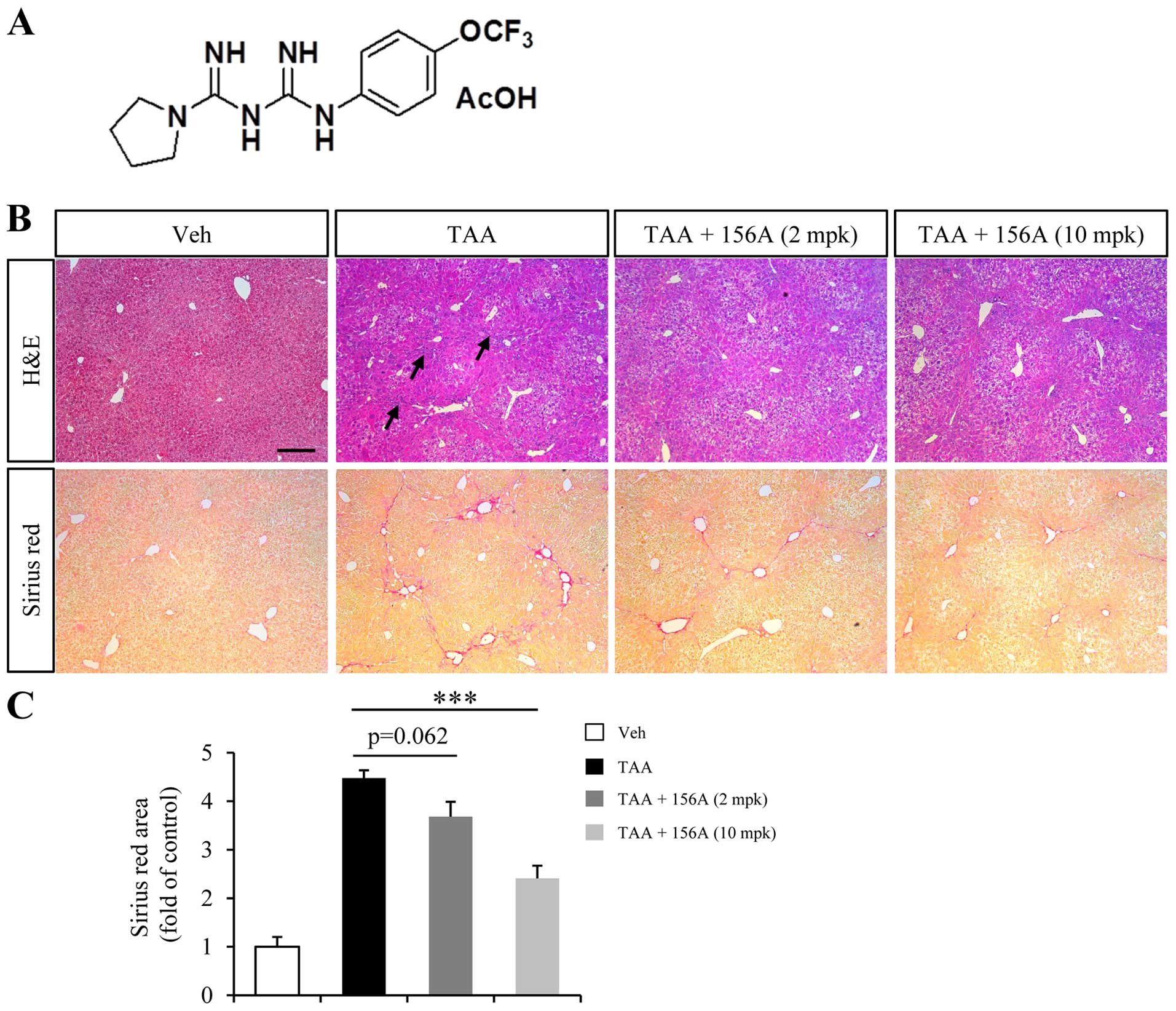
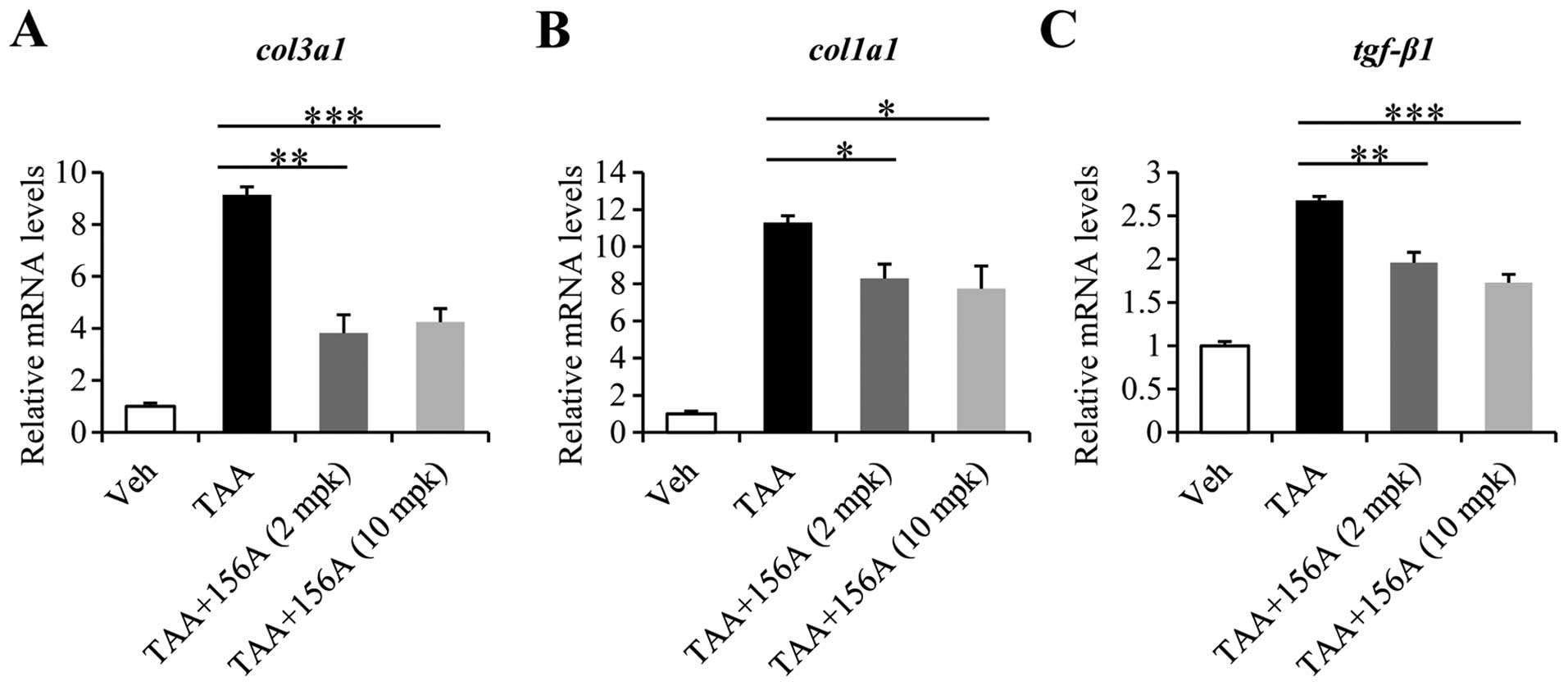
|
1
|
Lee SJ, Kim KH and Park KK: Mechanisms of
fibrogenesis in liver cirrhosis: The molecular aspects of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. World J Hepatol. 6:207–216.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP
and Fallowfield JA: Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of
wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:181–194. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iwakiri Y, Shah V and Rockey DC: Vascular
pathobiology in chronic liver disease and cirrhosis - current
status and future directions. J Hepatol. 61:912–924. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Langer DA, Das A, Semela D, Kang-Decker N,
Hendrickson H, Bronk SF, Katusic ZS, Gores GJ and Shah VH: Nitric
oxide promotes caspase-independent hepatic stellate cell apoptosis
through the generation of reactive oxygen species. Hepatology.
47:1983–1993. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deleve LD, Wang X and Guo Y: Sinusoidal
endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote
reversion to quiescence. Hepatology. 48:920–930. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grahame Hardie D: Regulation of
AMP-activated protein kinase by natural and synthetic activators.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 6:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vallianou NG, Evangelopoulos A and Kazazis
C: Metformin and cancer. Rev Diabet Stud. 10:228–235. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Salt IP and Palmer TM: Exploiting the
anti-inflammatory effects of AMP-activated protein kinase
activation. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 21:1155–1167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Haapasalo A,
Soininen H and Hiltunen M: AMP-activated protein kinase: A
potential player in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 118:460–474.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Pan Y, Kan M, Xiao X, Wang Y, Guan
F, Zhang X and Chen L: Hepatoprotective effects of berberine on
liver fibrosis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Life
Sci. 98:24–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tripathi DM, Erice E, Lafoz E,
García-Calderó H, Sarin SK, Bosch J, Gracia-Sancho J and
García-Pagán JC: Metformin reduces hepatic resistance and portal
pressure in cirrhotic rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 309:G301–G309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lim JY, Oh MA, Kim WH, Sohn HY and Park
SI: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TGF-β-induced fibrogenic
responses of hepatic stellate cells by targeting transcriptional
coactivator p300. J Cell Physiol. 227:1081–1089. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jeong HW, Hsu KC, Lee JW, Ham M, Huh JY,
Shin HJ, Kim WS and Kim JB: Berberine suppresses proinflammatory
responses through AMPK activation in macrophages. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 296:E955–E964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo T, Woo SL, Guo X, Li H, Zheng J,
Botchlett R, Liu M, Pei Y, Xu H, Cai Y, et al: Berberine
ameliorates hepatic steatosis and suppresses liver and adipose
tissue inflammation in mice with diet-induced obesity. Sci Rep.
6:226122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ju KD, Kim HJ, Tsogbadrakh B, Lee J, Ryu
H, Cho EJ, Hwang YH, Kim K, Yang J, Ahn C, et al: HL156A, a novel
AMP-activated protein kinase activator, is protective against
peritoneal fibrosis in an in vivo and in vitro model of peritoneal
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 310:F342–F350. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mobley AK, Tchaicha JH, Shin J, Hossain MG
and McCarty JH: Beta8 integrin regulates neurogenesis and
neurovascular homeostasis in the adult brain. J Cell Sci.
122:1842–1851. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shin MW, Bae SJ, Wee HJ, Lee HJ, Ahn BJ,
Le H, Lee EJ, Kim RH, Lee HS, Seo JH, et al: Ninjurin1 regulates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through direct binding. Int
J Oncol. 48:821–828. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Liu Y, Meyer C, Xu C, Weng H, Hellerbrand
C, ten Dijke P and Dooley S: Animal models of chronic liver
diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 304:G449–G468.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
DeLeve LD: Liver sinusoidal endothelial
cells in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 61:1740–1746. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Straub AC, Stolz DB, Ross MA,
Hernández-Zavala A, Soucy NV, Klei LR and Barchowsky A: Arsenic
stimulates sinusoidal endothelial cell capillarization and vessel
remodeling in mouse liver. Hepatology. 45:205–212. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Rockey DC: Current and future
anti-fibrotic therapies for chronic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis.
12:939–962. xi2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y,
Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, Pellicoro A, Raschperger E,
Betsholtz C, Ruminski PG, et al: Targeting of αv integrin
identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in
several organs. Nat Med. 19:1617–1624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Munger JS, Huang X, Kawakatsu H, Griffiths
MJ, Dalton SL, Wu J, Pittet JF, Kaminski N, Garat C, Matthay MA, et
al: The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta
1: A mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.
Cell. 96:319–328. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuhajda FP: AMP-activated protein kinase
and human cancer: Cancer metabolism revisited. Int J Obes. 32(Suppl
4): S36–S41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ferretti AC, Tonucci FM, Hidalgo F, Almada
E, Larocca MC and Favre C: AMPK and PKA interaction in the
regulation of survival of liver cancer cells subjected to glucose
starvation. Oncotarget. Feb 15–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Park SY, Lee YK, Kim HJ, Park OJ and Kim
YM: AMPK interacts with β-catenin in the regulation of
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and survival with
selenium treatment. Oncol Rep. 35:1566–1572. 2016.
|
|
30
|
Yang CC, Chang SF, Chao JK, Lai YL, Chang
WE, Hsu WH and Kuo WH: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase
attenuates hepatocellular carcinoma cell adhesion stimulated by
adipokine resistin. BMC Cancer. 14:1122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang DY and Friedman SL:
Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology.
56:769–775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seitz HK and Stickel F: Risk factors and
mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis with special emphasis on alcohol
and oxidative stress. Biol Chem. 387:349–360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I and
Donato F: Hepatocellular carcinoma in cir rhosis: Incidence and
risk factors. Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl 1): S35–S50. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|