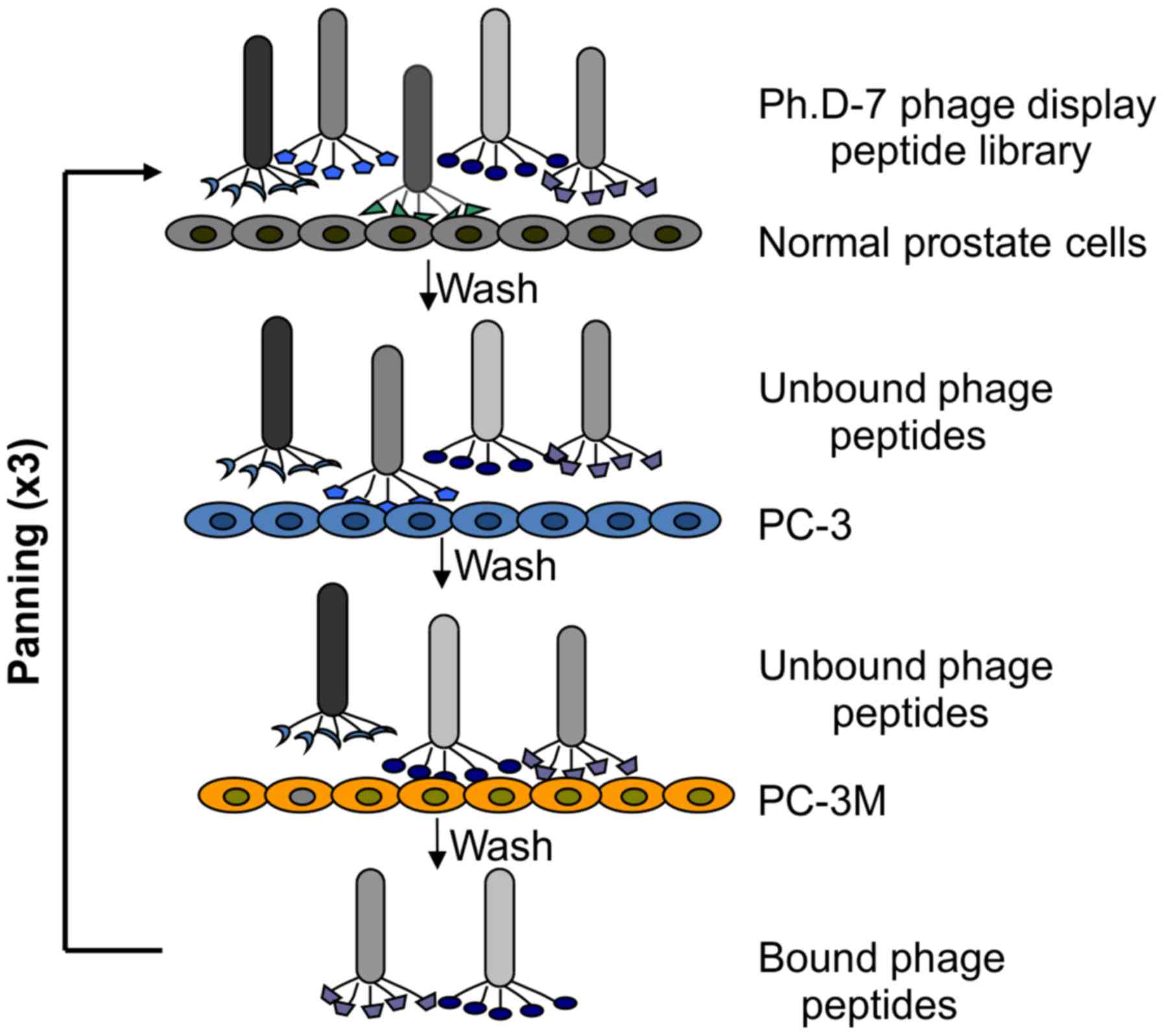
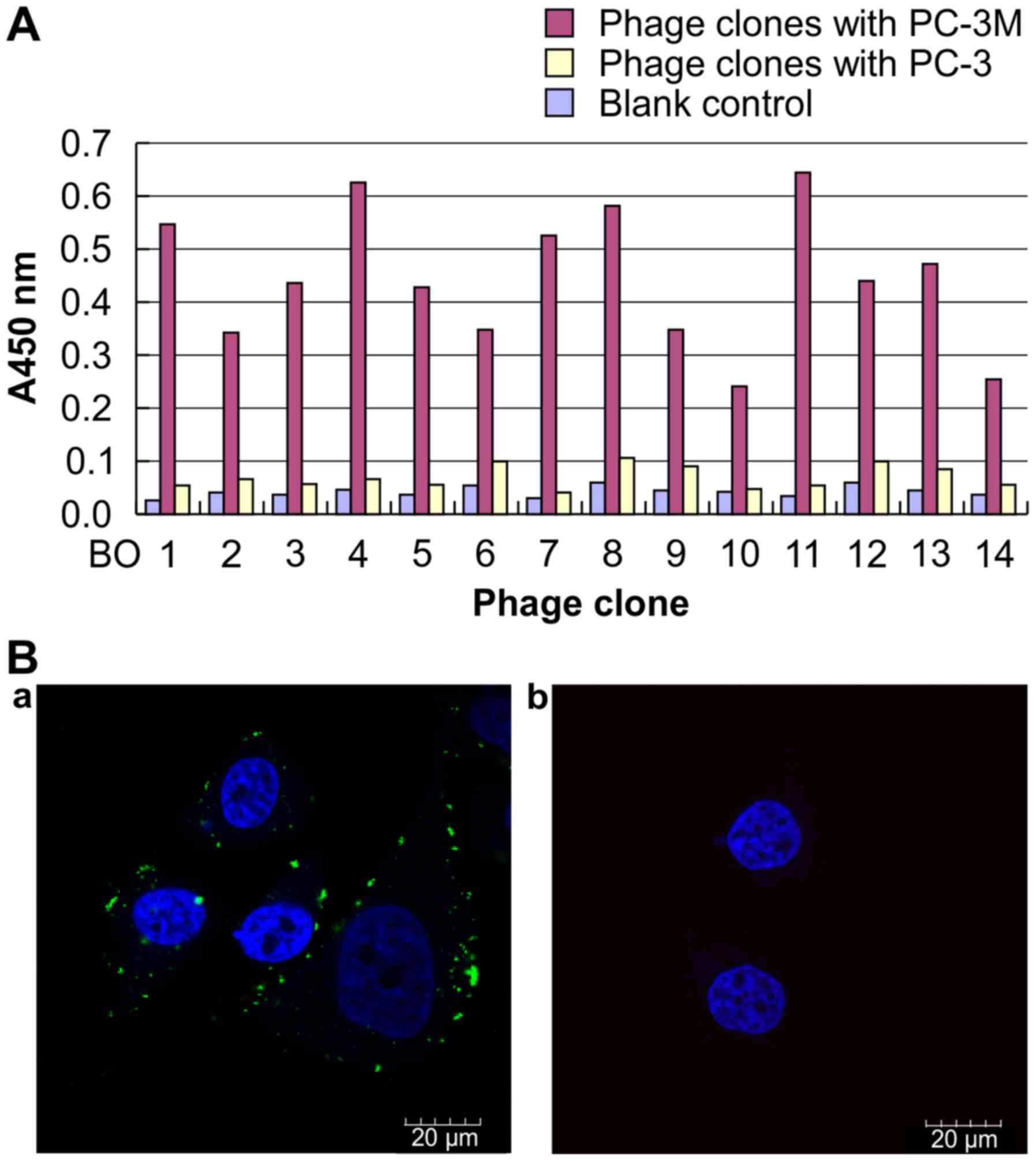
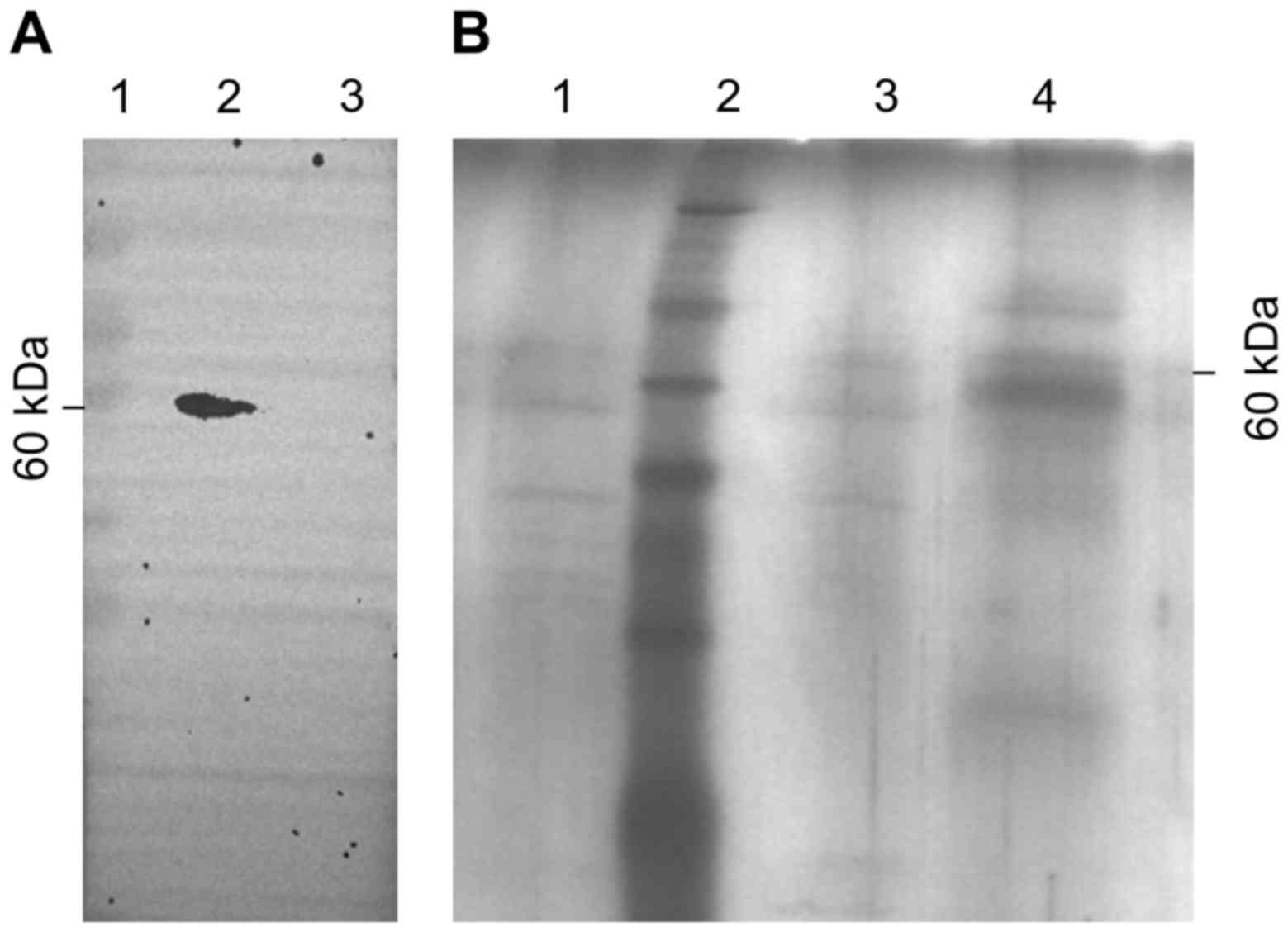
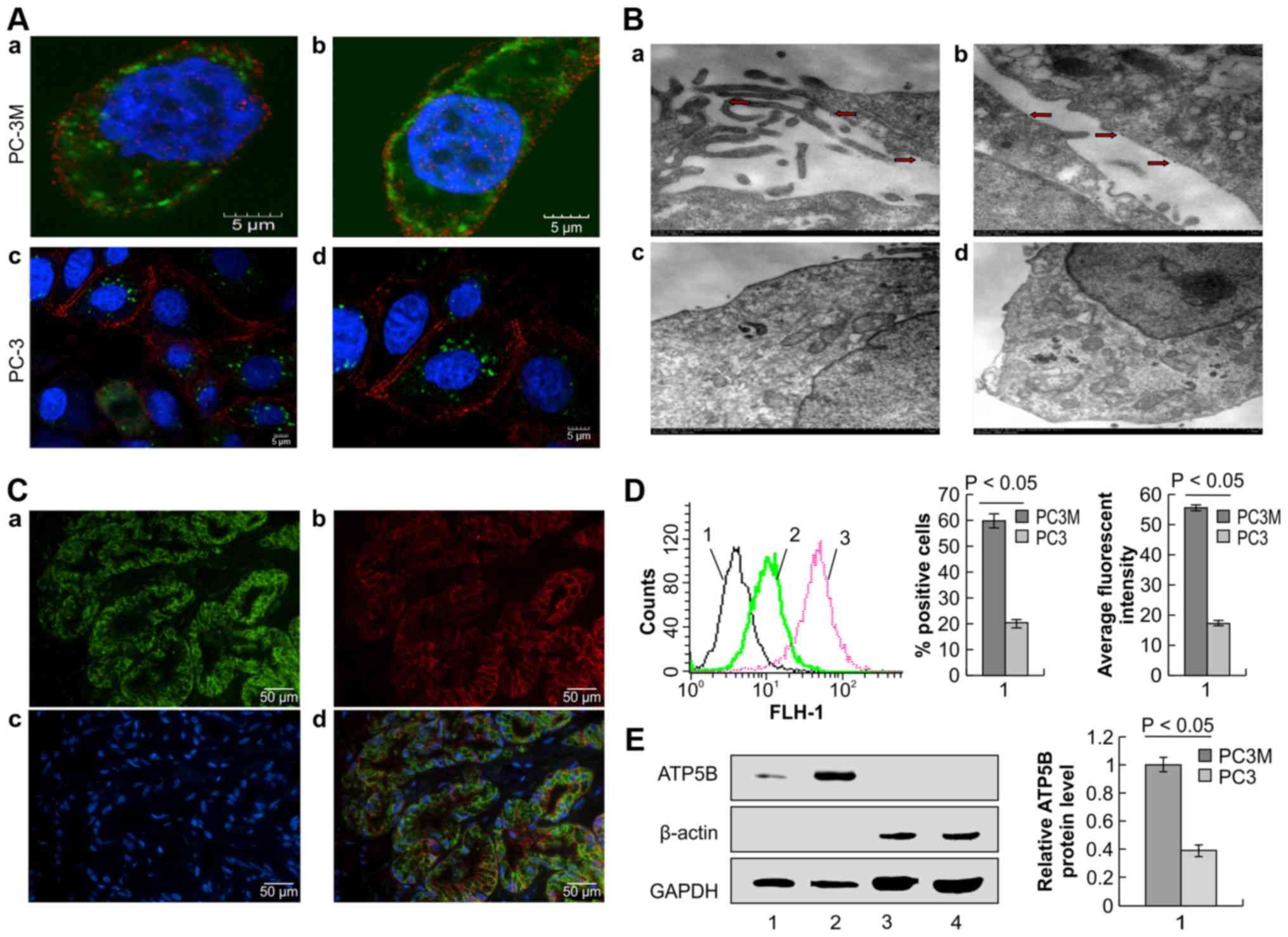
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kauffman EC, Robinson VL, Stadler WM,
Sokoloff MH and Rinker-Schaeffer CW: Metastasis suppression: The
evolving role of metastasis suppressor genes for regulating cancer
cell growth at the secondary site. J Urol. 169:1122–1133. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanash SM, Madoz-Gurpide J and Misek DE:
Identification of novel targets for cancer therapy using expression
proteomics. Leukemia. 16:478–485. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao J, Gao Y, Ju Y, Yang J, Wu Q, Zhang J,
Du X, Wang Z, Song Y, Li H, et al: Proteomics-based generation and
characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human liver
mitochondrial proteins. Proteomics. 6:427–437. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu B, Huang L, Sihlbom C, Burlingame A
and Marks JD: Towards proteome-wide production of monoclonal
antibody by phage display. J Mol Biol. 315:1063–1073. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chi SL and Pizzo SV: Cell surface F1Fo ATP
synthase: A new paradigm? Ann Med. 38:429–438. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu ZJ, Song QF, Jiang SS, Song Q, Wang W,
Zhang GH, Kan B, Chen LJ, Yang JL, Luo F, et al: Identification of
ATP synthase beta subunit (ATPB) on the cellsurface as a non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC) associated antigen. BMC Cancer. 9:162009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dowling P, Meleady P, Dowd A, Henry M,
Glynn S and Clynes M: Proteomic analysis of isolated membrane
fractions from superin- vasivecancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1774:93–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim BW, Choo HJ, Lee JW, Kim JH and Ko YG:
Extracellular ATP isgenerated by ATP synthase complex in adipocyte
lipid rafts. Exp Mol Med. 36:476–485. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong D, Jaron D, Buerk DG and Barbee KA:
Transport- dependent calcium signaling in spatially segregated
cellular caveolar domains. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
294:C856–C866. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bae TJ, Kim MS, Kim JW, Kim BW, Choo HJ,
Lee JW, Kim KB, Lee CS, Kim JH, Chang SY, et al: Lipid raft
proteome reveals ATP synthase complex in the cell surface.
Proteomics. 4:3536–3548. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ribatti D: Chicken chorioallantoic
membrane angiogenesis model. Methods Mol Biol. 843:47–57. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kariya Y, Kato K, Hayashizaki Y, Himeno S,
Tarui S and Matsubura K: Revision of consensus sequence of human
Alu repeats a review. Gene. 53:1–10. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Boyer PD: The ATP synthase - a splendid
molecular machine. Annu Rev Biochem. 66:717–749. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Larimer BM, Thomas WD, Smith GP and
Deutscher SL: Affinity maturation of an ERBB2-targeted SPECT
imaging peptide by in vivo phage display. Mol Imaging Biol.
16:449e582014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Goetz M and Wang TD: Molecular imaging in
gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastroenterology. 138:828e33.e8212010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Senior AE: ATP synthesis by oxidative
phosphorylation. Physiol Rev. 68:177–231. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stock D, Leslie AG and Walker JE:
Molecular architecture of the rotary motor in ATP synthase.
Science. 286:1700–1705. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma Z, Cao M, Liu Y, He Y, Wang Y, Yang C,
Wang W, Du Y, Zhou M and Gao F: Mitochondrial F1Fo-ATP synthase
translocates to cell surface in hepatocytes and has high activity
in tumor-like acidic and hypoxic environment. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 42:530–537. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Champagne E, Martinez LO and Collet Xand
Barbaras R: Ecto-F1Fo ATP synthase/F1 ATPase: metabolic and
immunological functions. Curr Opin Lipidol. 17:279–284. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jung KH, Song SH, Paik JY, Koh BH, Choe
YS, Lee EJ, Kim BT and Lee KH: Direct targeting of tumor cell
F1F0 ATP-synthase by radioiodine angiostatin
in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 22:704–712. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Das B, Mondragon MO, Sadeghian M, Hatcher
VB and Norin AJ: A novel ligand in lymphocyte-mediated
cytotoxicity: Expression of the beta subunit of H+
transporting ATP synthase on the surface of tumor cell lines. J Exp
Med. 180:273–281. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arakaki N, Nagao T, Niki R, Toyofuku A,
Tanaka H, Kuramoto Y, Emoto Y, Shibata H, Magota K and Higuti T:
Possible role of cell surface H -ATP synthase in the extracellular
ATP synthesis and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 1:931–939. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moser TL, Stack MS, Asplin I, Enghild JJ,
Højrup P, Everitt L, Hubchak S, Schnaper HW and Pizzo SV:
Angiostatin binds ATP synthase on the surface of human endothelial
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:2811–2816. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moser TL, Kenan DJ, Ashley TA, Roy JA,
Goodman MD, Misra UK, Cheek DJ and Pizzo SV: Endothelial cell
surface F1-F0 ATP synthase is active in ATP synthesis and is
inhibited by angiostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:6656–6661.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Notari L, Arakaki N, Mueller D, Meier S,
Amaral J and Becerra SP: Pigment epithelium-derived factor binds to
cell- surface F1-ATP synthase. FEBS J. 277:2192–2205.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rumjahn SM, Yokdang N, Baldwin KA, Thai J
and Buxton IL: Purinergic regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor signaling in angiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 100:1465–1470. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chi SL and Pizzo SV: Angiostatin is
directly cytotoxic to tumor cells at low extracellular pH: A
mechanism dependent on cell surface-associated ATP synthase. Cancer
Res. 66:875–882. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schwiebert EM and Zsembery A:
Extracellular ATP as a signaling molecule for epithelial cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1615:7–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bodin P and Burnstock G: Increased release
of ATP from endothelial cells during acute inflammation. Inflamm
Res. 47:351–354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Di Virgilio F: Dr. Jekyll/Mr. Hyde: The
dual role of extracellular ATP. J Auton Nerv Syst. 81:59–63. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ralevic V and Burnstock G: Receptors for
purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev. 50:413–492. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wen LT and Knowles AF: Extracellular ATP
and adenosine induce cell apoptosis of human hepatoma Li-7A cells
via the A3 adenosine receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 140:1009–1018. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schwiebert LM, Rice WC, Kudlow BA, Taylor
AL and Schwiebert EM: Extracellular ATP signaling and P2X
nucleotide receptors in monolayers of primary human vascular
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 282:C289–C301. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Burnstock G: Purinergic signaling and
vascular cell proliferation and death. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 22:364–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|