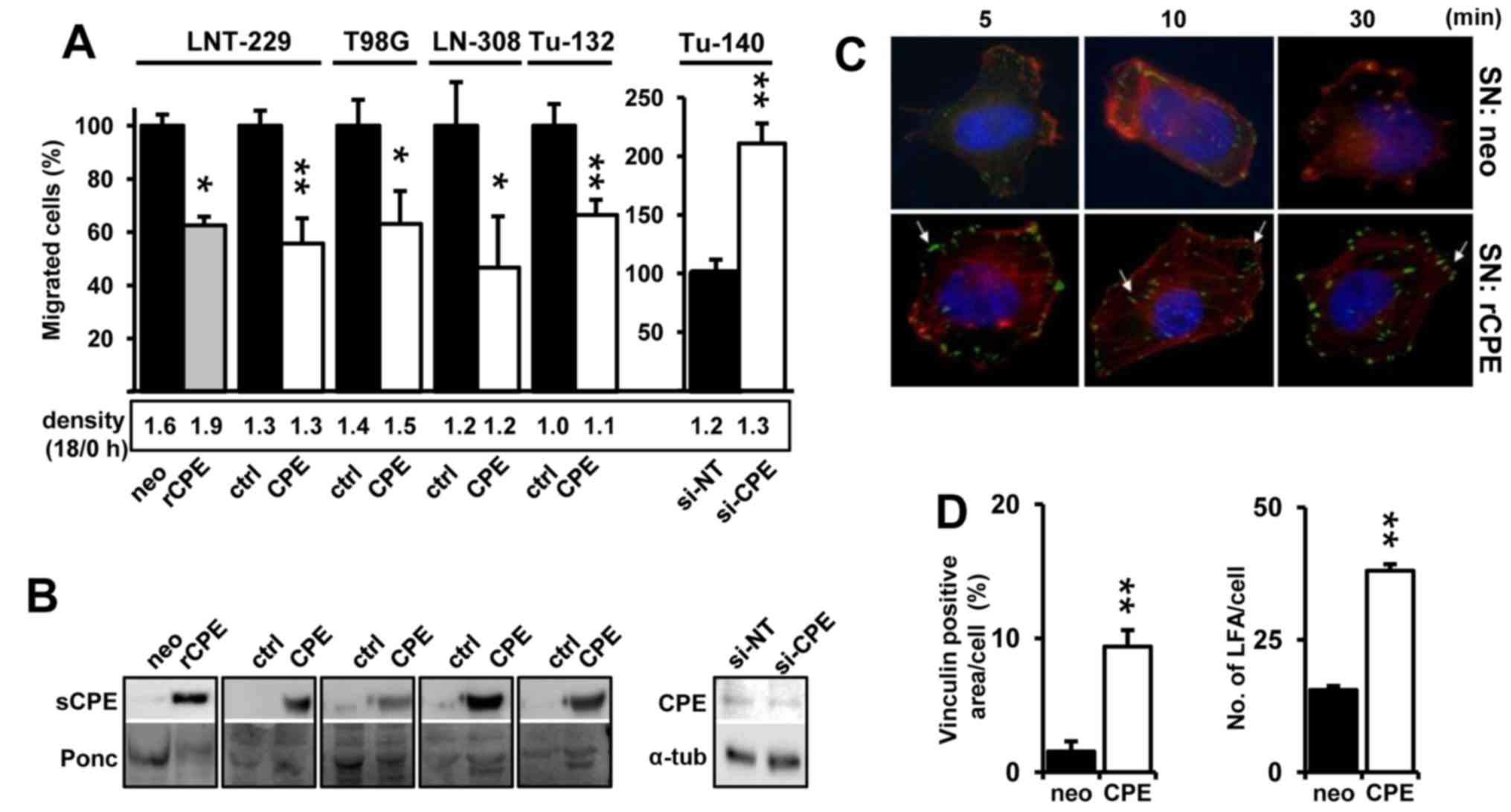
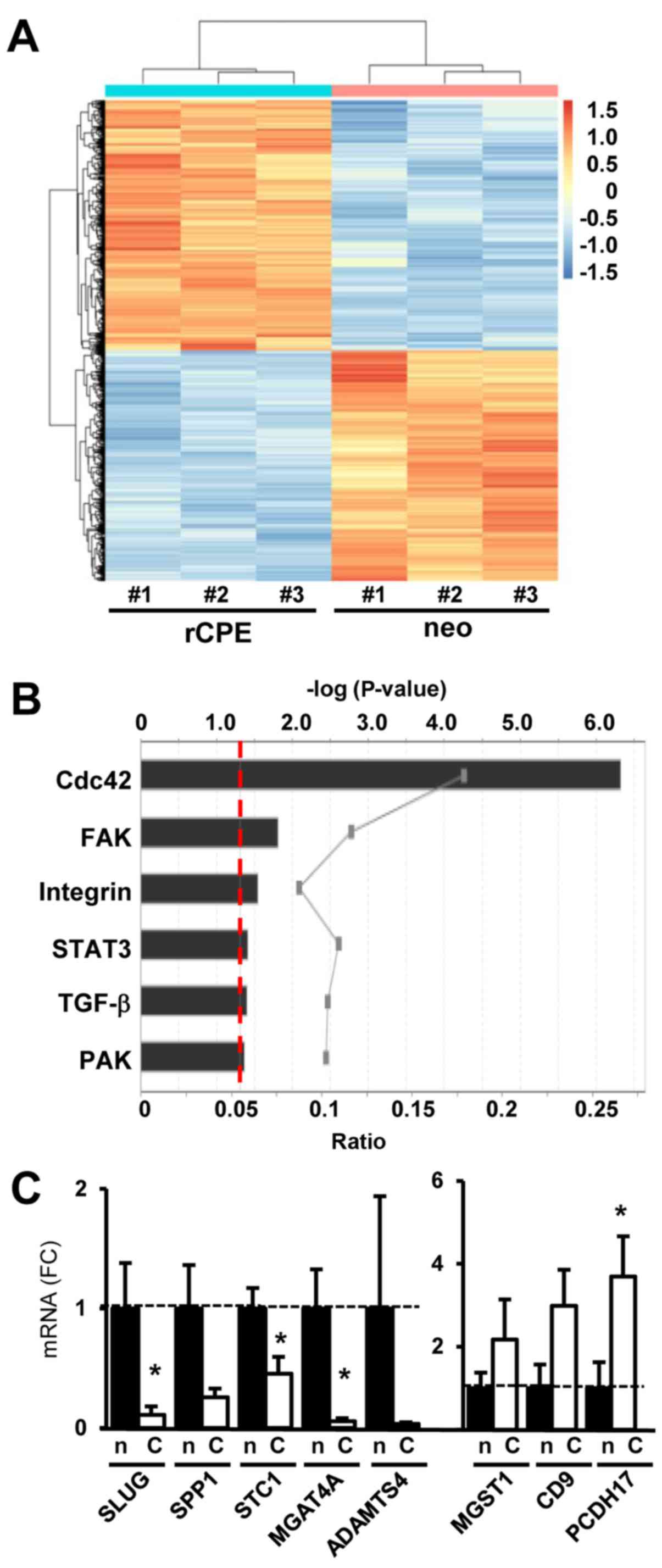
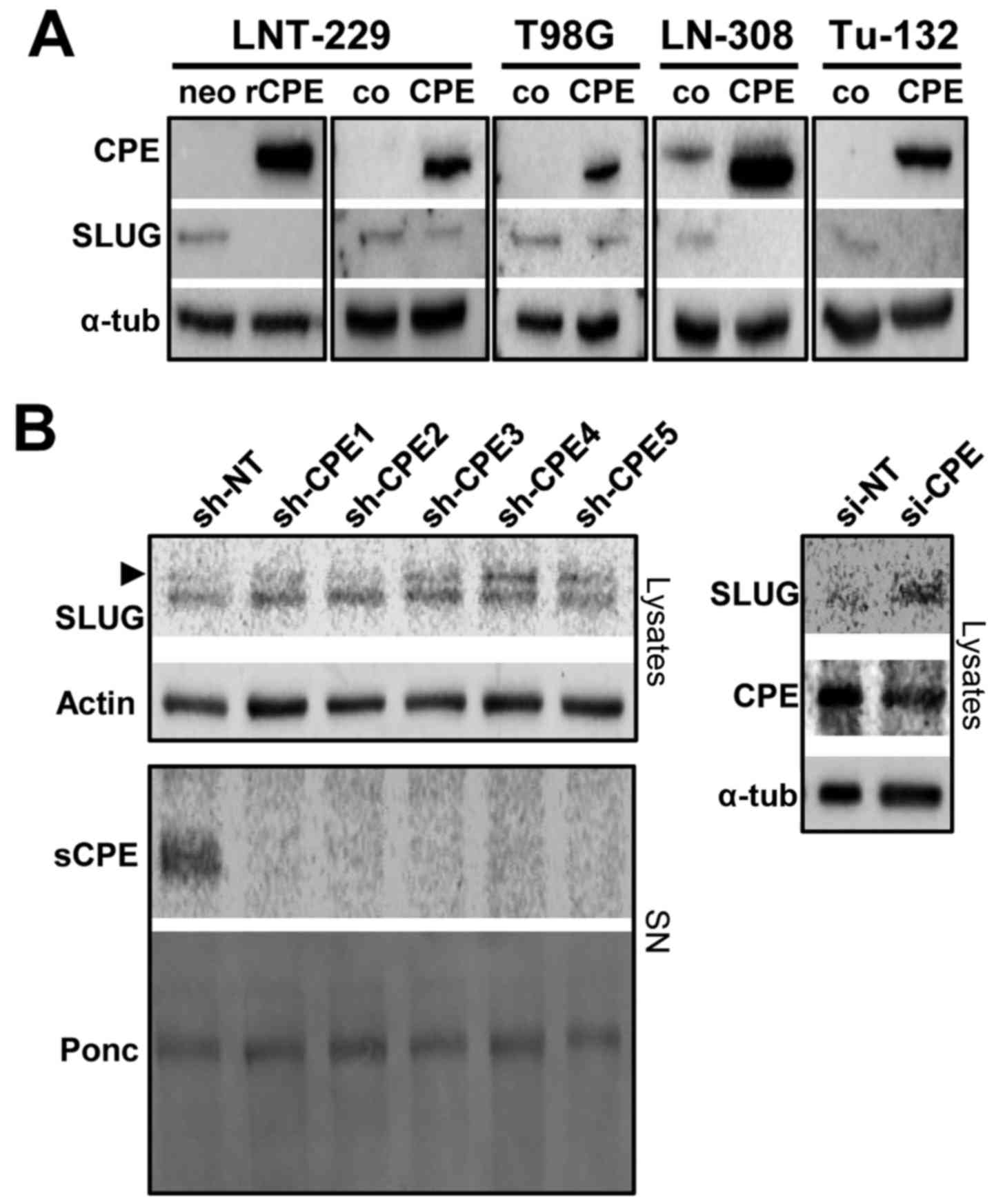
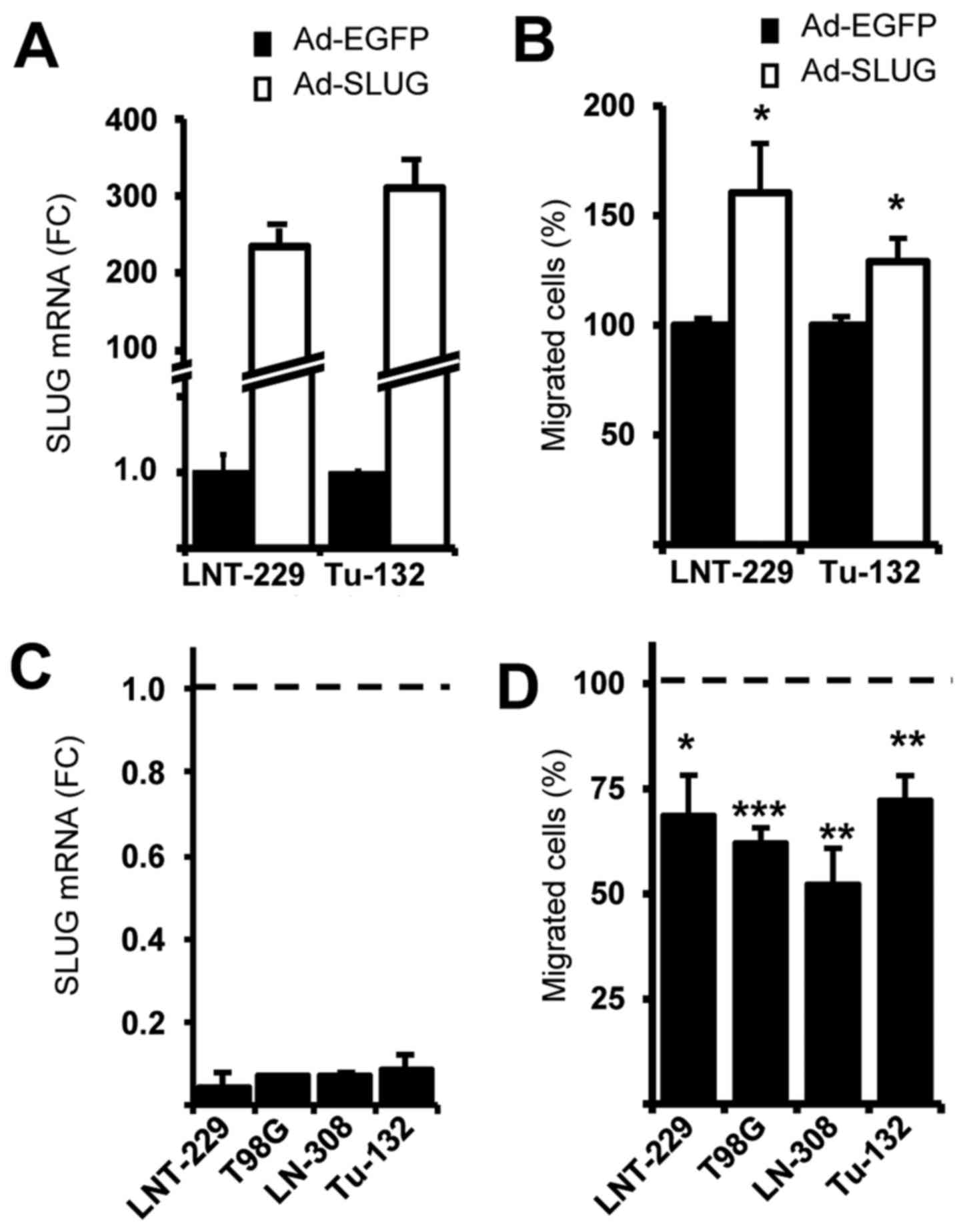
|
1
|
Zhong J, Paul A, Kellie SJ and O'Neill GM:
Mesenchymal migration as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma. J
Oncol. 2010:4301422010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest
WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, et
al: Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis,
delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in
neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 9:157–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
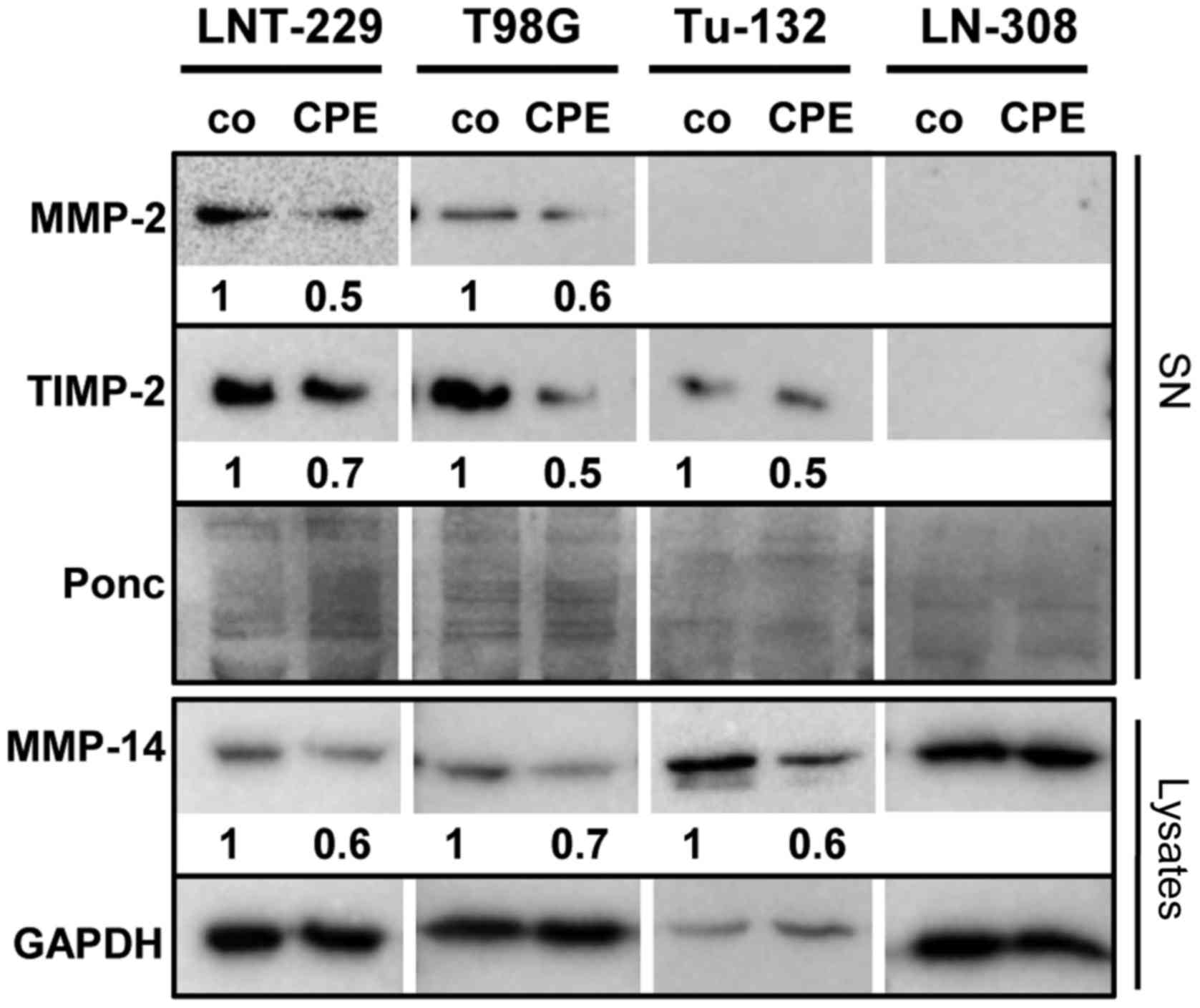
|
3
|
Iser IC, Pereira MB, Lenz G and Wink MR:
The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like process in
glioblastoma: An updated systematic review and in silico
investigation. Med Res Rev. 37:271–313. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Naumann U, Harter PN, Rubel J, Ilina E,
Blank AE, Esteban H and Mittelbronn M: Glioma cell migration and
invasion as potential target for novel treatment strategies. Transl
Neurosci. 4:314–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cawley NX, Wetsel WC, Murthy SR, Park JJ,
Pacak K and Loh YP: New roles of carboxypeptidase E in endocrine
and neural function and cancer. Endocr Rev. 33:216–253. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee TK, Murthy SR, Cawley NX, Dhanvantari
S, Hewitt SM, Lou H, Lau T, Ma S, Huynh T, Wesley RA, et al: An
N-terminal truncated carboxypeptidase E splice isoform induces
tumor growth and is a biomarker for predicting future metastasis in
human cancers. J Clin Invest. 121:880–892. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Höring E, Harter PN, Seznec J,
Schittenhelm J, Bühring HJ, Bhattacharyya S, von Hattingen E,
Zachskorn C, Mittelbronn M and Naumann U: The 'go or grow'
potential of gliomas is linked to the neuropeptide processing
enzyme carboxypeptidase E and mediated by metabolic stress. Acta
Neuropathol. 124:83–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Murthy SR, Thouennon E, Li WS, Cheng Y,
Bhupatkar J, Cawley NX, Lane M, Merchenthaler I and Loh YP:
Carboxypeptidase E protects hippocampal neurons during stress in
male mice by up-regulating prosurvival BCL2 protein expression.
Endocrinology. 154:3284–3293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weiler M, Bähr O, Hohlweg U, Naumann U,
Rieger J, Huang H, Tabatabai G, Krell HW, Ohgaki H, Weller M, et
al: BCL-xL: Time-dependent dissociation between modulation of
apoptosis and invasiveness in human malignant glioma cells. Cell
Death Differ. 13:1156–1169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang HW, Menon LG, Black PM, Carroll RS
and Johnson MD: SNAI2/Slug promotes growth and invasion in human
gliomas. BMC Cancer. 10:3012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Naumann U, Kügler S, Wolburg H, Wick W,
Rascher G, Schulz JB, Conseiller E, Bähr M and Weller M: Chimeric
tumor suppressor 1, a p53-derived chimeric tumor suppressor gene,
kills p53 mutant and p53 wild-type glioma cells in synergy with
irradiation and CD95 ligand. Cancer Res. 61:5833–5842.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler
KW and Vogelstein B: A simplified system for generating recombinant
adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:2509–2514. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Naumann U, Huang H, Wolburg H, Wischhusen
J, Weit S, Ohgaki H and Weller M: PCTAIRE3: A putative mediator of
growth arrest and death induced by CTS-1, a dominant-positive
p53-derived synthetic tumor suppressor, in human malignant glioma
cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:469–478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerfull approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
15
|
Giese A, Loo MA, Tran N, Haskett D, Coons
SW and Berens ME: Dichotomy of astrocytoma migration and
proliferation. Int J Cancer. 67:275–282. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bernardo MM and Fridman R: TIMP-2 (tissue
inhibitor of metal-loproteinase-2) regulates MMP-2 (matrix
metalloproteinase-2) activity in the extracellular environment
after pro-MMP-2 activation by MT1 (membrane type 1)-MMP. Biochem J.
374:739–745. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murthy SR, Dupart E, Al-Sweel N, Chen A,
Cawley NX and Loh YP: Carboxypeptidase E promotes cancer cell
survival, but inhibits migration and invasion. Cancer Lett.
341:204–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verbovšek U, Motaln H, Rotter A, Atai NA,
Gruden K, Van Noorden CJ and Lah TT: Expression analysis of all
protease genes reveals cathepsin K to be overexpressed in
glioblastoma. PLoS One. 9:e1118192014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng Y, Cawley NX and Loh YP:
Carboxypeptidase E/NFα1: A new neurotrophic factor against
oxidative stress-induced apoptotic cell death mediated by ERK and
PI3-K/AKT pathways. PLoS One. 8:e715782013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Skalka N, Caspi M, Caspi E, Loh YP and
Rosin-Arbesfeld R: Carboxypeptidase E: A negative regulator of the
canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Oncogene. 32:2836–2847. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Jeibmann A, Halama K, Witte HT, Kim SN,
Eikmeier K, Koos B, Klämbt C and Paulus W: Involvement of CD9 and
PDGFR in migration is evolutionarily conserved from Drosophila glia
to human glioma. J Neurooncol. 124:373–383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sobczak M, Boczek T, Ferenc B, Taha J,
Kozaczuk A, Wiktorska M, Sacewicz-Hofman I, Niewiarowska J and
Zylinska L: Functional characteristic of PC12 cells with reduced
microsomal glutathione transferase 1. Acta Biochim Pol. 57:589–596.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Haruki S, Imoto I, Kozaki K, Matsui T,
Kawachi H, Komatsu S, Muramatsu T, Shimada Y, Kawano T and Inazawa
J: Frequent silencing of protocadherin 17, a candidate tumour
suppressor for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis.
31:1027–1036. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dang Z, Shangguan J, Zhang C, Hu P, Ren Y,
Lv Z, Xiang H and Wang X: Loss of protocadherin-17 (PCDH-17)
promotes metastasis and invasion through hyperactivation of
EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 37:2527–2535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Held-Feindt J, Paredes EB, Blömer U,
Seidenbecher C, Stark AM, Mehdorn HM and Mentlein R:
Matrix-degrading proteases ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 (disintegrins and
metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs 4 and 5) are
expressed in human glioblastomas. Int J Cancer. 118:55–61. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee JK, Joo KM, Lee J, Yoon Y and Nam DH:
Targeting the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma:
The emerging role of MET signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1933–1944.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu DY, Yeh WL, Huang SM, Tang CH, Lin HY
and Chou SJ: Osteopontin increases heme oxygenase-1 expression and
subsequently induces cell migration and invasion in glioma cells.
Neuro-oncol. 14:1367–1378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Potapenko IO, Haakensen VD, Lüders T,
Helland A, Bukholm I, Sørlie T, Kristensen VN, Lingjaerde OC and
Børresen-Dale AL: Glycan gene expression signatures in normal and
malignant breast tissue; possible role in diagnosis and
progression. Mol Oncol. 4:98–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Niimi K, Yamamoto E, Fujiwara S, Shinjo K,
Kotani T, Umezu T, Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Ino K and Kikkawa F: High
expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase IVa promotes invasion
of choriocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 107:1969–1977. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fan J, Wang S, Yu S, He J, Zheng W and
Zhang J: N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase IVa regulates metastatic
potential of mouse hepatocarcinoma cells through glycosylation of
CD147. Glycoconj J. 29:323–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ide Y, Miyoshi E, Nakagawa T, Gu J,
Tanemura M, Nishida T, Ito T, Yamamoto H, Kozutsumi Y and Taniguchi
N: Aberrant expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IVa and
IVb (GnT-IVa and b) in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 341:478–482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tania M, Khan MA and Fu J: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and
metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:7335–7342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kahlert UD, Nikkhah G and Maciaczyk J:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular
event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 331:131–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chesnelong C and Luchman AH: STAT3 is a
key regulator of an 'EMT-like' process mediated by Slug in GBM.
Cancer Res. 76:25242016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Iwadate Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in glioblastoma progression. Oncol Lett. 11:1615–1620.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Geismann C, Arlt A, Bauer I, Pfeifer M,
Schirmer U, Altevogt P, Müerköster SS and Schäfer H: Binding of the
transcription factor Slug to the L1CAM promoter is essential for
transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β)-induced L1CAM expression in
human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
38:257–266. 2011.
|
|
38
|
Yang M, Li Y, Chilukuri K, Brady OA,
Boulos MI, Kappes JC and Galileo DS: L1 stimulation of human glioma
cell motility correlates with FAK activation. J Neurooncol.
105:27–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nagaishi M, Paulus W, Brokinkel B, Vital
A, Tanaka Y, Nakazato Y, Giangaspero F and Ohgaki H:
Transcriptional factors for epithelial-mesenchymal transition are
associated with mesenchymal differentiation in gliosarcoma. Brain
Pathol. 22:670–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goldberg L and Kloog Y: A Ras inhibitor
tilts the balance between Rac and Rho and blocks
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent glioblastoma cell
migration. Cancer Res. 66:11709–11717. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stepanenko AA, Andreieva SV, Korets KV,
Mykytenko DO, Baklaushev VP, Chekhonin VP and Dmitrenko VV: mTOR
inhibitor temsirolimus and MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 promote
chromosomal instability and cell type-dependent phenotype changes
of glioblastoma cells. Gene. 579:58–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Skalka N, Caspi M, Lahav-Ariel L, Loh YP,
Hirschberg K, Rosin-Arbesfeld R and Carboxypeptidase E:
Carboxypeptidase E (CPE) inhibits the secretion and activity of
Wnt3a. Oncogene. 35:6416–6428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arnaoutova I, Jackson CL, Al-Awar OS,
Donaldson JG and Loh YP: Recycling of Raft-associated prohormone
sorting receptor carboxypeptidase E requires interaction with ARF6.
Mol Biol Cell. 14:4448–4457. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sabe H: Requirement for Arf6 in cell
adhesion, migration, and cancer cell invasion. J Biochem.
134:485–489. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|