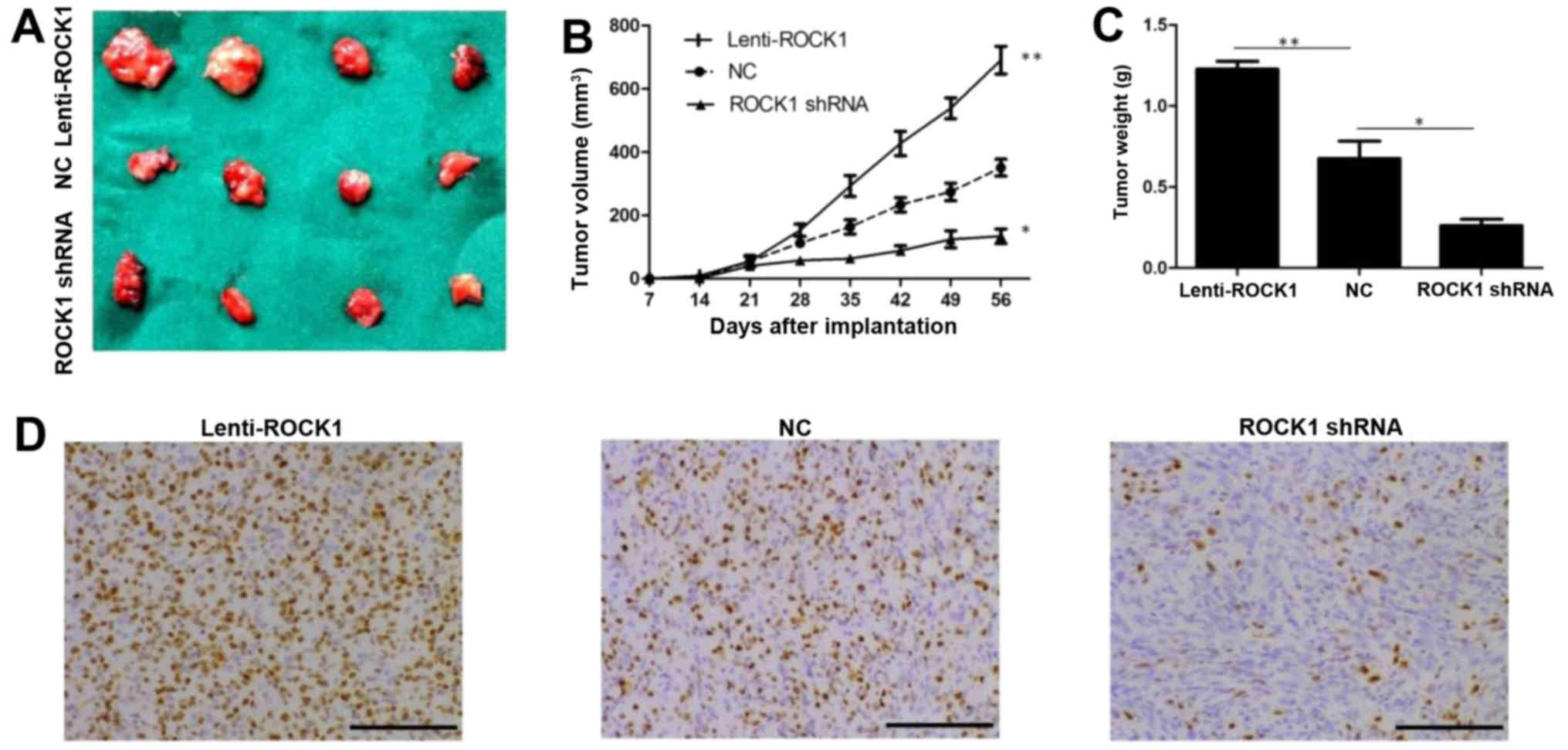
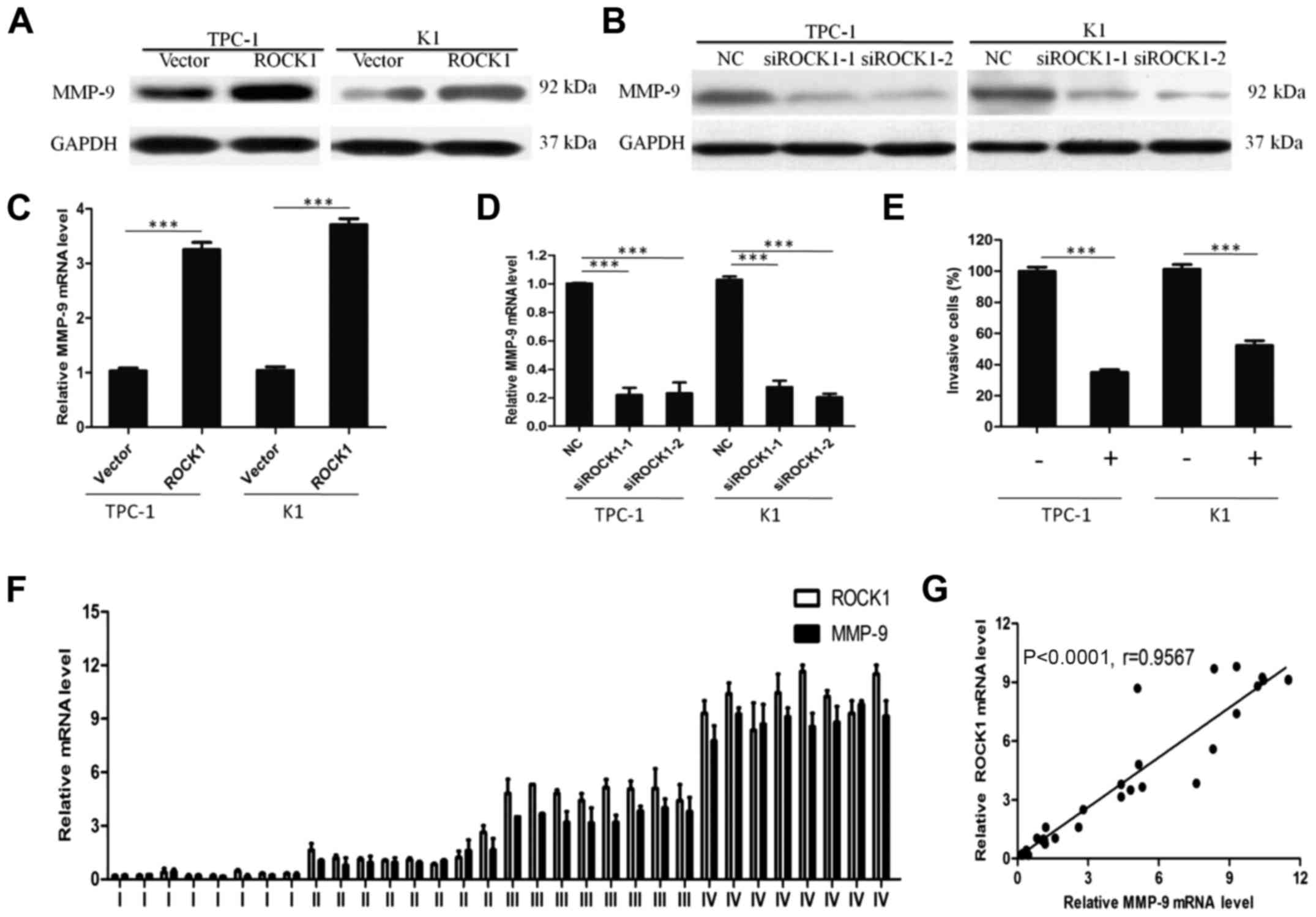
|
1
|
Zeiger MA and Schneider EB: BRAF V600E
mutation independently predicts central compartment lymph node
metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 20:3–4. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zivaljevic V, Slijepcevic N, Sipetic S,
Paunovic I, Diklic A, Zoric G and Kalezic N: Risk factors for
well-differentiated thyroid cancer in men. Tumori. 99:458–462.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sipos JA and Mazzaferri EL: Thyroid cancer
epidemiology and prognostic variables. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol).
22:395–404. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Huang X, Xu J, Su Q, Zhao J and Ma
J: miR-449 over-expression inhibits papillary thyroid carcinoma
cell growth by targeting RET kinase-β-catenin signaling pathway.
Int J Oncol. 49:1629–1637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng S, Serra S, Mercado M, Ezzat S and
Asa SL: A high-throughput proteomic approach provides distinct
signatures for thyroid cancer behavior. Clin Cancer Res.
17:2385–2394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Agrawal N, Akbani R, Aksoy BA, Ally A,
Arachchi H, Asa SL, Auman JT, Balasundaram M, Balu S, Baylin SB, et
al Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network: Integrated genomic
characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell. 159:676–690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Beninato T, Scognamiglio T, Kleiman DA,
Uccelli A, Vaca D, Fahey TJ III and Zarnegar R: Ten percent tall
cells confer the aggressive features of the tall cell variant of
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Surgery. 154:1331–1336; discussion
1336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee CW, Roh JL, Gong G, Cho KJ, Choi SH,
Nam SY and Kim SY: Risk factors for recurrence of papillary thyroid
carcinoma with clinically node-positive lateral neck. Ann Surg
Oncol. 22:117–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhu J, Wang X, Zhang X, Li P and Hou H:
Clinicopathological features of recurrent papillary thyroid cancer.
Diagn Pathol. 10:962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saito K, Ozawa Y, Hibino K and Ohta Y:
FilGAP, a Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase-regulated
GTPase-activating protein for Rac, controls tumor cell migration.
Mol Biol Cell. 23:4739–4750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banyard J, Anand-Apte B, Symons M and
Zetter BR: Motility and invasion are differentially modulated by
Rho family GTPases. Oncogene. 19:580–591. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morgan-Fisher M, Wewer UM and Yoneda A:
Regulation of ROCK activity in cancer. J Histochem Cytochem.
61:185–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Vigil D, Kim TY, Plachco A, Garton AJ,
Castaldo L, Pachter JA, Dong H, Chen X, Tokar B, Campbell SL, et
al: ROCK1 and ROCK2 are required for non-small cell lung cancer
anchorage-independent growth and invasion. Cancer Res.
72:5338–5347. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guan R, Xu X, Chen M, Hu H, Ge H, Wen S,
Zhou S and Pi R: Advances in the studies of roles of Rho/Rho-kinase
in diseases and the development of its inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem.
70:613–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Azab AK, Kleinstern J, Doviner V, Orkin B,
Srebnik M, Nissan A and Rubinstein A: Prevention of tumor
recurrence and distant metastasis formation in a breast cancer
mouse model by biodegradable implant of 131I-norcholesterol. J
Control Release. 123:116–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu FH, Kuo SF, Hsueh C, Chao TC and Lin
JD: Postoperative recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma with
lymph node metastasis. J Surg Oncol. 112:149–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Werb Z: ECM and cell surface proteolysis:
Regulating cellular ecology. Cell. 91:439–442. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bottino J, Gelaleti GB, Maschio LB,
Jardim-Perassi BV and de Campos Zuccari DA: Immunoexpression of
ROCK-1 and MMP-9 as prognostic markers in breast cancer. Acta
Histochem. 116:1367–1373. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang JR, Gan WJ, Li XM, Zhao YY, Li Y, Lu
XX, Li JM and Wu H: Orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 promotes
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating MMP-9 and
E-cadherin. Carcinogenesis. 35:2474–2484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao J, Liu X, Yang F, Liu T, Yan Q and
Yang X: By inhibiting Ras/Raf/ERK and MMP-9, knockdown of EpCAM
inhibits breast cancer cell growth and metastasis. Oncotarget.
6:27187–27198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM,
Schlumberger M, et al: 2015 American Thyroid Association Management
Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and
Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association
Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid
Cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Li J, Guan HY, Gong LY, Song LB, Zhang N,
Wu J, Yuan J, Zheng YJ, Huang ZS and Li M: Clinical significance of
sphingo-sine kinase-1 expression in human astrocytomas progression
and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6996–7003. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gong C, Qu S, Liu B, Pan S, Jiao Y, Nie Y,
Su F, Liu Q and Song E: MiR-106b expression determines the
proliferation paradox of TGF-β in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
34:84–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J,
Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, et al: CCL18 from tumor-associated
macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer
Cell. 19:541–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akaishi J, Sugino K, Kameyama K, Masaki C,
Matsuzu K, Suzuki A, Uruno T, Ohkuwa K, Shibuya H, Kitagawa W, et
al: Clinicopathologic features and outcomes in patients with
diffuse sclerosing variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J
Surg. 39:1728–1735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lochhead PA, Wickman G, Mezna M and Olson
MF: Activating ROCK1 somatic mutations in human cancer. Oncogene.
29:2591–2598. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pinner S and Sahai E: PDK1 regulates
cancer cell motility by antagonising inhibition of ROCK1 by RhoE.
Nat Cell Biol. 10:127–137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Yang S, Yang
C, Harmon D, Mankin H and Duan Z: ROCK1 as a potential therapeutic
target in osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res. 29:1259–1266. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Song Y, Wang Y, Luo J and Yu W:
MicroRNA-148a suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by
targeting ROCK1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 380:277–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mertsch S, Oellers P, Wendling M, Stracke
W and Thanos S: Dissecting the inter-substrate navigation of
migrating glioblastoma cells with the stripe assay reveals a
causative role of ROCK. Mol Neurobiol. 48:169–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Zhou X and Wei M: MicroRNA-144
suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1
and ROCK2. Oncotarget. 6:10297–10308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai H, Lin L, Cai H, Tang M and Wang Z:
Combined microRNA-340 and ROCK1 mRNA profiling predicts tumor
progression and prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma. Int J Mol Sci.
15:560–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu B, Huang Y, Niu X, Tao T, Jiang L, Tong
N, Chen S, Liu N, Zhu W and Chen M: Hsa-miR-146a-5p modulates
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells apoptosis by targeting
ROCK1. Prostate. 75:1896–1903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kroiss A, Vincent S, Decaussin-Petrucci M,
Meugnier E, Viallet J, Ruffion A, Chalmel F, Samarut J and Allioli
N: Androgen-regulated microRNA-135a decreases prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion through downregulating ROCK1 and ROCK2.
Oncogene. 34:2846–2855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Raviraj V, Fok S, Zhao J, Chien HY, Lyons
JG, Thompson EW and Soon L: Regulation of ROCK1 via Notch1 during
breast cancer cell migration into dense matrices. BMC Cell Biol.
13:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gilkes DM, Xiang L, Lee SJ, Chaturvedi P,
Hubbi ME, Wirtz D and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors mediate
coordinated RhoA-ROCK1 expression and signaling in breast cancer
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E384–E393. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Dai W, Teodoridis JM, Zeller C, Graham J,
Hersey J, Flanagan JM, Stronach E, Millan DW, Siddiqui N, Paul J,
et al: Systematic CpG islands methylation profiling of genes in the
wnt pathway in epithelial ovarian cancer identifies biomarkers of
progression-free survival. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4052–4062. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu H, Li W, Chen C, Pei Y and Long X:
MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via
downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 36:6313–6319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Shahryari V,
Arora S, Zaman MS, Chang I, Yamamura S, Chiyomaru T, Fukuhara S, et
al: MicroRNA-1280 inhibits invasion and metastasis by targeting
ROCK1 in bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e467432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kummer NT, Nowicki TS, Azzi JP, Reyes I,
Iacob C, Xie S, Swati I, Darzynkiewicz Z, Gotlinger KH, Suslina N,
et al: Arachidonate 5 lipoxygenase expression in papillary thyroid
carcinoma promotes invasion via MMP-9 induction. J Cell Biochem.
113:1998–2008. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brown-Clay JD, Shenoy DN, Timofeeva O,
Kallakury BV, Nandi AK and Banerjee PP: PBK/TOPK enhances
aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer via
β-catenin-TCF/LEF-mediated matrix metalloproteinases production and
invasion. Oncotarget. 6:15594–15609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wille C, Köhler C, Armacki M, Jamali A,
Gössele U, Pfizenmaier K, Seufferlein T and Eiseler T: Protein
kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating
matrix metalloproteinases. Mol Biol Cell. 25:324–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Ai F, Zhang X, Li X, Qin Z, Ye Q, Tian L,
Tang A, Li N, Li G, Ma J, et al: Up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinases in a mouse model of chemically induced
colitis-associated cancer: The role of microRNAs. Oncotarget.
6:5412–5425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Decock J, Thirkettle S, Wagstaff L and
Edwards DR: Matrix metalloproteinases: Protective roles in cancer.
J Cell Mol Med. 15:1254–1265. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hadler-Olsen E, Winberg JO and
Uhlin-Hansen L: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: Their value as
diagnostic and prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Tumour
Biol. 34:2041–2051. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|