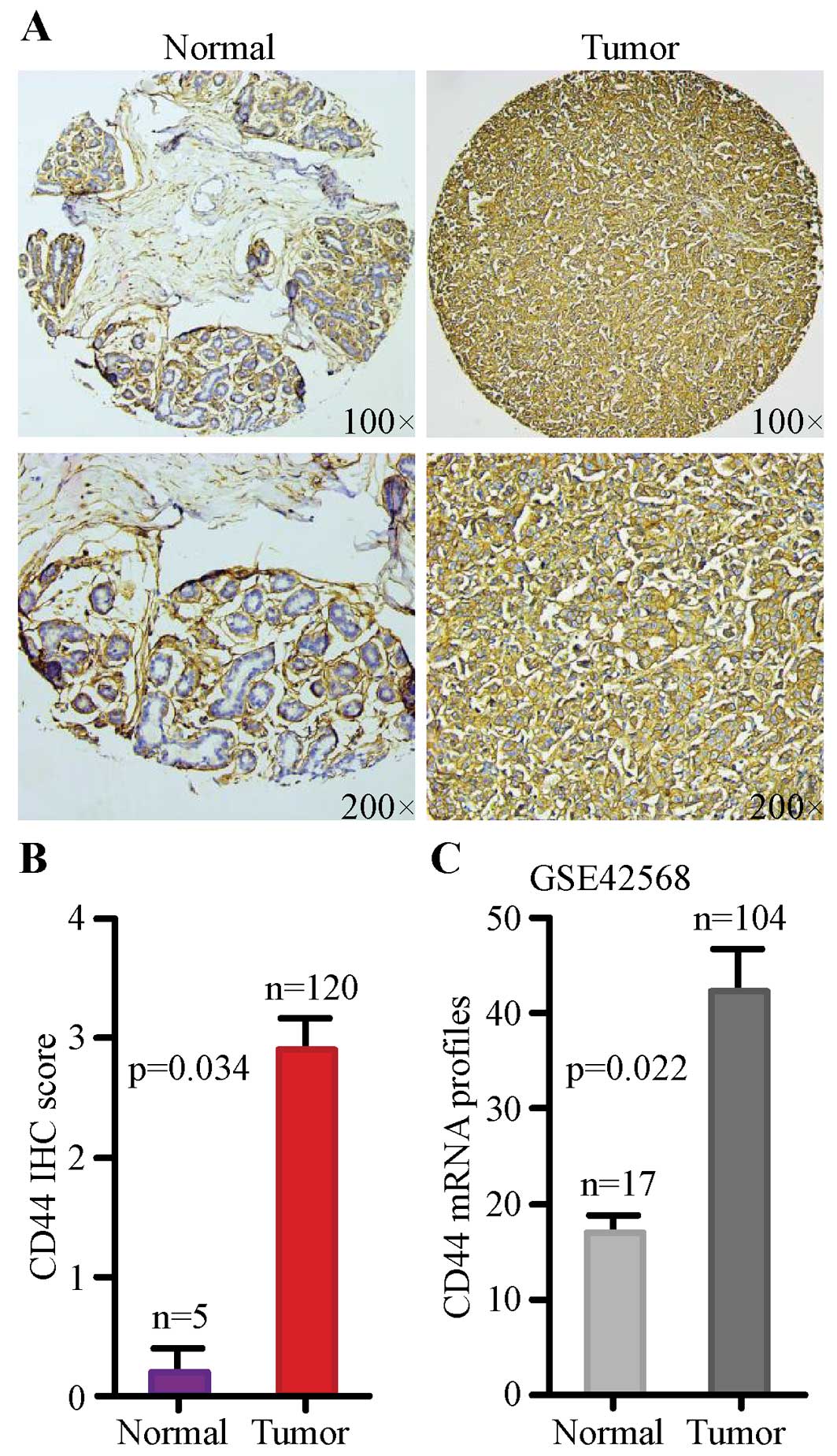
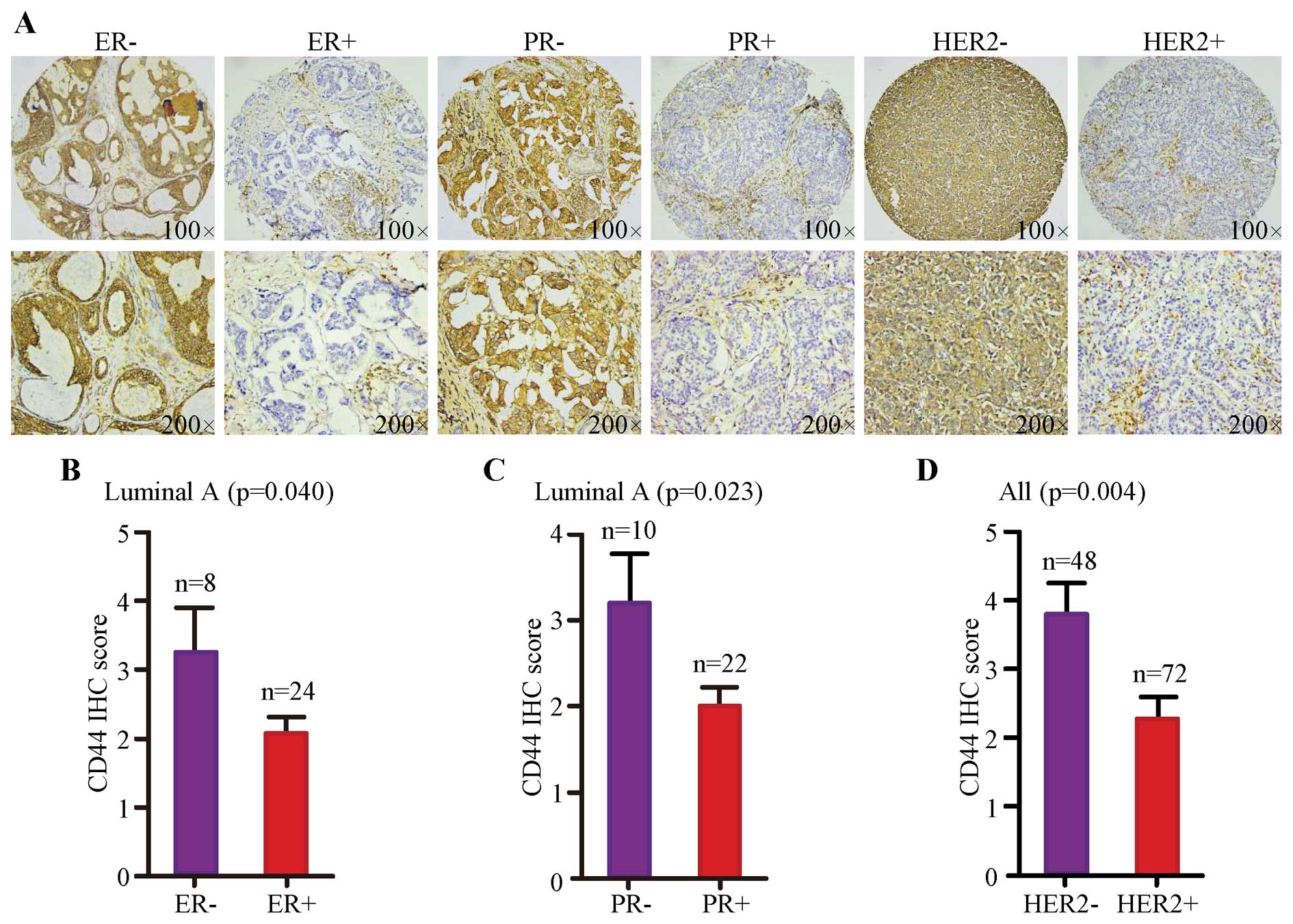
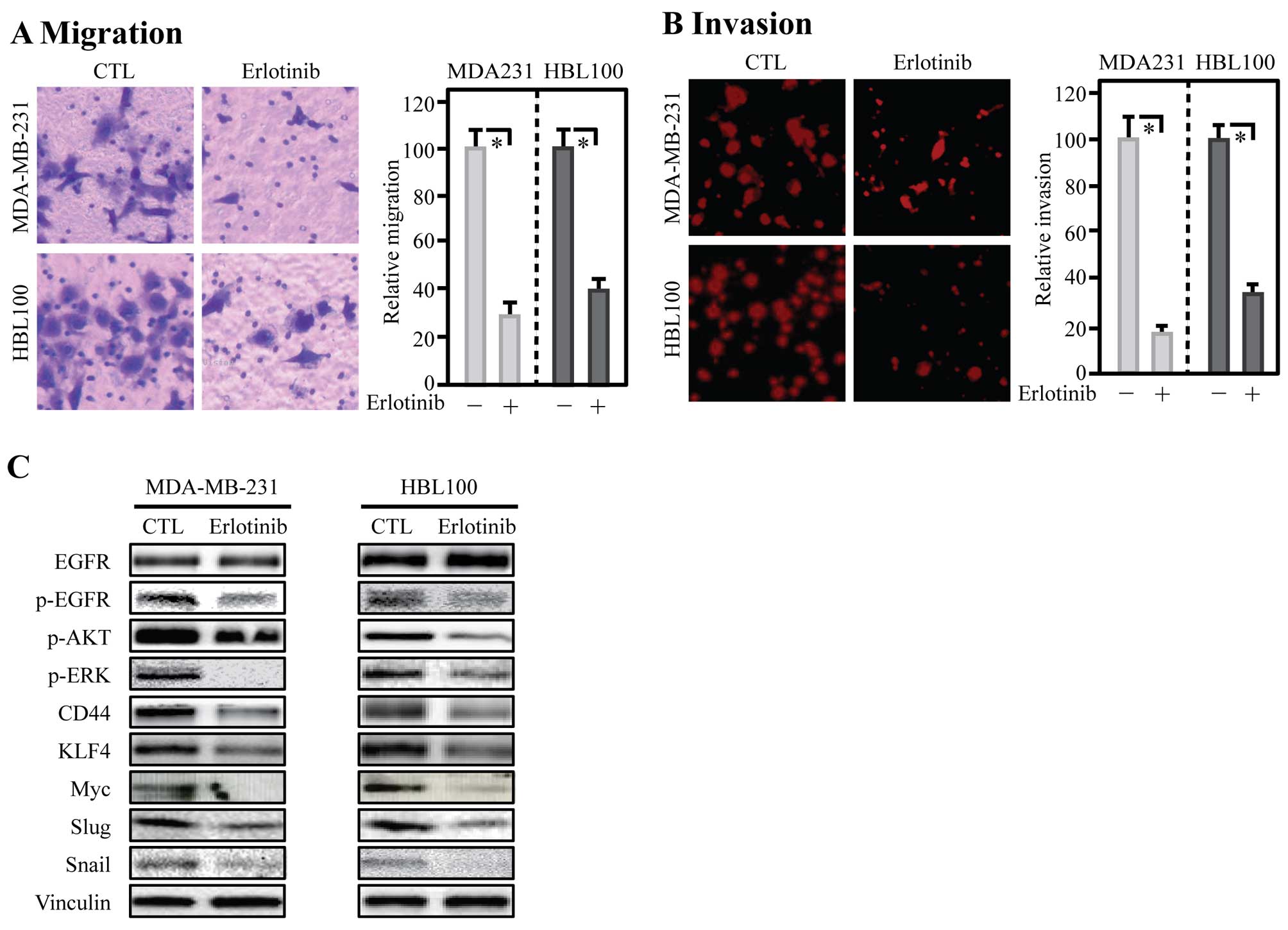
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Makki J: Diversity of breast carcinoma:
Histological subtypes and clinical relevance. Clin Med Insights
Pathol. 8:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells - perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Götte M and Yip GW: Heparanase,
hyaluronan, and CD44 in cancers: A breast carcinoma perspective.
Cancer Res. 66:10233–10237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu H, Tian Y, Yuan X, Wu H, Liu Q, Pestell
RG and Wu K: The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cancer development. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3783–3792. 2015.
|
|
6
|
Zöller M: CD44: Can a cancer-initiating
cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer.
11:254–267. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei X, Xu M, Wei Y, Huang F, Zhao T, Li X,
Feng R and Ye BH: The addition of rituximab to CHOP therapy alters
the prognostic significance of CD44 expression. J Hematol Oncol.
7:342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lv L, Liu HG, Dong SY, Yang F, Wang QX,
Guo GL, Pan YF and Zhang XH: Upregulation of CD44v6 contributes to
acquired chemoresistance via the modulation of autophagy in colon
cancer SW480 cells. Tumour Biol. Jan 9–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Erb U, Megaptche AP, Gu X, Büchler MW and
Zöller M: CD44 standard and CD44v10 isoform expression on leukemia
cells distinctly influences niche embedding of hematopoietic stem
cells. J Hematol Oncol. 7:292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Veale D, Ashcroft T, Marsh C, Gibson GJ
and Harris AL: Epidermal growth factor receptors in non-small cell
lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 55:513–516. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weichselbaum RR, Dunphy EJ, Beckett MA,
Tybor AG, Moran WJ, Goldman ME, Vokes EE and Panje WR: Epidermal
growth factor receptor gene amplification and expression in head
and neck cancer cell lines. Head Neck. 11:437–442. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klijn JG, Berns PM, Schmitz PI and Foekens
JA: The clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGF-R) in human breast cancer: A review on 5232 patients. Endocr
Rev. 13:3–17. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, Ashton
SE, Curry BJ, Barker AJ and Gibson KH: ZD1839 (Iressa): An orally
active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with
potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 62:5749–5754.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hidalgo M, Siu LL, Nemunaitis J, Rizzo J,
Hammond LA, Takimoto C, Eckhardt SG, Tolcher A, Britten CD, Denis
L, et al: Phase I and pharmacologic study of OSI-774, an epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with
advanced solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 19:3267–3279.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun W, Yuan X, Tian Y, Wu H, Xu H, Hu G
and Wu K: Non-invasive approaches to monitor EGFR-TKI treatment in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 8:952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niu FY and Wu YL: Novel agents and
strategies for overcoming EGFR TKIs resistance. Exp Hematol Oncol.
3:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Cao J, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen Z,
Peng W, Sun S, Zhao N, Wang J, Zhong D, et al: A phase I study of
AST1306, a novel irreversible EGFR and HER2 kinase inhibitor, in
patients with advanced solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 7:222014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gudadze M, Kankava K, Mariamidze A,
Mosidze T and Burkadze G: Distribution of CD44/CD24 positive cells
in ductal invasive carcinoma of breast of different grade and
molecular subtype. Georgian Med News. 222:50–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Zhou R, Yuan X, Han N, Zhou S, Xu
H, Guo M, Yu S, Zhang C, Yin T, et al: DACH1 is a novel predictive
and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma as a negative
regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 6:8621–8634.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie JW, Chen PC, Zheng CH, Li P, Wang JB,
Lin JX, Lu J, Chen QY, Cao LL, Lin M, et al: Evaluation of the
prognostic value and functional roles of CD44v6 in gastric cancer.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:1809–1817. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han N, Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Chu Q, Guo M,
Yu S, Chen Y and Wu K: DACH1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma invasion
and tumor growth by repressing CXCL5 signaling. Oncotarget.
6:5877–5888. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chu Q, Han N, Yuan X, Nie X, Wu H, Chen Y,
Guo M, Yu S and Wu K: DACH1 inhibits cyclin D1 expression, cellular
proliferation and tumor growth of renal cancer cells. J Hematol
Oncol. 7:732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du L, Wang H, He L, Zhang J, Ni B, Wang X,
Jin H, Cahuzac N, Mehrpour M, Lu Y, et al: CD44 is of functional
importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6751–6760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang D, Zhu H, Liu Y, Liu Q, Xie X, Zhou
Y, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Zhang Z and Su Z: The low chamber pancreatic
cancer cells had stem-like characteristics in modified transwell
system: Is it a novel method to identify and enrich cancer
stem-like cells? BioMed Res Int. 2014:7603032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie G, Yao Q, Liu Y, Du S, Liu A, Guo Z,
Sun A, Ruan J, Chen L, Ye C, et al: IL-6-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes the generation of breast
cancer stem-like cells analogous to mammosphere cultures. Int J
Oncol. 40:1171–1179. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Xu H, Tian Y, Yuan X, Liu Y, Wu H, Liu Q,
Wu GS and Wu K: Enrichment of CD44 in basal-type breast cancer
correlates with EMT, cancer stem cell gene profile, and prognosis.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:431–444. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Smith AD, Roda D and Yap TA: Strategies
for modern biomarker and drug development in oncology. J Hematol
Oncol. 7:702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cho Y, Lee HW, Kang HG, Kim HY, Kim SJ and
Chun KH: Cleaved CD44 intracellular domain supports activation of
stemness factors and promotes tumorigenesis of breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:8709–8721. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McFarlane S, Coulter JA, Tibbits P,
O'Grady A, McFarlane C, Montgomery N, Hill A, McCarthy HO, Young
LS, Kay EW, et al: CD44 increases the efficiency of distant
metastasis of breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:11465–11476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cho SH, Park YS, Kim HJ, Kim CH, Lim SW,
Huh JW, Lee JH and Kim HR: CD44 enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in association with colon cancer invasion. Int J Oncol.
41:211–218. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McFarlane S, McFarlane C, Montgomery N,
Hill A and Waugh DJ: CD44-mediated activation of α5β1-integrin,
cortactin and paxillin signaling underpins adhesion of basal-like
breast cancer cells to endothelium and fibronectin-enriched
matrices. Oncotarget. 6:36762–36773. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Uchino M, Kojima H, Wada K, Imada M, Onoda
F, Satofuka H, Utsugi T and Murakami Y: Nuclear beta-catenin and
CD44 upregulation characterize invasive cell populations in
non-aggressive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:4142010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bernardo GM, Lozada KL, Miedler JD,
Harburg G, Hewitt SC, Mosley JD, Godwin AK, Korach KS, Visvader JE,
Kaestner KH, et al: FOXA1 is an essential determinant of ERalpha
expression and mammary ductal morphogenesis. Development.
137:2045–2054. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kouros-Mehr H, Slorach EM, Sternlicht MD
and Werb Z: GATA-3 maintains the differentiation of the luminal
cell fate in the mammary gland. Cell. 127:1041–1055. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mitsudomi T and Yatabe Y: Epidermal growth
factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and
cancer. FEBS J. 277:301–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Okano J, Gaslightwala I, Birnbaum MJ,
Rustgi AK and Nakagawa H: Akt/protein kinase B isoforms are
differentially regulated by epidermal growth factor stimulation. J
Biol Chem. 275:30934–30942. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cattaneo F, Iaccio A, Guerra G, Montagnani
S and Ammendola R: NADPH-oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species
mediate EGFR transactivation by FPRL1 in WKYMVm-stimulated human
lung cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1126–1136. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brusevold IJ, Tveteraas IH, Aasrum M,
Ødegård J, Sandnes DL and Christoffersen T: Role of LPAR3, PKC and
EGFR in LPA-induced cell migration in oral squamous carcinoma
cells. BMC Cancer. 14:4322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tveteraas IH, Müller KM, Aasrum M, Ødegård
J, Dajani O, Guren T, Sandnes D and Christoffersen T: Mechanisms
involved in PGE2-induced transactivation of the epidermal growth
factor receptor in MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 31:722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoshida K, Fujino H, Otake S, Seira N,
Regan JW and Murayama T: Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression
by prostaglandin E2 stimulation of the prostanoid EP4 receptor via
coupling to Gαi and transactivation of the epidermal growth factor
receptor in HCA-7 human colon cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
718:408–417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zajac M, Law J, Cvetkovic DD, Pampillo M,
McColl L, Pape C, Di Guglielmo GM, Postovit LM, Babwah AV and
Bhattacharya M: GPR54 (KISS1R) transactivates EGFR to promote
breast cancer cell invasiveness. PLoS One. 6:e215992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kondapaka SB, Fridman R and Reddy KB:
Epidermal growth factor and amphiregulin up-regulate matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 70:722–726. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Kehlbach R and
Rodemann HP: Radiation-induced caveolin-1 associated EGFR
internalization is linked with nuclear EGFR transport and
activation of DNA-PK. Mol Cancer. 7:692008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Leinung M, Ernst B, Döring C, Wagenblast
J, Tahtali A, Diensthuber M, Stöver T and Geissler C: Expression of
ALDH1A1 and CD44 in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
and their value for carcinogenesis, tumor progression and cancer
stem cell identification. Oncol Lett. 10:2289–2294. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guo F, Parker Kerrigan BC, Yang D, Hu L,
Shmulevich I, Sood AK, Xue F and Zhang W: Post-transcriptional
regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. J Hematol Oncol. 7:192014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Opyrchal M, Salisbury JL, Iankov I, Goetz
MP, McCubrey J, Gambino MW, Malatino L, Puccia G, Ingle JN, Galanis
E, et al: Inhibition of Cdk2 kinase activity selectively targets
the CD44+/CD24−/low stem-like subpopulation
and restores chemosensitivity of SUM149PT triple-negative breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 45:1193–1199. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|