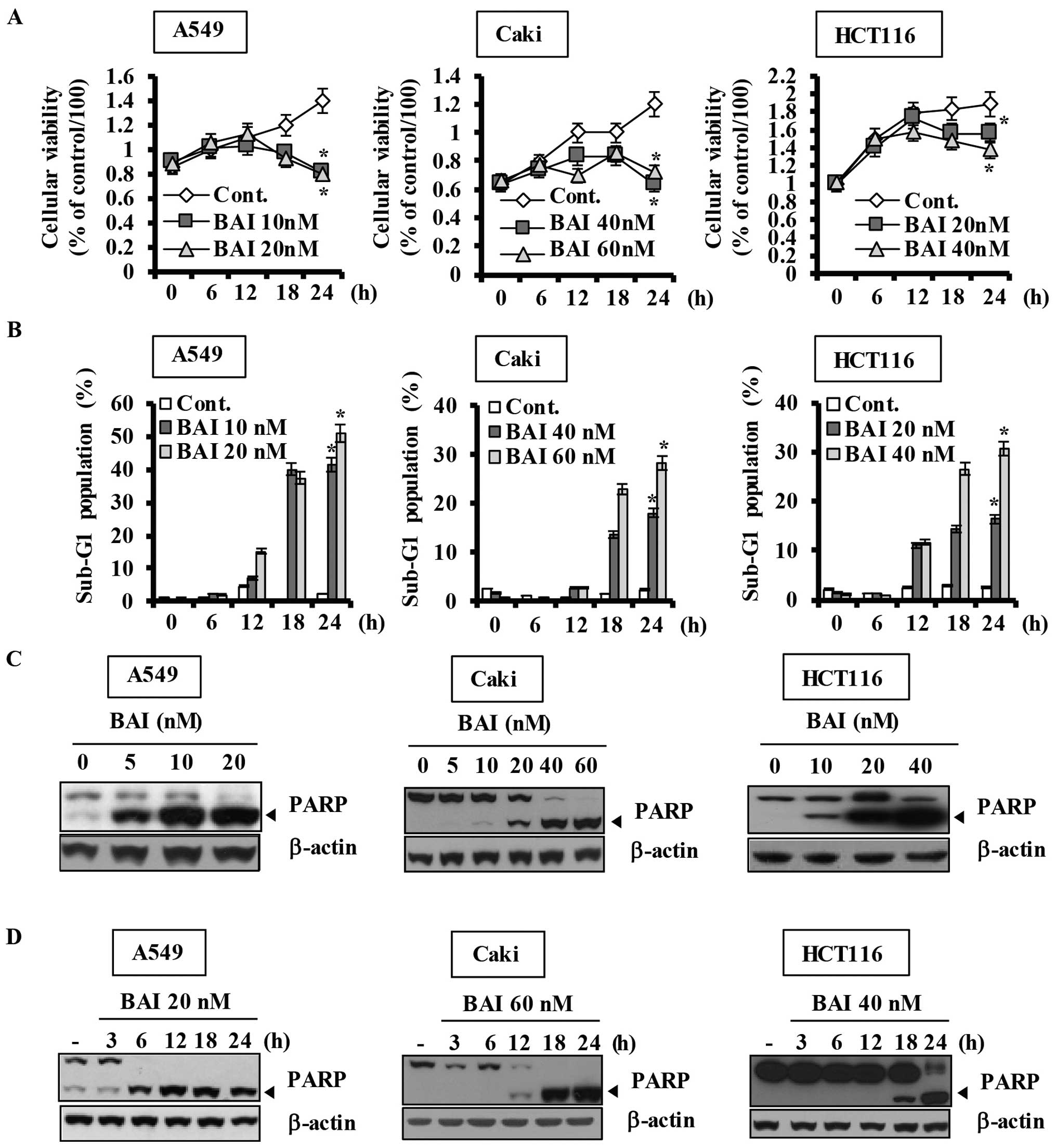
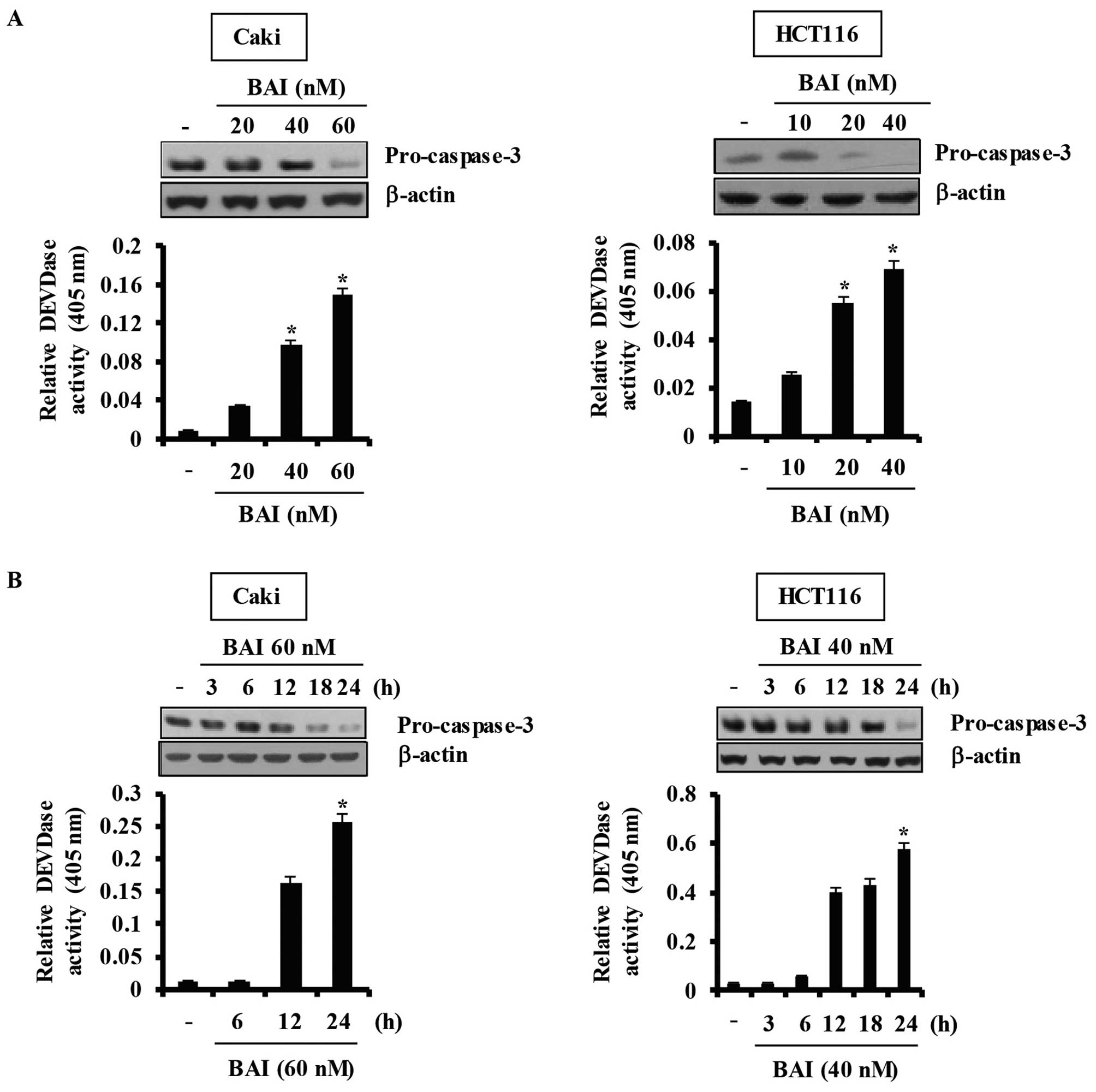
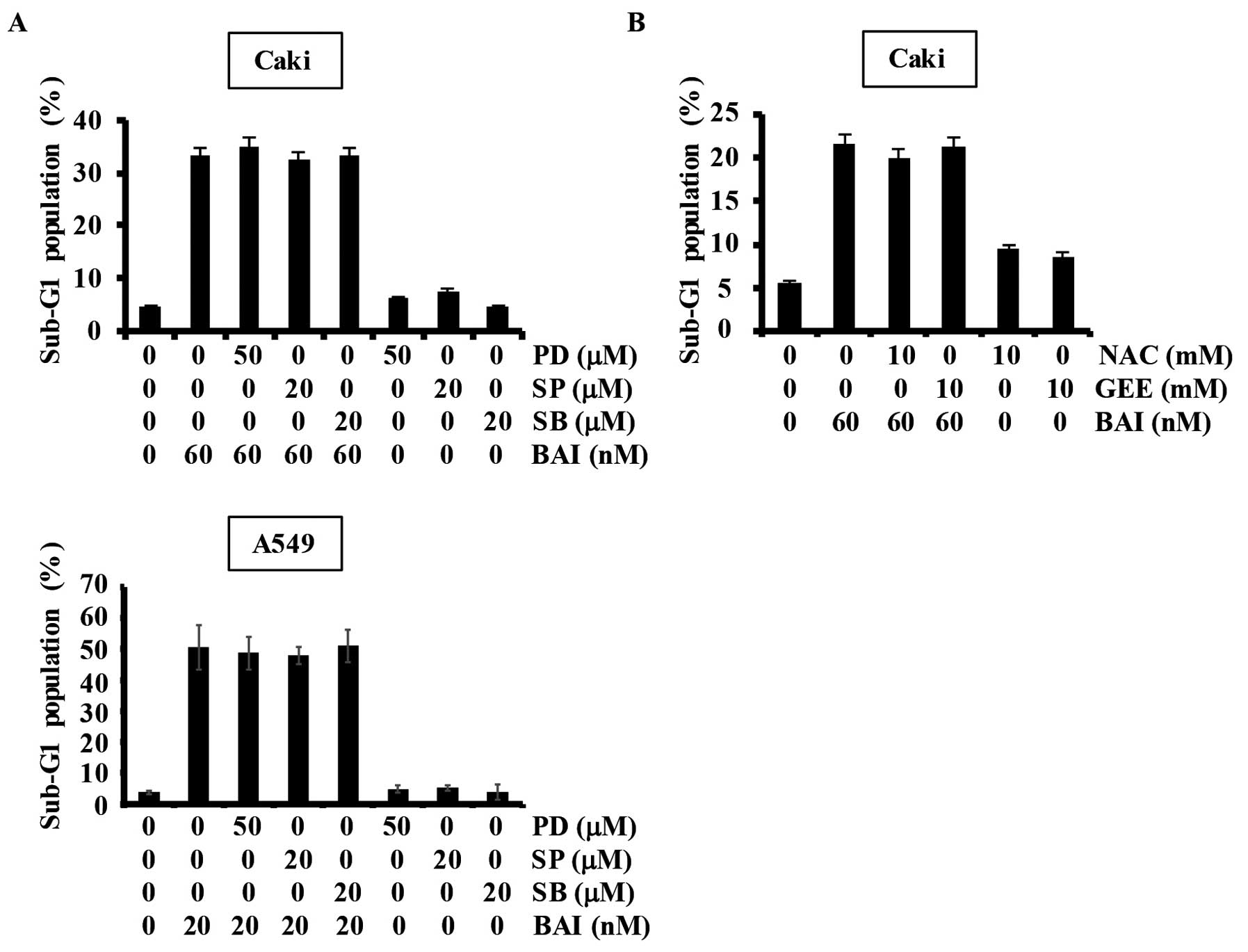
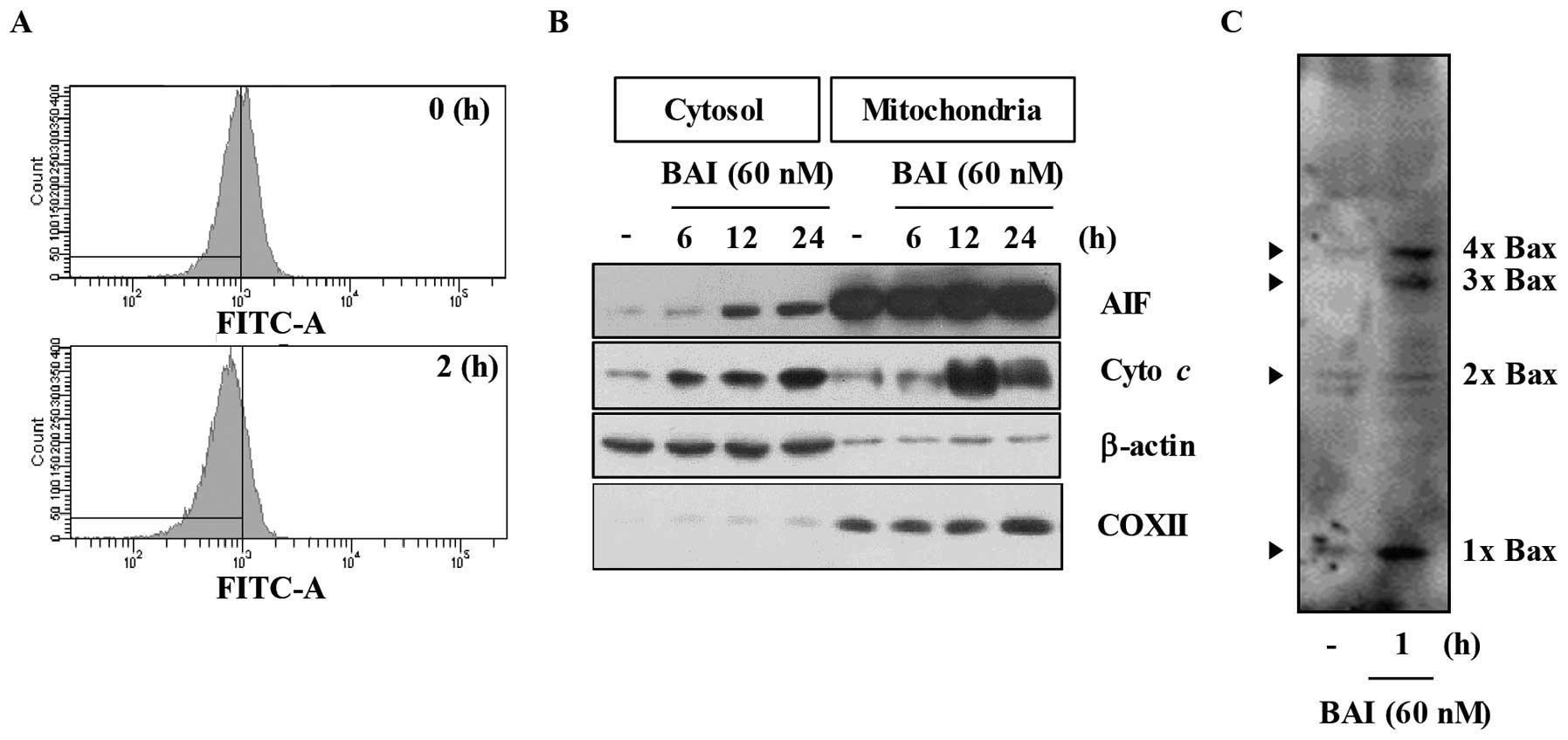
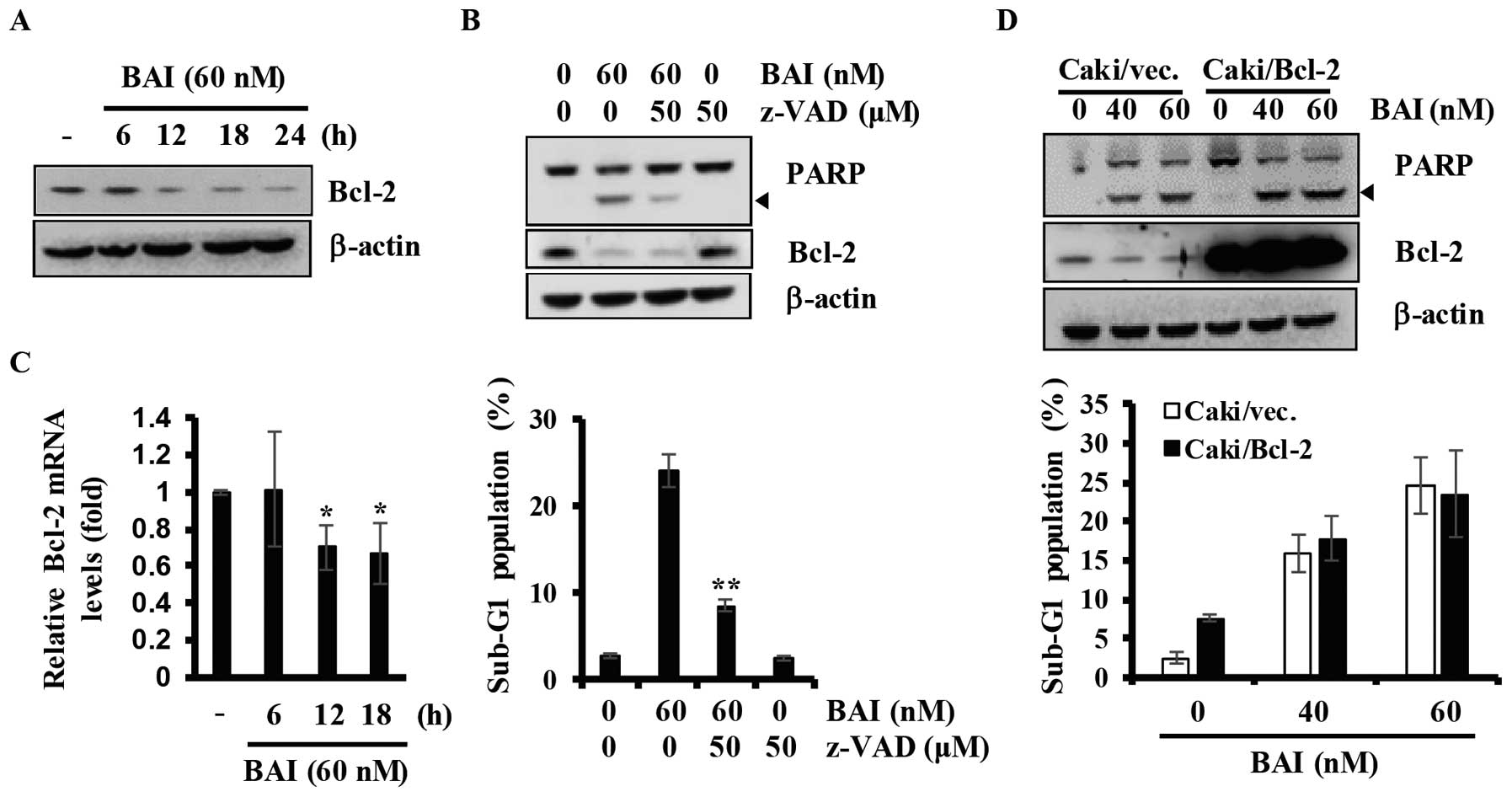
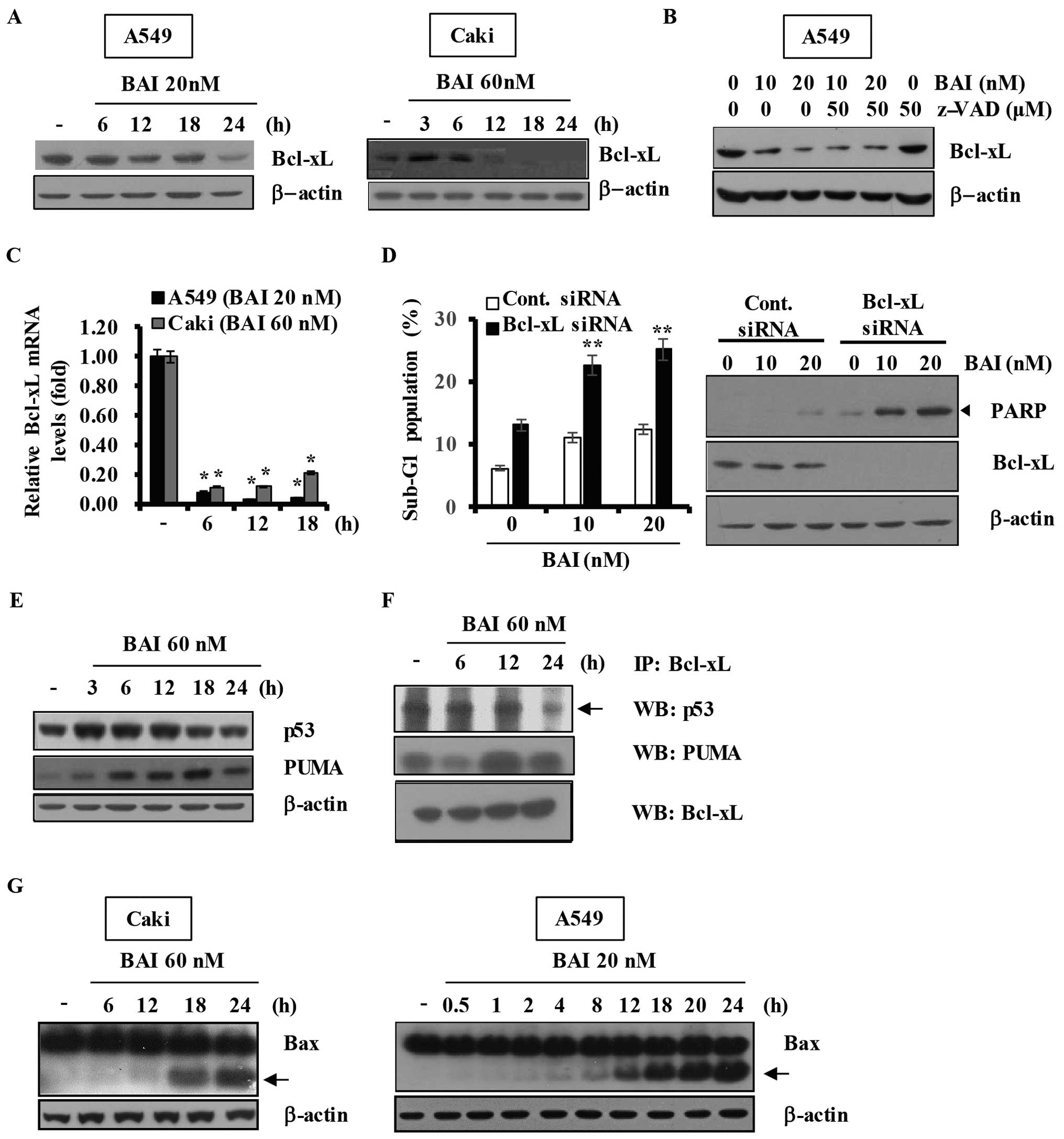
|
1
|
Lee J, Choi H, Kim KH, Jeong S, Park JW,
Baek CS and Lee SH: Synthesis and biological evaluation of
3,5-diaminoindazoles as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 18:2292–2295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim S, Lee J, Jang BC, Kwon TK and Park
JW: BAI, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor induces
apoptosis in A549 cells through activation of caspases and
inactivation of Akt. J Cell Biochem. 114:282–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shin HC, Song DW, Baek WK, Lee SR, Kwon
TK, Lee J, Park SH, Jang BC and Park JW: Anticancer activity and
differentially expressed genes in head and neck cancer cells
treated with a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor.
Chemotherapy. 55:353–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jang JH, Cho YC, Kim KH, Lee KS, Lee J,
Kim DE, Park JS, Jang BC, Kim S, Kwon TK, et al: BAI, a novel Cdk
inhibitor, enhances farnesyltransferase inhibitor LB42708-mediated
apoptosis in renal carcinoma cells through the downregulation of
Bcl-2 and c-FLIP (L). Int J Oncol. 45:1680–1690. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jacobson MD, Weil M and Raff MC:
Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 88:347–354.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Green DR and Llambi F: Cell death
signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:72015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kroemer G: The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and
its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 3:614–620. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Follis AV, Chipuk JE, Fisher JC, Yun MK,
Grace CR, Nourse A, Baran K, Ou L, Min L, White SW, et al: PUMA
binding induces partial unfolding within BCL-xL to disrupt p53
binding and promote apoptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 9:163–168. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu J, Wang Z, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and
Zhang L: PUMA mediates the apoptotic response to p53 in colorectal
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:1931–1936. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Graves JD, Campbell JS and Krebs EG:
Protein serine/threonine kinases of the MAPK cascade. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 766(1 Receptor Acti): 320–343. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Low HB and Zhang Y: Regulatory roles of
MAPK phosphatases in cancer. Immune Netw. 16:85–98. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Le Bras M, Rouy I and Brenner C: The
modulation of interorganelle cross-talk to control apoptosis. Med
Chem. 2:1–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chipuk JE, Bouchier-Hayes L, Kuwana T,
Newmeyer DD and Green DR: PUMA couples the nuclear and cytoplasmic
proapoptotic function of p53. Science. 309:1732–1735. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sawyers C: Targeted cancer therapy.
Nature. 432:294–297. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin
J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A,
Tarpey P, et al: Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution
revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med. 366:883–892.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ivanova D, Bakalova R, Lazarova D, Gadjeva
V and Zhelev Z: The impact of reactive oxygen species on anticancer
therapeutic strategies. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22:899–908. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walensky LD: BCL-2 in the crosshairs:
Tipping the balance of life and death. Cell Death Differ.
13:1339–1350. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fernandez-Luna JL: Regulation of
pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins and its contribution to cancer
progression and chemoresistance. Cell Signal. 20:1921–1926. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Azmi AS, Wang Z, Philip PA, Mohammad RM
and Sarkar FH: Emerging Bcl-2 inhibitors for the treatment of
cancer. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 16:59–70. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: Cytoplasmic
functions of the tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 458:1127–1130.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L,
Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR: Direct activation of
Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and
apoptosis. Science. 303:1010–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hemann MT, Zilfou JT, Zhao Z, Burgess DJ,
Hannon GJ and Lowe SW: Suppression of tumorigenesis by the p53
target PUMA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9333–9338. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeffers JR, Parganas E, Lee Y, Yang C,
Wang J, Brennan J, MacLean KH, Han J, Chittenden T, Ihle JN, et al:
Puma is an essential mediator of p53-dependent and -independent
apoptotic pathways. Cancer Cell. 4:321–328. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yanase N, Ohshima K, Ikegami H and
Mizuguchi J: Cytochrome c release, mitochondrial membrane
depolarization, caspase-3 activation, and Bax-alpha cleavage during
IFN-alpha-induced apoptosis in Daudi B lymphoma cells. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 20:1121–1129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim YH, Shin HC, Song DW, Lee SH, Furumai
T, Park JW and Kwon TK: Arisostatins A induces apoptosis through
the activation of caspase-3 and reactive oxygen species generation
in AMC-HN-4 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 309:449–456. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yeo JK, Cha SD, Cho CH, Kim SP, Cho JW,
Baek WK, Suh MH, Kwon TK, Park JW and Suh SI:
Se-methylselenocysteine induces apoptosis through caspase
activation and Bax cleavage mediated by calpain in SKOV-3 ovarian
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 182:83–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Gurp M, Festjens N, van Loo G, Saelens
X and Van den Abeele P: Mitochondrial intermembrane proteins in
cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:487–497. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|