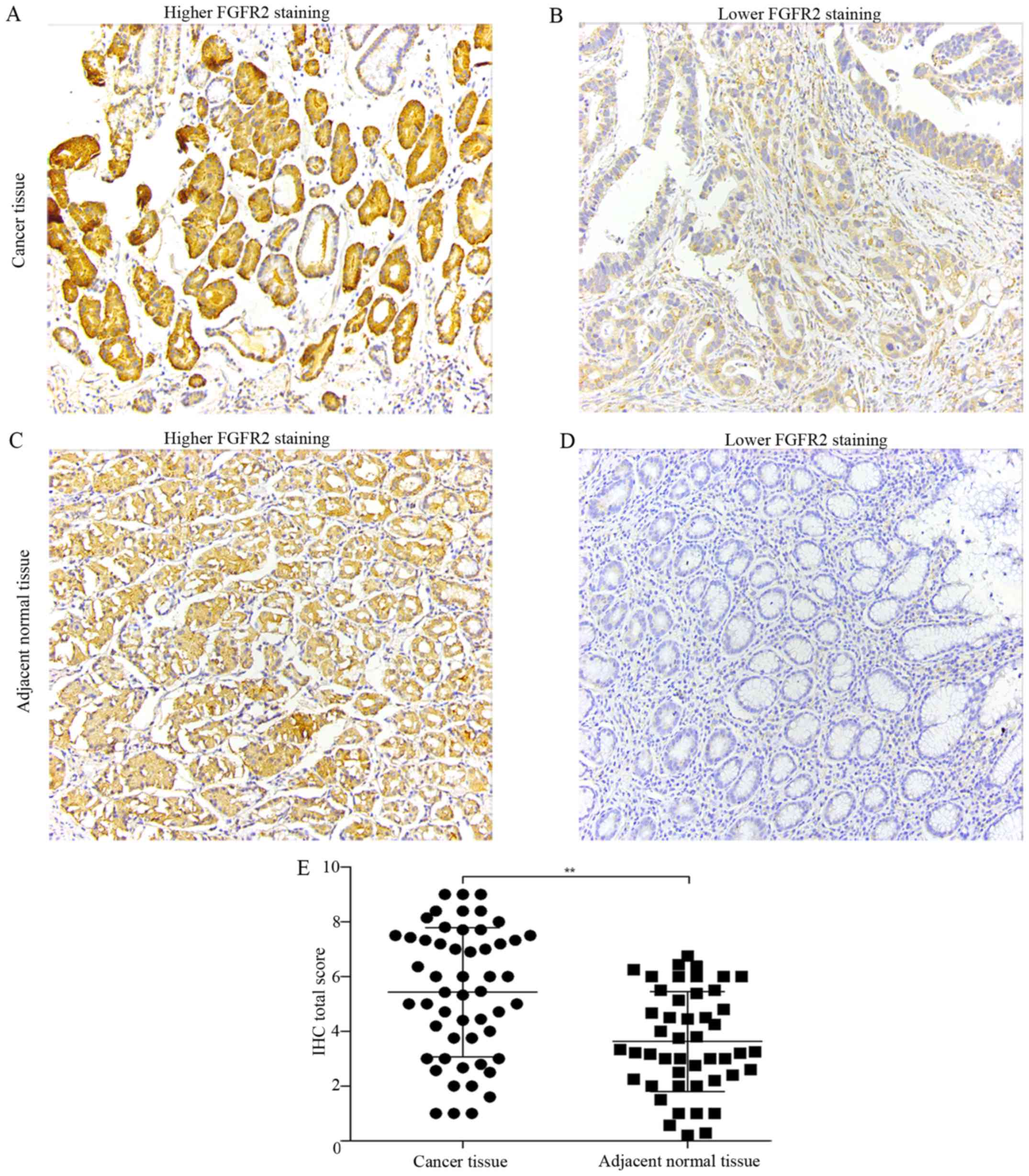
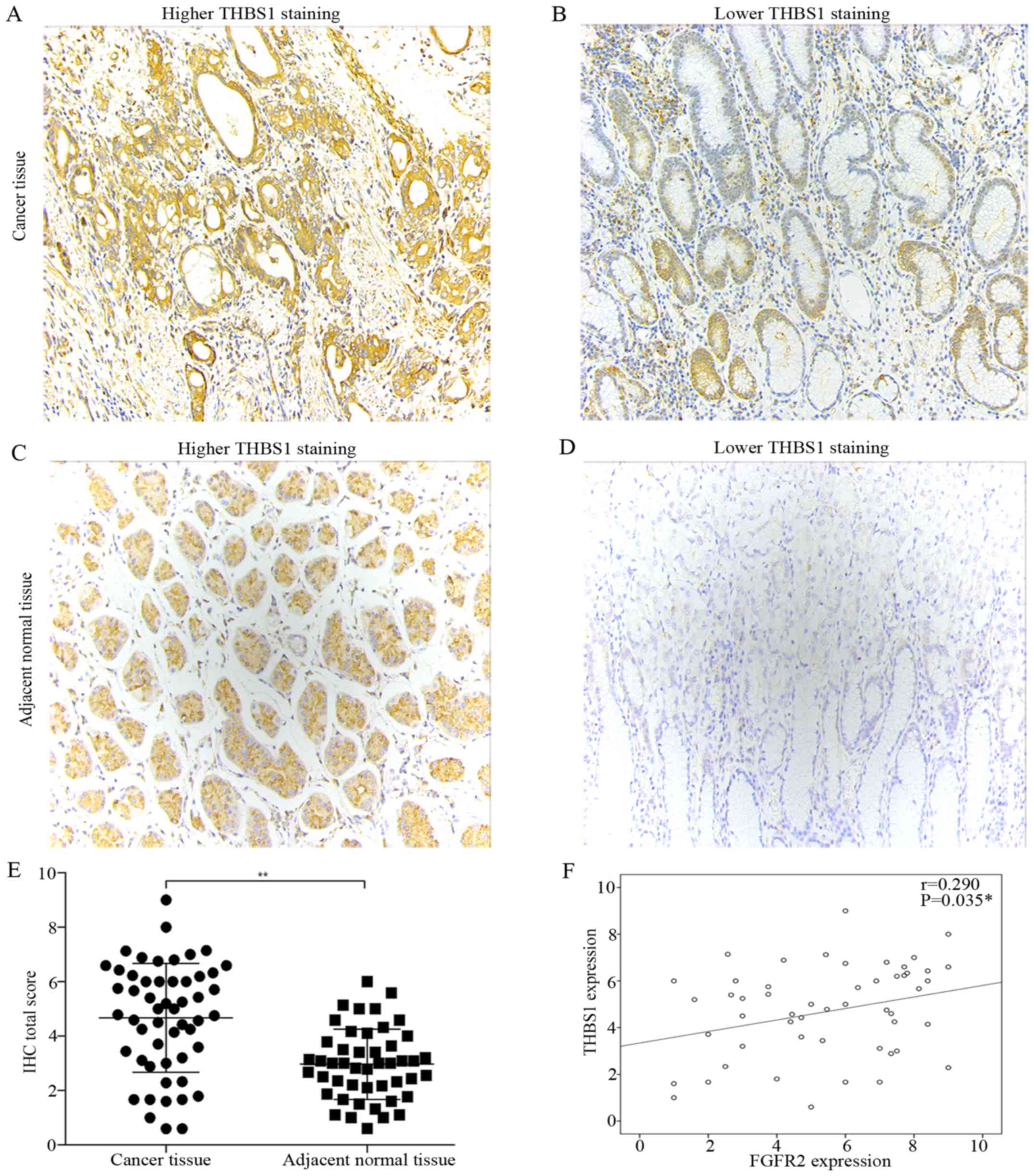
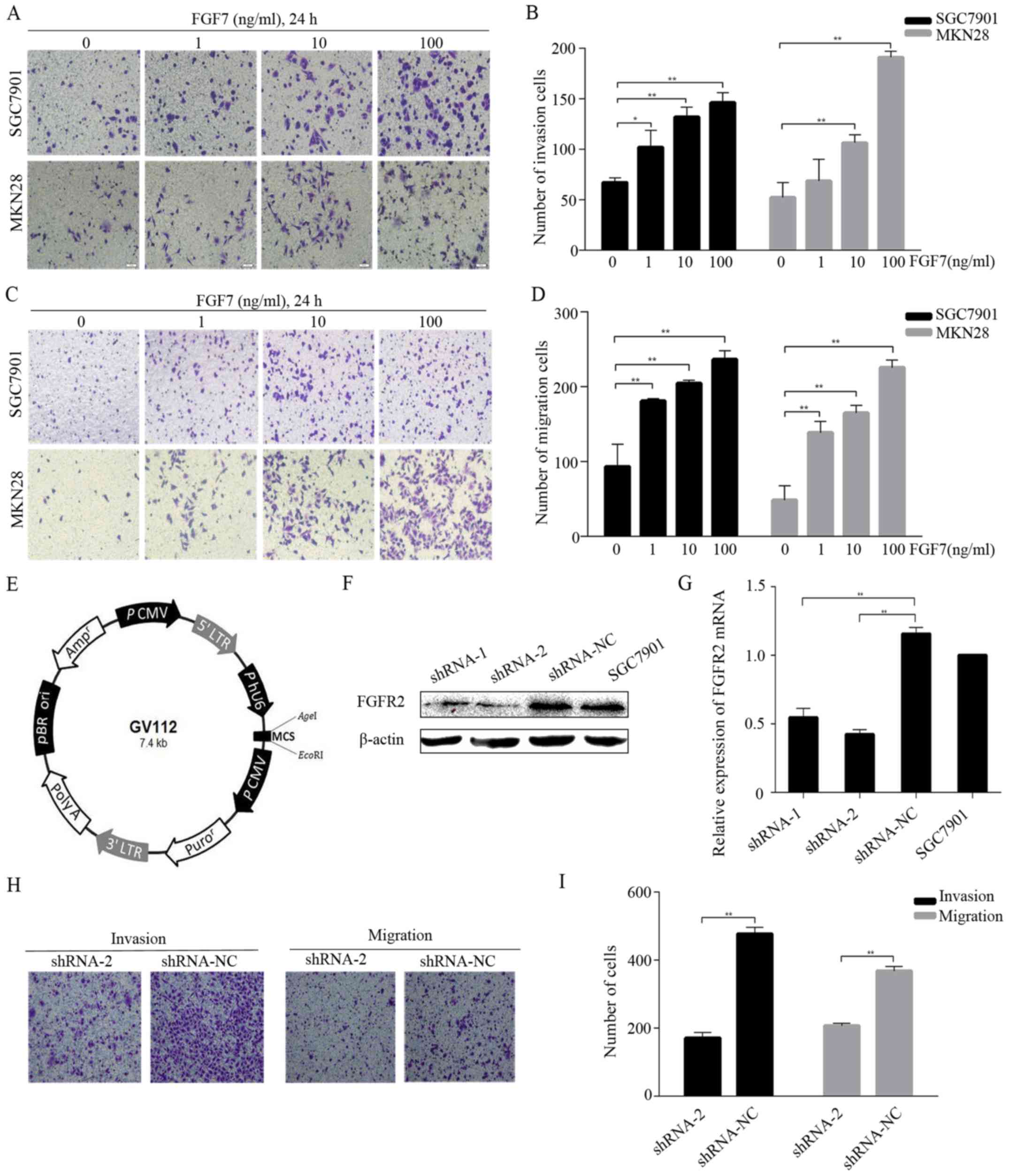
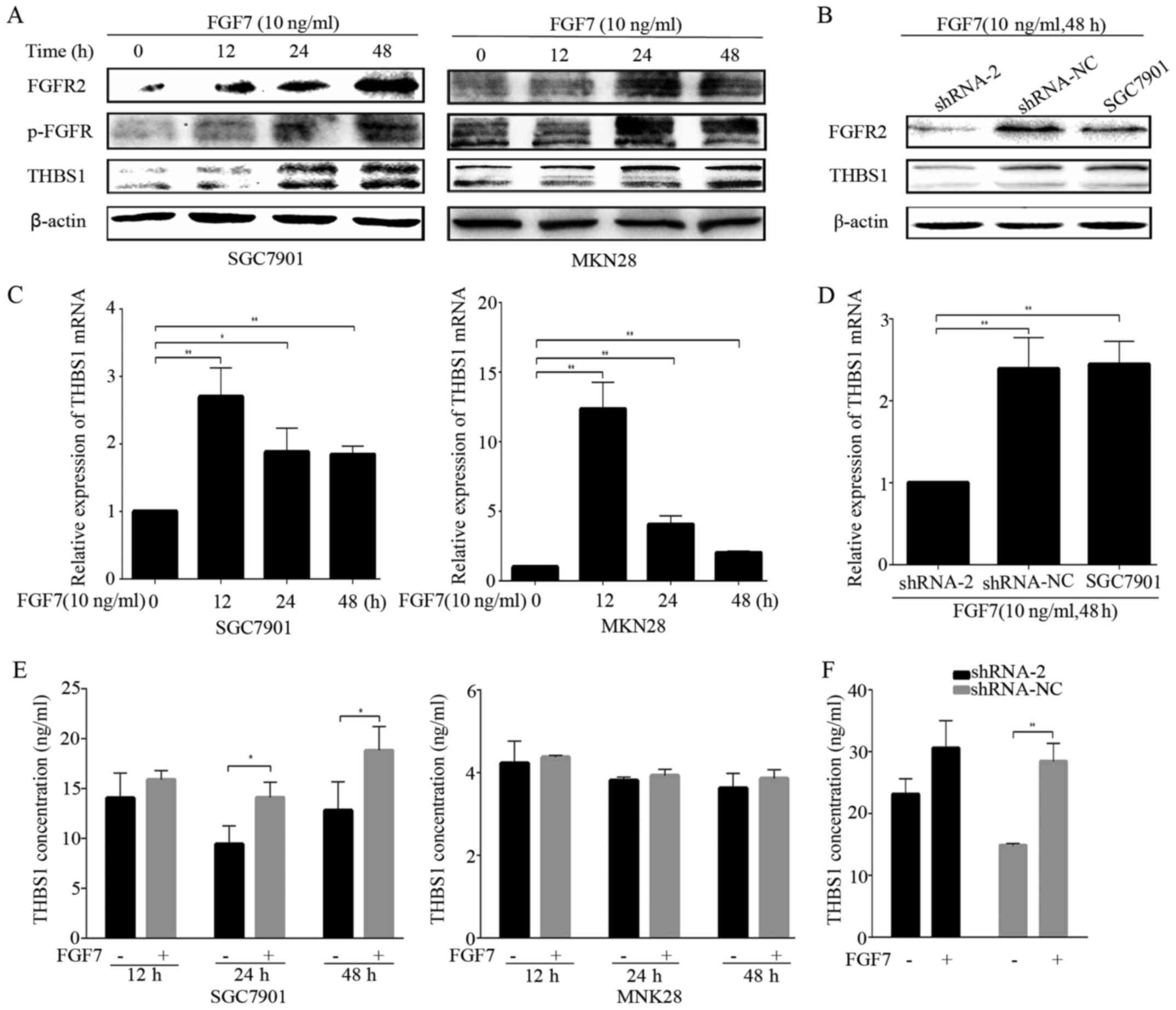
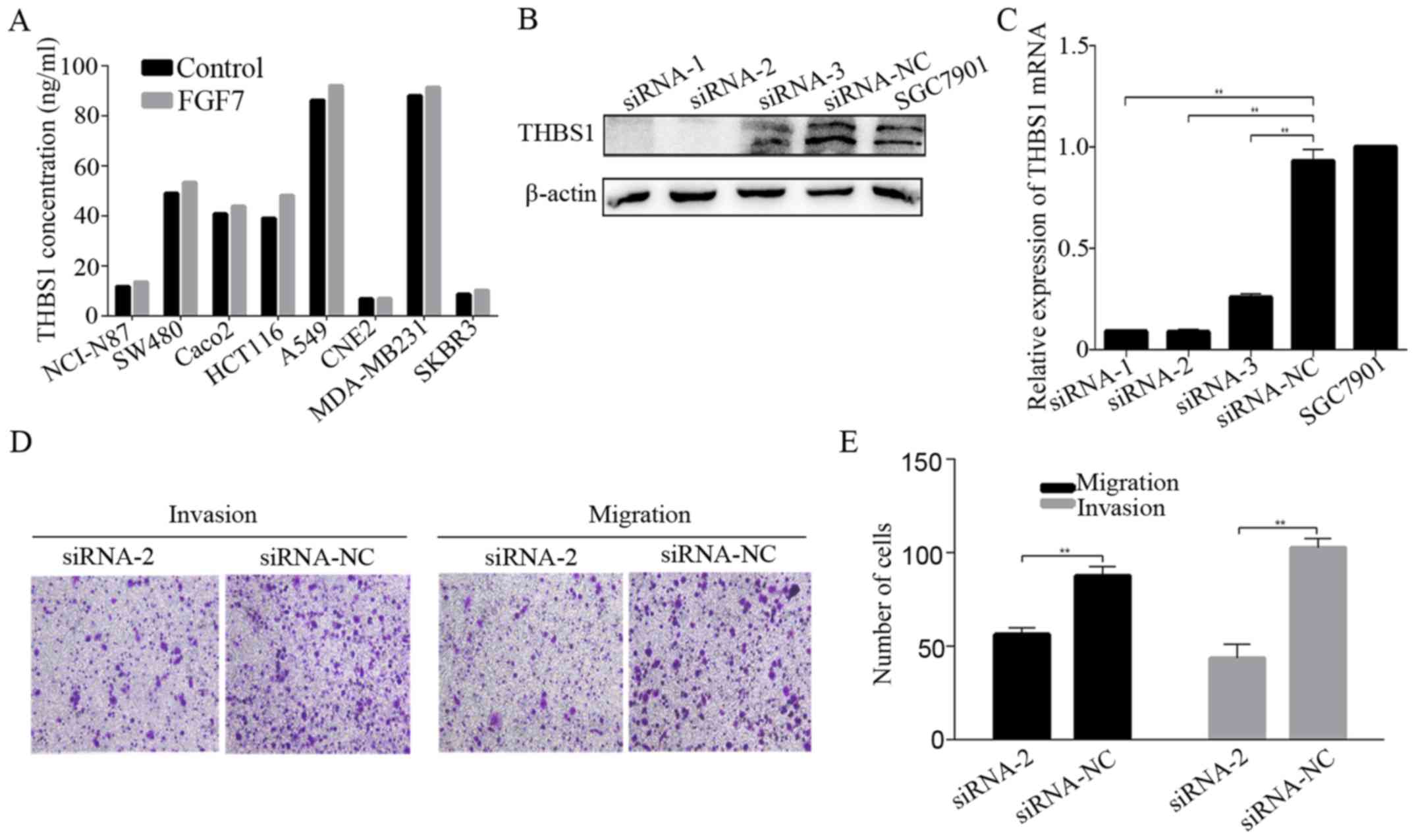
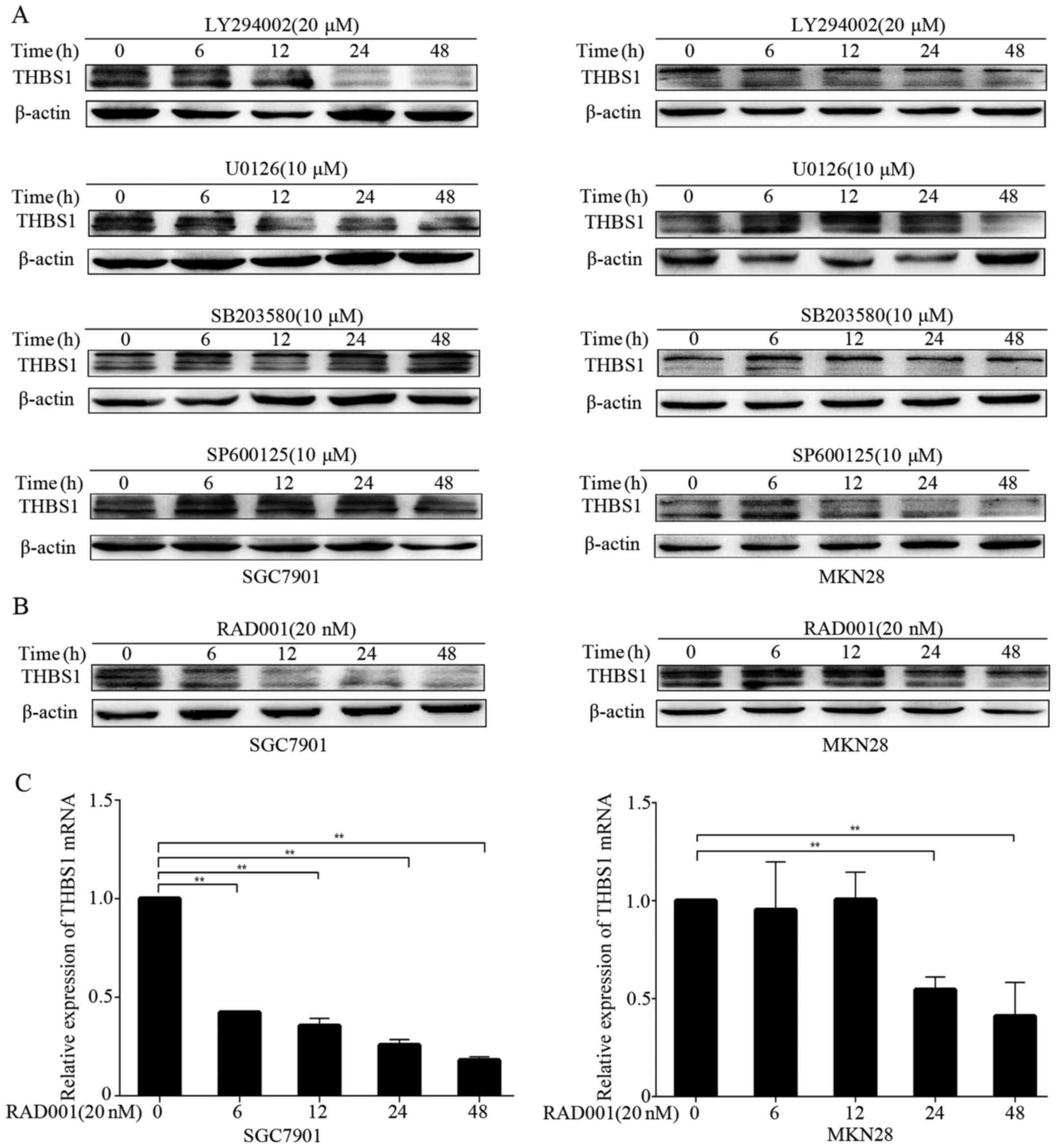
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T,
Kinoshita T, Fujii M, Nashimoto A, Furukawa H, Nakajima T, Ohashi
Y, Imamura H, et al ACTS-GC Group: Adjuvant chemotherapy for
gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med.
357:1810–1820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J,
Hundahl SA, Estes NC, Stemmermann GN, Haller DG, Ajani JA,
Gunderson LL, Jessup JM, et al: Chemoradiotherapy after surgery
compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or
gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 345:725–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al MAGIC Trial Participants: Perioperative
chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Power DG, Kelsen DP and Shah MA: Advanced
gastric cancer–slow but steady progress. Cancer Treat Rev.
36:384–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thrumurthy SG, Chaudry MA, Chau I and
Allum W: Does surgery have a role in managing incurable gastric
cancer? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:676–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beenken A and Mohammadi M: The FGF family:
Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:235–253. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Knights V and Cook SJ: De-regulated FGF
receptors as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
125:105–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Finch PW, Rubin JS, Miki T, Ron D and
Aaronson SA: Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a
paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 245:752–755.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grose R and Dickson C: Fibroblast growth
factor signaling in tumorigenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
16:179–186. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamayoshi T, Nagayasu T, Matsumoto K, Abo
T, Hishikawa Y and Koji T: Expression of keratinocyte growth
factor/fibroblast growth factor-7 and its receptor in human lung
cancer: Correlation with tumour proliferative activity and patient
prognosis. J Pathol. 204:110–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toyokawa T, Yashiro M and Hirakawa K:
Co-expression of keratinocyte growth factor and K-sam is an
independent prognostic factor in gastric carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
21:875–880. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cho K, Ishiwata T, Uchida E, Nakazawa N,
Korc M, Naito Z and Tajiri T: Enhanced expression of keratinocyte
growth factor and its receptor correlates with venous invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol. 170:1964–1974. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Toratani S, Sato JD, Kan
M, McKeehan WL and Okamoto T: Growth inhibition by keratinocyte
growth factor receptor of human salivary adenocarcinoma cells
through induction of differentiation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:11336–11340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ricol D, Cappellen D, El Marjou A,
Gil-Diez-de-Medina S, Girault JM, Yoshida T, Ferry G, Tucker G,
Poupon MF, Chopin D, et al: Tumour suppressive properties of
fibroblast growth factor receptor 2-IIIb in human bladder cancer.
Oncogene. 18:7234–7243. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Diez de Medina SG, Chopin D, El Marjou A,
Delouvée A, LaRochelle WJ, Hoznek A, Abbou C, Aaronson SA, Thiery
JP and Radvanyi F: Decreased expression of keratinocyte growth
factor receptor in a subset of human transitional cell bladder
carcinomas. Oncogene. 14:323–330. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carlson CB, Lawler J and Mosher DF:
Structures of thrombospondins. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:672–686. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baenziger NL, Brodie GN and Majerus PW: A
thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 68:240–243. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Borsotti P, Ghilardi C, Ostano P, Silini
A, Dossi R, Pinessi D, Foglieni C, Scatolini M, Lacal PM, Ferrari
R, et al: Thrombospondin-1 is part of a Slug-independent motility
and metastatic program in cutaneous melanoma, in association with
VEGFR-1 and FGF-2. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 28:73–81. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jayachandran A, Anaka M, Prithviraj P,
Hudson C, McKeown SJ, Lo PH, Vella LJ, Goding CR, Cebon J and
Behren A: Thrombospondin 1 promotes an aggressive phenotype through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human melanoma. Oncotarget.
5:5782–5797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pal SK, Nguyen CT, Morita KI, Miki Y,
Kayamori K, Yamaguchi A and Sakamoto K: THBS1 is induced by TGFB1
in the cancer stroma and promotes invasion of oral squamous cell
carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 5:730–739. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Roberts DD: Regulation of tumor growth and
metastasis by thrombospondin-1. FASEB J. 10:1183–1191.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nie S, Lo A, Wu J, Zhu J, Tan Z, Simeone
DM, Anderson MA, Shedden KA, Ruffin MT and Lubman DM: Glycoprotein
biomarker panel for pancreatic cancer discovered by quantitative
proteomics analysis. J Proteome Res. 13:1873–1884. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lyu T, Jia N, Wang J, Yan X, Yu Y, Lu Z,
Bast RC Jr, Hua K and Feng W: Expression and epigenetic regulation
of angiogenesis-related factors during dormancy and recurrent
growth of ovarian carcinoma. Epigenetics. 8:1330–1346. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perez-Janices N, Blanco-Luquin I, Tuñón
MT, Barba-Ramos E, Ibáñez B, Zazpe-Cenoz I, Martinez-Aguillo M,
Hernandez B, Martínez-Lopez E, Fernández AF, et al: EPB41L3, TSP-1
and RASSF2 as new clinically relevant prognostic biomarkers in
diffuse gliomas. Oncotarget. 6:368–380. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nomura S, Yoshitomi H, Takano S, Shida T,
Kobayashi S, Ohtsuka M, Kimura F, Shimizu H, Yoshidome H, Kato A,
et al: FGF10/FGFR2 signal induces cell migration and invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:305–313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Behrens C, Lin HY, Lee JJ, Raso MG, Hong
WK, Wistuba II and Lotan R: Immunohistochemical expression of basic
fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptors 1
and 2 in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6014–6022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bane AL, Pinnaduwage D, Colby S, Reedijk
M, Egan SE, Bull SB, O'Malley FP and Andrulis IL: Expression
profiling of familial breast cancers demonstrates higher expression
of FGFR2 in BRCA2-associated tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
117:183–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Byron SA, Gartside MG, Wellens CL, Mallon
MA, Keenan JB, Powell MA, Goodfellow PJ and Pollock PM: Inhibition
of activated fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 in endometrial
cancer cells induces cell death despite PTEN abrogation. Cancer
Res. 68:6902–6907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Byron SA and Pollock PM: FGFR2 as a
molecular target in endometrial cancer. Future Oncol. 5:27–32.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han N, Kim MA, Lee HS and Kim WH:
Evaluation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 expression,
heterogeneity and clinical significance in gastric cancer.
Pathobiology. 82:269–279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ahn S, Lee J, Hong M, Kim ST, Park SH,
Choi MG, Lee JH, Sohn TS, Bae JM, Kim S, et al: FGFR2 in gastric
cancer: protein overexpression predicts gene amplification and high
H-index predicts poor survival. Mod Pathol. 29:1095–1103. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Zhou Y, Jiang K, Shen Z, Ye Y and
Wang S: Evaluation of the seventh AJCC TNM staging system for
gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Tumour Biol.
35:8525–8532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tokunaga R, Imamura Y, Nakamura K,
Ishimoto T, Nakagawa S, Miyake K, Nakaji Y, Tsuda Y, Iwatsuki M,
Baba Y, et al: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 expression, but
not its genetic amplification, is associated with tumor growth and
worse survival in esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:19748–19761. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakazawa K, Yashiro M and Hirakawa K:
Keratinocyte growth factor produced by gastric fibroblasts
specifically stimulates proliferation of cancer cells from
scirrhous gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:8848–8852.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sommer A, Kopitz C, Schatz CA, Nising CF,
Mahlert C, Lerchen HG, Stelte-Ludwig B, Hammer S, Greven S,
Schuhmacher J, et al: Preclinical efficacy of the auristatin-based
antibody-drug conjugate BAY 1187982 for the treatment of
FGFR2-positive solid tumors. Cancer Res. 76:6331–6339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanaka K, Sonoo H, Kurebayashi J, Nomura
T, Ohkubo S, Yamamoto Y and Yamamoto S: Inhibition of infiltration
and angiogenesis by thrombospondin-1 in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1125–1131. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maeda K, Nishiguchi Y, Yashiro M, Yamada
S, Onoda N, Sawada T, Kang SM and Hirakawa K: Expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor and thrombospondin-1 in
colorectal carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 5:373–378. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Clezardin P, Frappart L, Clerget M,
Pechoux C and Delmas PD: Expression of thrombospondin (TSP1) and
its receptors (CD36 and CD51) in normal, hyperplastic, and
neoplastic human breast. Cancer Res. 53:1421–1430. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kasper HU, Ebert M, Malfertheiner P,
Roessner A, Kirkpatrick CJ and Wolf HK: Expression of
thrombospondin-1 in pancreatic carcinoma: correlation with
microvessel density. Virchows Archiv. 438:116–120. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grossfeld GD, Ginsberg DA, Stein JP,
Bochner BH, Esrig D, Groshen S, Dunn M, Nichols PW, Taylor CR,
Skinner DG, et al: Thrombospondin-1 expression in bladder cancer:
Association with p53 alterations, tumor angiogenesis, and tumor
progression. J Natl Cancer Inst. 89:219–227. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kwak C, Jin RJ, Lee C, Park MS and Lee SE:
Thrombospondin-1, vascular endothelial growth factor expression and
their relationship with p53 status in prostate cancer and benign
prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 89:303–309. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin XD, Chen SQ, Qi YL, Zhu JW, Tang Y and
Lin JY: Overexpression of thrombospondin-1 in stromal
myofibroblasts is associated with tumor growth and nodal metastasis
in gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 106:94–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nakao T, Kurita N, Komatsu M, Yoshikawa K,
Iwata T, Utsunomiya T and Shimada M: Expression of thrombospondin-1
and Ski are prognostic factors in advanced gastric cancer. Int J
Clin Oncol. 16:145–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang J, Ito R, Oue N, Zhu X, Kitadai Y,
Yoshida K, Nakayama H and Yasui W: Expression of thrombospondin-1
is correlated with microvessel density in gastric carcinoma.
Virchows Archiv. 442:563–568. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Radziwon-Balicka A, Santos-Martinez MJ,
Corbalan JJ, O'Sullivan S, Treumann A, Gilmer JF, Radomski MW and
Medina C: Mechanisms of platelet-stimulated colon cancer invasion:
Role of clusterin and thrombospondin 1 in regulation of the
P38MAPK-MMP-9 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 35:324–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Firlej V, Mathieu JR, Gilbert C, Lemonnier
L, Nakhlé J, Gallou-Kabani C, Guarmit B, Morin A, Prevarskaya N,
Delongchamps NB, et al: Thrombospondin-1 triggers cell migration
and development of advanced prostate tumors. Cancer Res.
71:7649–7658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang TN, Qian X, Granick MS, Solomon MP,
Rothman VL, Berger DH and Tuszynski GP: Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1)
promotes the invasive properties of human breast cancer. J Surg
Res. 63:39–43. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yee KO, Connolly CM, Duquette M,
Kazerounian S, Washington R and Lawler J: The effect of
thrombospondin-1 on breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 114:85–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Yu H, Tyrrell D, Cashel J, Guo NH, Vogel
T, Sipes JM, Lam L, Fillit HM, Hartman J, et al: Specificities of
heparin-binding sites from the amino-terminus and type 1 repeats of
thrombospondin-1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 374:13–23. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Taraboletti G, Rusnati M, Ragona L and
Colombo G: Targeting tumor angiogenesis with TSP-1-based compounds:
Rational design of antiangiogenic mimetics of endogenous
inhibitors. Oncotarget. 1:662–673. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Morandi V, Cherradi SE, Lambert S,
Fauvel-Lafève F, Legrand YJ and Legrand C: Proinflammatory
cytokines (interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha) down
regulate synthesis and secretion of thrombospondin by human
endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 160:367–377. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Loganadane LD, Berge N, Legrand C and
Fauvel-Lafève F: Endothelial cell proliferation regulated by
cytokines modulates thrombospondin-1 secretion into the
subendothelium. Cytokine. 9:740–746. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Doll JA, Reiher FK, Crawford SE, Pins MR,
Campbell SC and Bouck NP: Thrombospondin-1, vascular endothelial
growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 are key functional
regulators of angiogenesis in the prostate. Prostate. 49:293–305.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tarkkonen K, Ruohola J and Härkönen P:
Fibroblast growth factor 8 induced downregulation of thrombospondin
1 is mediated by the MEK/ERK and PI3K pathways in breast cancer
cells. Growth Factors. 28:256–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dailey L, Ambrosetti D, Mansukhani A and
Basilico C: Mechanisms underlying differential responses to FGF
signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:233–247. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hong L, Han Y, Liu J and Brain L:
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2: A therapeutic target in
gastric cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:759–765. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|