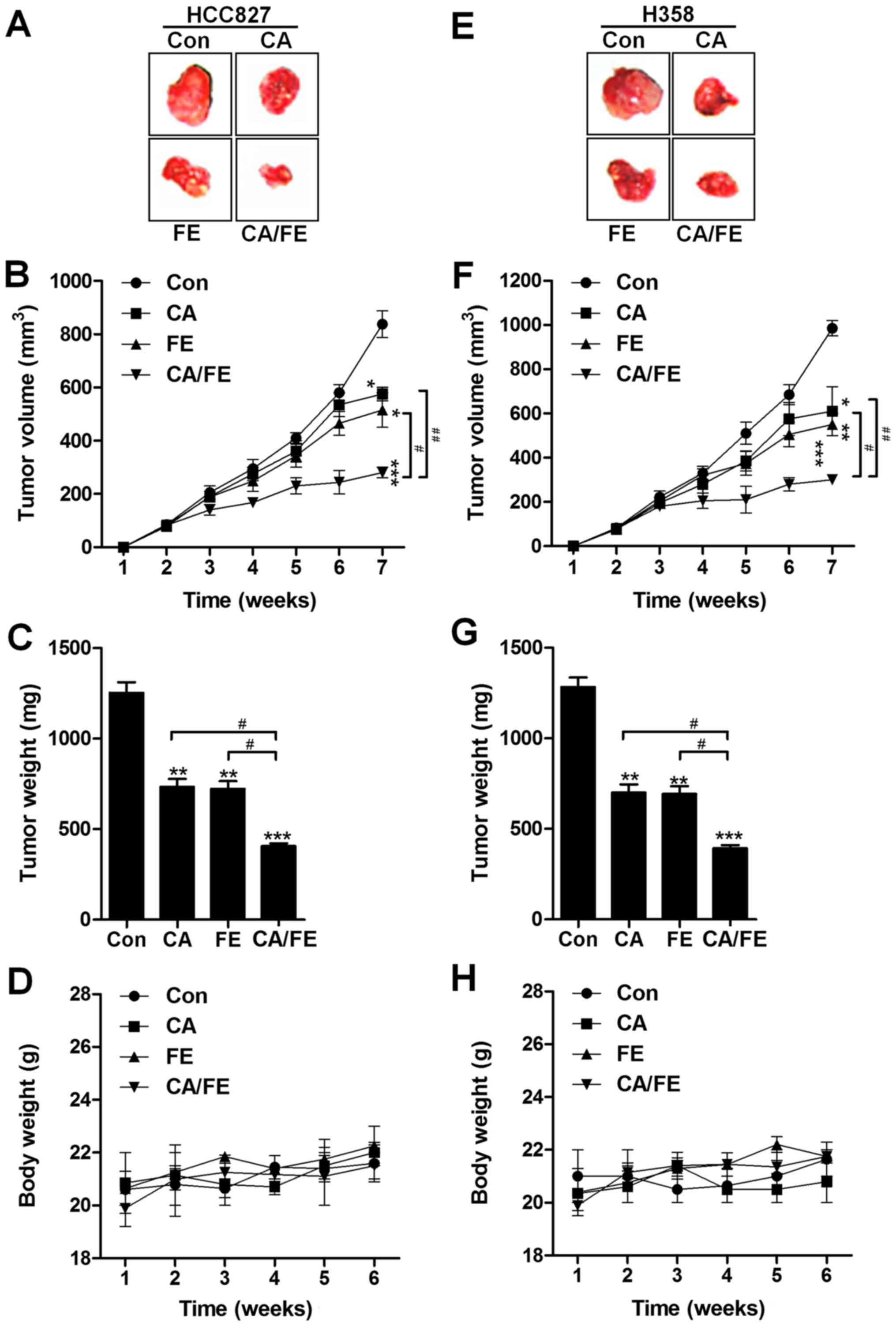
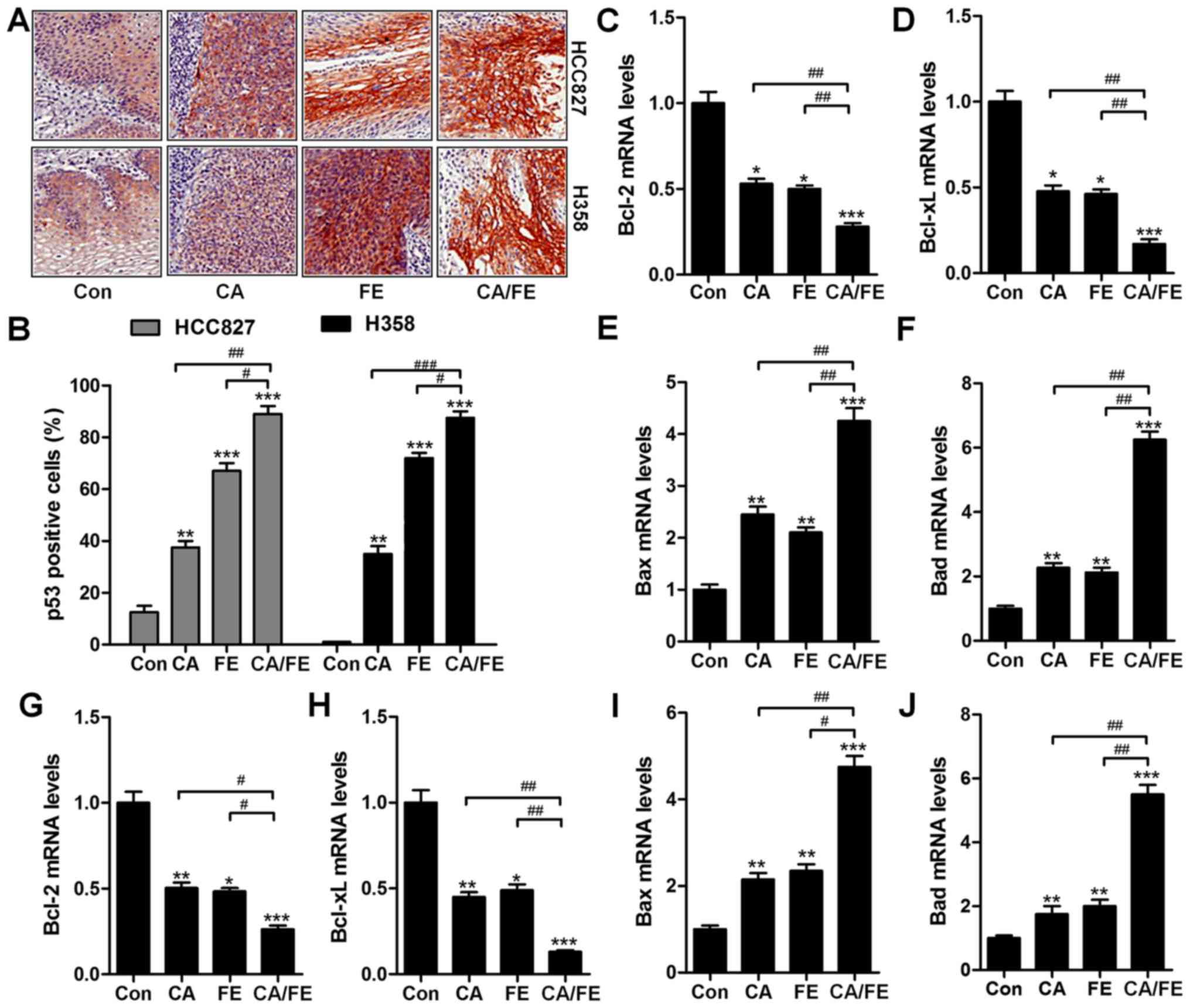
|
1
|
Zhang XY and Zhang P: Sensitization
strategies in lung cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 12:3669–3673.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alberg AJ, Ford JG and Samet JM; American
College of Chest Physicians: Epidemiology of lung cancer: ACCP
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest.
132(Suppl): 29S–55S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cui Y, Wang G, Li Y, Wang Y, Wang X and Bi
H: Optical coherence tomography and histopathology of macular
uveitis. Optom Vis Sci. 91:1335–1342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou ZP, Qiang FY, Zhang T, Sun L, Jia T,
Zhu XC and Xu H: Treatment of experimental autoimmune uveitis in
rats with arsenic trioxide. Chin Ophthalmic Res. 28:306–310.
2010.
|
|
7
|
Mira A, Tanaka A, Tateyama Y, Kondo R and
Shimizu K: Comparative biological study of roots, stems, leaves,
and seeds of Angelica shikokiana Makino. J Ethnopharmacol.
148:980–987. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheung S and Tai J: Anti-proliferative and
antioxidant properties of rosemary Rosmarinus officinalis. Oncol
Rep. 17:1525–1531. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Steiner M, Priel I, Giat J, Levy J,
Sharoni Y and Danilenko M: Carnosic acid inhibits proliferation and
augments differentiation of human leukemic cells induced by
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and retinoic acid. Nutr Cancer.
41:135–144. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Murtaza I, Adhami VM, Hafeez BB, Saleem M
and Mukhtar H: Fisetin, a natural flavonoid, targets chemoresistant
human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through DR3-mediated
inhibition of NF-kappaB. Int J Cancer. 125:2465–2473. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Cheng Y, Qu W, Sun Y, Wang Z, Wang H
and Tian B: Fisetin, a dietary flavonoid, induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis through activation of p53 and inhibition of NF-kappa
B pathways in bladder cancer cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
108:84–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ying TH, Yang SF, Tsai SJ, Hsieh SC, Huang
YC, Bau DT and Hsieh YH: Fisetin induces apoptosis in human
cervical cancer HeLa cells through ERK1/2-mediated activation of
caspase-8-/caspase-3-dependent pathway. Arch Toxicol. 86:263–273.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Khan N, Asim M, Afaq F, Abu Zaid M and
Muhtar H: A novel dietary flavonoid fisetin inhibits androgen
receptor signaling and tumor growth in athymic nude mice. Cancer
Res. 68:8555–8563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szliszka E, Helewski KJ, Mizgala E and
Krol W: The dietary flavonol fisetin enhances the
apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 39:771–779. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang PM, Tseng HH, Peng CW, Chen WS and
Chiu SJ: Dietary flavonoid fisetin targets caspase-3-deficient
human breast cancer MCF-7 cells by induction of
caspase-7-associated apoptosis and inhibition of autophagy. Int J
Oncol. 40:469–478. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Liang J, Deng X, Wu FS and Tang YF:
Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of human hepatic stellate
cells treated with natural taurine. Mol Med Rep. 7:1442–1452.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li DW, Li JH, Wang YD and Li GR:
Atorvastatin protects endothelial colony-forming cells against
H2O2-induced oxidative damage by regulating
the expression of annexin A2. Mol Med Rep. 12:7941–7948.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai JJ, Qi ZX, Chen LC, Yao Y, Gong Y and
Mao Y: miR-124 suppresses the migration and invasion of glioma
cells in vitro via Capn4. Oncol Rep. 35:284–290. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Joshi A, Allen R, Kroetz D, Schaller M,
Dalton J, Kunkel S and Gallagher K: Histone methyltransferase,
Setdb2, regulates wound healing in a diet-induced obesity model of
diabetes (IRM9P 601). J Immunol. 194(Suppl 1): 130.102015.
|
|
20
|
Lyons AB, Blake SJ and Doherty KV: Flow
cytometric analysis of cell division by dilution of CFSE and
related dyes. Curr Protoc Cytom Chapter. 9:112013.
|
|
21
|
Polikepahad S, Knight JM, Naghavi AO, Oplt
T, Creighton CJ, Shaw C, Benham AL, Kim J, Soibam B, Harris RA, et
al: Proinflammatory role for let-7 microRNAS in experimental
asthma. J Biol Chem. 285:30139–30149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cagin YF, Parlakpinar H, Vardi N, Polat A,
Atayan Y, Erdogan MA and Tanbek K: Effects of dexpanthenol on
acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Exp Ther Med. 12:2958–2964.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trussardi-Regnier A, Lavenus S, Gorisse MC
and Dufer J: Thalidomide alters nuclear architecture without ABCB1
gene modulation in drug-resistant myeloma cells. Int J Oncol.
35:641–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schultz DR and Harrington WJ Jr:
Apoptosis: Programmed cell death at a molecular level. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 32:345–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ashkenazi A, Holland P and Eckhardt SG:
Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: The potential of
recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL). J Clin Oncol.
26:3621–3630. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan Y, Xu R, Peach M, Huang CP,
Branstetter D, Novotny W, Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG and Holland PM:
Evaluation of pharmacodynamic biomarkers in a Phase 1a trial of
dulanermin (rhApo2L/TRAIL) in patients with advanced tumours. Br J
Cancer. 105:1830–1838. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wiezorek J, Holland P and Graves J: Death
receptor agonists as a targeted therapy for cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:1701–1708. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dimberg LY, Anderson CK, Camidge R,
Behbakht K, Thorburn A and Ford HL: On the TRAIL to successful
cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against
TRAIL-based therapeutics. Oncogene. 32:1341–1350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT and Matthay RA:
Lung cancer: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest
Med. 32:605–644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ganti AK, Siedlik E, Marr AS, Loberiza FR
Jr and Kessinger A: Predictive ability of Charlson comorbidity
index on outcomes from lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 34:593–596.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yao J, Wang YW, Fang BB, Zhang SJ and
Cheng BL: piR-651 and its function in 95-D lung cancer cells.
Biomed Rep. 4:546–550. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hou DX, Fukuda M, Johnson JA, Miyamori K,
Ushikai M and Fujii M: Fisetin induces transcription of
NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase gene through an antioxidant responsive
element-involved activation. Int J Oncol. 18:1175–1179.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Daliani DD, Tannir NM, Papandreou CN, Wang
X, Swisher S, Wood CG, Swanson DA, Logothetis CJ and Jonasch E:
Prospective assessment of systemic therapy followed by surgical
removal of metastases in selected patients with renal cell
carcinoma. BJU Int. 104:456–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL- induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jin Z, McDonald ER III, Dicker DT and
El-Deiry WS: Deficient tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor transport to the
cell surface in human colon cancer cells selected for resistance to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:35829–35839. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim HS, Lee JW, Soung YH, Park WS, Kim SY,
Lee JH, Park JY, Cho YG, Kim CJ, Jeong SW, et al: Inactivating
mutations of caspase-8 gene in colorectal carcinomas.
Gastroenterology. 125:708–715. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cummins JM, Kohli M, Rago C, Kinzler KW,
Vogelstein B and Bunz F: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
(XIAP) is a nonredundant modulator of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis in human
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:3006–3008. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang S, Ong CN and Shen HM: Involvement
of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in parthenolide-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 211:175–188.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SL, Trang KT, Kim SH, Kim IH, Lee SO,
Lee ST, Kim DG and Kim SW: Parthenolide suppresses tumor growth in
a xenograft model of colorectal cancer cells by inducing
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 41:1547–1553.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carlisi D, D'Anneo A, Angileri L,
Lauricella M, Emanuele S, Santulli A, Vento R and Tesoriere G:
Parthenolide sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL by
inducing the expression of death receptors through inhibition of
STAT3 activation. J Cell Physiol. 226:1632–1641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vasilevskaya IA and O'Dwyer PJ:
17-Allylamino-17- demethoxygeldanamycin overcomes TRAIL resistance
in colon cancer cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:580–589. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, Wilson
TR, McLaughlin K and Johnston PG: Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated
colon cancer cell death: The roles of p53, TRAIL receptors, and
c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2026–2036. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pennarun B, Meijer A, de Vries EG,
Kleibeuker JH, Kruyt F and de Jong S: Playing the DISC: Turning on
TRAIL death receptor- mediated apoptosis in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1805:123–140. 2010.
|
|
45
|
Jung YH, Heo J, Lee YJ, Kwon TK and Kim
YH: Quercetin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells via increased protein stability of death receptor 5. Life
Sci. 86:351–357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|