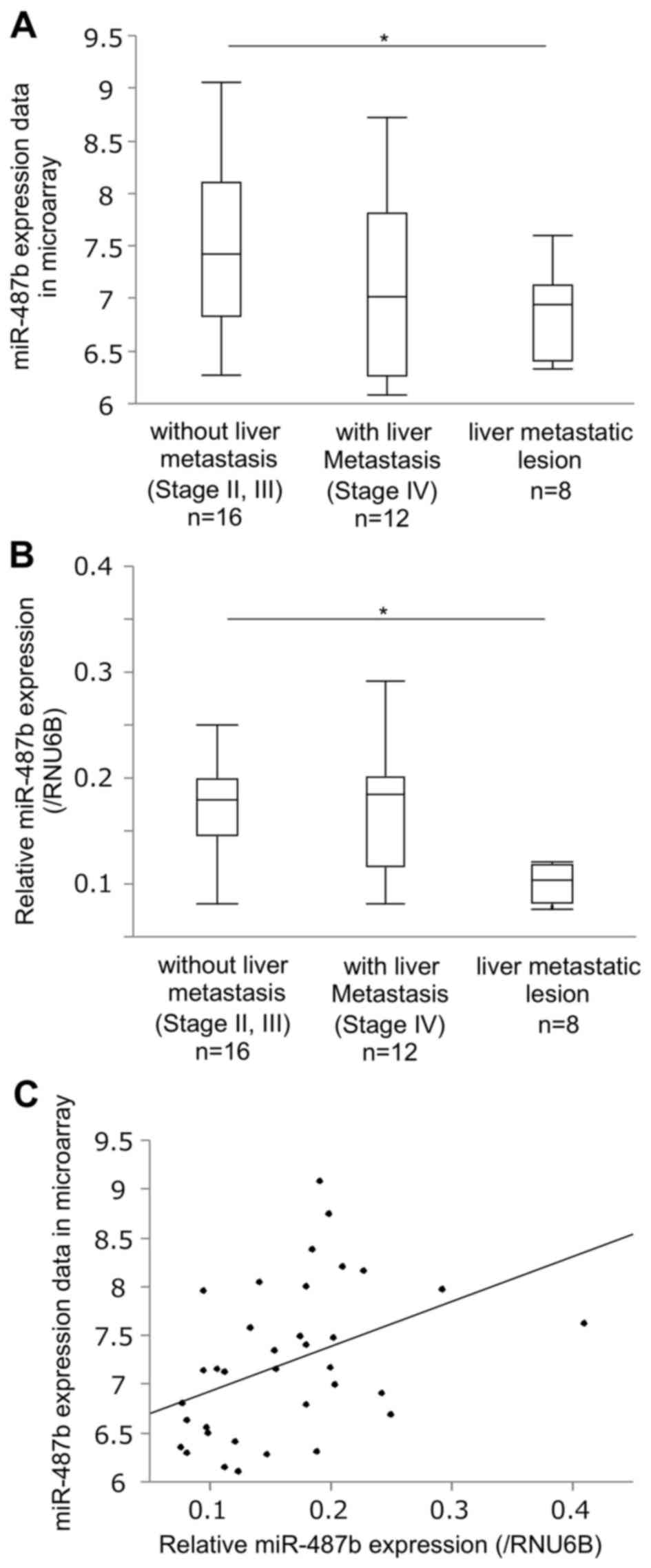
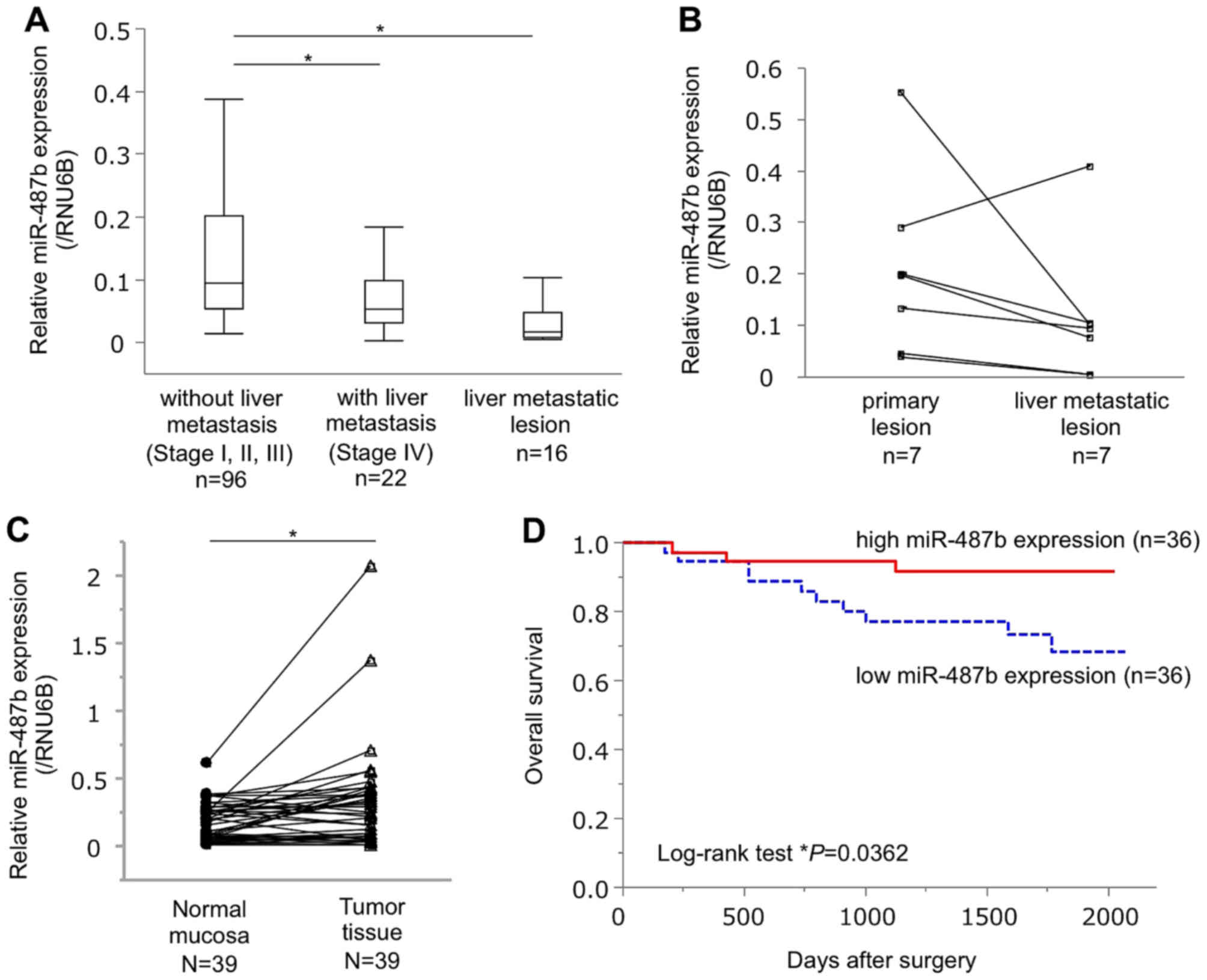
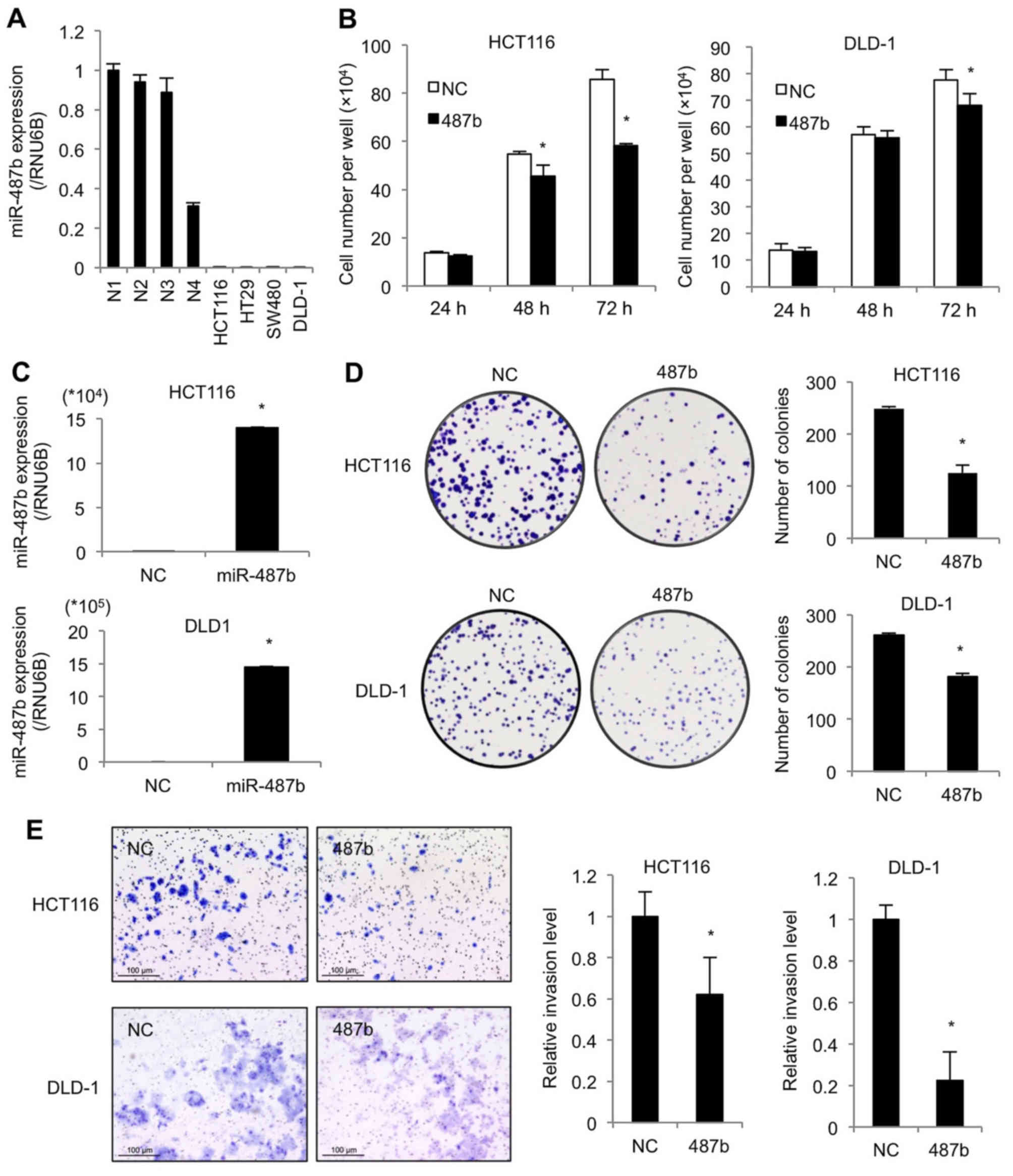
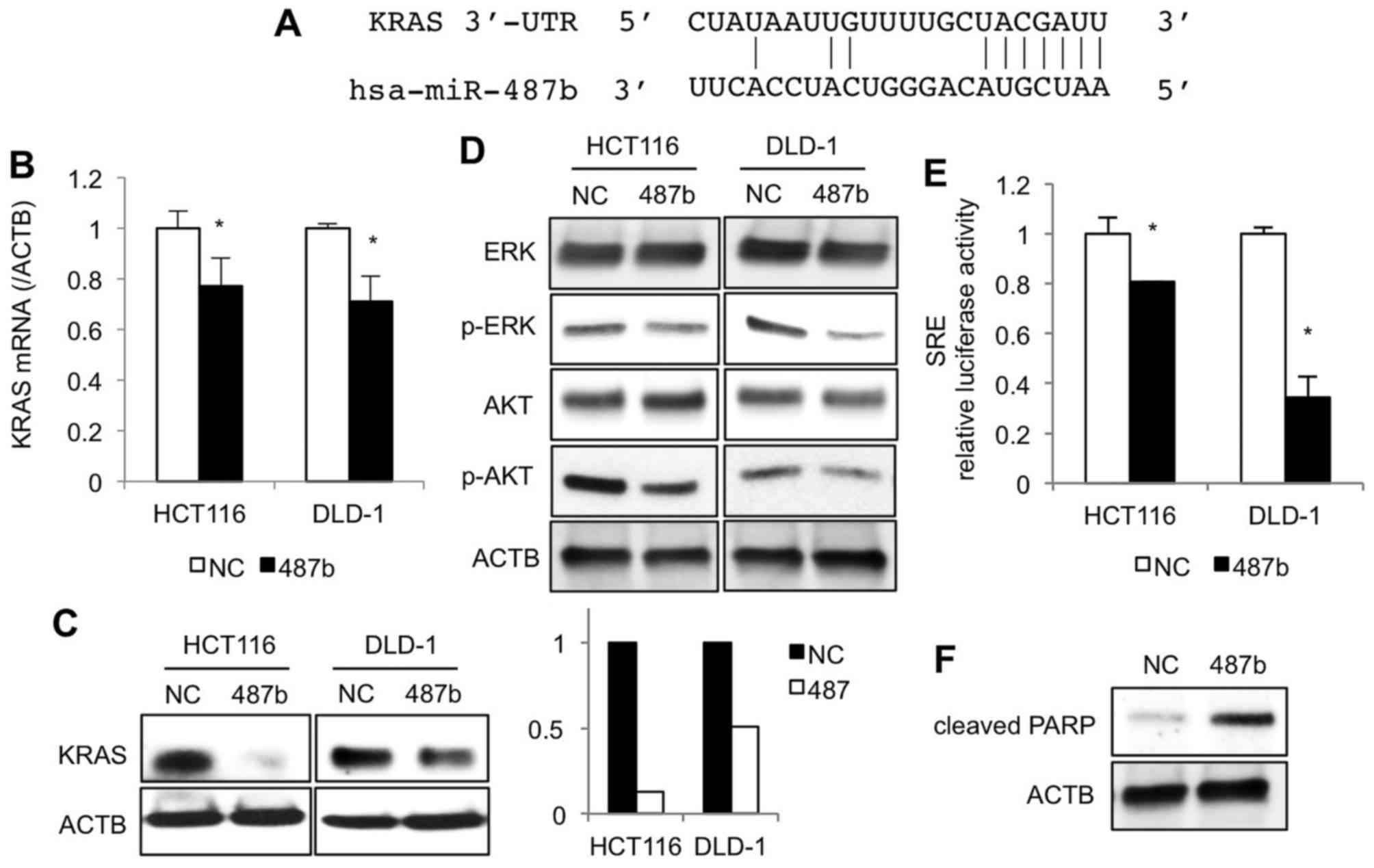
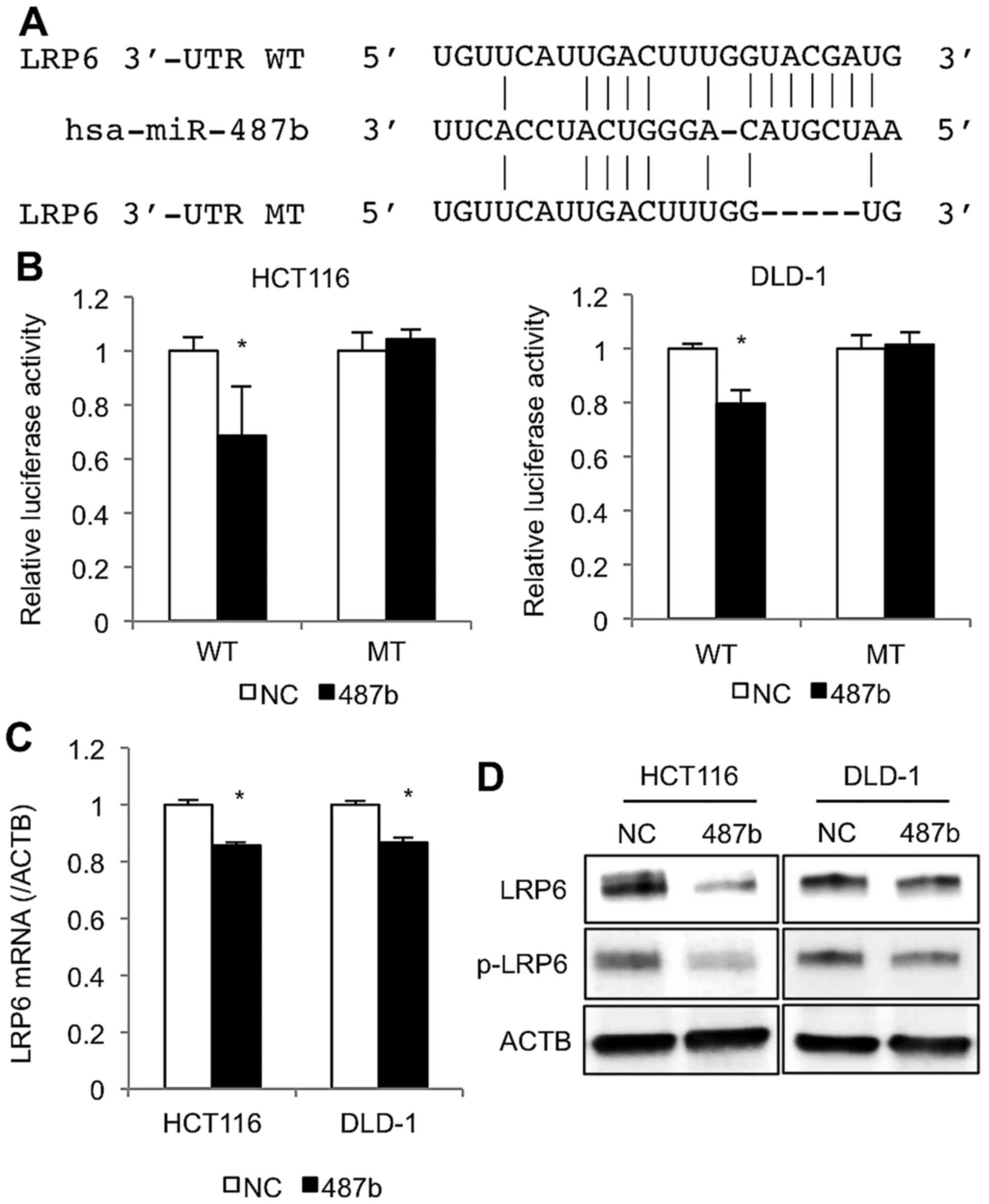
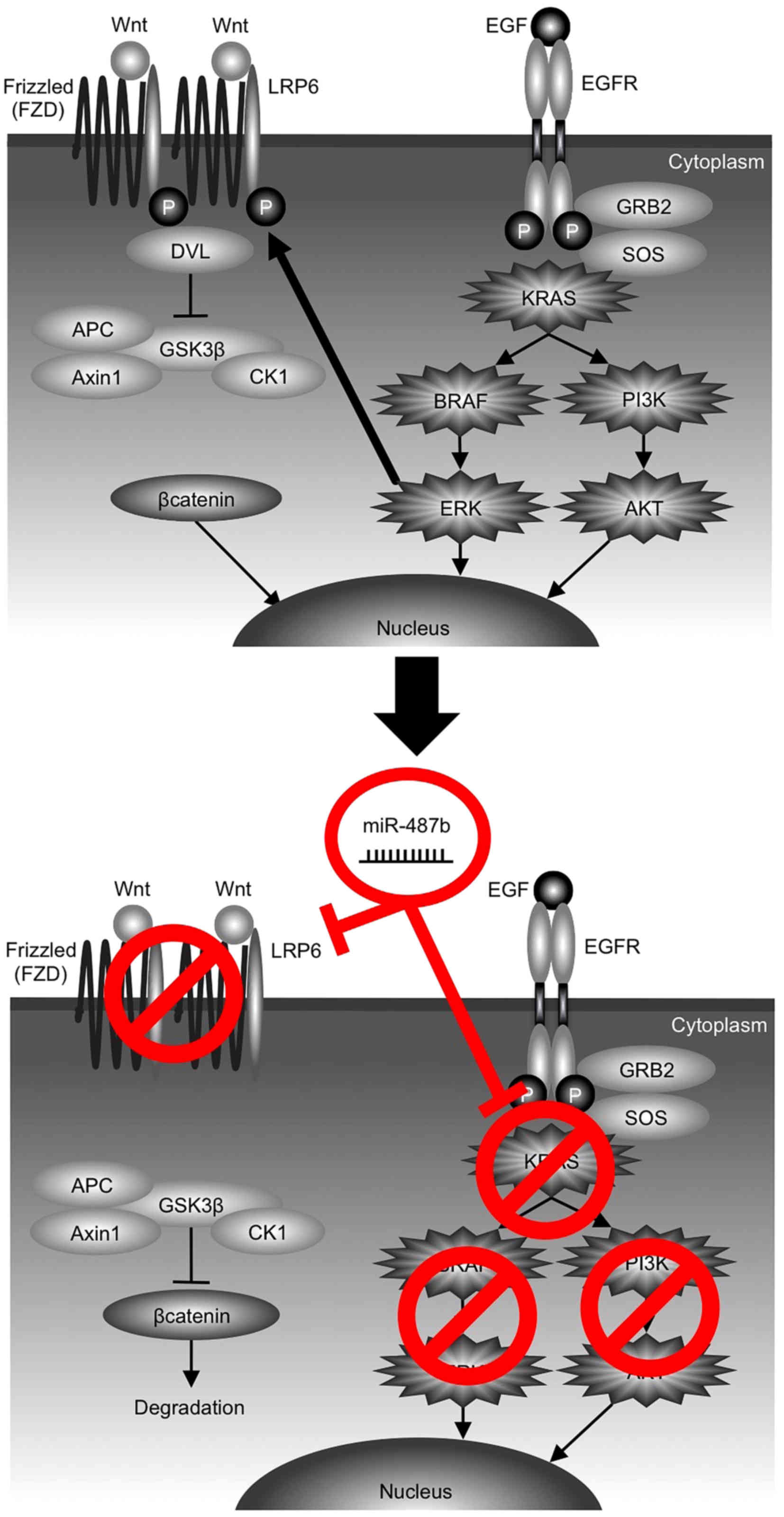
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kopetz S, Chang GJ, Overman MJ, Eng C,
Sargent DJ, Larson DW, Grothey A, Vauthey JN, Nagorney DM and
McWilliams RR: Improved survival in metastatic colorectal cancer is
associated with adoption of hepatic resection and improved
chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 27:3677–3683. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leonard GD, Brenner B and Kemeny NE:
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before liver resection for patients with
unresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2038–2048. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amano R, Yamada N, Nakata B, Kimura K,
Yashiro M, Ohira M and Hirakawa K: Prognostic indicator for the
resection of liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Surg Today.
44:1287–1292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sorski L, Levi B, Shaashua L, Neeman E,
Benish M, Matzner P, Hoffman A and Ben-Eliyahu S: Impact of
surgical extent and sex on the hepatic metastasis of colon cancer.
Surg Today. 44:1925–1934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen K and Rajewsky N: The evolution of
gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev
Genet. 8:93–103. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang H, Li Y and Lai M: The microRNA
network and tumor metastasis. Oncogene. 29:937–948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: MicroRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stiegelbauer V, Perakis S, Deutsch A, Ling
H, Gerger A and Pichler M: MicroRNAs as novel predictive biomarkers
and therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:11727–11735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu WK, Law PT, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu
K, Yu J and Sung JJ: MicroRNA in colorectal cancer: From benchtop
to bedside. Carcinogenesis. 32:247–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
US National Institutes of Health: A
multicenter phase I study of MRX34, microRNA miR-RX34 liposomal
injection. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01829971.
Accessed May 27, 2016.
|
|
16
|
Mokutani Y, Uemura M, Munakata K, Okuzaki
D, Haraguchi N, Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Hata T, Murata K,
Takemasa I, et al: Down-regulation of microRNA-132 is associated
with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. Feb
11–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xi S, Xu H, Shan J, Tao Y, Hong JA,
Inchauste S, Zhang M, Kunst TF, Mercedes L and Schrump DS:
Cigarette smoke mediates epigenetic repression of miR-487b during
pulmonary carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 123:1241–1261. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stewart DJ: Wnt signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt3562014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gattolliat CH, Thomas L, Ciafrè SA,
Meurice G, Le Teuff G, Job B, Richon C, Combaret V, Dessen P,
Valteau-Couanet D, et al: Expression of miR-487b and miR-410
encoded by 14q32.31 locus is a prognostic marker in neuroblastoma.
Br J Cancer. 105:1352–1361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yamamoto H, Murata K, Fukunaga M, Ohnishi
T, Noura S, Miyake Y, Kato T, Ohtsuka M, Nakamura Y, Takemasa I, et
al: Micrometastasis volume in lymph nodes determines disease
recurrence rate of stage II colorectal cancer: A prospective
multicenter trial. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3201–3208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamabe A, Konno M, Tanuma N, Shima H,
Tsunekuni K, Kawamoto K, Nishida N, Koseki J, Mimori K, Gotoh N, et
al: Role of pyruvate kinase M2 in transcriptional regulation
leading to epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:15526–15531. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hiraki M, Nishimura J, Takahashi H, Wu X,
Takahashi Y, Miyo M, Nishida N, Uemura M, Hata T, Takemasa I, et
al: Concurrent targeting of KRAS and AKT by miR-4689 is a novel
treatment against mutant KRAS colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 4:e2312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji D, Chen Z, Li M, Zhan T, Yao Y, Zhang
Z, Xi J, Yan L and Gu J: MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and
liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor
suppressor WIF-1. Mol Cancer. 13:862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen DL, Wang ZQ, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ, Zhang
DS, Luo HY, Wang F, Qiu MZ, Wang DS, Ren C, et al: Identification
of microRNA-214 as a negative regulator of colorectal cancer liver
metastasis by way of regulation of fibroblast growth factor
receptor 1 expression. Hepatology. 60:598–609. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weinstein IB: Disorders in cell circuitry
during multistage carcinogenesis: The role of homeostasis.
Carcinogenesis. 21:857–864. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weinstein IB, Begemann M, Zhou P, Han EK,
Sgambato A, Doki Y, Arber N, Ciaparrone M and Yamamoto H: Disorders
in cell circuitry associated with multistage carcinogenesis:
Exploitable targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Clin Cancer
Res. 3:2696–2702. 1997.
|
|
28
|
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC and Tong SL: miR-132 inhibits colorectal
cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6515–6522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin CW, Li XR, Zhang Y, Hu G, Guo YH, Zhou
JY, Du J, Lv L, Gao K, Zhang Y, et al: TAp63 suppress metastasis
via miR-133b in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 110:2310–2320.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kara M, Yumrutas O, Ozcan O, Celik OI,
Bozgeyik E, Bozgeyik I and Tasdemir S: Differential expressions of
cancer-associated genes and their regulatory miRNAs in colorectal
carcinoma. Gene. 567:81–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, Li S, Xu L, Li X, Li
Y, Li Z, Ng SS, Sung JJ, et al: miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal
cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage
II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 34:4142–4152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E,
Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Moskovits N, Bentwich Z and Oren M:
Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Krell J, Frampton AE, Mirnezami R, Harding
V, De Giorgio A, Roca Alonso L, Cohen P, Ottaviani S, Colombo T,
Jacob J, et al: Growth arrest-specific transcript 5 associated
snoRNA levels are related to p53 expression and DNA damage in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e985612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smakman N, Borel Rinkes IH, Voest EE and
Kranenburg O: Control of colorectal metastasis formation by K-Ras.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1756:103–114. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pretlow TP and Pretlow TG: Mutant KRAS in
aberrant crypt foci (ACF): Initiation of colorectal cancer? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1756:83–96. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Misale S, Yaeger R, Hobor S, Scala E,
Janakiraman M, Liska D, Valtorta E, Schiavo R, Buscarino M,
Siravegna G, et al: Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired
resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature.
486:532–536. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diaz LA Jr, Williams RT, Wu J, Kinde I,
Hecht JR, Berlin J, Allen B, Bozic I, Reiter JG, Nowak MA, et al:
The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR
blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature. 486:537–540.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Lu W, He X, Schwartz AL and Bu G:
LRP6 expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by altering beta-catenin subcellular distribution.
Oncogene. 23:9129–9135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu CC, Prior J, Piwnica-Worms D and Bu G:
LRP6 overexpression defines a class of breast cancer subtype and is
a target for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:5136–5141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tung EK, Wong BY, Yau TO and Ng IO:
Upregulation of the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 promotes
hepatocarcinogenesis and enhances cell invasion. PLoS One.
7:e365652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Du C, Lv Z, Cao L, Ding C, Gyabaah OA, Xie
H, Zhou L, Wu J and Zheng S: MiR-126-3p suppresses tumor metastasis
and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting LRP6 and
PIK3R2. J Transl Med. 12:2592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Y, Zheng D, Xiong Y, Xue C, Chen G,
Yan B and Ye Q: miR-202 suppresses cell proliferation in human
hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating LRP6
post-transcriptionally. FEBS Lett. 588:1913–1920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zeng XC, Liu FQ, Yan R, Yi HM, Zhang T,
Wang GY, Li Y and Jiang N: Downregulation of miR-610 promotes
proliferation and tumorigenicity and activates Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
13:2612014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lemieux E, Cagnol S, Beaudry K, Carrier J
and Rivard N: Oncogenic KRAS signalling promotes the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway through LRP6 in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 34:4914–4927.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Krejci P, Aklian A, Kaucka M, Sevcikova E,
Prochazkova J, Masek JK, Mikolka P, Pospisilova T, Spoustova T,
Weis M, et al: Receptor tyrosine kinases activate canonical
WNT/β-catenin signaling via MAP kinase/LRP6 pathway and direct
β-catenin phosphorylation. PLoS One. 7:e358262012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N,
Clevers H, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Activation of
beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in
beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bienz M and Clevers H: Linking colorectal
cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell. 103:311–320. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cancer Genome Atlas N; Cancer Genome Atlas
Network: Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon
and rectal cancer. Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Masuda M, Uno Y, Ohbayashi N, Ohata H,
Mimata A, Kukimoto-Niino M, Moriyama H, Kashimoto S, Inoue T, Goto
N, et al: TNIK inhibition abrogates colorectal cancer stemness. Nat
Commun. 7:125862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|