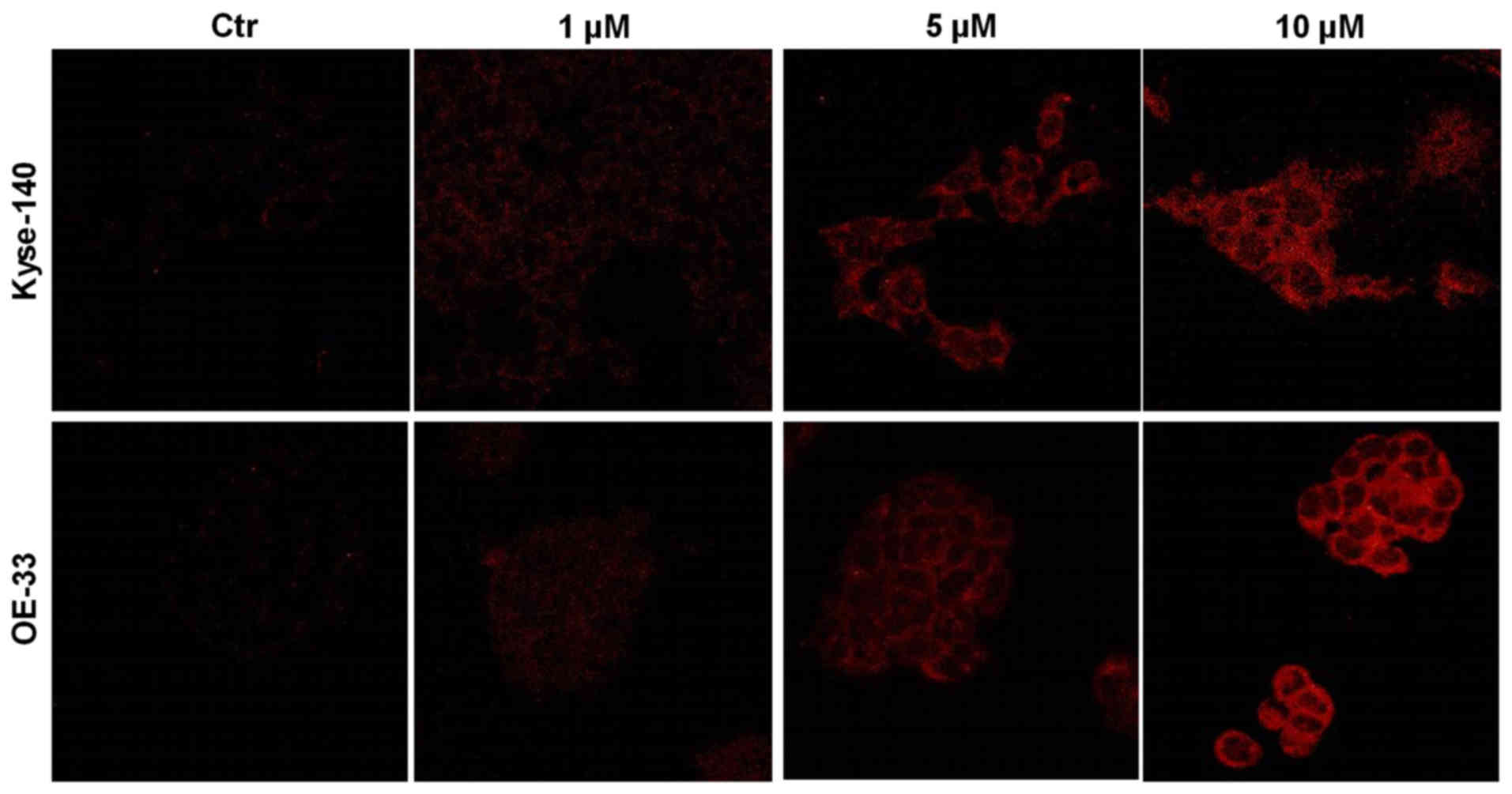
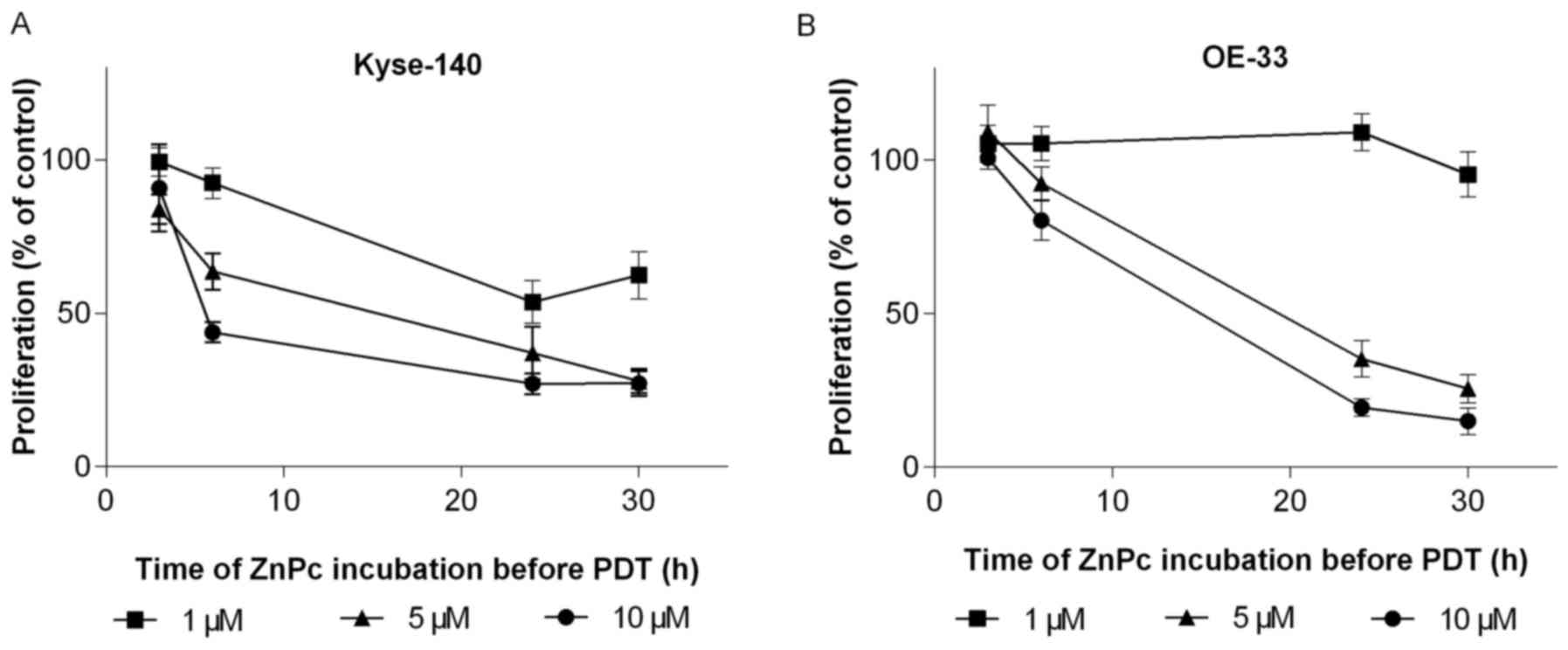
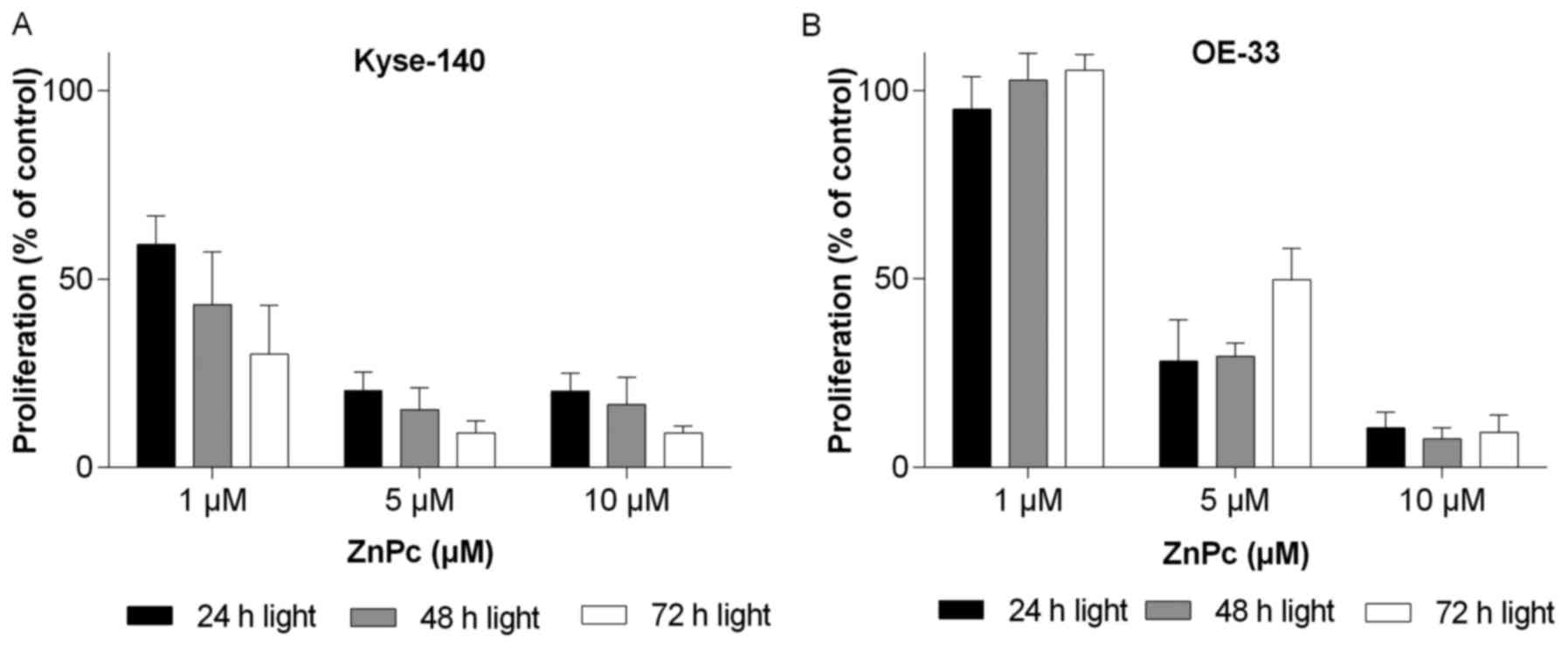
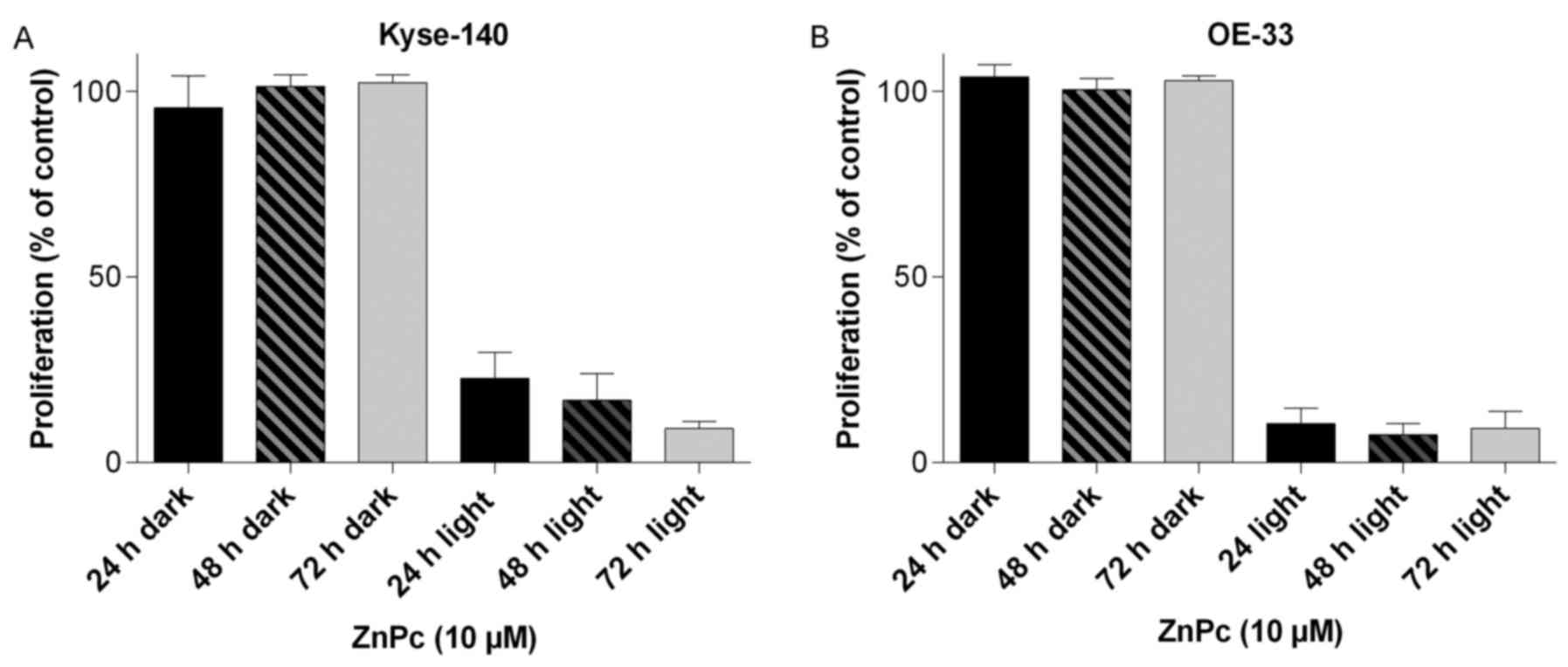
|
1
|
Thrift AP: The epidemic of oesophageal
carcinoma: Where are we now? Cancer Epidemiol. 41:88–95. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ireland CJ, Thompson SK, Laws TA and
Esterman A: Risk factors for Barrett's esophagus: A scoping review.
Cancer Causes Control. 27:301–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meves V, Behrens A and Pohl J: Diagnostics
and early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Viszeralmedizin.
31:315–318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chang TL, Tsai YF, Chao YK and Wu MY:
Quality-of-life measures as predictors of post-esophagectomy
survival of patients with esophageal cancer. Qual Life Res.
25:465–475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sutter AP, Höpfner M, Huether A, Maaser K
and Scherübl H: Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor by
erlotinib (Tarceva) for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 118:1814–1822. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Triesscheijn M, Baas P, Schellens JHM and
Stewart FA: Photodynamic therapy in oncology. Oncologist.
11:1034–1044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi E, Yang CK, Leem C, Park Y, Chang J-E,
Cho S and Jheon S: Clinical outcome of photodynamic therapy in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Photochem Photobiol B.
141:20–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shishkova N, Kuznetsova O and Berezov T:
Photodynamic therapy in gastroenterology. J Gastrointest Cancer.
44:251–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Höpfner M, Maaser K, Theiss A, Lenz M,
Sutter AP, Kashtan H, von Lampe B, Riecken EO, Zeitz M and Scherübl
H: Hypericin activated by an incoherent light source has
photodynamic effects on esophageal cancer cells. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 18:239–247. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Castano AP, Demidova TN and Hamblin MR:
Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part one-photosensitizers,
photochemistry and cellular localization. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther.
1:279–293. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu M, Tai C, Sain M, Hu AT and Chou F:
Photodynamic applications of phthalocyanines. J Photochem Photobiol
Chem. 165:131–136. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Josefsen LB and Boyle RW: Photodynamic
therapy: Novel third- generation photosensitizers one step closer?
Br J Pharmacol. 154:1–3. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang Z, Shao J, Yang T, Wang J and Jia L:
Pharmaceutical development, composition and quantitative analysis
of phthalocyanine as the photosensitizer for cancer photodynamic
therapy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 87:98–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kuzyniak W, Ermilov EA, Atilla D, Gürek
AG, Nitzsche B, Derkow K, Hoffmann B, Steinemann G, Ahsen V and
Höpfner M: Tetra-triethyleneoxysulfonyl substituted zinc
phthalocyanine for photodynamic cancer therapy. Photodiagn Photodyn
Ther. 13:148–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Atilla D, Saydan N, Durmuş M, Gürek AG,
Khan T, Rück A, Walt H, Nyokong T and Ahsen V: Synthesis and
photodynamic potential of tetra- and octa-triethyleneoxysulfonyl
substituted zinc phthalocyanines. J Photochem Photobiol Chem.
186:298–307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nitzsche B, Gloesenkamp C, Schrader M,
Ocker M, Preissner R, Lein M, Zakrzewicz A, Hoffmann B and Höpfner
M: Novel compounds with antiangiogenic and antiproliferative
potency for growth control of testicular germ cell tumours. Br J
Cancer. 103:18–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gloesenkamp C, Nitzsche B, Lim AR, Normant
E, Vosburgh E, Schrader M, Ocker M, Scherübl H and Höpfner M: Heat
shock protein 90 is a promising target for effective growth
inhibition of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Int J Oncol.
40:1659–1667. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Höpfner M, Huether A, Sutter AP, Baradari
V, Schuppan D and Scherübl H: Blockade of IGF-1 receptor tyrosine
kinase has antineoplastic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1435–1448. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huether A, Höpfner M, Baradari V, Schuppan
D and Scherübl H: Sorafenib alone or as combination therapy for
growth control of cholangiocarcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol.
73:1308–1317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nitzsche B, Gloesenkamp C, Schrader M,
Hoffmann B, Zengerling F, Balabanov S, Honecker F and Höpfner M:
Anti-tumour activity of two novel compounds in cisplatin- resistant
testicular germ cell cancer. Br J Cancer. 107:1853–1863. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weiss A, van Beijnum JR, Bonvin D,
Jichlinski P, Dyson PJ, Griffioen AW and Nowak-Sliwinska P:
Low-dose angiostatic tyrosine kinase inhibitors improve
photodynamic therapy for cancer: Lack of vascular normalization. J
Cell Mol Med. 18:480–491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Jin H, Bao J, Fang F, Wei J and
Wang A: Intravenous repeated-dose toxicity study of
ZnPcS2P2-based-photodynamic therapy in Wistar rats. Photochem
Photobiol Sci. 5:1006–1017. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tiwari DK, Jin T and Behari J:
Bio-distribution and toxicity assessment of intravenously injected
anti-HER2 antibody conjugated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in Wistar rats.
Int J Nanomed. 6:463–475. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Gloesenkamp CR, Nitzsche B, Ocker M, Di
Fazio P, Quint K, Hoffmann B, Scherübl H and Höpfner M: AKT
inhibition by triciribine alone or as combination therapy for
growth control of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Int
J Oncol. 40:876–888. 2012.
|
|
25
|
Huang Z: A review of progress in clinical
photodynamic therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 4:283–293. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fayter D, Corbett M, Heirs M, Fox D and
Eastwood A: A systematic review of photodynamic therapy in the
treatment of pre-cancerous skin conditions, Barrett's oesophagus
and cancers of the biliary tract, brain, head and neck, lung,
oesophagus and skin. Health Technol Assess. 14:1–288. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rodrigues JR, Charris J, Ferrer R, Gamboa
N, Angel J, Nitzsche B, Hoepfner M, Lein M, Jung K and Abramjuk C:
Effect of quinolinyl acrylate derivatives on prostate cancer in
vitro and in vivo. Invest New Drugs. 30:1426–1433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Qumseya BJ, David W and Wolfsen HC:
Photodynamic therapy for Barrett's esophagus and esophageal
carcinoma. Clin Endosc. 46:30–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mordon S, Cochrane C, Tylcz JB, Betrouni
N, Mortier L and Koncar V: Light emitting fabric technologies for
photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 12:1–8. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oleinick NL, Morris RL and Belichenko I:
The role of apoptosis in response to photodynamic therapy: What,
where, why, and how. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 1:1–21. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Morgan J, Potter WR and Oseroff AR:
Comparison of photodynamic targets in a carcinoma cell line and its
mitochondrial DNA-deficient derivative. Photochem Photobiol.
71:747–757. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shao J, Dai Y, Zhao W, Xie J, Xue J, Ye J
and Jia L: Intracellular distribution and mechanisms of actions of
photosensitizer Zinc(II)-phthalocyanine solubilized in Cremophor EL
against human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Cancer Lett.
330:49–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tynga IM, Houreld NN and Abrahamse H: The
primary subcellular localization of Zinc phthalocyanine and its
cellular impact on viability, proliferation and structure of breast
cancer cells (MCF-7). J Photochem Photobiol B. 120:171–176. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nanashima A, Isomoto H, Abo T, Nonaka T,
Morisaki T, Arai J, Takagi K, Ohnita K, Shoji H, Urabe S, et al:
How to access photodynamic therapy for bile duct carcinoma. Ann
Transl Med. 2:232014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Z, Hsu Y, Li L, Wang L, Song X-D,
Yow CMN, Lei X, Musani AI, Luo R-C and Day BJ: Photodynamic therapy
of cancer - Challenges of multidrug resistance. J Innov Opt Health
Sci. 8:15300022015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Juarranz A, Jaén P, Sanz-Rodríguez F,
Cuevas J and González S: Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic
principles and applications. Clin Transl Oncol. 10:148–154. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gupta SC, Hevia D, Patchva S, Park B, Koh
W and Aggarwal BB: Upsides and downsides of reactive oxygen species
for cancer: The roles of reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis,
prevention, and therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1295–1322. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Nowis D, Makowski M, Stoktosa T, Legat M,
Issat T and Gołab J: Direct tumor damage mechanisms of photodynamic
therapy. Acta Biochim Pol. 52:339–352. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
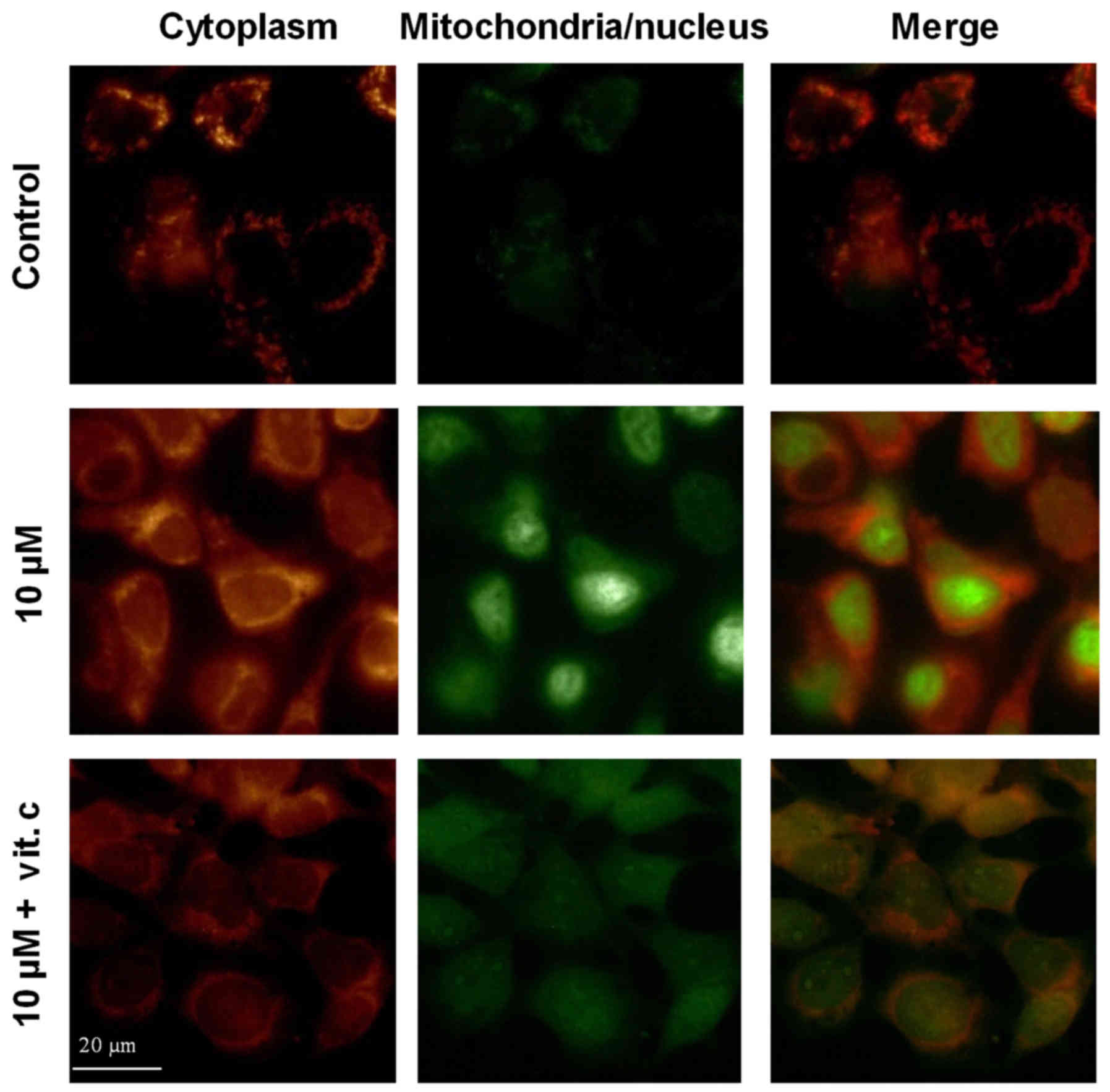
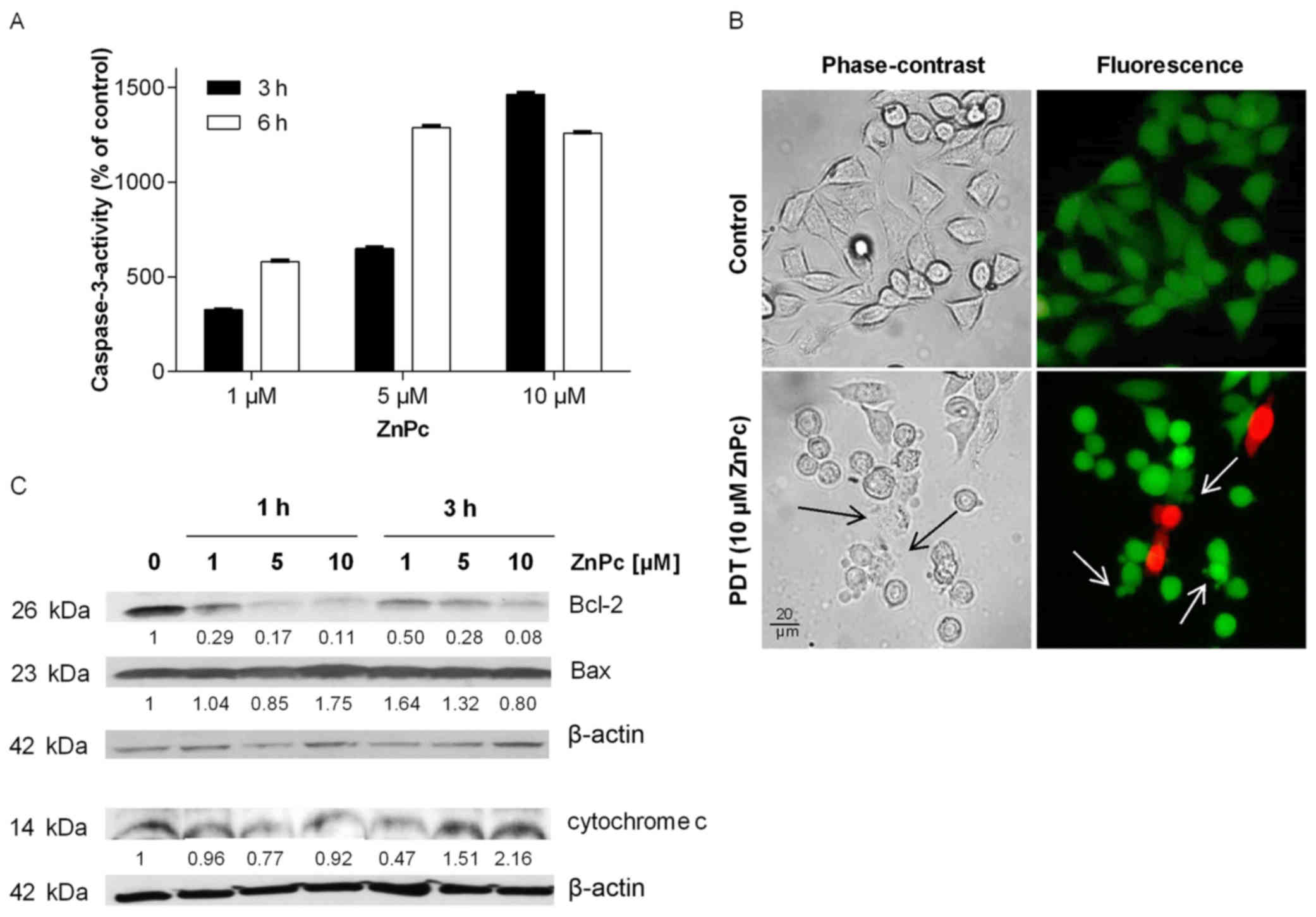
Grimm S, Mvondo D, Grune T and Breusing N:
The outcome of 5-ALA-mediated photodynamic treatment in melanoma
cells is influenced by vitamin C and heme oxygenase-1. Biofactors.
37:17–24. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nicholson DW: From bench to clinic with
apoptosis-based therapeutic agents. Nature. 407:810–816. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Abrahamse H and Hamblin MR: New
photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem J. 473:347–364.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moeno S, Krause RWM, Ermilov EA, Kuzyniak
W and Höpfner M: Synthesis and characterization of novel zinc
phthalocyanines as potential photosensitizers for photodynamic
therapy of cancers. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 13:963–970. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang A, Li Y, Zhou L, Yuan L, Lu S, Lin Y,
Zhou J and Wei S: Charge dependent photodynamic activity of alanine
based zinc phthalocyanines. J Photochem Photobiol B. 141:10–19.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vargas A, Zeisser-Labouèbe M, Lange N,
Gurny R and Delie F: The chick embryo and its chorioallantoic
membrane (CAM) for the in vivo evaluation of drug delivery systems.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 59:1162–1176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
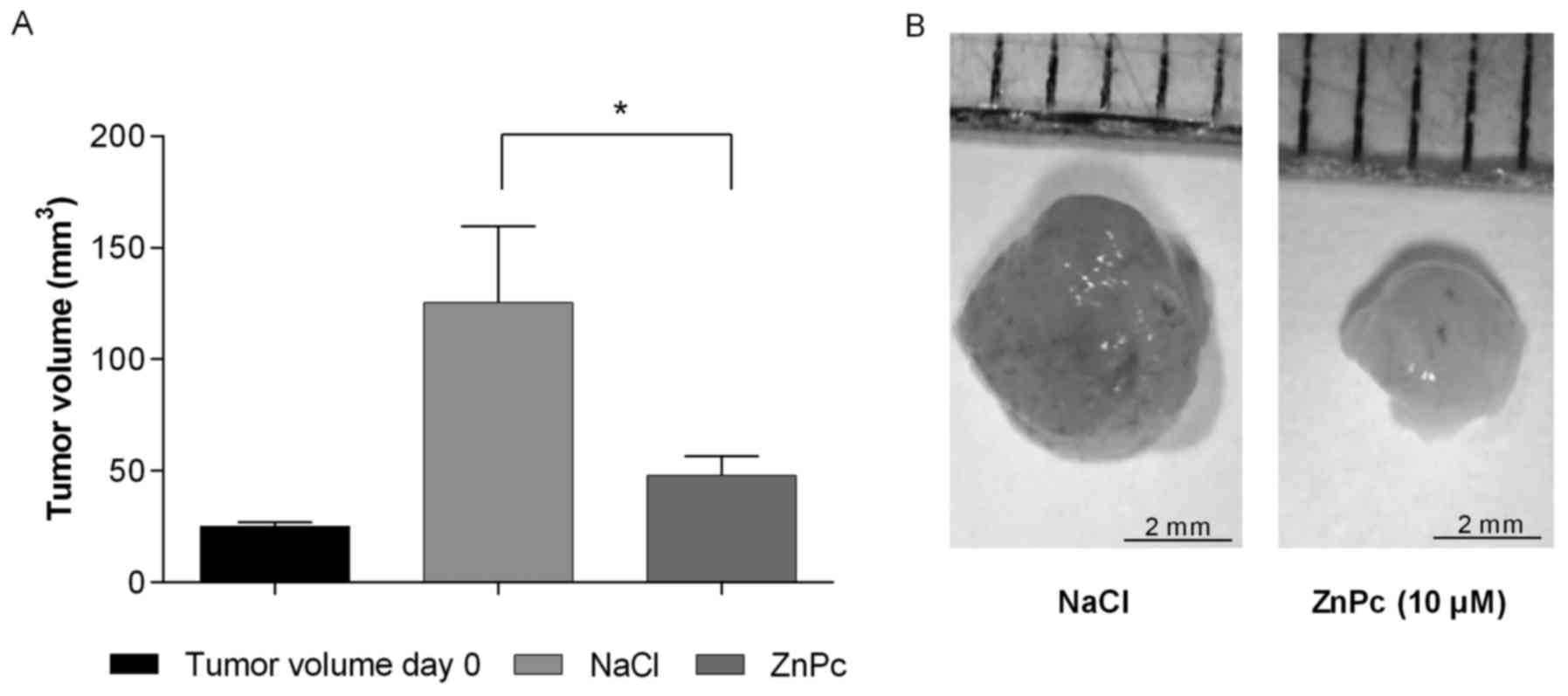
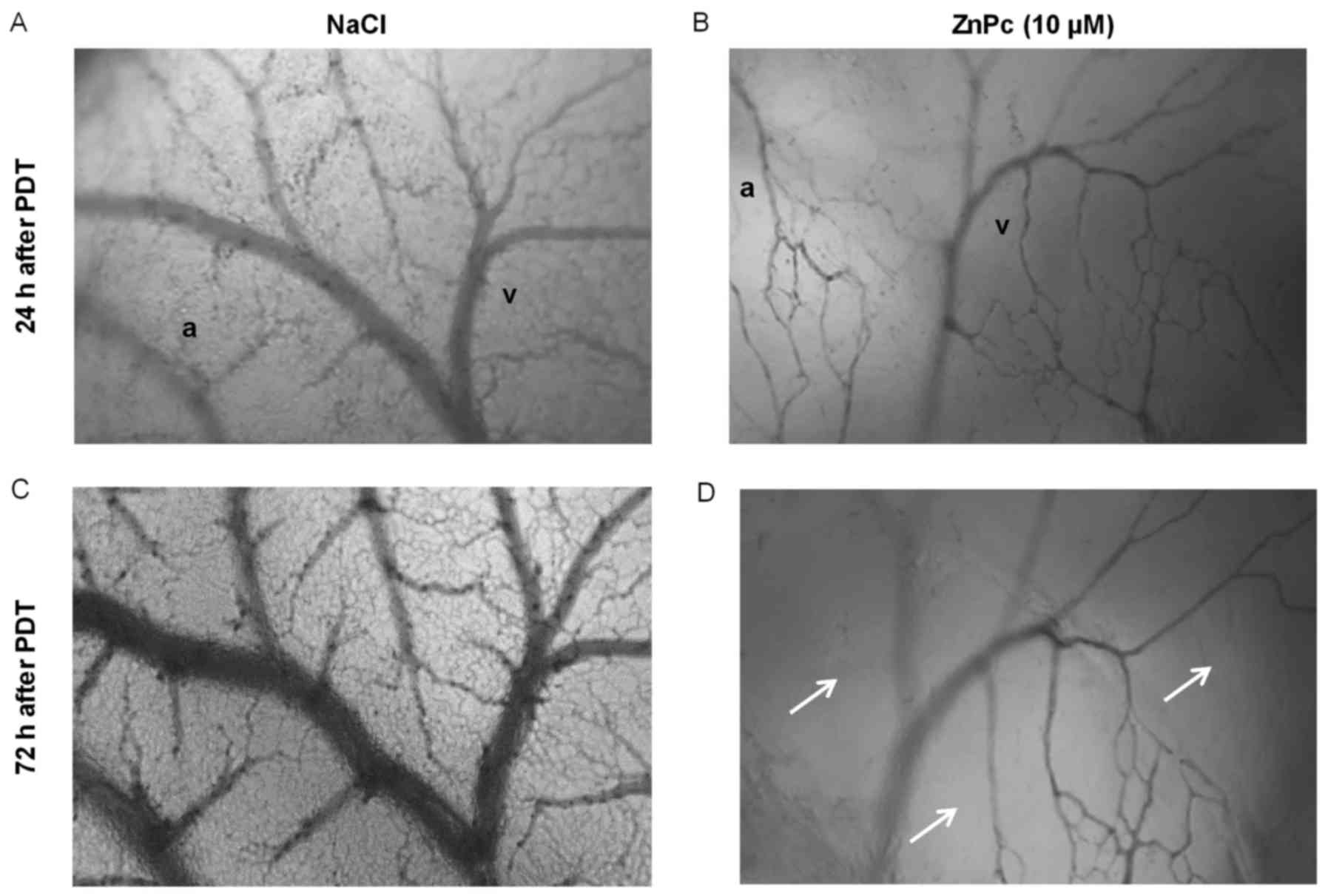
Nowak-Sliwinska P, van Beijnum JR, van
Berkel M, van den Bergh H and Griffioen AW: Vascular regrowth
following photodynamic therapy in the chicken embryo
chorioallantoic membrane. Angiogenesis. 13:281–292. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chan WM, Lim TH, Pece A, Silva R and
Yoshimura N: Verteporfin PDT for non-standard indications - a
review of current literature. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
248:613–626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fingar VH, Kik PK, Haydon PS, Cerrito PB,
Tseng M, Abang E and Wieman TJ: Analysis of acute vascular damage
after photodynamic therapy using benzoporphyrin derivative (BPD).
Br J Cancer. 79:1702–1708. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Tumor
microvasculature and microenvironment: Targets for
anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res. 74:72–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|