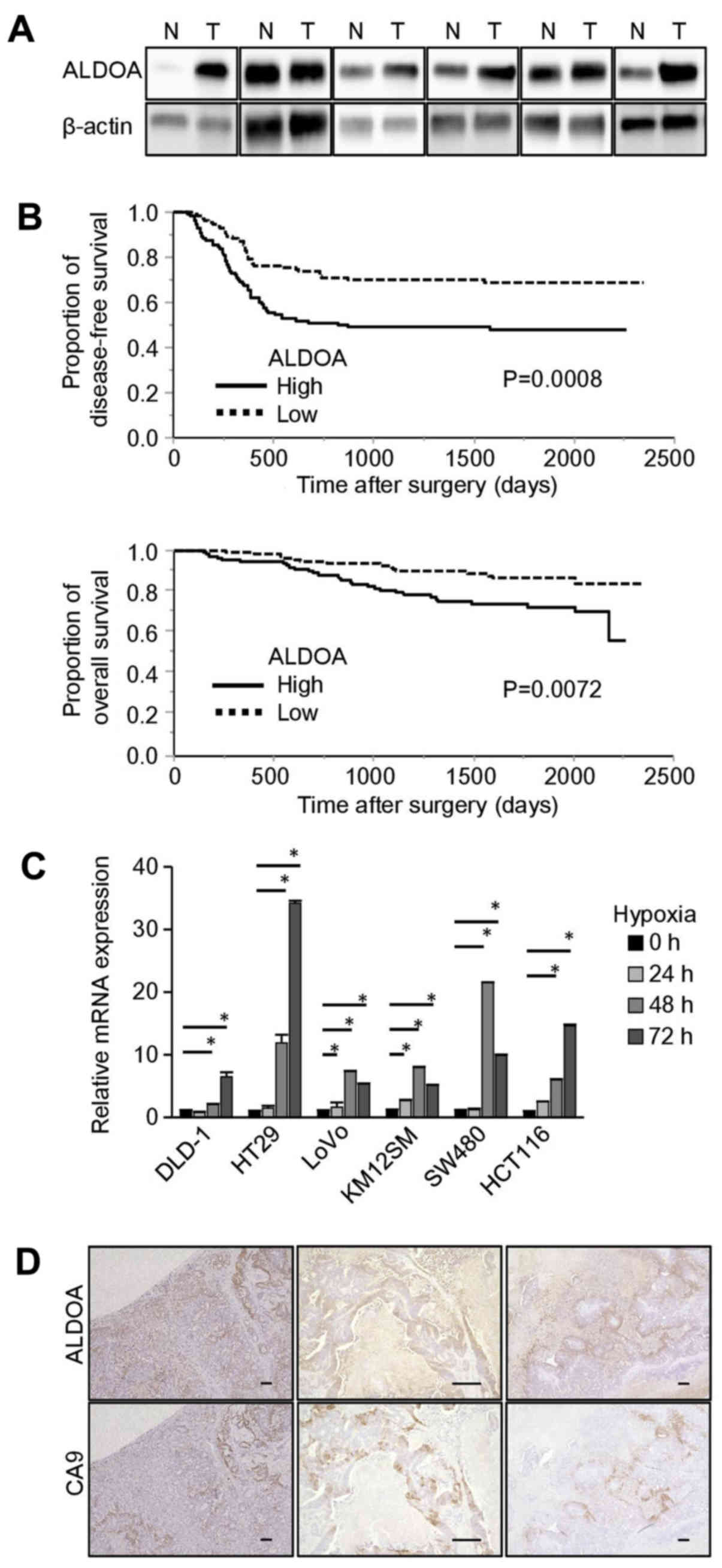
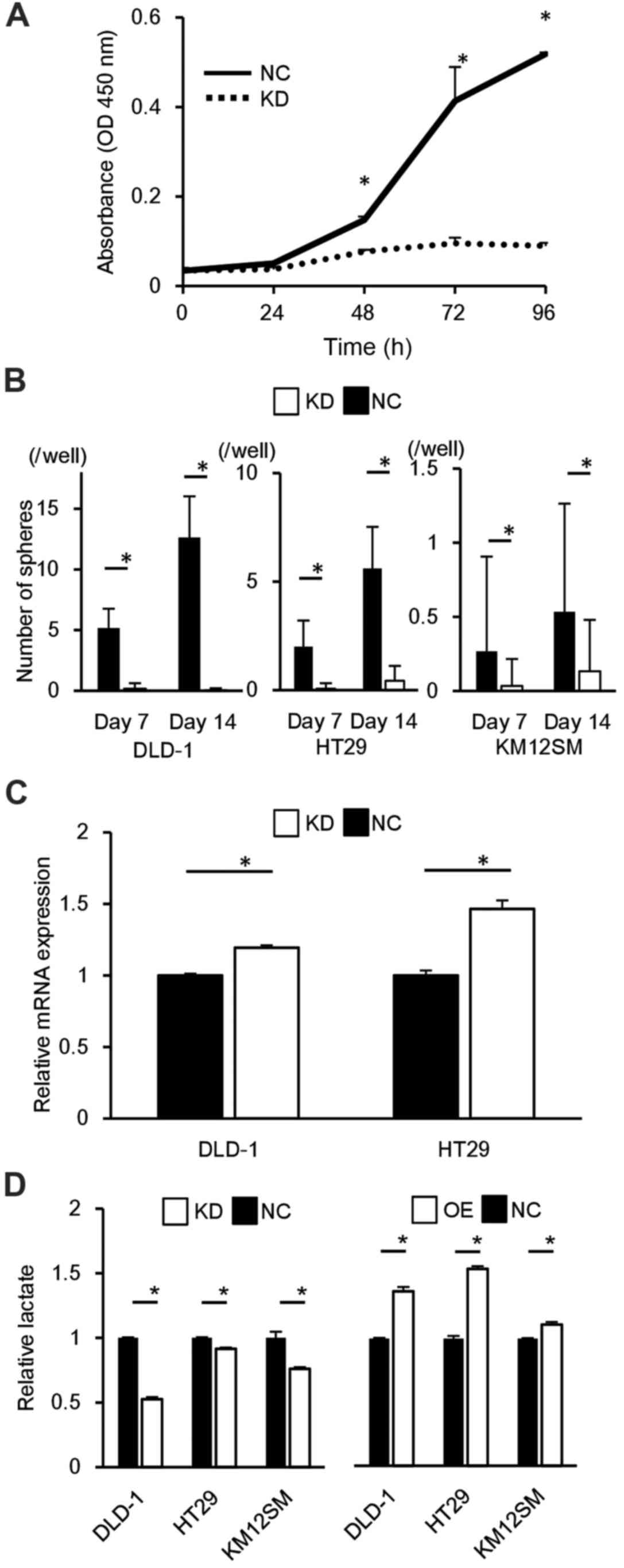
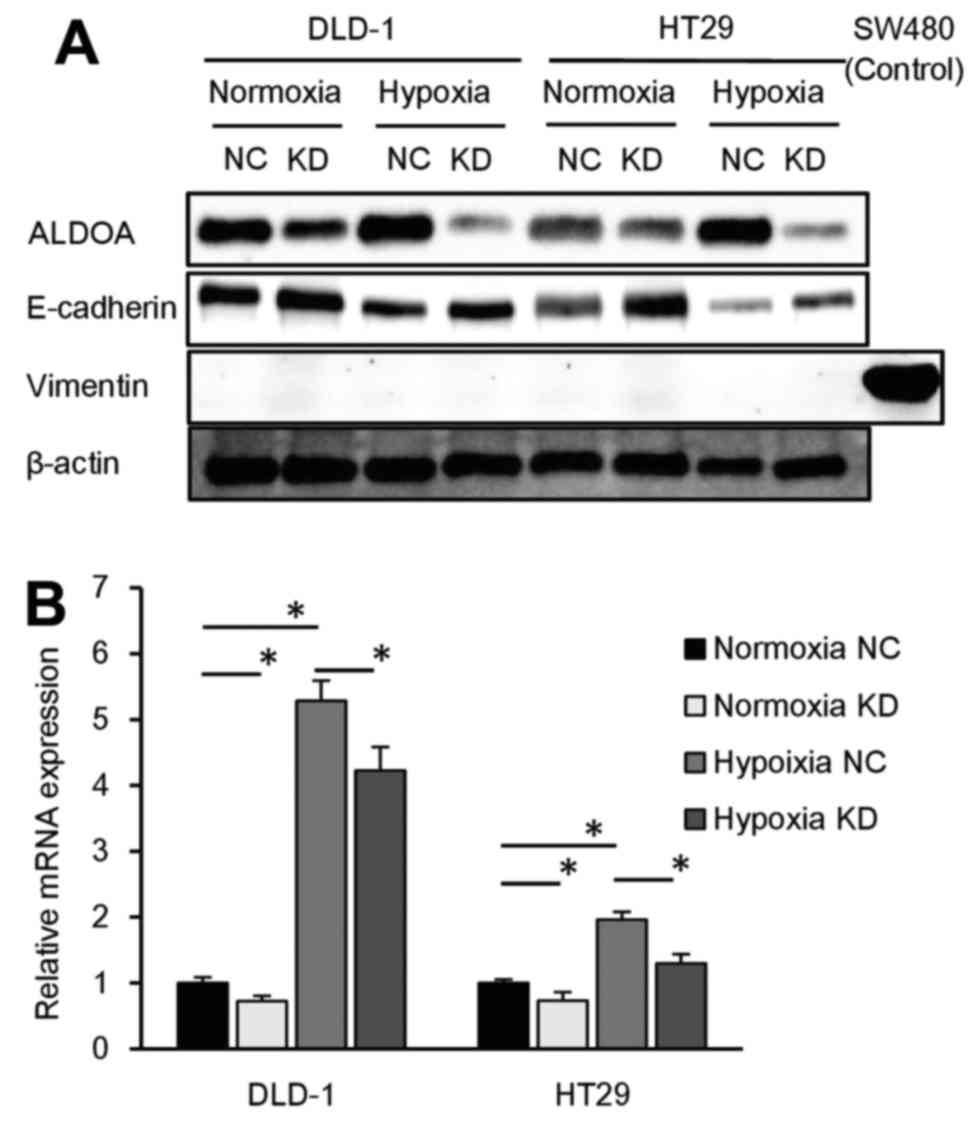
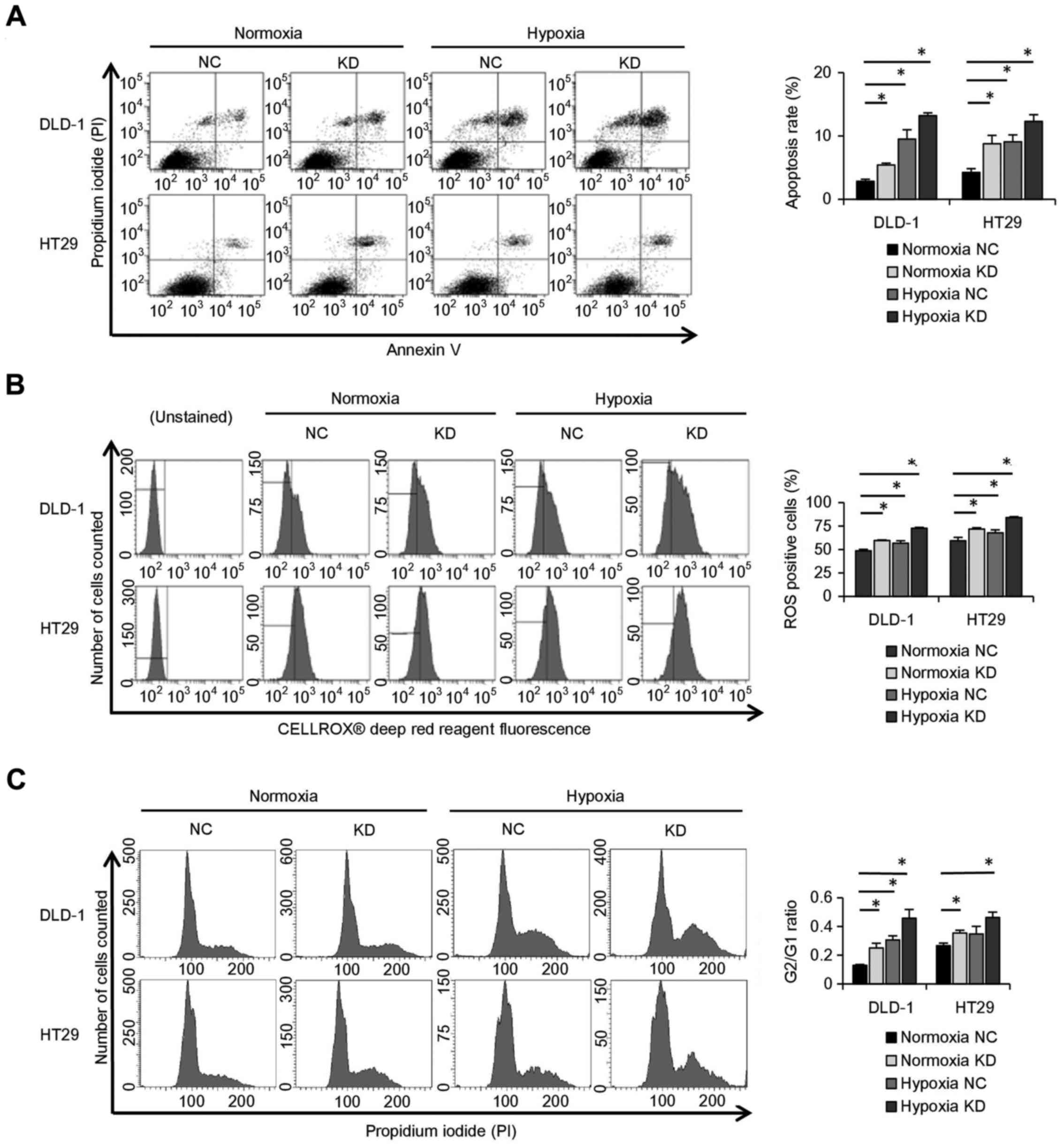
|
1
|
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle
PR and Büchler MW: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 365:153–165. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beppu N, Yoshie H, Kimura F, Aihara T, Doi
H, Kamikonya N, Matsubara N, Tomita N, Yanagi H and Yamanaka N:
Clinicopathological outcomes of preoperative chemoradiotherapy
using S-1 plus Irinotecan for T4 lower rectal cancer. Surg Today.
46:852–859. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Saeki H, Emi Y, Kumashiro R, Otsu H,
Kawano H, Ando K, Ida S, Kimura Y, Tokunaga E, Oki E, et al: Impact
of second-line and later cetuximab-containing therapy and KRAS
genotypes in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A
multicenter study in Japan. Surg Today. 44:1457–1464. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jensen RL: Brain tumor hypoxia:
Tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, imaging, pseudoprogression, and as a
therapeutic target. J Neurooncol. 92:317–335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vaupel P, Briest S and Höckel M: Hypoxia
in breast cancer: Pathogenesis, characterization and
biological/therapeutic implications. Wien Med Wochenschr.
152:334–342. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y,
Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, et al: Hypoxia induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by
hypoxia-inducible factor -1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 13:1–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee GW, Go SI, Cho YJ, Jeong YY, Kim HC,
Duk Lee J, Hwang YS, Ko GH, Lee JH, Kim DC, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and excision repair cross-complementing
1 in patients with small cell lung cancer who received front-line
platinum-based chemotherapy: A retrospective study. J Thorac Oncol.
7:528–534. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang D, Ma Y, Liu J, Trope CG, Holm R,
Nesland JM and Suo Z: The hypoxic microenvironment upgrades
stem-like properties of ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
12:2012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Higgins LH, Withers HG, Garbens A, Love
HD, Magnoni L, Hayward SW and Moyes CD: Hypoxia and the metabolic
phenotype of prostate cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1787:1433–1443. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang LH, Chen CH, Huang DY, Pai HC, Pan
SL and Teng CM: Thrombin induces expression of twist and cell
motility via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α translational pathway
in colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 226:1060–1068. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Uemura M, Yamamoto H, Takemasa I, Mimori
K, Hemmi H, Mizushima T, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, Doki Y,
et al: Jumonji domain containing 1A is a novel prognostic marker
for colorectal cancer: In vivo identification from hypoxic tumor
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:4636–4646. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uemura M, Yamamoto H, Takemasa I, Mimori
K, Mizushima T, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Doki Y and Mori M:
Hypoxia-inducible adrenomedullin in colorectal cancer. Anticancer
Res. 31:507–514. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto H, Tei M, Uemura M, Takemasa I,
Uemura Y, Murata K, Fukunaga M, Ohue M, Ohnishi T, Ikeda K, et al:
Ephrin-A1 mRNA is associated with poor prognosis of colorectal
cancer. Int J Oncol. 42:549–555. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Noda T, Yamamoto H, Takemasa I, Yamada D,
Uemura M, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Eguchi H, Tanemura M,
et al: PLOD2 induced under hypoxia is a novel prognostic factor for
hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Liver Int.
32:110–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Munakata K, Uemura M, Takemasa I, Ozaki M,
Konno M, Nishimura J, Hata T, Mizushima T, Haraguchi N, Noura S, et
al: SCGB2A1 is a novel prognostic marker for colorectal cancer
associated with chemoresistance and radioresistance. Int J Oncol.
44:1521–1528. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tochio T, Tanaka H, Nakata S and Hosoya H:
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase A is involved in HaCaT cell
migration by inducing lamellipodia formation. J Dermatol Sci.
58:123–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM and Wang GL:
Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 269:23757–23763.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sharp FR and Bernaudin M: HIF1 and oxygen
sensing in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 5:437–448. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Yang TT, Zhou Y, Wang W, Qiu XC,
Gao J, Li CX, Long H, Ma BA, Ma Q, et al: Proteomic profiling of
osteosarcoma cells identifies ALDOA and SULT1A3 as negative
survival markers of human osteosarcoma. Mol Carcinog. 53:138–144.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Long F, Cai X, Luo W, Chen L and Li K:
Role of aldolase A in osteosarcoma progression and metastasis: In
vitro and in vivo evidence. Oncol Rep. 32:2031–2037.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du S, Guan Z, Hao L, Song Y, Wang L, Gong
L, Liu L, Qi X, Hou Z and Shao S: Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A
is a potential metastasis-associated marker of lung squamous cell
carcinoma and promotes lung cell tumorigenesis and migration. PLoS
One. 9:e858042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shimizu T, Inoue K, Hachiya H, Shibuya N,
Shimoda M and Kubota K: Frequent alteration of the protein
synthesis of enzymes for glucose metabolism in hepatocellular
carcinomas. J Gastroenterol. 49:1324–1332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Munakata K, Uemura M, Tanaka S, Kawai K,
Kitahara T, Miyo M, Kano Y, Nishikawa S, Fukusumi T, Takahashi Y,
et al: Cancer stem-like properties in colorectal cancer cells with
low proteasome activity. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5277–5286. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meng MB, Wang HH, Guo WH, Wu ZQ, Zeng XL,
Zaorsky NG, Shi HS, Qian D, Niu ZM, Jiang B, et al: Targeting
pyruvate kinase M2 contributes to radiosensitivity of non-small
cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
356:985–993. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pitroda SP, Wakim BT, Sood RF, Beveridge
MG, Beckett MA, MacDermed DM, Weichselbaum RR and Khodarev NN:
STAT1-dependent expression of energy metabolic pathways links
tumour growth and radioresistance to the Warburg effect. BMC Med.
7:682009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ritterson Lew C and Tolan DR: Targeting of
several glycolytic enzymes using RNA interference reveals aldolase
affects cancer cell proliferation through a non-glycolytic
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 287:42554–42563. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|