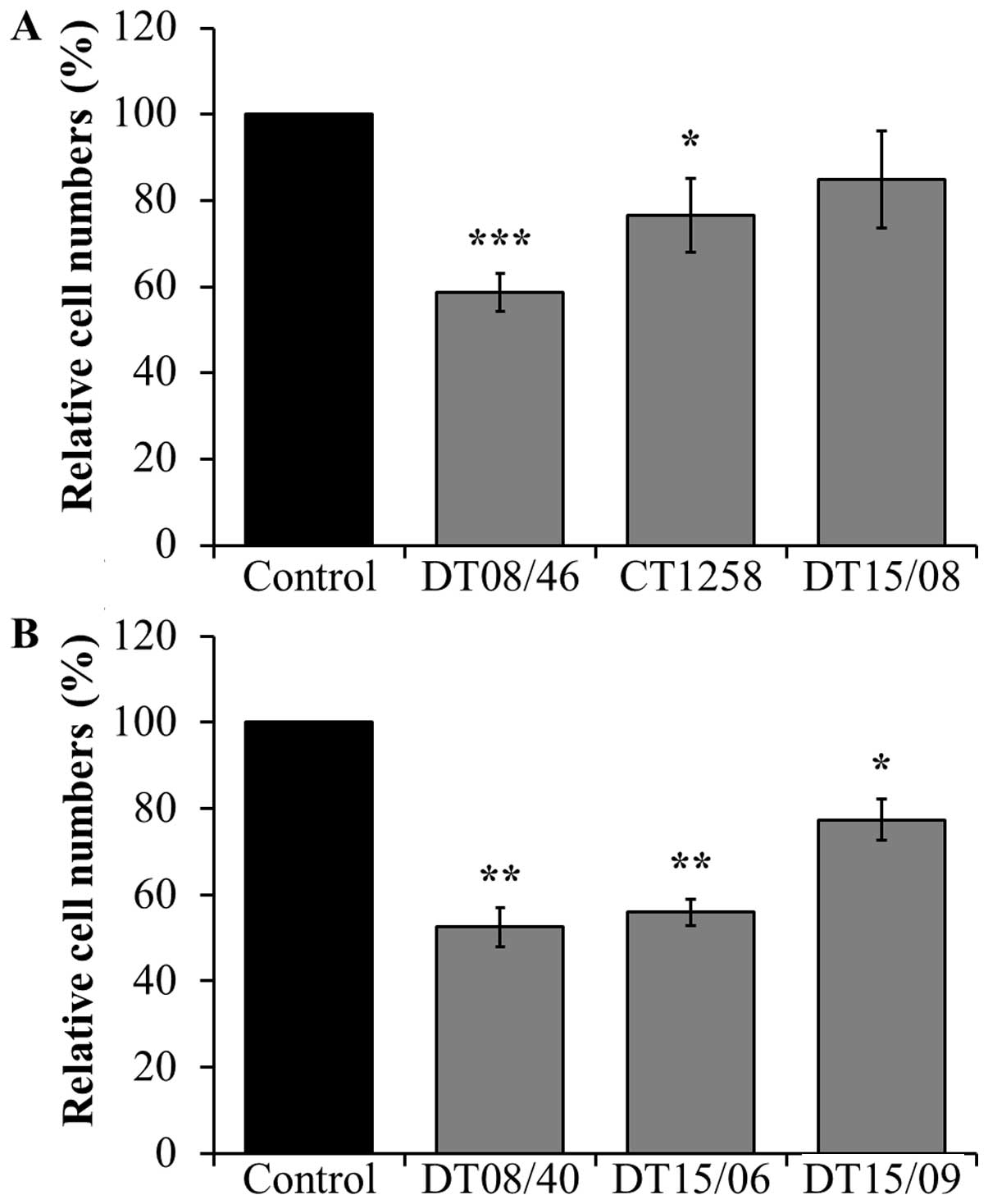
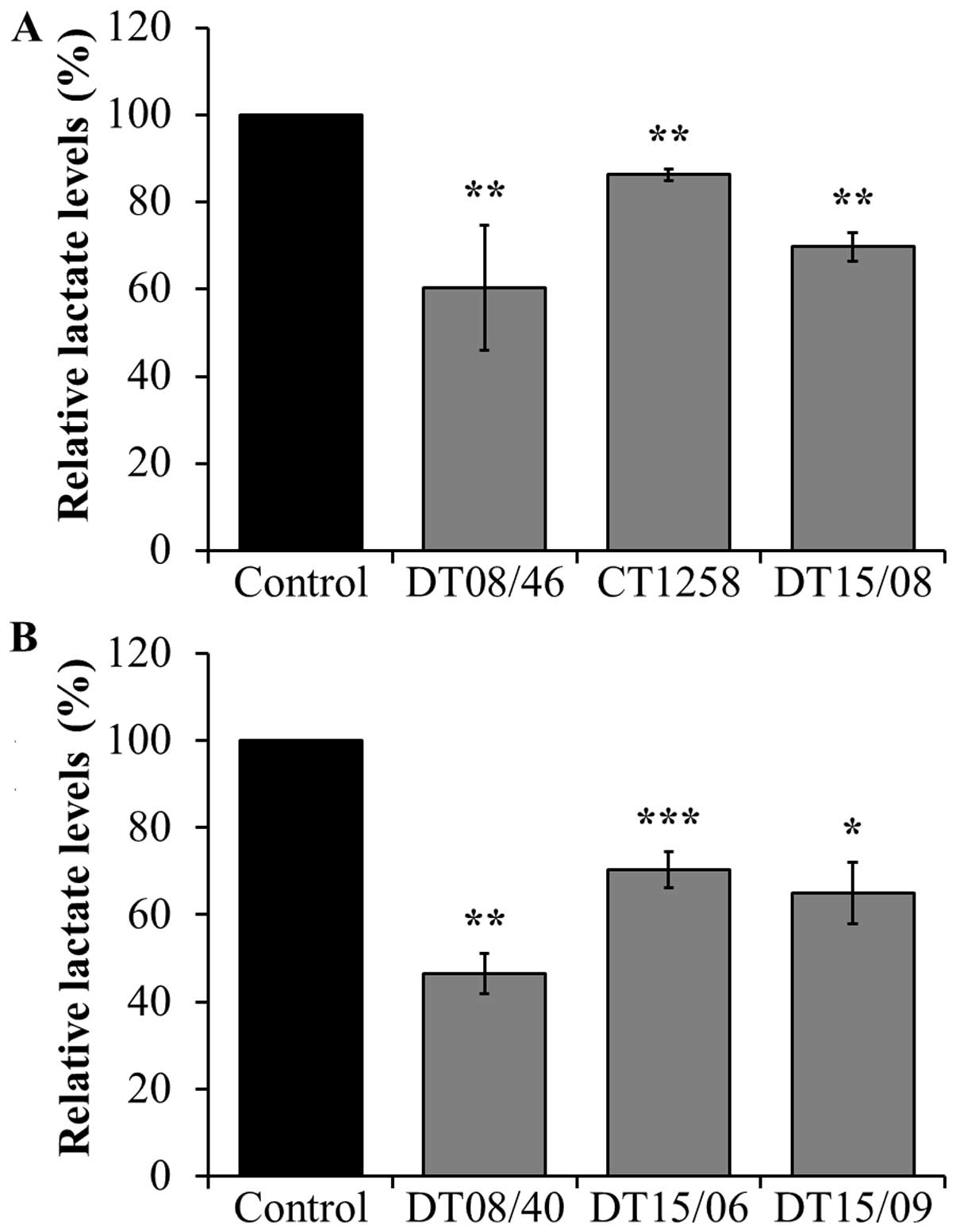
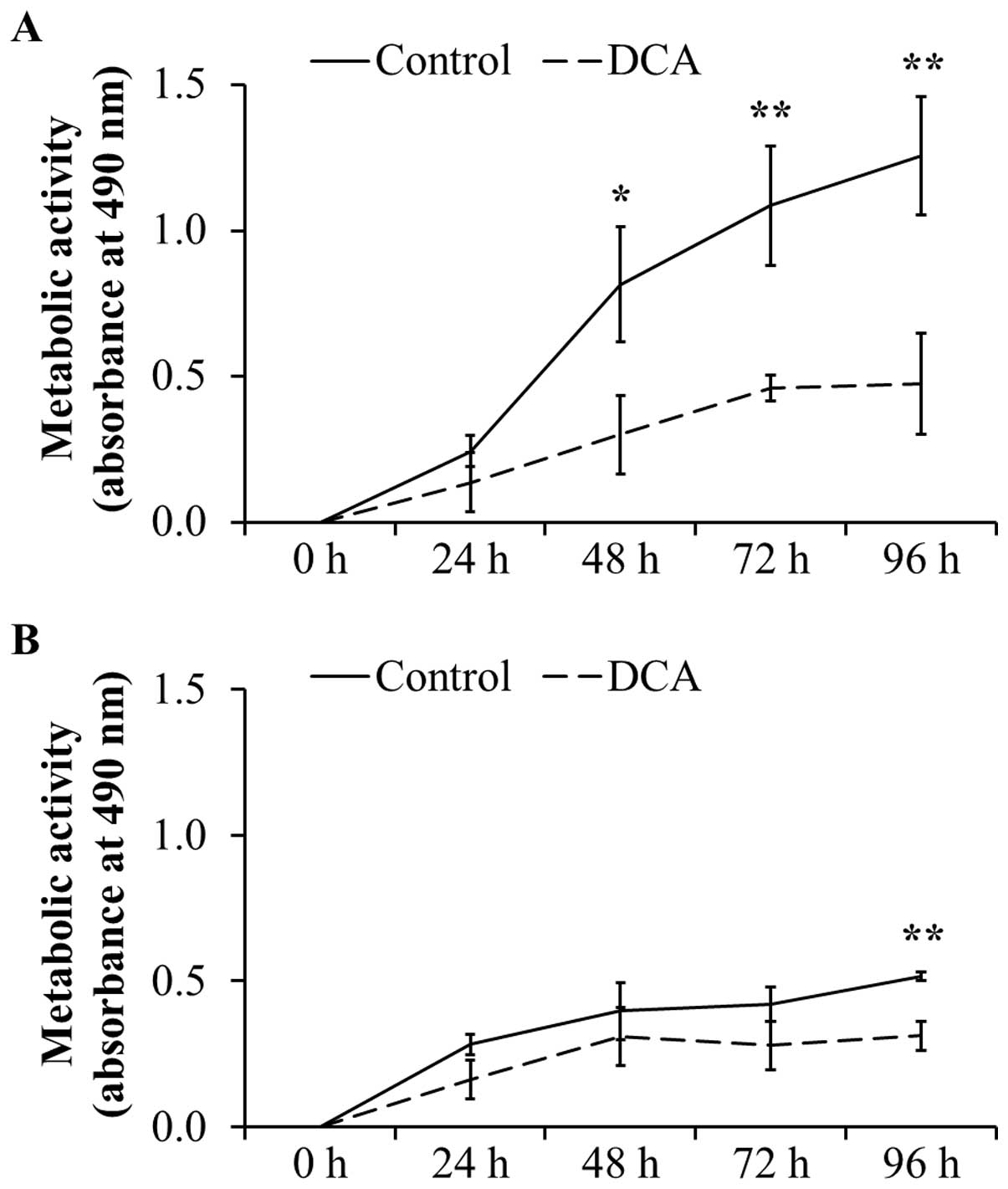
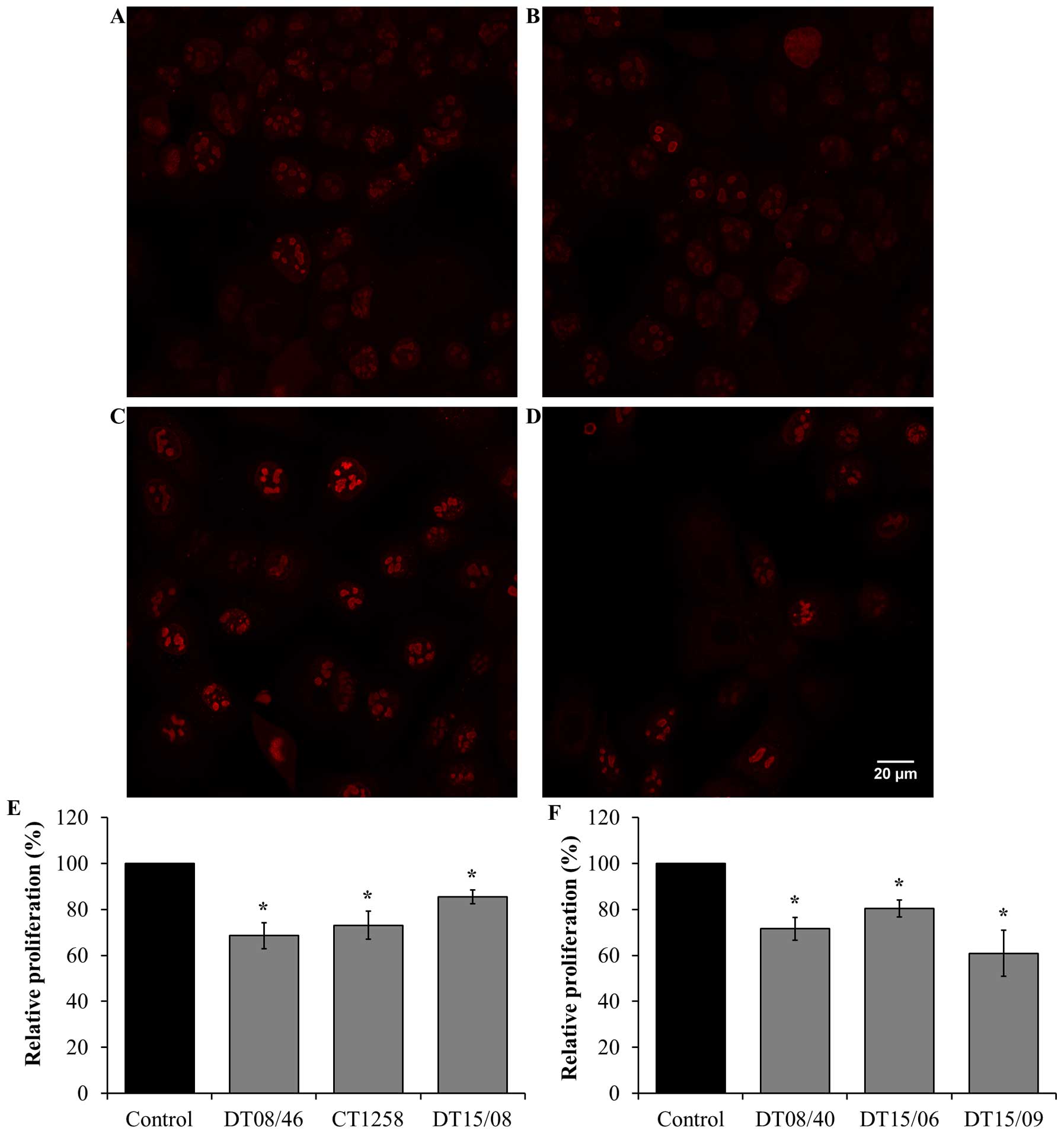
|
1
|
Vail DM: Supporting the veterinary cancer
patient on chemotherapy: Neutropenia and gastrointestinal toxicity.
Top Companion Anim Med. 24:122–129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cornell KK, Bostwick DG, Cooley DM, Hall
G, Harvey HJ, Hendrick MJ, Pauli BU, Render JA, Stoica G, Sweet DC,
et al: Clinical and pathologic aspects of spontaneous canine
prostate carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 76 cases. Prostate.
45:173–183. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mutsaers AJ, Widmer WR and Knapp DW:
Canine transitional cell carcinoma. J Vet Intern Med. 17:136–144.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sutendra G and Michelakis ED: Pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase as a novel therapeutic target in oncology.
Front Oncol. 3:382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stacpoole PW: The pharmacology of
dichloroacetate. Metabolism. 38:1124–1144. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
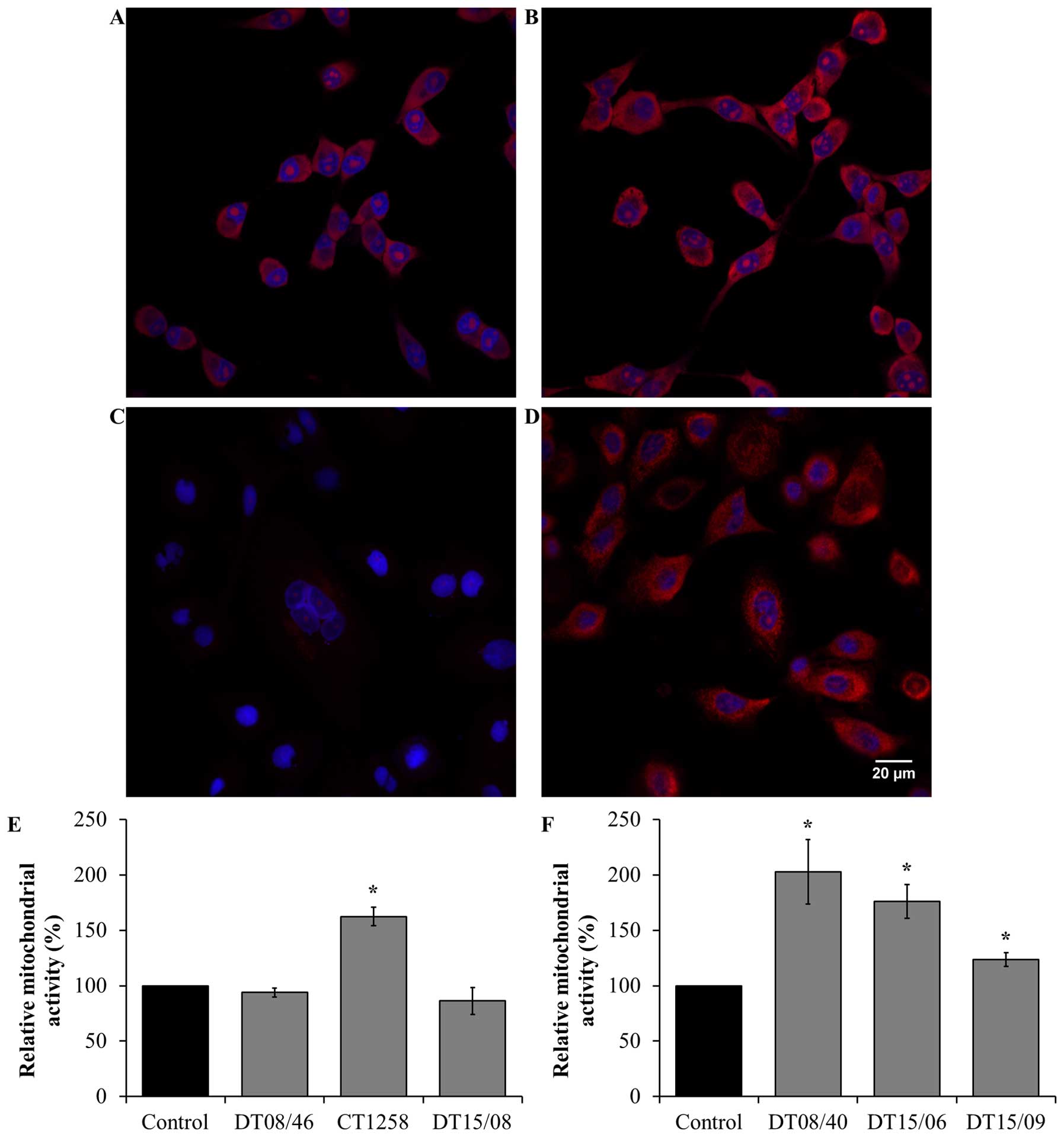
|
|
6
|
Stacpoole PW, Gilbert LR, Neiberger RE,
Carney PR, Valenstein E, Theriaque DW and Shuster JJ: Evaluation of
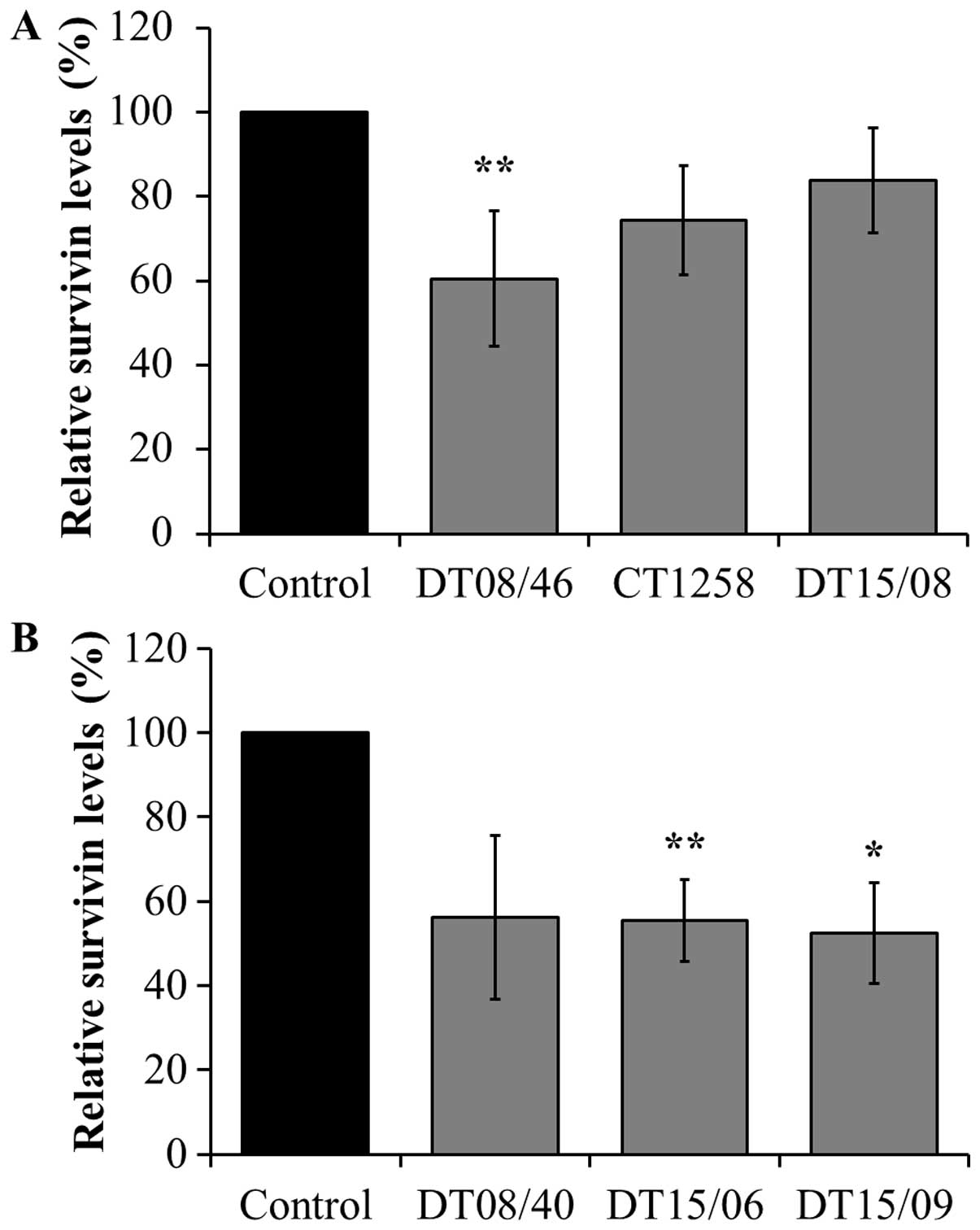
long-term treatment of children with congenital lactic acidosis
with dichloroacetate. Pediatrics. 121:e1223–e1228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
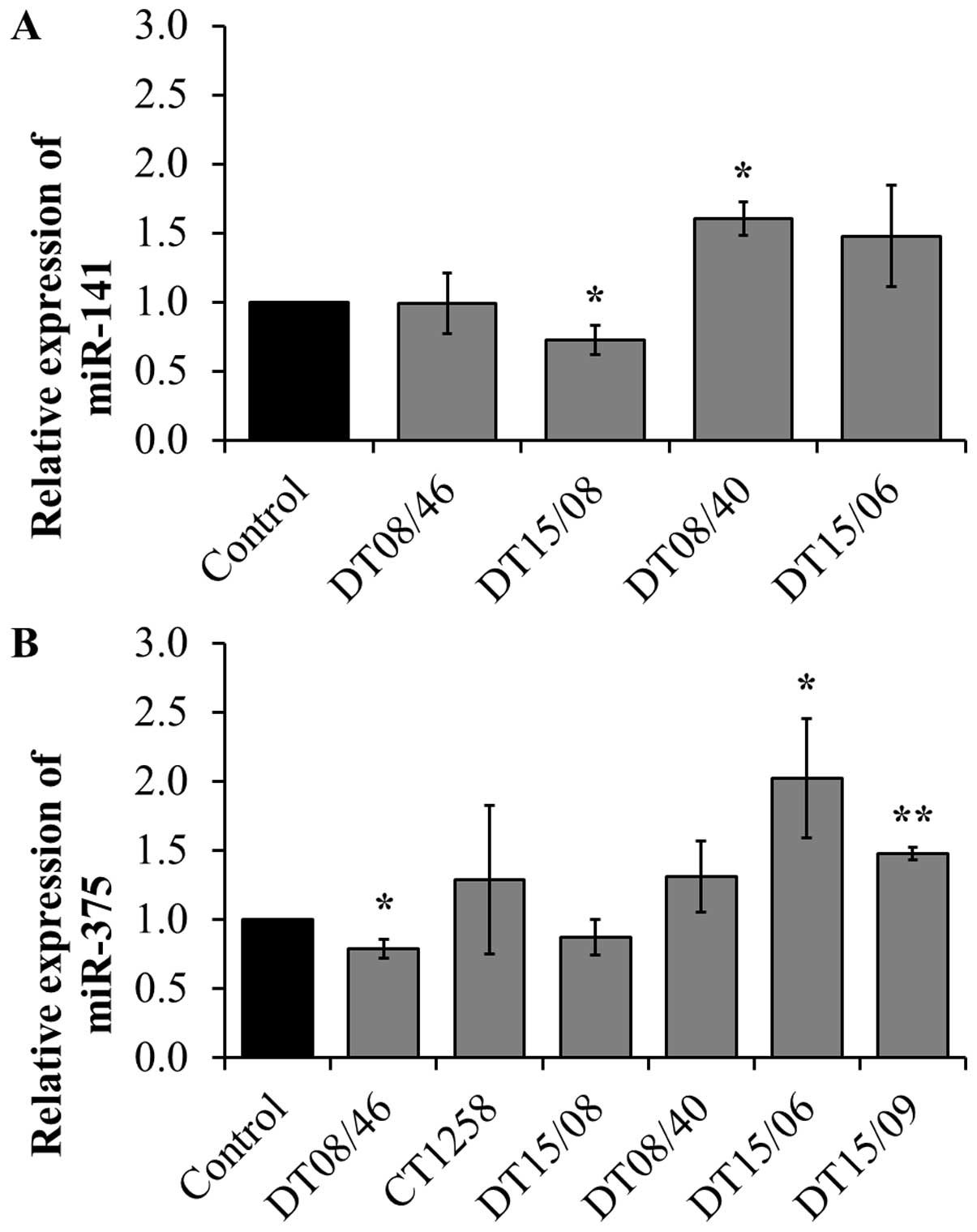
7
|
Stacpoole PW, Kerr DS, Barnes C, Bunch ST,
Carney PR, Fennell EM, Felitsyn NM, Gilmore RL, Greer M, Henderson
GN, et al: Controlled clinical trial of dichloroacetate for
treatment of congenital lactic acidosis in children. Pediatrics.
117:1519–1531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moore GW, Swift LL, Rabinowitz D, Crofford
OB, Oates JA and Stacpoole PW: Reduction of serum cholesterol in
two patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia by
dichloroacetate. Atherosclerosis. 33:285–293. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stacpoole PW, Moore GW and Kornhauser DM:
Metabolic effects of dichloroacetate in patients with diabetes
mellitus and hyperlipoproteinemia. N Engl J Med. 298:526–530. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kato T, Niizuma S, Inuzuka Y, Kawashima T,
Okuda J, Tamaki Y, Iwanaga Y, Narazaki M, Matsuda T, Soga T, et al:
Analysis of metabolic remodeling in compensated left ventricular
hypertrophy and heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 3:420–430. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sánchez-Aragó M, Chamorro M and Cuezva JM:
Selection of cancer cells with repressed mitochondria triggers
colon cancer progression. Carcinogenesis. 31:567–576. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR,
Board PG and Blackburn AC: Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by
dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:253–260. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saed GM, Fletcher NM, Jiang ZL, Abu-Soud
HM and Diamond MP: Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis of epithelial
ovarian cancer cells through a mechanism involving modulation of
oxidative stress. Reprod Sci. 18:1253–1261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong JY, Huggins GS, Debidda M, Munshi NC
and De Vivo I: Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial
cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 109:394–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Michelakis ED, Sutendra G, Dromparis P,
Webster L, Haromy A, Niven E, Maguire C, Gammer TL, Mackey JR,
Fulton D, et al: Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with
dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med. 2:31ra342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kinnaird A, Dromparis P, Saleme B, Gurtu
V, Watson K, Paulin R, Zervopoulos S, Stenson T, Sutendra G, Pink
DB, et al: Metabolic modulation of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
with dichloroacetate, an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase. Eur Urol. 69:734–744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Delaney LM, Ho N, Morrison J, Farias NR,
Mosser DD and Coomber BL: Dichloroacetate affects proliferation but
not survival of human colorectal cancer cells. Apoptosis. 20:63–74.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Madhok BM, Yeluri S, Perry SL, Hughes TA
and Jayne DG: Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis and cell-cycle
arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 102:1746–1752.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ruggieri V, Agriesti F, Scrima R,
Laurenzana I, Perrone D, Tataranni T, Mazzoccoli C, Lo Muzio L,
Capitanio N and Piccoli C: Dichloroacetate, a selective
mitochondria-targeting drug for oral squamous cell carcinoma: A
metabolic perspective of treatment. Oncotarget. 6:1217–1230. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Xintaropoulou C, Ward C, Wise A, Marston
H, Turnbull A and Langdon SP: A comparative analysis of inhibitors
of the glycolysis pathway in breast and ovarian cancer cell line
models. Oncotarget. 6:25677–25695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cicmanec JL, Condie LW, Olson GR and Wang
SR: 90-Day toxicity study of dichloroacetate in dogs. Fundam Appl
Toxicol. 17:376–389. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maisenbacher HW III, Shroads AL III, Zhong
G, Daigle AD, Abdelmalak MM, Samper IS, Mincey BD, James MO and
Stacpoole PW: Pharmacokinetics of oral dichloroacetate in dogs. J
Biochem Mol Toxicol. 27:522–525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lukas G, Vyas KH, Brindle SD, Le Sher AR
and Wagner WE Jr: Biological disposition of sodium dichloroacetate
in animals and humans after intravenous administration. J Pharm
Sci. 69:419–421. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park R, Arieff AI, Leach W and Lazarowitz
VC: Treatment of lactic acidosis with dichloroacetate in dogs. J
Clin Invest. 70:853–862. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Racker E: History of the Pasteur effect
and its pathobiology. Mol Cell Biochem. 5:17–23. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Warburg O, Wind F and Negelein E: Über den
Stoffwechsel von Tumoren im Körper. Klin Wochenschr. 5:829–832.
1926.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL and
Dang CV: HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to
hypoxia. Cell Metab. 3:177–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lum JJ, Bui T, Gruber M, Gordan JD,
DeBerardinis RJ, Covello KL, Simon MC and Thompson CB: The
transcription factor HIF-1alpha plays a critical role in the growth
factor-dependent regulation of both aerobic and anaerobic
glycolysis. Genes Dev. 21:1037–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Butler EB and Tan M: Targeting
cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Plas DR and Thompson CB: Cell metabolism
in the regulation of programmed cell death. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 13:75–78. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Simon D, Knebel JW, Baumgartner W,
Aufderheide M, Meyer-Lindenberg A and Nolte I: In vitro efficacy of
chemotherapeutics as determined by 50% inhibitory concentrations in
cell cultures of mammary gland tumors obtained from dogs. Am J Vet
Res. 62:1825–1830. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Knapp DW, Chan TC, Kuczek T, Reagan WJ and
Park B: Evaluation of in vitro cytotoxicity of nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs against canine tumor cells. Am J Vet Res.
56:801–805. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sartin EA, Barnes S, Toivio-Kinnucan M,
Wright JC and Wolfe LG: Heterogenic properties of clonal cell lines
derived from canine mammary carcinomas and sensitivity to tamoxifen
and doxorubicin. Anticancer Res. 13:229–236. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Winkler S, Murua Escobar H, Eberle N,
Reimann-Berg N, Nolte I and Bullerdiek J: Establishment of a cell
line derived from a canine prostate carcinoma with a highly
rearranged karyotype. J Hered. 96:782–785. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bonnet S, Archer SL, Allalunis-Turner J,
Haromy A, Beaulieu C, Thompson R, Lee CT, Lopaschuk GD, Puttagunta
L, Bonnet S, et al: A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is
suppressed in cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and
inhibits cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 11:37–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao W, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, Namiki K,
Sakai Y, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C and Rosser CJ: Dichloroacetate
(DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate
cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate. 68:1223–1231. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ho N and Coomber BL: Pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase expression and metabolic changes following
dichloroacetate exposure in anoxic human colorectal cancer cells.
Exp Cell Res. 331:73–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Stockwin LH, Yu SX, Borgel S, Hancock C,
Wolfe TL, Phillips LR, Hollingshead MG and Newton DL: Sodium
dichloroacetate selectively targets cells with defects in the
mitochondrial ETC. Int J Cancer. 127:2510–2519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xie J, Wang BS, Yu DH, Lu Q, Ma J, Qi H,
Fang C and Chen HZ: Dichloroacetate shifts the metabolism from
glycolysis to glucose oxidation and exhibits synergistic growth
inhibition with cisplatin in HeLa cells. Int J Oncol. 38:409–417.
2011.
|
|
40
|
Feuerecker B, Seidl C, Pirsig S, Bruchelt
G and Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R: DCA promotes progression of
neuroblastoma tumors in nude mice. Am J Cancer Res. 5:812–820.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abemayor E, Kovachich GB and Haugaard N:
Effects of dichloroacetate on brain pyruvate dehydrogenase. J
Neurochem. 42:38–42. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McPherson NO, Zander-Fox D and Lane M:
Stimulation of mitochondrial embryo metabolism by dichloroacetic
acid in an aged mouse model improves embryo development and
viability. Fertil Steril. 101:1458–1466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou N, Qu Y, Xu C and Tang Y:
Upregulation of microRNA-375 increases the cisplatin-sensitivity of
human gastric cancer cells by regulating ERBB2. Exp Ther Med.
11:625–630. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou J, Song S, He S, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Yi
B, Zhang B, Qin G and Li D: MicroRNA-375 targets PDK1 in pancreatic
carcinoma and suppresses cell growth through the Akt signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 33:950–956. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang L, Song G, Liu M, Chen B, Chen Y,
Shen Y, Zhu J and Zhou X: MicroRNA-375 overexpression influences
P19 cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation through the
Notch signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:47–55. 2016.
|
|
48
|
Zaharie F, Muresan MS, Petrushev B, Berce
C, Gafencu GA, Selicean S, Jurj A, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Lisencu CI,
Pop LA, et al: Exosome-carried microRNA-375 inhibits cell
progression and dissemination via Bcl-2 blocking in colon cancer. J
Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 24:435–443. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Costa-Pinheiro P, Ramalho-Carvalho J,
Vieira FQ, Torres-Ferreira J, Oliveira J, Gonçalves CS, Costa BM,
Henrique R and Jerónimo C: MicroRNA-375 plays a dual role in
prostate carcinogenesis. Clin Epigenetics. 7:422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Z, Lei H and Sun Q: MicroRNA-141 and
its associated gene FUS modulate proliferation, migration and
cisplatin chemosensitivity in neuroblastoma cell lines. Oncol Rep.
35:2943–2951. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mahdavinezhad A, Mousavi-Bahar SH,
Poorolajal J, Yadegarazari R, Jafari M, Shabab N and Saidijam M:
Evaluation of miR-141, miR-200c, miR-30b Expression and
Clinicopathological features of bladder cancer. Int J Mol Cell Med.
4:32–39. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, Fälth M,
Haese A, Steuber T, Beissbarth T, Kuner R and Sültmann H:
Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in
prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:608–616. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Xue X, You S, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Zou GZ, Wang
PC, Zhao YL, Xu Y, Jia L, Zhang X, et al: Mitaplatin increases
sensitivity of tumor cells to cisplatin by inducing mitochondrial
dysfunction. Mol Pharm. 9:634–644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Porten SP, Leapman MS and Greene KL:
Intravesical chemotherapy in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Indian J Urol. 31:297–303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Song D, Wientjes MG, Gan Y and Au JL:
Bladder tissue pharmacokinetics and antitumor effect of
intravesical 5-fluorouridine. Clin Cancer Res. 3:901–909.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Abbo AH, Jones DR, Masters AR, Stewart JC,
Fourez L and Knapp DW: Phase I clinical trial and pharmacokinetics
of intravesical mitomycin C in dogs with localized transitional
cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. J Vet Intern Med.
24:1124–1130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|