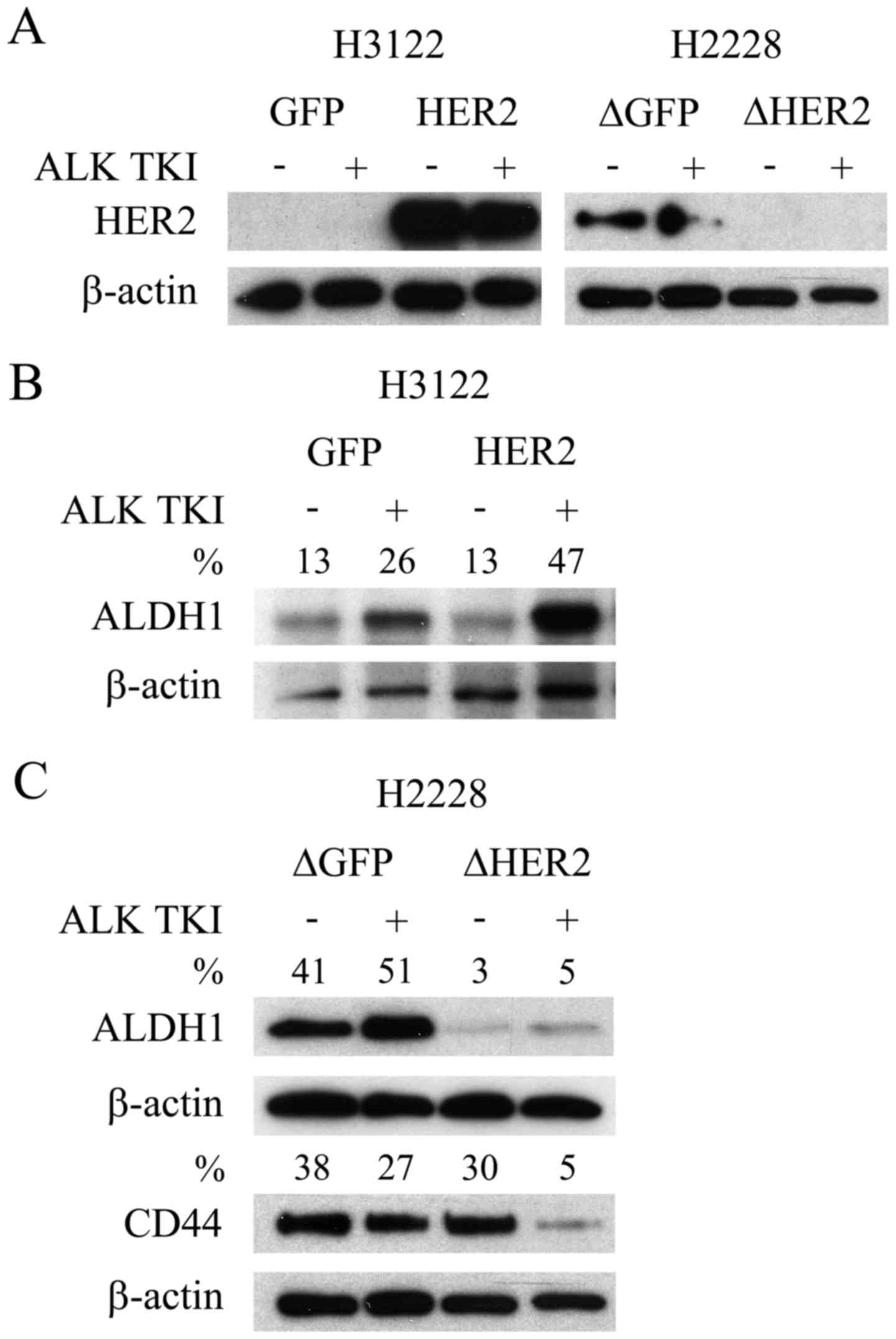
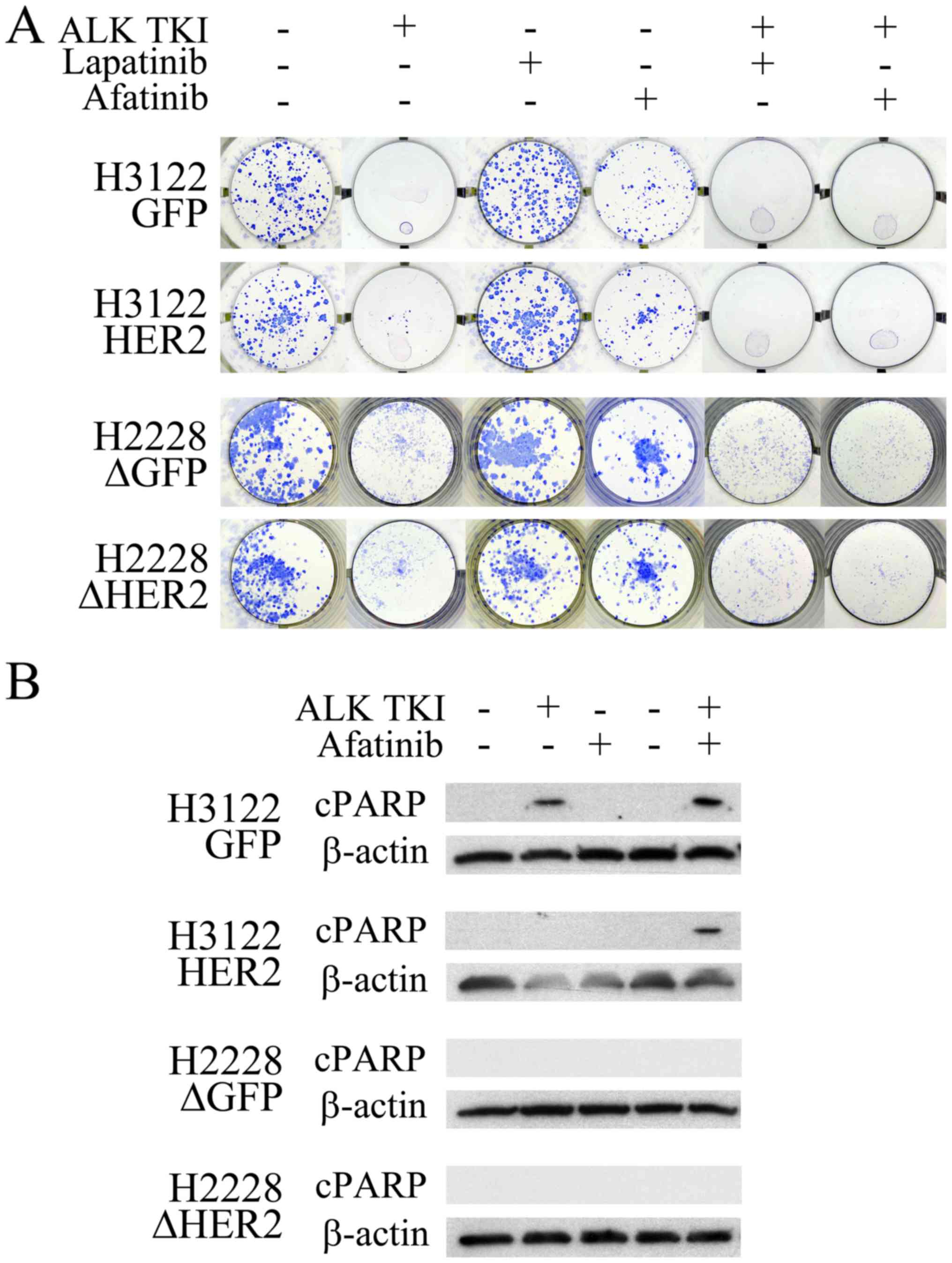
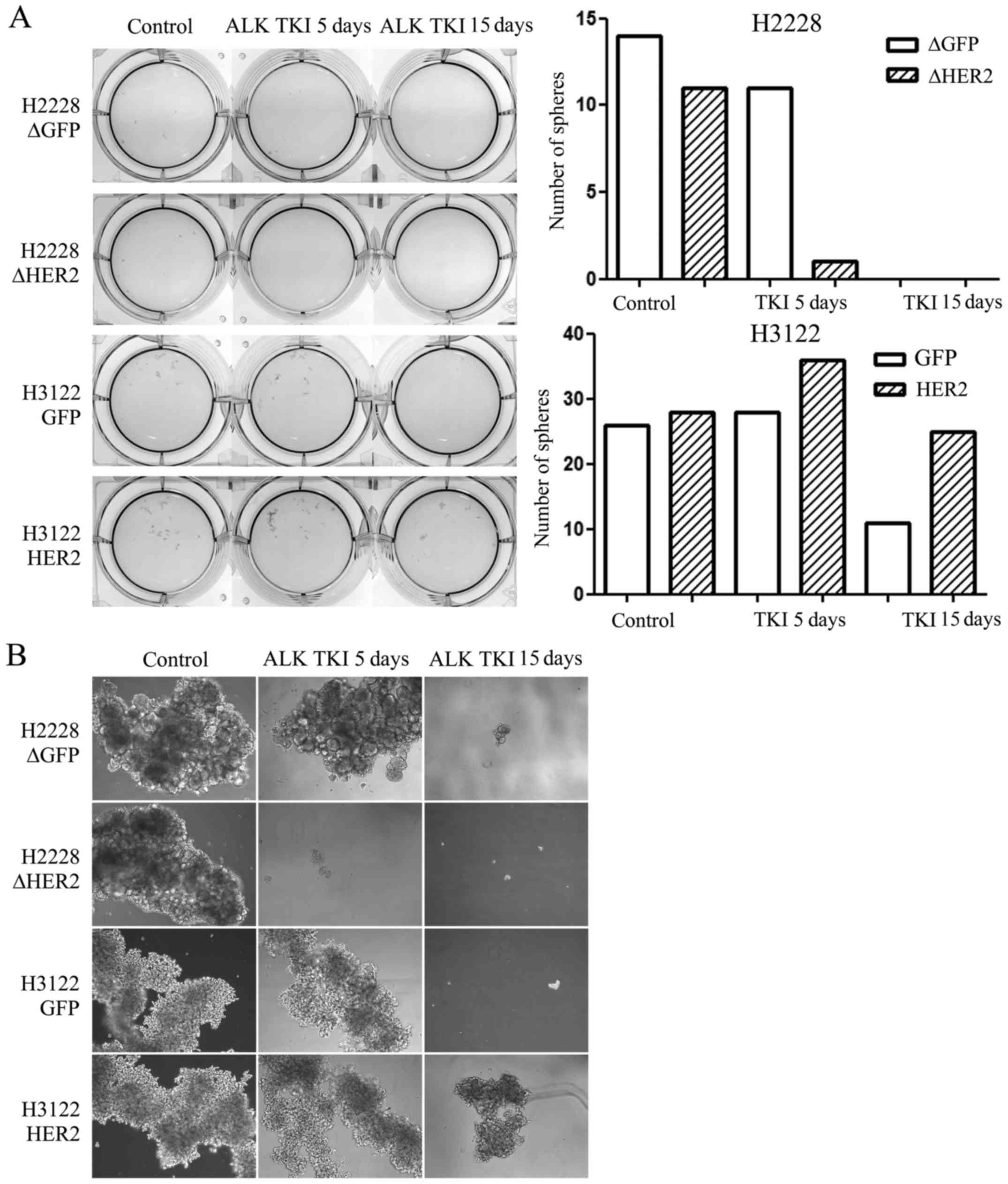
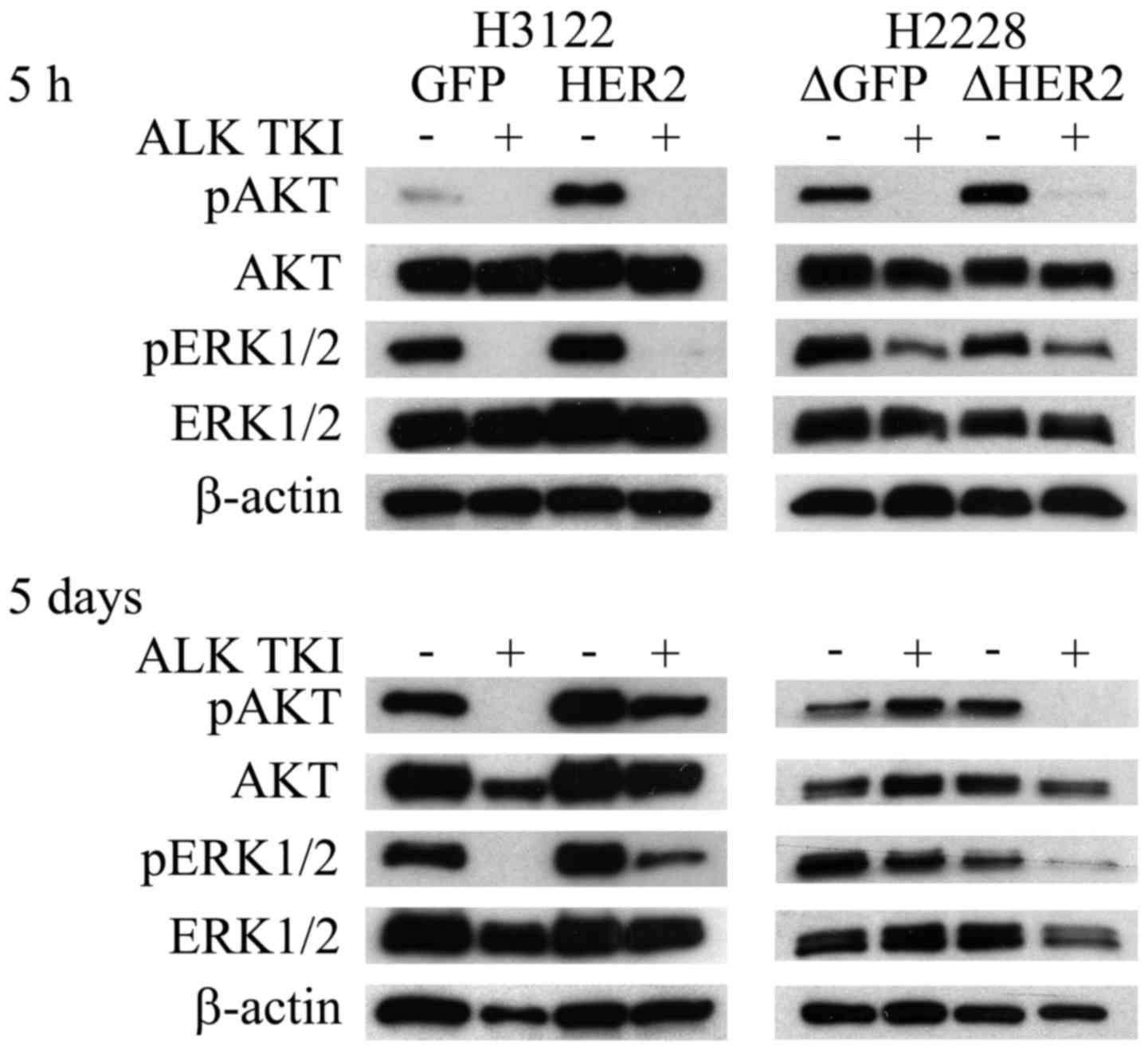
|
1
|
Doebele RC, Pilling AB, Aisner DL,
Kutateladze TG, Le AT, Weickhardt AJ, Kondo KL, Linderman DJ,
Heasley LE, Franklin WA, et al: Mechanisms of resistance to
crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1472–1482. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S,
Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K,
Hatanaka H, et al: Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK
fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koivunen JP, Mermel C, Zejnullahu K,
Murphy C, Lifshits E, Holmes AJ, Choi HG, Kim J, Chiang D, Thomas
R, et al: EML4-ALK fusion gene and efficacy of an ALK kinase
inhibitor in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4275–4283. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Cola A, Volpe S, Budani MC, Ferracin M,
Lattanzio R, Turdo A, D'Agostino D, Capone E, Stassi G, Todaro M,
et al: miR-205-5p-mediated downregulation of ErbB/HER receptors in
breast cancer stem cells results in targeted therapy resistance.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e18232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jokinen E, Laurila N, Koivunen P and
Koivunen JP: Combining targeted drugs to overcome and prevent
resistance of solid cancers with some stem-like cell features.
Oncotarget. 5:9295–9307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shien K, Toyooka S, Yamamoto H, Soh J,
Jida M, Thu KL, Hashida S, Maki Y, Ichihara E, Asano H, et al:
Acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors is associated with a
manifestation of stem cell-like properties in cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 73:3051–3061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C,
Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC,
et al: Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to
chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:672–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takebe N, Miele L, Harris PJ, Jeong W,
Bando H, Kahn M, Yang SX and Ivy SP: Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and
Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 12:445–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell
JA, Rampaul RS, Blamey RW, Robertson JF, Nicholson RI and Ellis IO:
Expression and co-expression of the members of the epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) family in invasive breast carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 91:1532–1542. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs
H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M,
et al: Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2
for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med.
344:783–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suo Z, Risberg B, Kalsson MG, Willman K,
Tierens A, Skovlund E and Nesland JM: EGFR family expression in
breast carcinomas. c-erbB-2 and c-erbB-4 receptors have different
effects on survival. J Pathol. 196:17–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ithimakin S, Day KC, Malik F, Zen Q,
Dawsey SJ, Bersano-Begey TF, Quraishi AA, Ignatoski KW, Daignault
S, Davis A, et al: HER2 drives luminal breast cancer stem cells in
the absence of HER2 amplification: Implications for efficacy of
adjuvant trastuzumab. Cancer Res. 73:1635–1646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clark PA, Iida M, Treisman DM, Kalluri H,
Ezhilan S, Zorniak M, Wheeler DL and Kuo JS: Activation of multiple
ERBB family receptors mediates glioblastoma cancer stem-like cell
resistance to EGFR-targeted inhibition. Neoplasia. 14:420–428.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Korkaya H, Paulson A, Iovino F and Wicha
MS: HER2 regulates the mammary stem/progenitor cell population
driving tumorigenesis and invasion. Oncogene. 27:6120–6130. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sette G, Salvati V, Mottolese M, Visca P,
Gallo E, Fecchi K, Pilozzi E, Duranti E, Policicchio E, Tartaglia
M, et al: Tyr1068-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) predicts cancer stem cell targeting by erlotinib in
preclinical models of wild-type EGFR lung cancer. Cell Death Dis.
6:e18502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schulze WX, Deng L and Mann M:
Phosphotyrosine interactome of the ErbB-receptor kinase family. Mol
Syst Biol. 1:00082005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Serra V, Scaltriti M, Prudkin L, Eichhorn
PJ, Ibrahim YH, Chandarlapaty S, Markman B, Rodriguez O, Guzman M,
Rodriguez S, et al: PI3K inhibition results in enhanced HER
signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast
cancer. Oncogene. 30:2547–2557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hynes NE and Lane HA: ERBB receptors and
cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:341–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hegde GV, de la Cruz CC, Chiu C, Alag N,
Schaefer G, Crocker L, Ross S, Goldenberg D, Merchant M, Tien J, et
al: Blocking NRG1 and other ligand-mediated Her4 signaling enhances
the magnitude and duration of the chemotherapeutic response of
non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Transl Med. 5:171ra182013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Malanchi I, Peinado H, Kassen D, Hussenet
T, Metzger D, Chambon P, Huber M, Hohl D, Cano A, Birchmeier W, et
al: Cutaneous cancer stem cell maintenance is dependent on
beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 452:650–653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Korkaya H, Paulson A, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Ginestier C, Brown M, Dutcher J, Clouthier SG and Wicha MS:
Regulation of mammary stem/progenitor cells by
PTEN/Akt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS Biol. 7:e10001212009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anido J, Sáez-Borderías A, Gonzàlez-Juncà
A, Rodón L, Folch G, Carmona MA, Prieto-Sánchez RM, Barba I,
Martínez-Sáez E, Prudkin L, et al: TGF-β receptor inhibitors target
the CD44high/Id1high glioma-initiating cell
population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 18:655–668. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Katayama R, Shaw AT, Khan TM,
Mino-Kenudson M, Solomon BJ, Halmos B, Jessop NA, Wain JC, Yeo AT,
Benes C, et al: Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in
ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci Transl Med. 4:120ra172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Isozaki H, Ichihara E, Takigawa N, Ohashi
K, Ochi N, Yasugi M, Ninomiya T, Yamane H, Hotta K, Sakai K, et al:
Non-small cell lung cancer cells acquire resistance to the ALK
inhibitor alectinib by activating alternative receptor tyrosine
kinases. Cancer Res. 76:1506–1516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sasaki T, Koivunen J, Ogino A, Yanagita M,
Nikiforow S, Zheng W, Lathan C, Marcoux JP, Du J, Okuda K, et al: A
novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to
ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 71:6051–6060. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Okabe T, Sakai K,
Tanaka K, Hayashi H, Kaneda H, Takezawa K, Kuwata K, Yamaguchi H,
et al: Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of
acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:6219–6226. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Paik S, Kim C and Wolmark N: HER2 status
and benefit from adjuvant trastuzumab in breast cancer. N Engl J
Med. 358:1409–1411. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Perez EA, Reinholz MM, Hillman DW, Tenner
KS, Schroeder MJ, Davidson NE, Martino S, Sledge GW, Harris LN,
Gralow JR, et al: HER2 and chromosome 17 effect on patient outcome
in the N9831 adjuvant trastuzumab trial. J Clin Oncol.
28:4307–4315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Todaro M, Gaggianesi M, Catalano V,
Benfante A, Iovino F, Biffoni M, Apuzzo T, Sperduti I, Volpe S,
Cocorullo G, et al: CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and
reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis.
Cell Stem Cell. 14:342–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xia P and Xu XY: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical
application. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1602–1609. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu Y, Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liu J, Ma
Y and Zhang J: Antitumor effect of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus in
combination with trastuzumab on human breast cancer stem cells in
vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 33:1349–1362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Holbro T, Beerli RR, Maurer F, Koziczak M,
Barbas CF III and Hynes NE: The ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimer functions
as an oncogenic unit: ErbB2 requires ErbB3 to drive breast tumor
cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8933–8938. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vaught DB, Stanford JC, Young C, Hicks DJ,
Wheeler F, Rinehart C, Sánchez V, Koland J, Muller WJ, Arteaga CL,
et al: HER3 is required for HER2-induced preneoplastic changes to
the breast epithelium and tumor formation. Cancer Res.
72:2672–2682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|