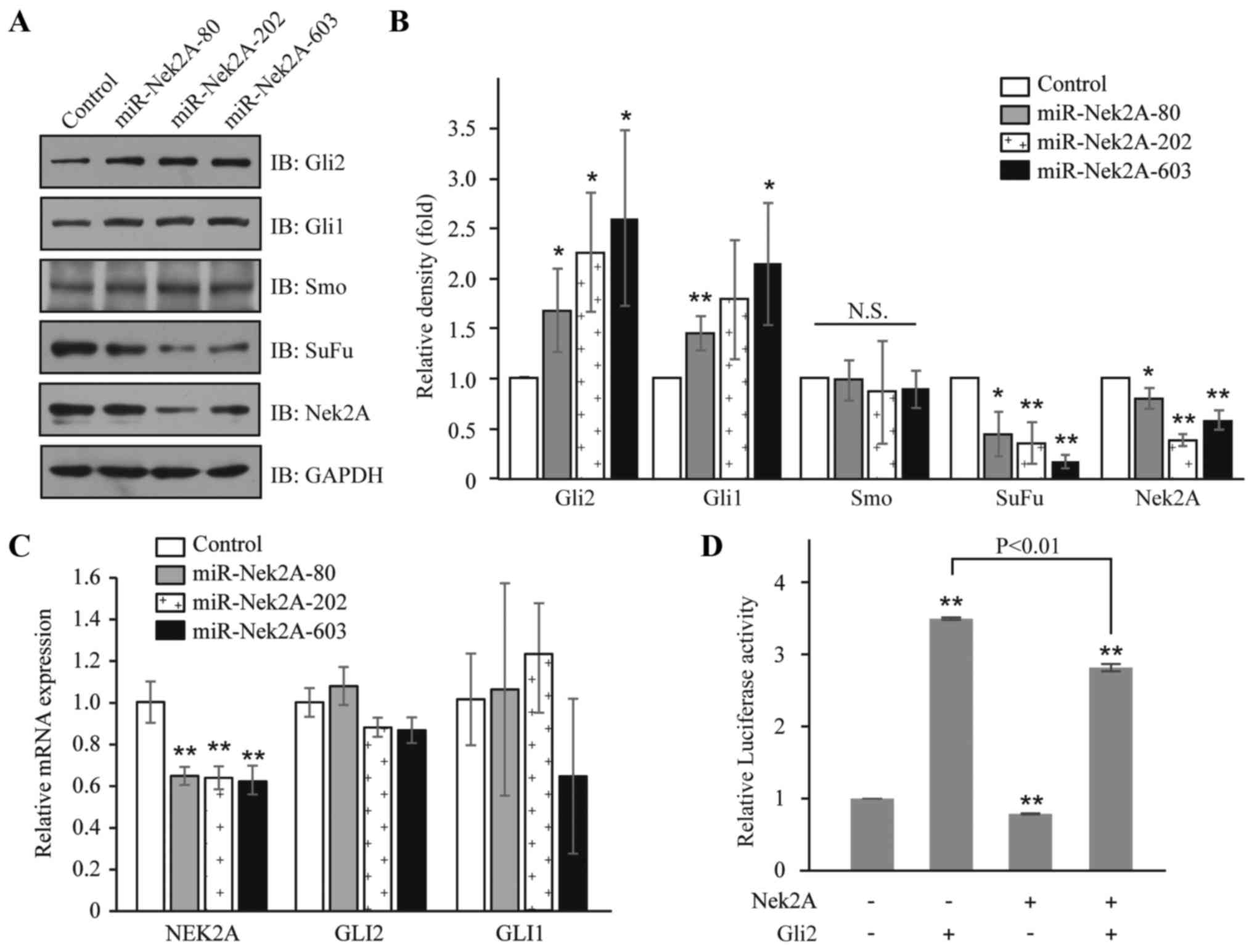
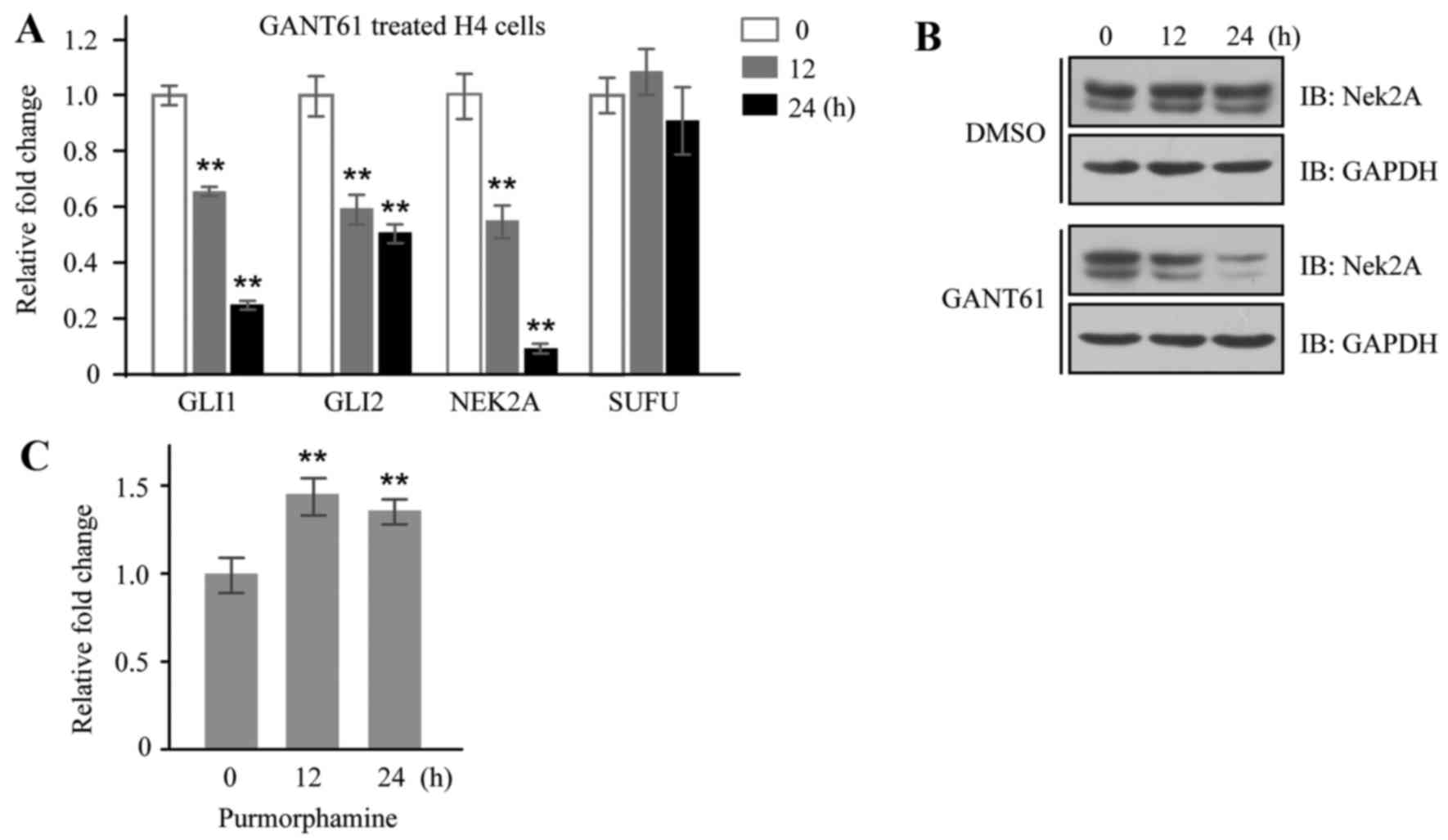
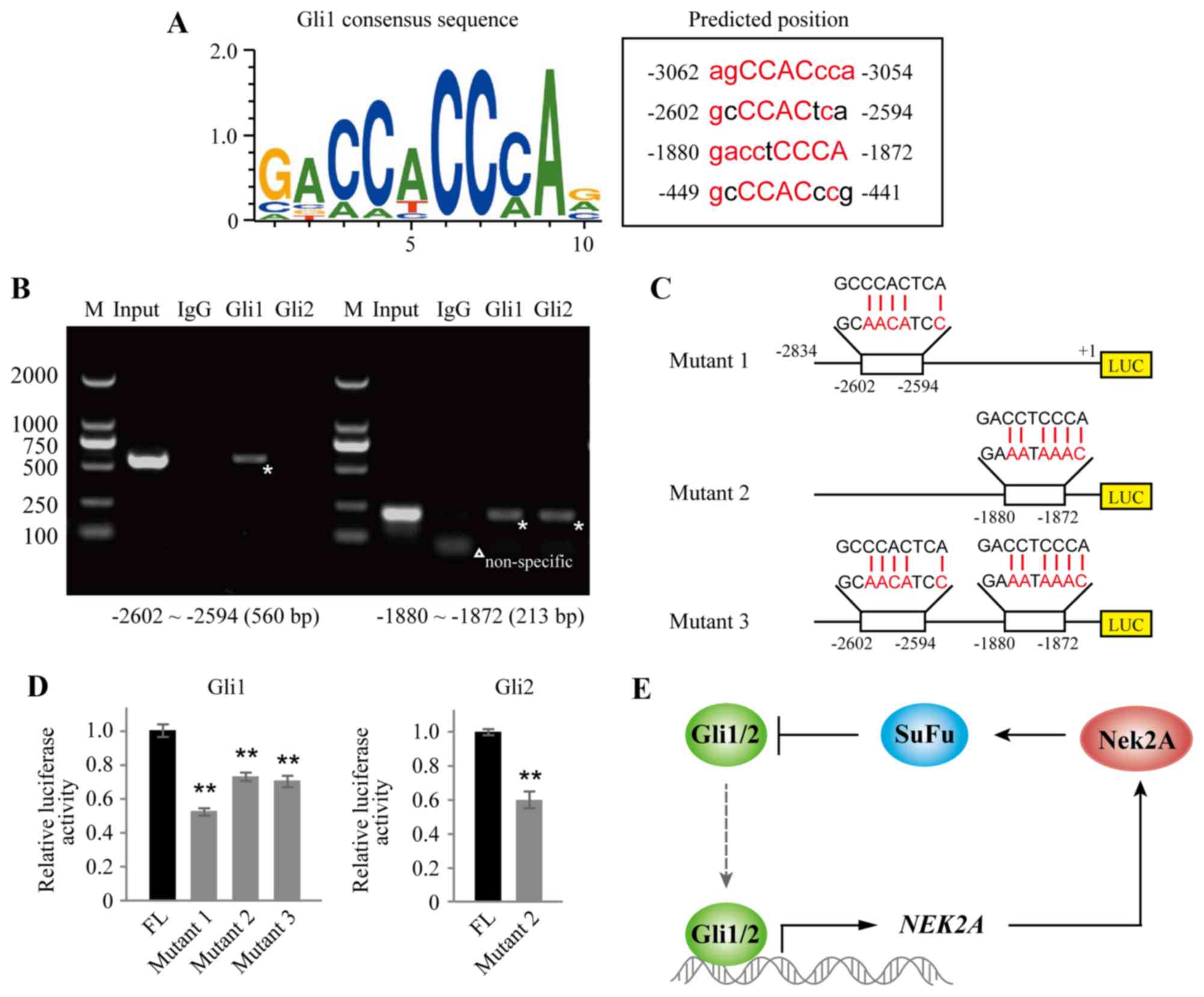
|
1
|
Cooper AF, Yu KP, Brueckner M, Brailey LL,
Johnson L, McGrath JM and Bale AE: Cardiac and CNS defects in a
mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development.
132:4407–4417. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Svärd J, Heby-Henricson K, Persson-Lek M,
Rozell B, Lauth M, Bergström A, Ericson J, Toftgård R and Teglund
S: Genetic elimination of Suppressor of fused reveals an essential
repressor function in the mammalian Hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev
Cell. 10:187–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stone DM, Murone M, Luoh S, Ye W, Armanini
MP, Gurney A, Phillips H, Brush J, Goddard A, de Sauvage FJ, et al:
Characterization of the human suppressor of fused, a negative
regulator of the zinc-finger transcription factor Gli. J Cell Sci.
112:4437–4448. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barnfield PC, Zhang X, Thanabalasingham V,
Yoshida M and Hui CC: Negative regulation of Gli1 and Gli2
activator function by Suppressor of fused through multiple
mechanisms. Differentiation. 73:397–405. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kise Y, Morinaka A, Teglund S and Miki H:
Sufu recruits GSK3beta for efficient processing of Gli3. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 387:569–574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng SY and Bishop JM: Suppressor of
Fused represses Gli-mediated transcription by recruiting the
SAP18-mSin3 corepressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:5442–5447. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Heydeck W, Zeng H and Liu A: Dual
function of suppressor of fused in Hh pathway activation and mouse
spinal cord patterning. Dev Biol. 362:141–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen MH, Wilson CW, Li YJ, Law KK, Lu CS,
Gacayan R, Zhang X, Hui CC and Chuang PT: Cilium-independent
regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is
evolutionarily conserved. Genes Dev. 23:1910–1928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Pan Y and Wang B: Suppressor of
fused and Spop regulate the stability, processing and function of
Gli2 and Gli3 full-length activators but not their repressors.
Development. 137:2001–2009. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, Hui CC,
Mainprize TG, Zhang X, Agatep R, Chiappa S, Gao L, Lowrance A, et
al: Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet.
31:306–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pastorino L, Ghiorzo P, Nasti S,
Battistuzzi L, Cusano R, Marzocchi C, Garrè ML, Clementi M and
Scarrà GB: Identification of a SUFU germline mutation in a family
with Gorlin syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 149A:1539–1543. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM,
Kindblom LG, Toftgård R and Undén AB: Deregulation of the hedgehog
signalling pathway: A possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in
human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol.
208:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sharpe HJ, Pau G, Dijkgraaf GJ,
Basset-Seguin N, Modrusan Z, Januario T, Tsui V, Durham AB, Dlugosz
AA, Haverty PM, et al: Genomic analysis of smoothened inhibitor
resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 27:327–341. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheng T, Li C, Zhang X, Chi S, He N, Chen
K, McCormick F, Gatalica Z and Xie J: Activation of the hedgehog
pathway in advanced prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 3:292004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yue S, Chen Y and Cheng SY: Hedgehog
signaling promotes the degradation of tumor suppressor Sufu through
the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Oncogene. 28:492–499. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Yue S, Xie L, Pu XH, Jin T and
Cheng SY: Dual phosphorylation of suppressor of fused (Sufu) by PKA
and GSK3beta regulates its stability and localization in the
primary cilium. J Biol Chem. 286:13502–13511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Hu G, Huang X, Rao H, Xiong
X, Luo Z, Lu Q and Luo S: Nek2A phosphorylates and stabilizes SuFu:
A new strategy of Gli2/Hedgehog signaling regulatory mechanism.
Cell Signal. 28:1304–1313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayward DG and Fry AM: Nek2 kinase in
chromosome instability and cancer. Cancer Lett. 237:155–166. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fry AM, Meraldi P and Nigg EA: A
centrosomal function for the human Nek2 protein kinase, a member of
the NIMA family of cell cycle regulators. EMBO J. 17:470–481. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mayor T, Hacker U, Stierhof YD and Nigg
EA: The mechanism regulating the dissociation of the centrosomal
protein C-Nap1 from mitotic spindle poles. J Cell Sci.
115:3275–3284. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fry AM, Mayor T, Meraldi P, Stierhof YD,
Tanaka K and Nigg EA: C-Nap1, a novel centrosomal coiled-coil
protein and candidate substrate of the cell cycle-regulated protein
kinase Nek2. J Cell Biol. 141:1563–1574. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bahe S, Stierhof YD, Wilkinson CJ, Leiss F
and Nigg EA: Rootletin forms centriole-associated filaments and
functions in centrosome cohesion. J Cell Biol. 171:27–33. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rapley J, Baxter JE, Blot J, Wattam SL,
Casenghi M, Meraldi P, Nigg EA and Fry AM: Coordinate regulation of
the mother centriole component nlp by nek2 and plk1 protein
kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1309–1324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takahashi Y, Iwaya T, Sawada G, Kurashige
J, Matsumura T, Uchi R, Ueo H, Takano Y, Eguchi H, Sudo T, et al:
Up-regulation of NEK2 by microRNA-128 methylation is associated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:205–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Neal CP, Fry AM, Moreman C, McGregor A,
Garcea G, Berry DP and Manson MM: Overexpression of the Nek2 kinase
in colorectal cancer correlates with beta-catenin relocalization
and shortened cancer-specific survival. J Surg Oncol. 110:828–838.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cappello P, Blaser H, Gorrini C, Lin DC,
Elia AJ, Wakeham A, Haider S, Boutros PC, Mason JM, Miller NA, et
al: Role of Nek2 on centrosome duplication and aneuploidy in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 33:2375–2384. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu CM, Zhu J, Guo XE, Chen W, Qiu XL, Ngo
B, Chien R, Wang YV, Tsai CY, Wu G, et al: Novel small molecules
disrupting Hec1/Nek2 interaction ablate tumor progression by
triggering Nek2 degradation through a death-trap mechanism.
Oncogene. 34:1220–1230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu X, Gao Y, Lu Y, Zhang J, Li L and Yin
F: Upregulation of NEK2 is associated with drug resistance in
ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:745–754. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Zhong X, Guan X, Liu W and Zhang L:
Aberrant expression of NEK2 and its clinical significance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 8:1470–1476.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stricker TP, Henriksen KJ, Tonsgard JH,
Montag AG, Krausz TN and Pytel P: Expression profiling of 519
kinase genes in matched malignant peripheral nerve sheath
tumor/plexiform neurofibroma samples is discriminatory and
identifies mitotic regulators BUB1B, PBK and NEK2 as overexpressed
with transformation. Mod Pathol. 26:930–943. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo SW, Zhang C, Zhang B, Kim CH, Qiu YZ,
Du QS, Mei L and Xiong WC: Regulation of heterochromatin
remodelling and myogenin expression during muscle differentiation
by FAK interaction with MBD2. EMBO J. 28:2568–2582. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Joshi H, Nord SH, Frigessi A,
Børresen-Dale AL and Kristensen VN: Overrepresentation of
transcription factor families in the genesets underlying breast
cancer subtypes. BMC Genomics. 13:1992012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Y and Struhl G: In vivo evidence that
Patched and Smoothened constitute distinct binding and transducing
components of a Hedgehog receptor complex. Development.
125:4943–4948. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sinha S and Chen JK: Purmorphamine
activates the Hedgehog pathway by targeting Smoothened. Nat Chem
Biol. 2:29–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nüsslein-Volhard C and Wieschaus E:
Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila.
Nature. 287:795–801. 1980. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huangfu D and Anderson KV: Signaling from
Smo to Ci/Gli: Conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways
from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development. 133:3–14. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Holtz AM, Peterson KA, Nishi Y, Morin S,
Song JY, Charron F, McMahon AP and Allen BL: Essential role for
ligand-dependent feedback antagonism of vertebrate hedgehog
signaling by PTCH1, PTCH2 and HHIP1 during neural patterning.
Development. 140:3423–3434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tenzen T, Allen BL, Cole F, Kang JS,
Krauss RS and McMahon AP: The cell surface membrane proteins Cdo
and Boc are components and targets of the Hedgehog signaling
pathway and feedback network in mice. Dev Cell. 10:647–656. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fukasawa K: Oncogenes and tumour
suppressors take on centrosomes. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:911–924. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hayward DG, Clarke RB, Faragher AJ, Pillai
MR, Hagan IM and Fry AM: The centrosomal kinase Nek2 displays
elevated levels of protein expression in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 64:7370–7376. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Landi MT, Dracheva T, Rotunno M, Figueroa
JD, Liu H, Dasgupta A, Mann FE, Fukuoka J, Hames M, Bergen AW, et
al: Gene expression signature of cigarette smoking and its role in
lung adenocarcinoma development and survival. PLoS One.
3:e16512008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barbagallo F, Paronetto MP, Franco R,
Chieffi P, Dolci S, Fry AM, Geremia R and Sette C: Increased
expression and nuclear localization of the centrosomal kinase Nek2
in human testicular seminomas. J Pathol. 217:431–441. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Andréasson U, Dictor M, Jerkeman M,
Berglund M, Sundström C, Linderoth J, Rosenquist R, Borrebaeck CA
and Ek S: Identification of molecular targets associated with
transformed diffuse large B cell lymphoma using highly purified
tumor cells. Am J Hematol. 84:803–808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kobune M, Takimoto R, Murase K, Iyama S,
Sato T, Kikuchi S, Kawano Y, Miyanishi K, Sato Y, Niitsu Y, et al:
Drug resistance is dramatically restored by hedgehog inhibitors in
CD34+ leukemic cells. Cancer Sci. 100:948–955. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Amable L, Fain J, Gavin E and Reed E: Gli1
contributes to cellular resistance to cisplatin through altered
cellular accumulation of the drug. Oncol Rep. 32:469–474.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|