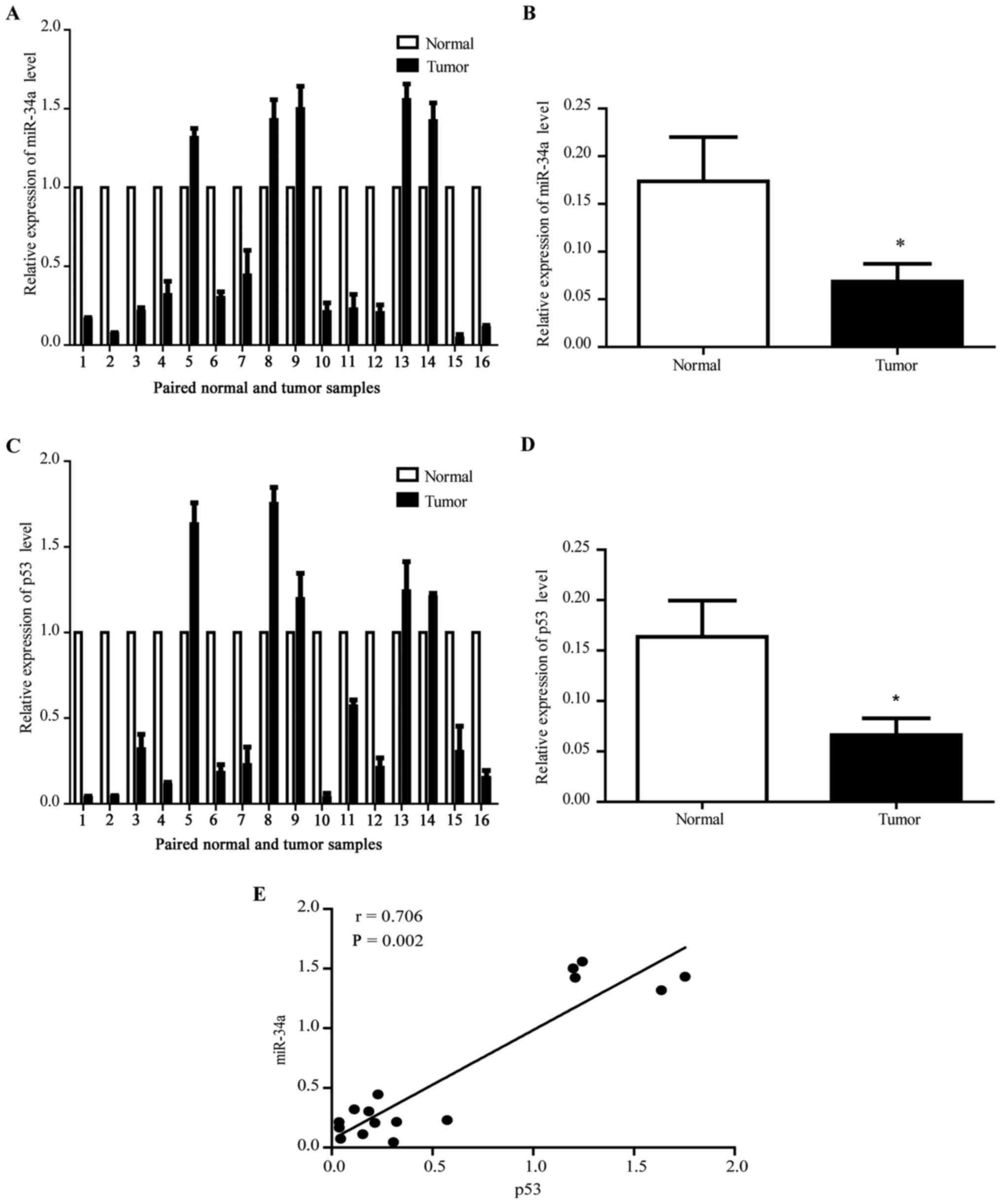
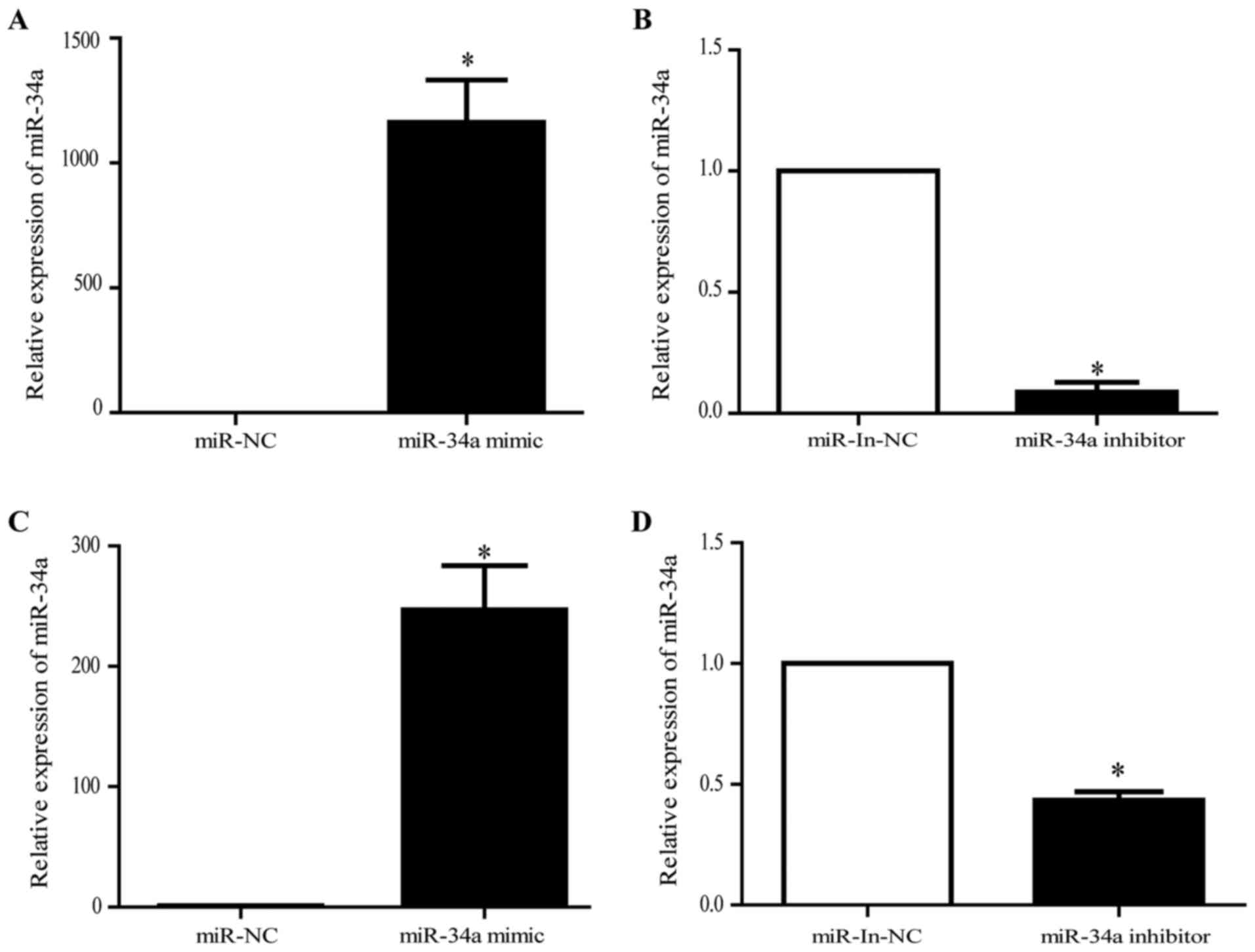
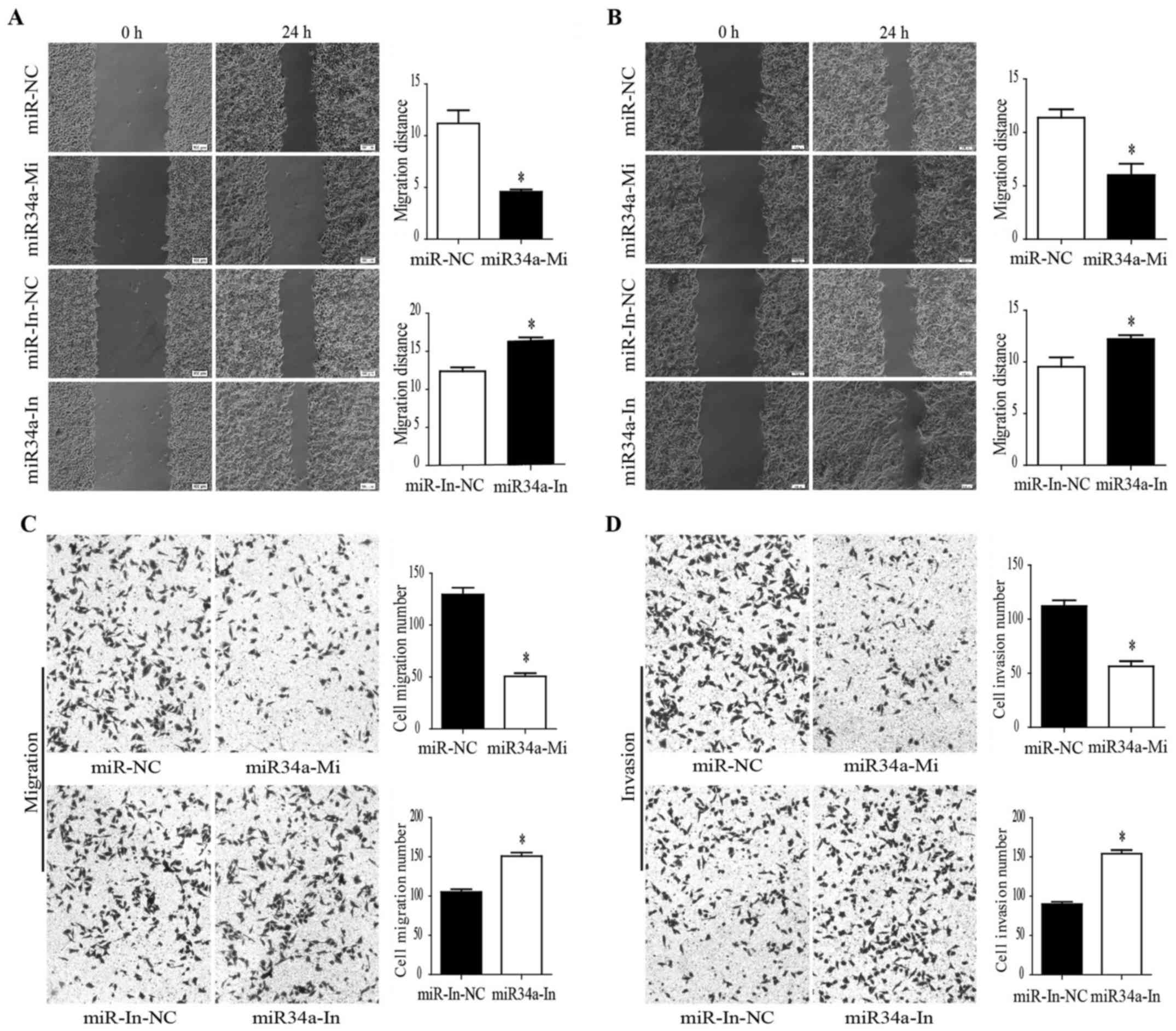
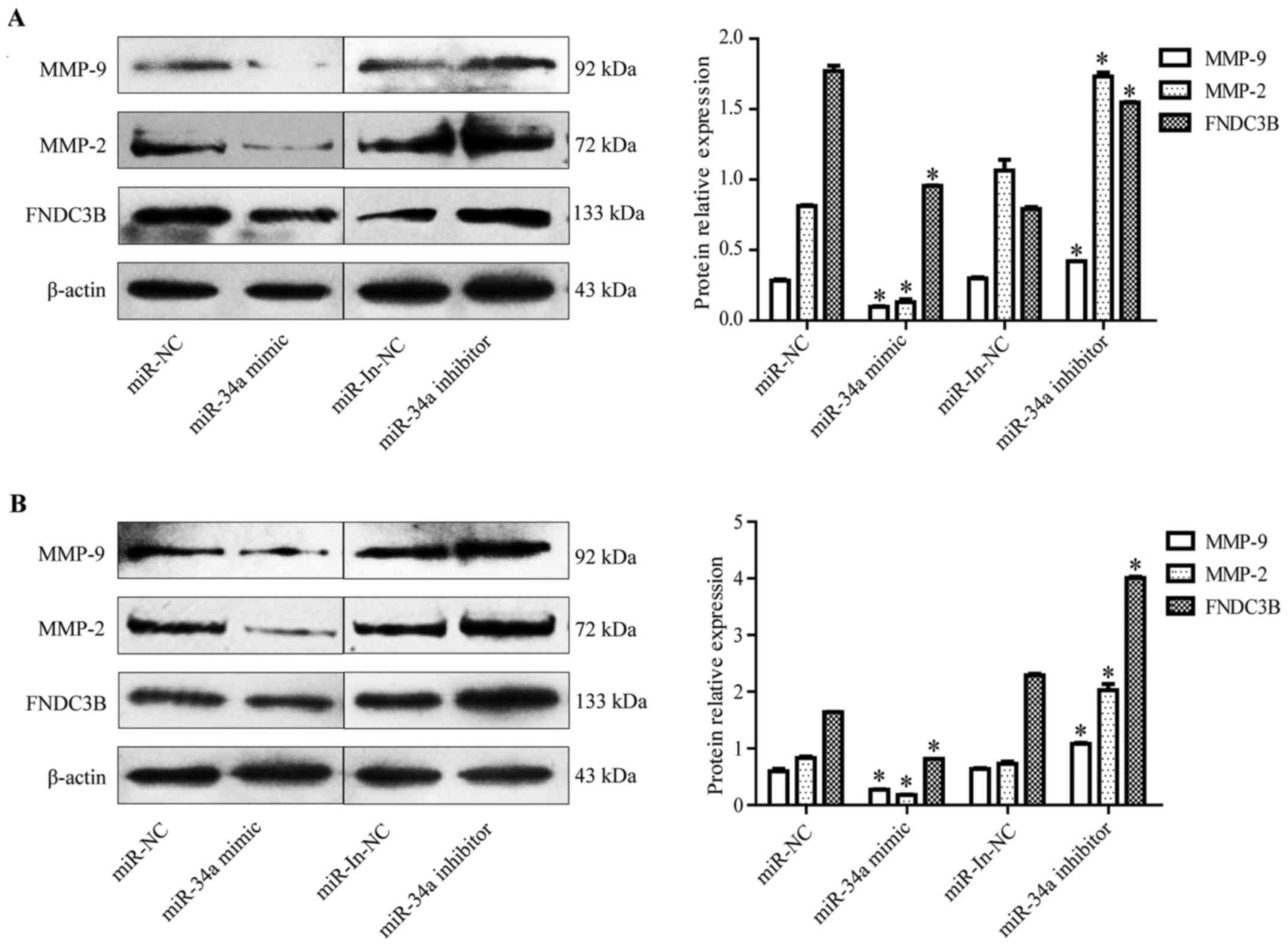
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H and Zhang S: The
updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011.
Chin J Cancer. 34:502–507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gamliel Z and Krasna MJ: Multimodality
treatment of esophageal cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 85:621–630.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee KH, Goan YG, Hsiao M, Lee CH, Jian SH,
Lin JT, Chen YL and Lu PJ: MicroRNA-373 (miR-373)
post-transcriptionally regulates large tumor suppressor, homolog 2
(LATS2) and stimulates proliferation in human esophageal cancer.
Exp Cell Res. 315:2529–2538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Zheng D, Zhang B, Liu L, Ou J, Chen
W, Xiong S, Gu Y and Yang J: Mir-208 promotes cell proliferation by
repressing SOX6 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 12:1962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Tian X, Liu F, Zhao Y, Sun M, Chen
D, Lu C, Wang Z, Shi X, Zhang Q, et al: Detection of HPV DNA in
esophageal cancer specimens from different regions and ethnic
groups: A descriptive study. BMC Cancer. 10:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Kamberov YG,
Wilder EL, Klein PS and Rustgi AK: Wnt-1 but not epidermal growth
factor induces beta-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent transcription
in esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:277–282. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang L, Leung AC, Ko JM, Lo PH, Tang JC,
Srivastava G, Oshimura M, Stanbridge EJ, Daigo Y, Nakamura Y, et
al: Tumor suppressive role of a 2.4 Mb 9q33-q34 critical region and
DEC1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:697–705.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV,
Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, et
al: miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia LF, Wei SB, Mitchelson K, Gao Y, Zheng
YF, Meng Z, Gan YH and Yu GY: miR-34a inhibits migration and
invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting MMP9 and
MMP14. PLoS One. 9:e1084352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Phatak P, Byrnes KA, Mansour D, Liu L, Cao
S, Li R, Rao JN, Turner DJ, Wang JY and Donahue JM: Overexpression
of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances
sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and
indirectly through CUG-BP1. Oncogene. 35:2087–2097. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Duursma AM, Kedde M, Schrier M, le Sage C
and Agami R: miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region.
RNA. 14:872–877. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S,
Park JK, Dai Z, Liu CG, Schmittgen TD, Reinhold WC, Croce CM, et
al: MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gallardo E, Navarro A, Viñolas N, Marrades
RM, Diaz T, Gel B, Quera A, Bandres E, Garcia-Foncillas J, Ramirez
J, et al: miR-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in surgically
resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 30:1903–1909.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu J, Wu G, Lv L, Ren YF, Zhang XJ, Xue
YF, Li G, Lu X, Sun Z and Tang KF: MicroRNA-34a inhibits migration
and invasion of colon cancer cells via targeting to Fra-1.
Carcinogenesis. 33:519–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, Srivastava RK
and Shankar S: Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for
treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer
stem cells. PLoS One. 6:e240992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun H, Tian J, Xian W, Xie T and Yang X:
miR-34a inhibits proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells
by targeting orphan nuclear receptor HNF4G. Dis Markers.
2015:8792542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Corney DC, Hwang CI, Matoso A, Vogt M,
Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, Kamat AA, Sood AK, Ellenson LH,
Hermeking H, et al: Frequent downregulation of miR-34 family in
human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1119–1128. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, Xing R,
Sun Z and Zheng X: Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a
induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 582:1564–1568. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei JS, Song YK, Durinck S, Chen QR, Cheuk
AT, Tsang P, Zhang Q, Thiele CJ, Slack A, Shohet J, et al: The MYCN
oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene. 27:5204–5213.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan D, Zhou X, Chen X, Hu DN, Dong XD,
Wang J, Lu F, Tu L and Qu J: MicroRNA-34a inhibits uveal melanoma
cell proliferation and migration through downregulation of c-Met.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1559–1565. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kang J, Kim E, Kim W, Seong KM, Youn H,
Kim JW, Kim J and Youn B: Rhamnetin and cirsiliol induce
radiosensitization and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) by miR-34a-mediated suppression of Notch-1
expression in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
288:27343–27357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Catania A,
Li Y, Schiff D, Purow B and Abounader R: microRNA-34a is tumor
suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle.
9:1031–1036. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, Song B, Ma W, Lu Y,
Zhao L, Li J, Yang B and Li L: MicroRNA-34a suppresses the breast
cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1
pathway. Cancer Sci. 106:700–708. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bu P, Chen KY, Chen JH, Wang L, Walters J,
Shin YJ, Goerger JP, Sun J, Witherspoon M, Rakhilin N, et al: A
microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets Notch in colon
cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 12:602–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park EY, Chang E, Lee EJ, Lee HW, Kang HG,
Chun KH, Woo YM, Kong HK, Ko JY, Suzuki H, et al: Targeting of
miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and
chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 74:7573–7582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu MY, Fu J, Xiao X, Wu J and Wu RC:
MiR-34a regulates therapy resistance by targeting HDAC1 and HDAC7
in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 354:311–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li XJ, Ji MH, Zhong SL, Zha QB, Xu JJ,
Zhao JH and Tang JH: MicroRNA-34a modulates chemosensitivity of
breast cancer cells to adriamycin by targeting Notch1. Arch Med
Res. 43:514–521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ghandadi M and Sahebkar A: MicroRNA-34a
and its target genes: Key factors in cancer multidrug resistance.
Curr Pharm Des. 22:933–939. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nie J, Ge X, Geng Y, Cao H, Zhu W, Jiao Y,
Wu J, Zhou J and Cao J: miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion
of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1.
Oncol Rep. 34:311–317. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jones KB, Salah Z, Del Mare S, Galasso M,
Gaudio E, Nuovo GJ, Lovat F, LeBlanc K, Palatini J, Randall RL, et
al: miRNA signatures associate with pathogenesis and progression of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:1865–1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Maire G, Martin JW, Yoshimoto M,
Chilton-MacNeill S, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Analysis of
miRNA-gene expression-genomic profiles reveals complex mechanisms
of microRNA deregulation in osteosarcoma. Cancer Genet.
204:138–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cui X, Zhao Z, Liu D, Guo T, Li S, Hu J,
Liu C, Yang L, Cao Y, Jiang J, et al: Inactivation of miR-34a by
aberrant CpG methylation in Kazakh patients with esophageal
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin X, Xu XY, Chen QS and Huang C:
Clinical significance of microRNA-34a in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Genet Mol Res. 14:17684–17691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Choi JD and Lee JS: Interplay between
epigenetics and genetics in cancer. Genomics Inform. 11:164–173.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A,
Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J and Hermeking
H: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chim CS, Wong KY, Qi Y, Loong F, Lam WL,
Wong LG, Jin DY, Costello JF and Liang R: Epigenetic inactivation
of the miR-34a in hematological malignancies. Carcinogenesis.
31:745–750. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E
and O'Higgins N: Metalloproteinases: Role in breast carcinogenesis,
invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2:252–257. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Samantaray S, Sharma R, Chattopadhyaya TK,
Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Increased expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
130:37–44. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Ma J, Guo Q, Duan F, Tang F, Zheng
P, Zhao Z and Lu G: Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 22:664–667. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen CF, Hsu EC, Lin KT, Tu PH, Chang HW,
Lin CH, Chen YJ, Gu DL, Lin CH, Wu JY, et al: Overlapping
high-resolution copy number alterations in cancer genomes
identified putative cancer genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 52:1690–1701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tominaga K, Kondo C, Johmura Y, Nishizuka
M and Imagawa M: The novel gene fad104, containing a fibronectin
type III domain, has a significant role in adipogenesis. FEBS Lett.
577:49–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nishizuka S, Ramalingam S, Spurrier B,
Washburn FL, Krishna R, Honkanen P, Young L, Tsutomu S, Steeg PS
and Austin J: Quantitative protein network monitoring in response
to DNA damage. J Proteome Res. 7:803–808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cai C, Rajaram M, Zhou X, Liu Q, Marchica
J, Li J and Powers RS: Activation of multiple cancer pathways and
tumor maintenance function of the 3q amplified oncogene FNDC3B.
Cell Cycle. 11:1773–1781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fan X, Chen X, Deng W, Zhong G, Cai Q and
Lin T: Up-regulated microRNA-143 in cancer stem cells
differentiation promotes prostate cancer cells metastasis by
modulating FNDC3B expression. BMC Cancer. 13:612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lu Y, Yi Y, Liu P, Wen W, James M, Wang D
and You M: Common human cancer genes discovered by integrated
gene-expression analysis. PLoS One. 2:e11492007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang Y, Li D, Yang Y and Jiang G: An
integrated analysis of the effects of microRNA and mRNA on
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 12:945–952.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Genovese G, Ergun A, Shukla SA, Campos B,
Hanna J, Ghosh P, Quayle SN, Rai K, Colla S, Ying H, et al:
microRNA regulatory network inference identifies miR-34a as a novel
regulator of TGF-β signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Discov.
2:736–749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L and Wu
D: microRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human
cholangio-carcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer. 15:4692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhou Q, Dong Wang L, Du F, Zhou Y, Rui
Zhang Y, Liu B, Wei Feng C, Gao SS, Fan ZM, Yang CS, et al: Changes
of TGFbeta1 and TGFbetaRII expression in esophageal precancerous
and cancerous lesions: A study of a high-risk population in Henan,
northern China. Dis Esophagus. 15:74–79. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA,
Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, Feldmann G, Yamakuchi M,
Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ, et al: Transactivation of miR-34a by p53
broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol
Cell. 26:745–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|