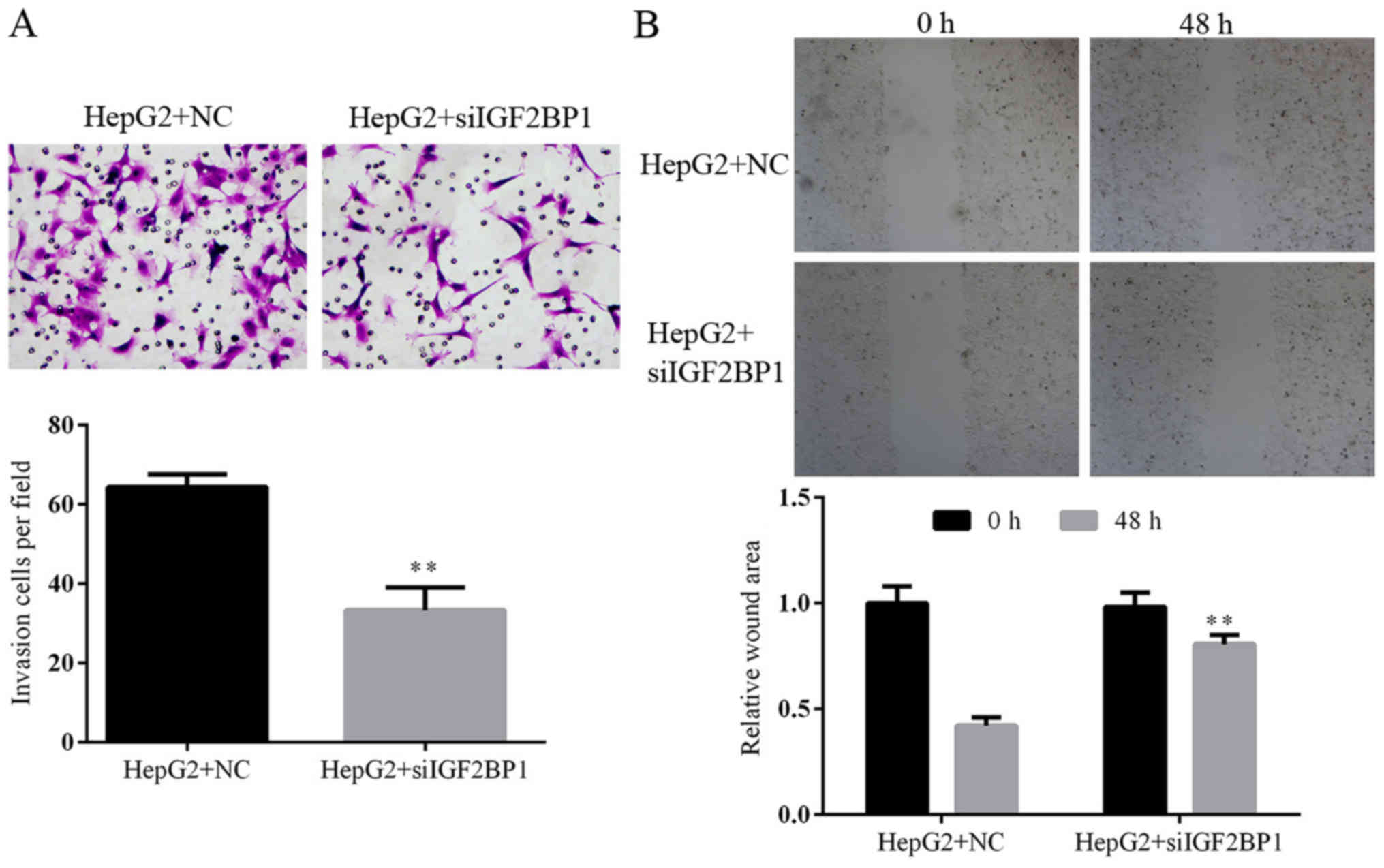
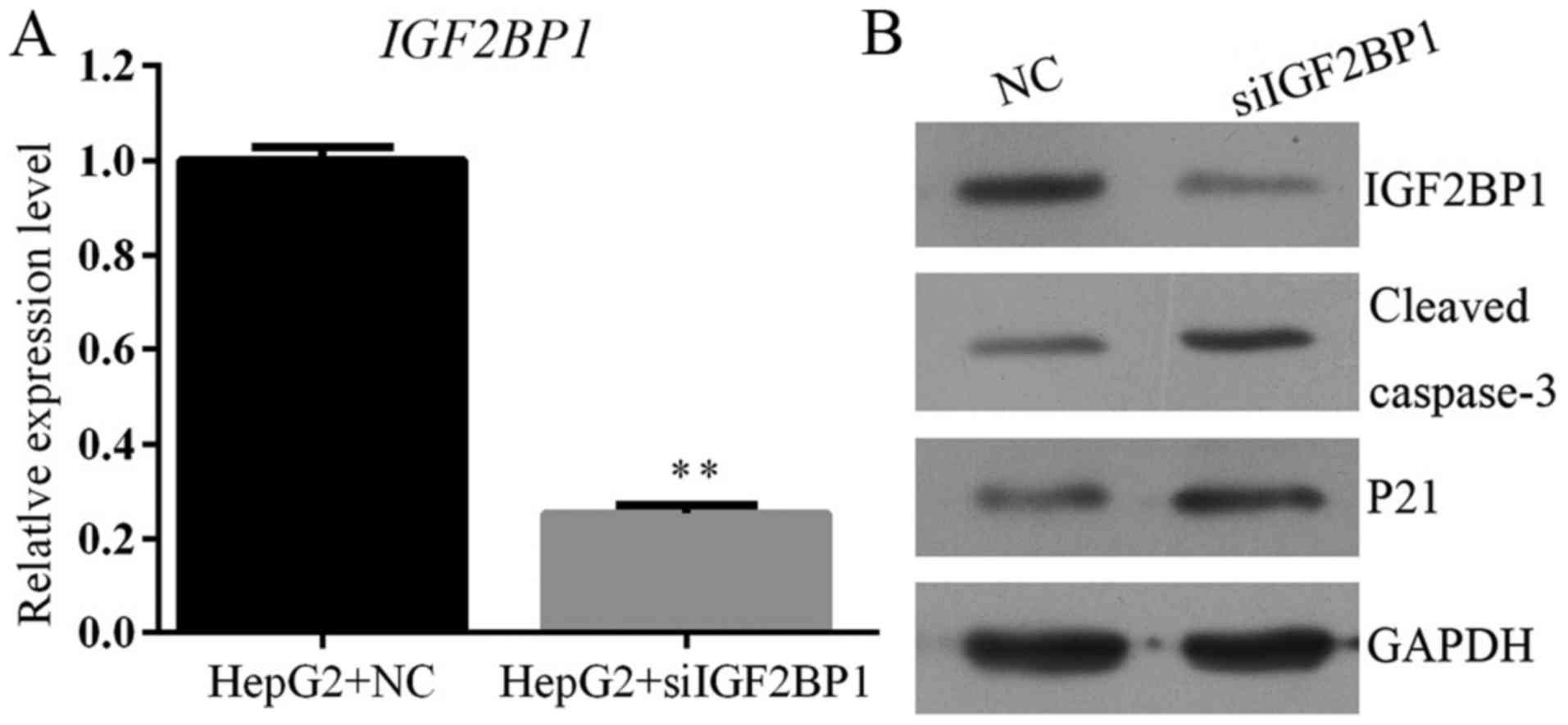
|
1
|
Shi L, Peng F, Tao Y, Fan X and Li N:
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Virus
Res. 223:131–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al Salloom AA: An update of biochemical
markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Health Sci (Qassim).
10:121–136. 2016.
|
|
3
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Jia HL, He P,
Zanetti KA, Kammula US, Chen Y, Qin LX, Tang ZY, et al: Prediction
of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of the liver
microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 10:99–111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tejeda-Maldonado J, García-Juárez I,
Aguirre-Valadez J, González-Aguirre A, Vilatobá-Chapa M,
Armengol-Alonso A, Escobar-Penagos F, Torre A, Sánchez-Ávila JF and
Carrillo-Pérez DL: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma: An update. World J Hepatol. 7:362–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non- coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M and
Mattick JS: Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J Pathol.
220:126–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang F, Bi J, Xue X, Zheng L, Zhi K, Hua J
and Fang G: Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to
proliferation of gastric cancer cells. FEBS J. 279:3159–3165. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang JL, Zheng L, Hu YW and Wang Q:
Characteristics of long non-coding RNA and its relation to
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:507–514. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang X, Xie X, Xiao YF, Xie R, Hu CJ, Tang
B, Li BS and Yang SM: The emergence of long non-coding RNAs in the
tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
360:119–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Y, Meng XM, Huang C, Wu BM, Zhang L, Lv
XW and Li J: Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into hepatocelluar
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 344:20–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Zhang P, Wan X, Su X, Kong Z,
Zhai Q, Xiang X, Li L and Li Y: Downregulation of long non-coding
RNA HCG11 predicts a poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 83:936–941. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Li J, Koirala P, Ding X, Chen B,
Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang C, Zhang X and Mo YY: Long non-coding RNAs as
prognostic markers in human breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:20584–20596. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu Y, Chen T, Li G, Yu X, Lu Y, Wang H and
Teng L: LncRNAs: Emerging biomarkers in gastric cancer. Future
Oncol. 11:2427–2441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu Z, Yang L, Cai L, Zhang M, Cheng X,
Yang X and Xu J: Detection of epithelial to mesenchymal transition
in airways of a bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis model derived
from an α-smooth muscle actin-Cre transgenic mouse. Respir Res.
8:12007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gutschner T, Hämmerle M, Pazaitis N, Bley
N, Fiskin E, Uckelmann H, Heim A, Groβ M, Hofmann N, Geffers R, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1)
is an important protumorigenic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 59:1900–1911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Cheng J, Zeng Z, Wang Y, Li X,
Xie Q, Jia J, Yan Y, Guo Z, Gao J, et al: Comprehensive profiling
of novel microRNA-9 targets and a tumor suppressor role of
microRNA-9 via targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:42040–42052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Zhang CZ, Lu SX, Chen GG, Li LZ,
Liu LL, Yi C, Fu J, Hu W, Wen JM, et al: miR-625 suppresses tumour
migration and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 34:965–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Yamamoto N, Shibutani
T and Akahane K: Mitochondrial regulation of cell death:
Mitochondria are essential for procaspase 3-p21 complex formation
to resist Fas-mediated cell death. Mol Cell Biol. 19:3842–3847.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shibata C, Otsuka M, Kishikawa T, Ohno M,
Yoshikawa T, Takata A and Koike K: Diagnostic and therapeutic
application of noncoding RNAs for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 7:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deng L, Yang SB, Xu FF and Zhang JH: Long
noncoding RNA CCAT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression
by functioning as let-7 sponge. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:182015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Quagliata L, Matter MS, Piscuoglio S,
Arabi L, Ruiz C, Procino A, Kovac M, Moretti F, Makowska Z,
Boldanova T, et al: Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP/HOXA13 expression is
associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatology. 59:911–923. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Bell JL, Wächter K, Mühleck B, Pazaitis N,
Köhn M, Lederer M and Hüttelmaier S: Insulin-like growth factor 2
mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): Post-transcriptional drivers of
cancer progression? Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:2657–2675. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Farina KL, Hüttelmaier S, Musunuru K,
Darnell R and Singer RH: Two ZBP1 KH domains facilitate β-actin
mRNA localization, granule formation, and cytoskeletal attachment.
J Cell Biol. 160:77–87. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hüttelmaier S, Zenklusen D, Lederer M,
Dictenberg J, Lorenz M, Meng X, Bassell GJ, Condeelis J and Singer
RH: Spatial regulation of beta-actin translation by Src-dependent
phosphorylation of ZBP1. Nature. 438:512–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bernstein PL, Herrick DJ, Prokipcak RD and
Ross J: Control of c-myc mRNA half-life in vitro by a protein
capable of binding to a coding region stability determinant. Genes
Dev. 6:642–654. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ioannidis P, Mahaira LG, Perez SA,
Gritzapis AD, Sotiropoulou PA, Kavalakis GJ, Antsaklis AI,
Baxevanis CN and Papamichail M: CRD-BP/IMP1 expression
characterizes cord blood CD34+ stem cells and affects
c-myc and IGF-II expression in MCF-7 cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
280:20086–20093. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|