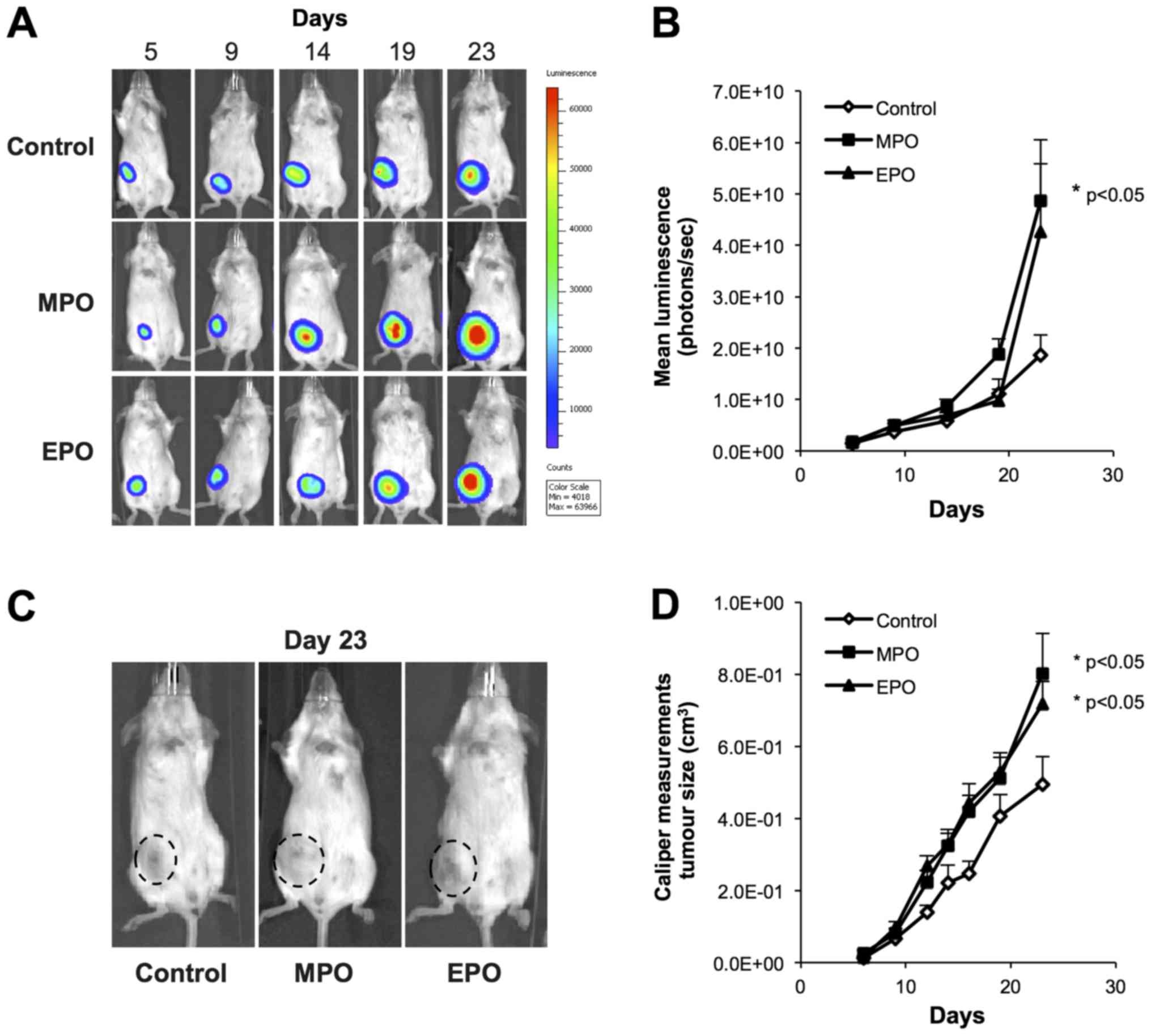
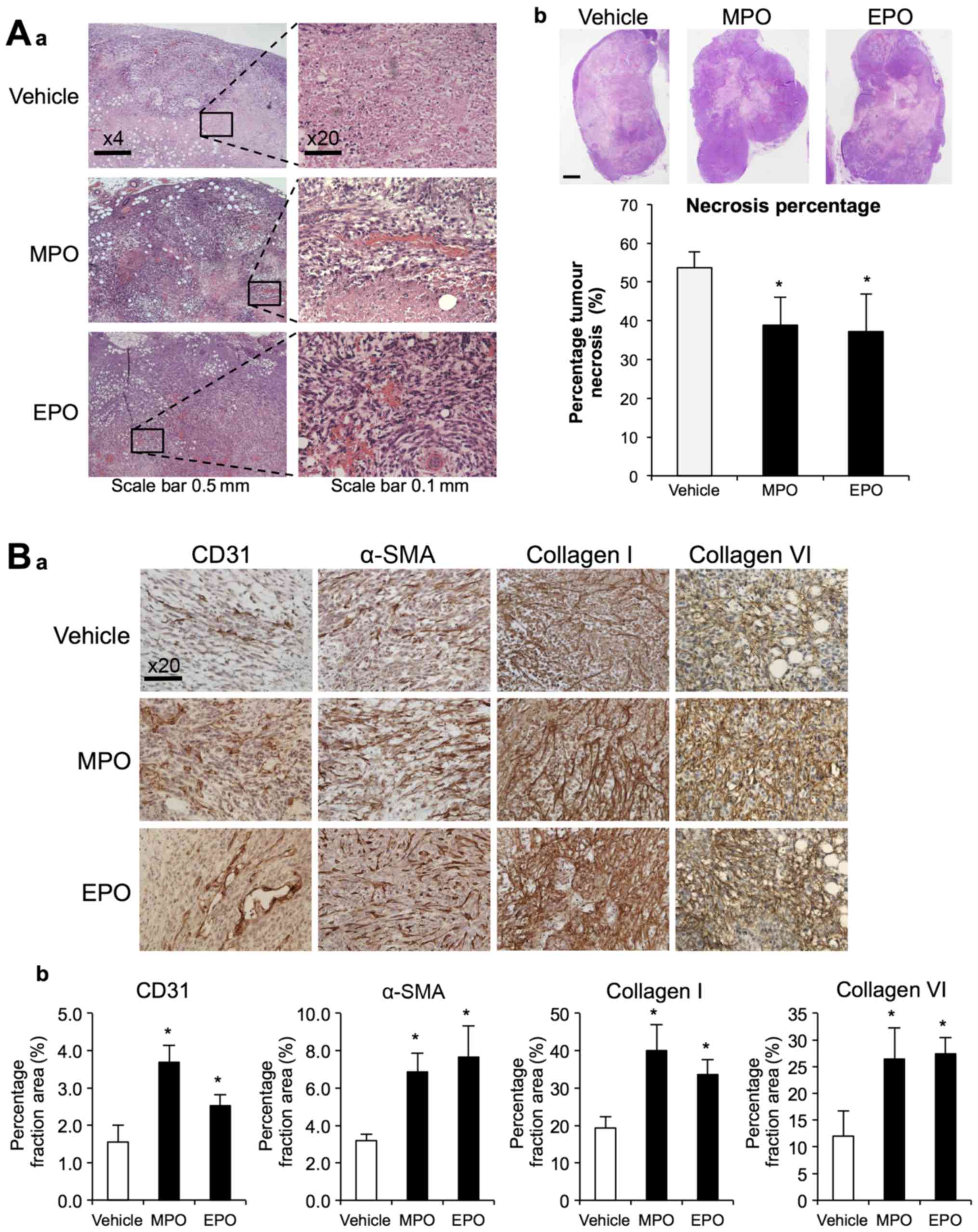
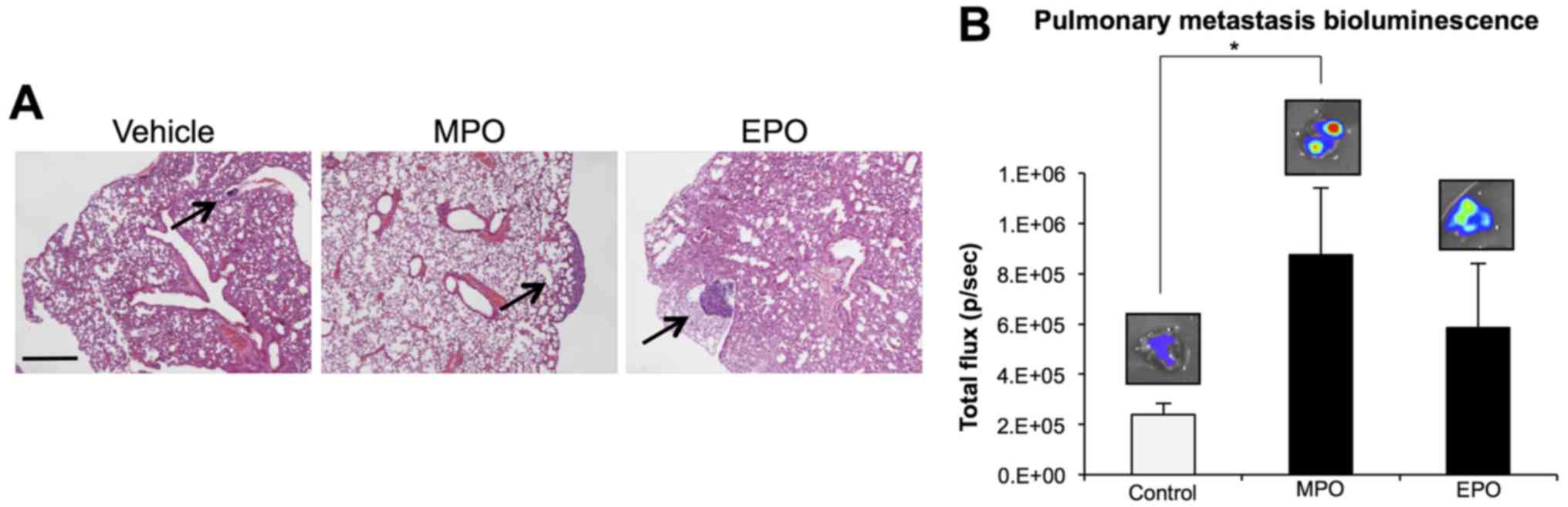
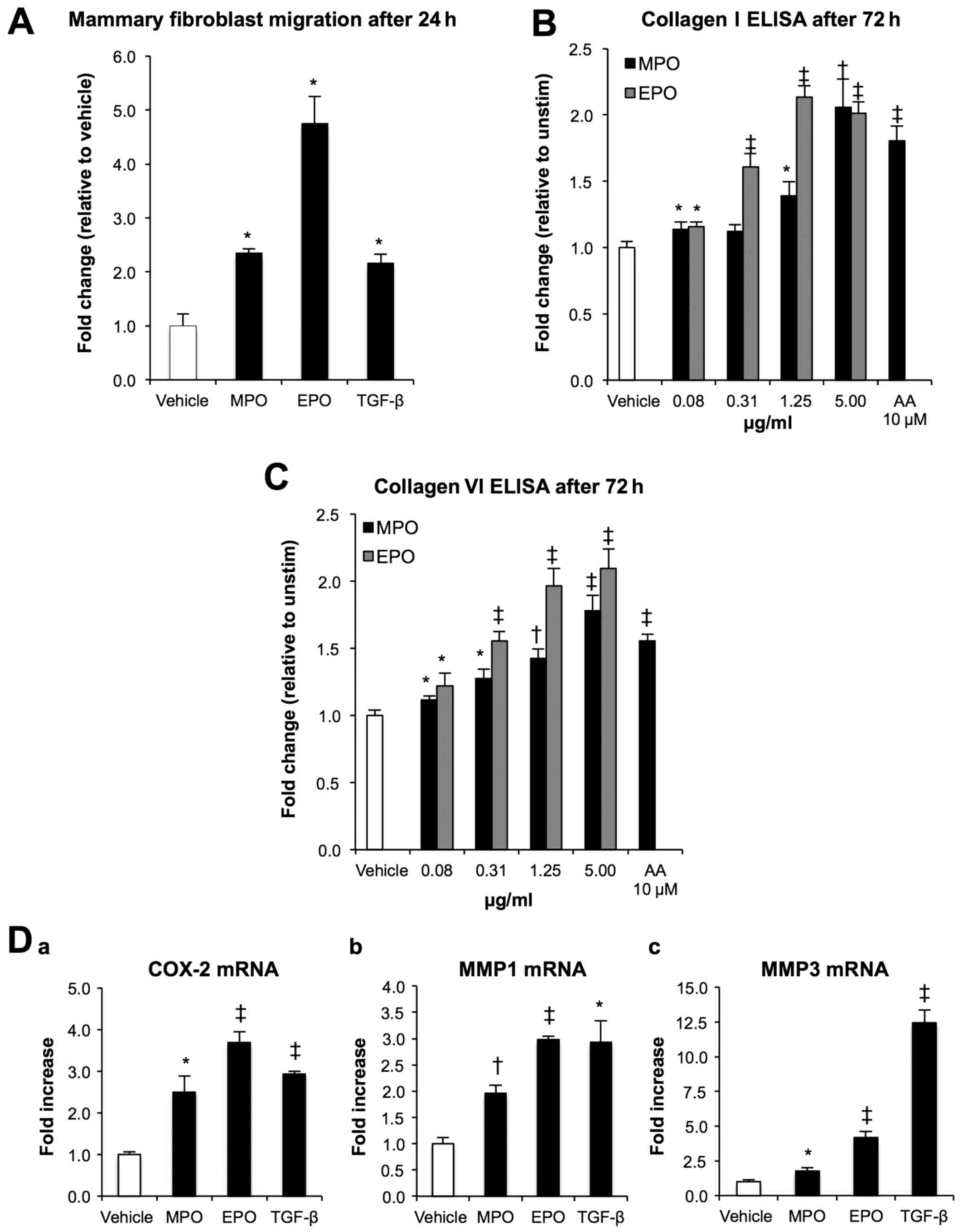
|
1
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galdiero MR, Bonavita E, Barajon I,
Garlanda C, Mantovani A and Jaillon S: Tumor associated macrophages
and neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology. 218:1402–1410. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Samoszuk MK, Nguyen V, Gluzman I and Pham
JH: Occult deposition of eosinophil peroxidase in a subset of human
breast carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 148:701–706. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Deng Q, Pan Y, He B, Ying H, Sun
H, Liu X and Wang S: Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in breast cancer. FEBS Open Bio. 5:502–507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
García-Mendoza MG, Inman DR, Ponik SM,
Jeffery JJ, Sheerar DS, Van Doorn RR and Keely PJ: Neutrophils
drive accelerated tumor progression in the collagen-dense mammary
tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 18:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Swierczak A, Mouchemore KA, Hamilton JA
and Anderson RL: Neutrophils: Important contributors to tumor
progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 34:735–751.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wculek SK and Malanchi I: Neutrophils
support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer
cells. Nature. 528:413–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tabariès S, Ouellet V, Hsu BE, Annis MG,
Rose AA, Meunier L, Carmona E, Tam CE, Mes-Masson AM and Siegel PM:
Granulocytic immune infiltrates are essential for the efficient
formation of breast cancer liver metastases. Breast Cancer Res.
17:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stockmann C, Schadendorf D, Klose R and
Helfrich I: The impact of the immune system on tumor: Angiogenesis
and vascular remodeling. Front Oncol. 4:692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Samoszuk M, Lin F, Rim P and Strathearn G:
New marker for blood vessels in human ovarian and endometrial
cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1867–1871. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cormier SA, Taranova AG, Bedient C, Nguyen
T, Protheroe C, Pero R, Dimina D, Ochkur SI, O'Neill K, Colbert D,
et al: Pivotal Advance: Eosinophil infiltration of solid tumors is
an early and persistent inflammatory host response. J Leukoc Biol.
79:1131–1139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ambrosone CB, Barlow WE, Reynolds W,
Livingston RB, Yeh IT, Choi JY, Davis W, Rae JM, Tang L, Hutchins
LR, et al: Myeloperoxidase genotypes and enhanced efficacy of
chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer in SWOG-8897. J Clin
Oncol. 27:4973–4979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
DeNichilo MO, Panagopoulos V, Rayner TE,
Borowicz RA, Greenwood JE and Evdokiou A: Peroxidase enzymes
regulate collagen extracellular matrix biosynthesis. Am J Pathol.
185:1372–1384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Panagopoulos V, Zinonos I, Leach DA, Hay
SJ, Liapis V, Zysk A, Ingman WV, DeNichilo MO and Evdokiou A:
Uncovering a new role for peroxidase enzymes as drivers of
angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 68:128–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hanahan D and Coussens LM: Accessories to
the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 21:309–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Keskin D, Kim J, Cooke VG, Wu CC, Sugimoto
H, Gu C, De Palma M, Kalluri R and LeBleu VS: Targeting vascular
pericytes in hypoxic tumors increases lung metastasis via
angio-poietin-2. Cell Rep. 10:1066–1081. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rangan GK and Tesch GH: Quantification of
renal pathology by image analysis. Nephrology (Carlton).
12:553–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Castelló-Cros R and Cukierman E:
Stromagenesis during tumorigenesis: Characterization of
tumor-associated fibroblasts and stroma-derived 3D matrices.
Methods Mol Biol. 522:275–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kenny HA, Krausz T, Yamada SD and Lengyel
E: Use of a novel 3D culture model to elucidate the role of
mesothelial cells, fibroblasts and extra-cellular matrices on
adhesion and invasion of ovarian cancer cells to the omentum. Int J
Cancer. 121:1463–1472. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fisher KE, Pop A, Koh W, Anthis NJ,
Saunders WB and Davis GE: Tumor cell invasion of collagen matrices
requires coordinate lipid agonist-induced G-protein and
membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1-dependent signaling. Mol
Cancer. 5:692006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Villa JC, Chiu D, Brandes AH, Escorcia FE,
Villa CH, Maguire WF, Hu CJ, de Stanchina E, Simon MC, Sisodia SS,
et al: Nontranscriptional role of Hif-1α in activation of
γ-secretase and notch signaling in breast cancer. Cell Rep.
8:1077–1092. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leach DA, Need EF, Trotta AP, Grubisha MJ,
DeFranco DB and Buchanan G: Hic-5 influences genomic and
non-genomic actions of the androgen receptor in prostate
myofibroblasts. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 384:185–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pulaski BA and Ostrand-Rosenberg S:
Reduction of established spontaneous mammary carcinoma metastases
following immunotherapy with major histocompatibility complex class
II and B7.1 cell-based tumor vaccines. Cancer Res. 58:1486–1493.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P: Cancer associated
fibroblasts: The dark side of the coin. Am J Cancer Res. 1:482–497.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Provenzano PP, Eliceiri KW, Campbell JM,
Inman DR, White JG and Keely PJ: Collagen reorganization at the
tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Med.
4:382006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu
W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Genes
that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 436:518–524.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang N, Francis KP, Prakash A and Ansaldi
D: Enhanced detection of myeloperoxidase activity in deep tissues
through luminescent excitation of near-infrared nanoparticles. Nat
Med. 19:500–505. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nozawa H, Chiu C and Hanahan D:
Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a
mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:12493–12498. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rymaszewski AL, Tate E, Yimbesalu JP,
Gelman AE, Jarzembowski JA, Zhang H, Pritchard KA Jr and Vikis HG:
The role of neutrophil myeloperoxidase in models of lung tumor
development. Cancers (Basel). 6:1111–1127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ahn J, Gammon MD, Santella RM, Gaudet MM,
Britton JA, Teitelbaum SL, Terry MB, Neugut AI, Josephy PD and
Ambrosone CB: Myeloperoxidase genotype, fruit and vegetable
consumption, and breast cancer risk. Cancer Res. 64:7634–7639.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pabalan N, Jarjanazi H, Sung L, Li H and
Ozcelik H: Menopausal status modifies breast cancer risk associated
with the myeloperoxidase (MPO) G463A polymorphism in Caucasian
women: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e323892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Serganova I, Rizwan A, Ni X, Thakur SB,
Vider J, Russell J, Blasberg R and Koutcher JA: Metabolic imaging:
A link between lactate dehydrogenase A, lactate, and tumor
phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6250–6261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cox TR and Erler JT: Remodeling and
homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: Implications for fibrotic
diseases and cancer. Dis Model Mech. 4:165–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
van 't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ,
He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ,
Witteveen AT, et al: Gene expression profiling predicts clinical
outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 415:530–536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Iyengar P, Espina V, Williams TW, Lin Y,
Berry D, Jelicks LA, Lee H, Temple K, Graves R, Pollard J, et al:
Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor
progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the
tumor/stroma micro-environment. J Clin Invest. 115:1163–1176. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR, Lakins JN,
Rozenberg GI, Gefen A, Reinhart-King CA, Margulies SS, Dembo M,
Boettiger D, et al: Tensional homeostasis and the malignant
phenotype. Cancer Cell. 8:241–254. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Acerbi I, Cassereau L, Dean I, Shi Q, Au
A, Park C, Chen YY, Liphardt J, Hwang ES and Weaver VM: Human
breast cancer invasion and aggression correlates with ECM
stiffening and immune cell infiltration. Integr Biol. 7:1120–1134.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Riching KM, Cox BL, Salick MR, Pehlke C,
Riching AS, Ponik SM, Bass BR, Crone WC, Jiang Y, Weaver AM, et al:
3D collagen alignment limits protrusions to enhance breast cancer
cell persistence. Biophys J. 107:2546–2558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Egeblad M, Rasch MG and Weaver VM: Dynamic
interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 22:697–706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Eck SM, Côté AL, Winkelman WD and
Brinckerhoff CE: CXCR4 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are elevated
in breast carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and in normal mammary
fibroblasts exposed to factors secreted by breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 7:1033–1044. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sternlicht MD, Safarians S, Rivera SP and
Barsky SH: Characterizations of the extracellular matrix and
proteinase inhibitor content of human myoepithelial tumors. Lab
Invest. 74:781–796. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sympson CJ, Bissell MJ and Werb Z: Mammary
gland tumor formation in transgenic mice overexpressing
stromelysin-1. Semin Cancer Biol. 6:159–163. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Holliday DL, Hughes S, Shaw JA, Walker RA
and Jones JL: Intrinsic genetic characteristics determine
tumor-modifying capacity of fibroblasts: Matrix metalloproteinase-3
5A/5A genotype enhances breast cancer cell invasion. Breast Cancer
Res. 9:R672007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu H, Kato Y, Erzinger SA, Kiriakova GM,
Qian Y, Palmieri D, Steeg PS and Price JE: The role of MMP-1 in
breast cancer growth and metastasis to the brain in a xenograft
model. BMC Cancer. 12:5832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M,
Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA and Massagué J: A multigenic
program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell.
3:537–549. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gupta GP, Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Bos PD,
Kim JY, Nadal C, Gomis RR, Manova-Todorova K and Massagué J:
Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in
lung metastasis. Nature. 446:765–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient
neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Park SW, Kim HS, Choi MS, Jeong WJ, Heo
DS, Kim KH and Sung MW: The effects of the stromal cell-derived
cyclo-oxygenase-2 metabolite prostaglandin E2 on the proliferation
of colon cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:516–523. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|