgae Navicula incerta
induces apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. BMB Rep.
47:433–438. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Song JL, Choi JH, Seo JH, Kil JH and Park
KY: Antioxidative effects of fermented sesame sauce against
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in LLC-PK1 porcine renal
tubule cells. Nutr Res Pract. 8:138–145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sayers TJ: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptosis signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 60:1173–1180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
MacKenzie SH and Clark AC: Targeting cell
death in tumors by activating caspases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
8:98–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brenner D and Mak TW: Mitochondrial cell
death effectors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:871–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hensley P, Mishra M and Kyprianou N:
Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Biol Chem. 394:831–843.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y,
Davidson NE and Poirier GG: Specific proteolytic cleavage of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 53:3976–3985.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Danson S, Dean E, Dive C and Ranson M:
IAPs as a target for anticancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
7:785–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
de Graaf AO, de Witte T and Jansen JH:
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: New therapeutic targets in
hematological cancer? Leukemia. 18:1751–1759. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kardeh S, Ashkani-Esfahani S and Alizadeh
AM: Paradoxical action of reactive oxygen species in creation and
therapy of cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 735:150–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ and Márquez
J: Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: An update. Arch
Toxicol. 86:1649–1665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boneh A: Regulation of mitochondrial
oxidative phosphorylation by second messenger-mediated signal
transduction mechanisms. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:1236–1248. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fleury C, Mignotte B and Vayssière JL:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling.
Biochimie. 84:131–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zafarullah M, Li WQ, Sylvester J and Ahmad
M: Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 60:6–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|