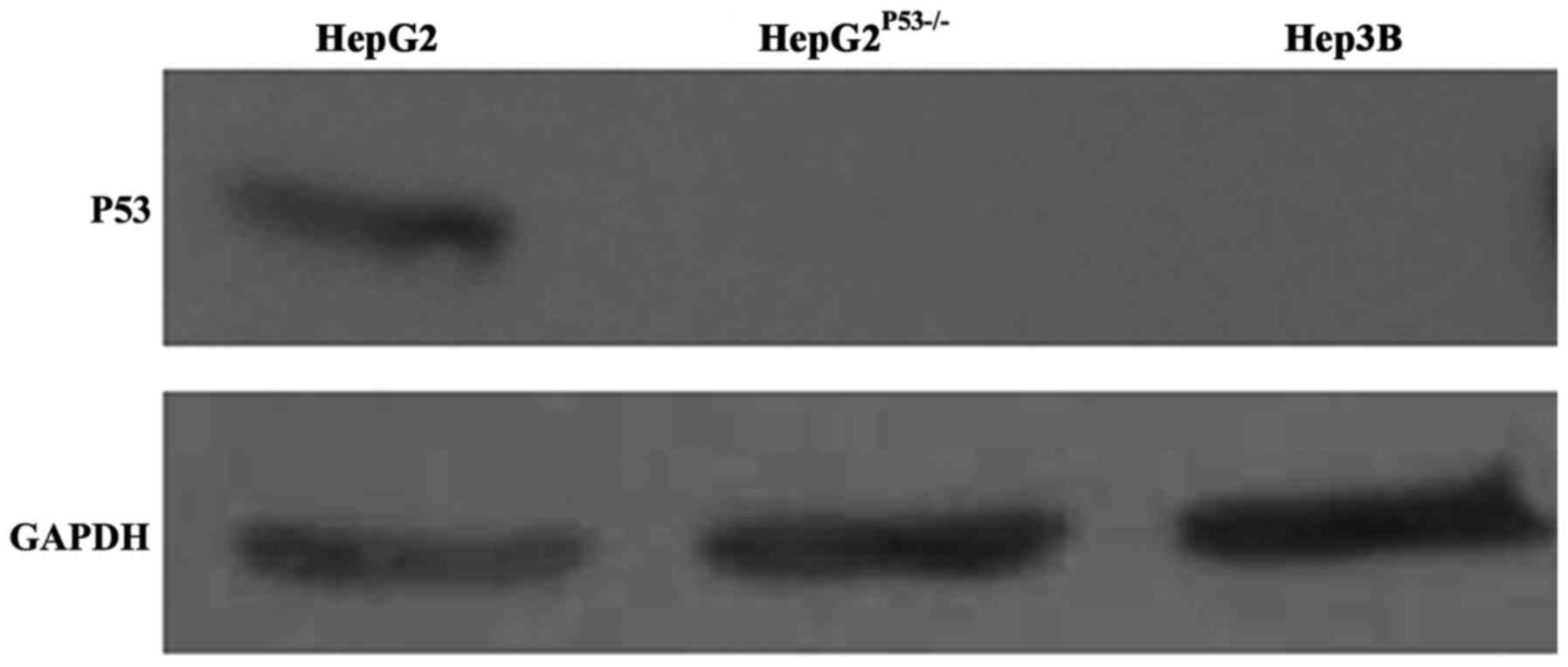
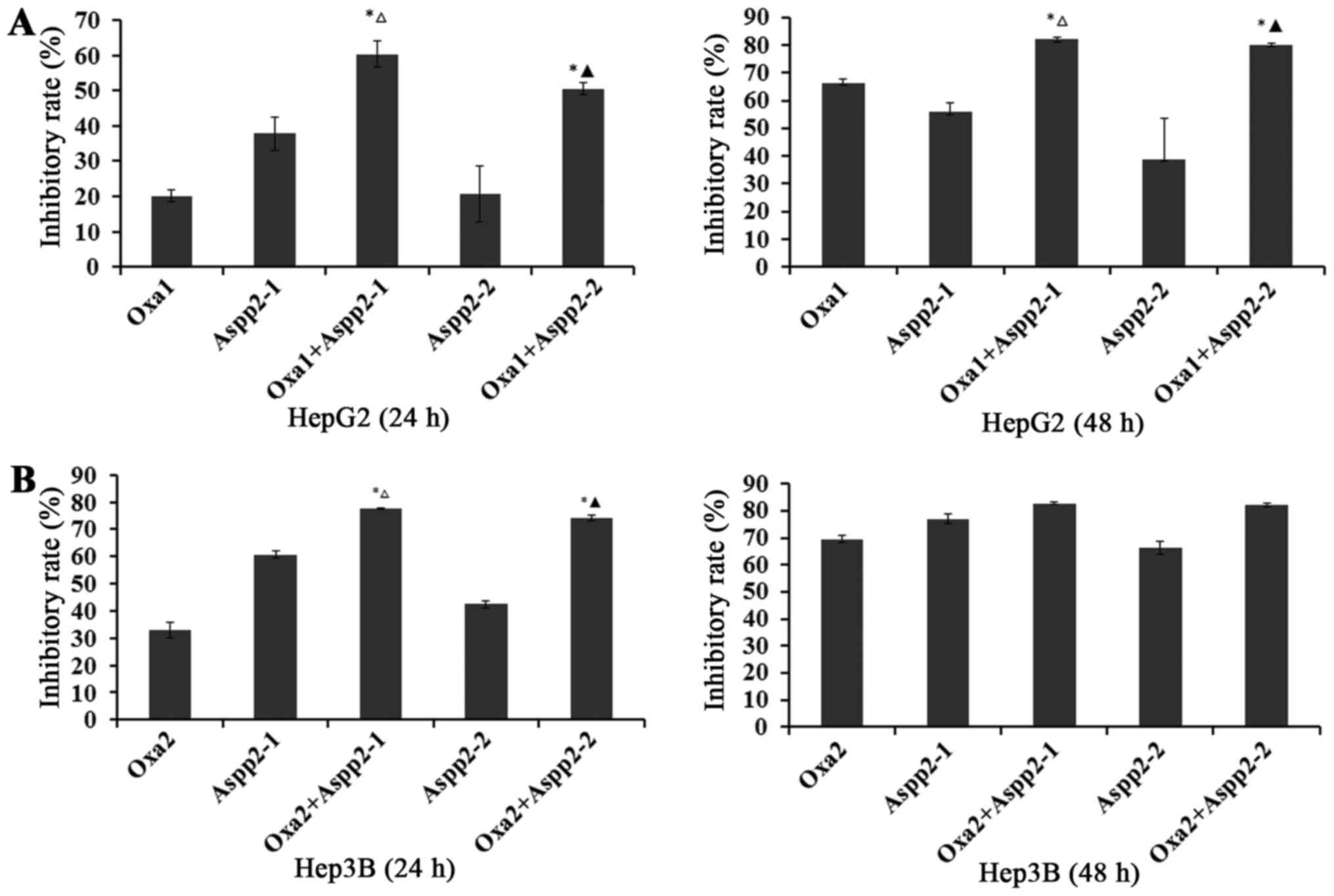
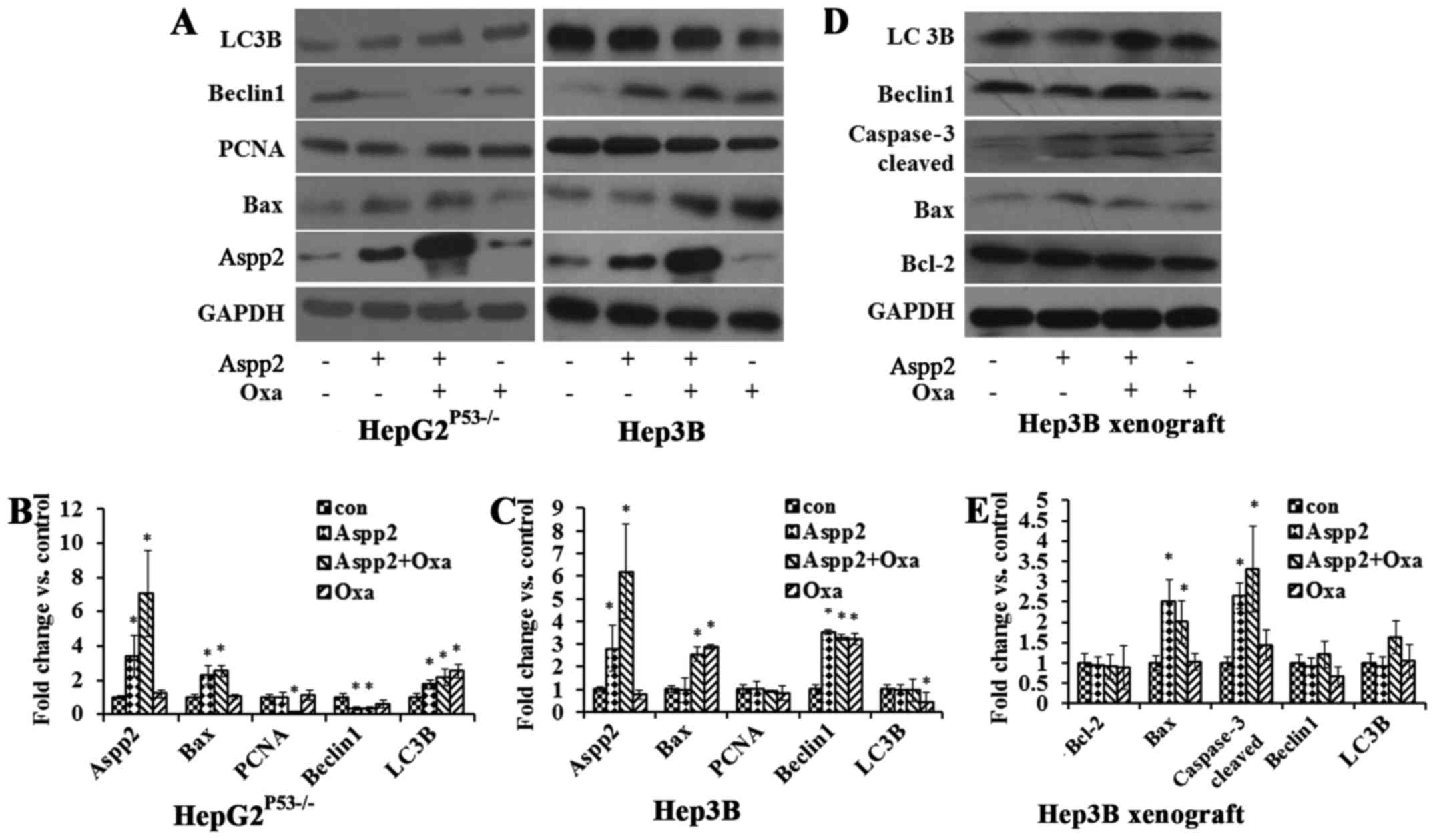
|
1
|
Lamarca A, Mendiola M and Barriuso J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Exploring the impact of ethnicity on
molecular biology. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 105:65–72. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Connell LC, Harding JJ and Abou-Alfa GK:
Advanced hepatocellular cancer: The currentstate of future
research. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 17:432016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Grandhi MS, Kim AK, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM,
Kamel IR, Ghasebeh MA and Pawlik TM: Hepatocellular carcinoma: From
diagnosis to treatment. Surg Oncol. 25:74–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao C, Fan L, Qi F, Ou S, Yu L, Yi X, Ni
B, Zheng Z, Lu J, Zhang C, et al: Raltitrexed plus
oxaliplatin-based transarterial chemoembolization in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs.
27:689–694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vijayvergia N, Li T, Wong YN, Hall MJ,
Cohen SJ and Dotan E: Chemotherapy use and adoption of new agents
is affected by age and comorbidities in patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. Cancer. 122:3191–3198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ihara K, Yamaguchi S, Ueno N, Tani Y,
Shida Y, Ogata H, Domeki Y, Okamoto K, Nakajima M, Sasaki K, et al:
Expression of DNA double-strand break repair proteins predicts the
response and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients undergoing
oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Oncol Rep. 35:1349–1355. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhao C, Fan L, Qi F, Ou S, Yu L, Yi X, Ni
B, Zheng Z, Lu J, Zhang C, et al: Raltitrexed plus
oxaliplatin-based transarterial chemoembolization in patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs.
27:689–694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao S, Zhang PJ, Guo JH, Chen H, Xu HF,
Liu P, Yang RJ and Zhu X: Chemoembolization alone vs combined
chemoembolization and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in
inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:10443–10452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu L, Zheng YH, Han L and Qin SK:
Efficacy and safety of the oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in the
treatment of advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A
meta-analysis of prospective studies. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e49932016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xie YS, Zhang YH, Liu SP, Liu SQ, Peng CW,
Wu L, Luo HS and Li Y: Synergistic gastric cancer inhibition by
chemogenetherapy with recombinant human adenovirus p53 and
epirubicin: An in vitro and in vivo study. Oncol Rep. 24:1613–1620.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen S, Chen J, Xi W, Xu W and Yin G:
Clinical therapeutic effect and biological monitoring of p53 gene
in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 37:24–29.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sangro B, Mazzolini G, Ruiz M, Ruiz J,
Quiroga J, Herrero I, Qian C, Benito A, Larrache J, Olagüe C, et
al: A phase I clinical trial of thymidine kinase-based gene therapy
in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:837–843.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu ZJ, Lu X, Zhang Y, Zhong S, Gu SZ,
Zhang XB, Yang X and Xin HM: Downregulated mRNA expression of ASPP
and the hypermethylation of the 5′-untranslated region in cancer
cell lines retaining wild-type p53. FEBS Lett. 579:1587–1590. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mori T, Okamoto H, Takahashi N, Ueda R and
Okamoto T: Aberrant overexpression of 53BP2 mRNA in lung cancer
cell lines. FEBS Lett. 465:124–128. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu WK, Jiang XY, Ren JK and Zhang ZX:
Expression pattern of the ASPP family members in endometrial
endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Onkologie. 33:500–503. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mak VC, Lee L, Siu MK, Wong OG, Lu X, Ngan
HY, Wong ES and Cheung AN: Downregulation of ASPP2 in
choriocarcinoma contributes to increased migratory potential
through Src signaling pathway activation. Carcinogenesis.
34:2170–2177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schittenhelm MM, Illing B, Ahmut F, Rasp
KH, Blumenstock G, Döhner K, Lopez CD and Kampa-Schittenhelm KM:
Attenuated expression of apoptosis stimulating protein of p53-2
(ASPP2) in human acute leukemia is associated with therapy failure.
PLoS One. 8:e801932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Li B, Li CJ and Li LJ: Key points of
basic theories and clinical practice in rAd-p53 (Gendicine™) gene
therapy for solid malignant tumors. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
15:437–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen GX, Zhang S, He XH, Liu SY, Ma C and
Zou XP: Clinical utility of recombinant adenoviral human p53 gene
therapy: Current perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1901–1909.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi Y, Han Y, Xie F, Wang A, Feng X, Li N,
Guo H and Chen D: ASPP2 enhances oxaliplatin (L-OHP)-induced
colorectal cancer cell apoptosis in a p53-independent manner by
inhibiting cell autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 19:535–543. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Wang S, XU JJ, Liu XN and Chen DX: Quality
control of human ASPP2 recombinant adenovirus, 2016. Zhongguo Yao
Li Xue Tong Bao. 32:885–888. 2016.In Chinese.
|
|
22
|
Amer MH: Gene therapy for cancer: Present
status and future perspective. Mol Cell Ther. 2:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sheridan C: Gene therapy finds its niche.
Nat Biotechnol. 29:121–128. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tazawa H, Kagawa S and Fujiwara T:
Advances in adenovirus-mediated p53 cancer gene therapy. Expert
Opin Biol Ther. 13:1569–1583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiocca EA, Abbed KM, Tatter S, Louis DN,
Hochberg FH, Barker F, Kracher J, Grossman SA, Fisher JD, Carson K,
et al: A phase I open-label, dose-escalation, multi-institutional
trial of injection with an E1B-Attenuated adenovirus, ONYX-015,
into the peritumoral region of recurrent malignant gliomas, in the
adjuvant setting. Mol Ther. 10:958–966. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Block SL, Nolan T, Sattler C, Barr E,
Giacoletti KE, Marchant CD, Castellsagué X, Rusche SA, Lukac S,
Bryan JT, et al Protocol 016 Study Group: Comparison of the
immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a prophylactic quadrivalent
human papillomavirus (types 6, 11, 16, and 18) L1 virus-like
particle vaccine in male and female adolescents and young adult
women. Pediatrics. 118:2135–2145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kantoff PW, Schuetz TJ, Blumenstein BA,
Glode LM, Bilhartz DL, Wyand M, Manson K, Panicali DL, Laus R,
Schlom J, et al: Overall survival analysis of a phase II randomized
controlled trial of a Poxviral-based PSA-targeted immunotherapy in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1099–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van Putten EH, Dirven CM, van den Bent MJ
and Lamfers ML: Sitimagene ceradenovec: A gene-based drug for the
treatment of operable high-grade glioma. Future Oncol. 6:1691–1710.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu J, Li W, Deng M, Liu D, Ma Q and Feng
X: Immunohistochemical determination of p53 protein overexpression
for predicting p53 gene mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016.11:e01596362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu J, Ma Q, Zhang M, Wang X, Zhang D, Li
W, Wang F and Wu E: Alterations of TP53 are associated with a poor
outcome for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 48:2328–2338.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qi LN, Bai T, Chen ZS, Wu FX, Chen YY, De
Xiang B, Peng T, Han ZG and Li LQ: The p53 mutation spectrum in
hepatocellular carcinoma from Guangxi, China: Role of chronic
hepatitis B virus infection and aflatoxin B1 exposure. Liver Int.
35:999–1009. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bravo R, Fey SJ, Bellatin J, Larsen PM,
Arevalo J and Celis JE: Identification of a nuclear and of a
cytoplasmic polypeptide whose relative proportions are sensitive to
changes in the rate of cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res.
136:311–319. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin S, Li Z, Huang J, Miao Z, Zhang J, Lu
C and Xu H and Xu H: Prognostic value and clinicopathological
significance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in
gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:319–327. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma S, Yang J, Li J and Song J: The
clinical utility of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen
expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:7405–7412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Pantanowitz L, Moses AV and Früh K: CD31
immunohistochemical staining in Kaposi Sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 136:1329author reply 1330. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Delou JM, Biasoli D and Borges HL: The
complex link between apoptosis and autophagy: A promising new role
for RB. An Acad Bras Cienc. 88:2257–2275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ryter SW, Mizumura K and Choi AM: The
impact of autophagy on cell death modalities. Int J Cell Biol.
2014:5026762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Su M, Mei Y and Sinha S: Role of the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer, 2013. J Oncol.
2013:1027352013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li L, Zhao GD, Shi Z, Qi LL, Zhou LY and
Fu ZX: The Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in the
occurrence and development of HCC. Oncol Lett. 12:3045–3050.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM and Sabatini DM:
Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
17:596–603. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cao Z, Liu LZ, Dixon DA, Zheng JZ,
Chandran B and Jiang BH: Insulin-like growth factor-I induces
cyclooxygenase-2 expression via PI3K.MAPK and PKC sign aling
pathways in human ovarian cancer cells, 2007. Cel Signal.
19:1542–1553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Matei D, Kelich S, Cao L, Menning N,
Emerson RE, Rao J, Jeng MH and Sledge GW: PDGF BB induces VEGF
secretion in ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:1951–1959. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park CM, Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Lee HC, Kim MS,
Lee SH, Park IC, Rhee CH and Hong SI: Ionizing radiation enhances
matrix metal-loproteinase-2 secretion and invasion of glioma cells
through Src/epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated p38/Akt and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. Cancer Res.
66:8511–8519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou Q, Wong CH, Lau CP, Hui CW, Lui VW,
Chan SL and Yeo W: Enhanced antitumor activity with combining
effect of mTOR inhibition and microtubule stabilization in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Hepatol. 2013:1038302013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mali SB: Review of STAT3 (Signal
Transducers and Activators of Transcription) in head and neck
cancer. Oral Oncol. 51:565–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li CJ, Li YC, Zhang DR and Pan JH: Signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 function in lung
cancer. J Cancer Res Ther. 9(Suppl 2): S67–S73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, Li
F, Nachiyappan A, Dai X, Swamy SN, Ahn KS, Kumar AP, Tan BK, et al:
Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription
(STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1835:46–60. 2013.
|