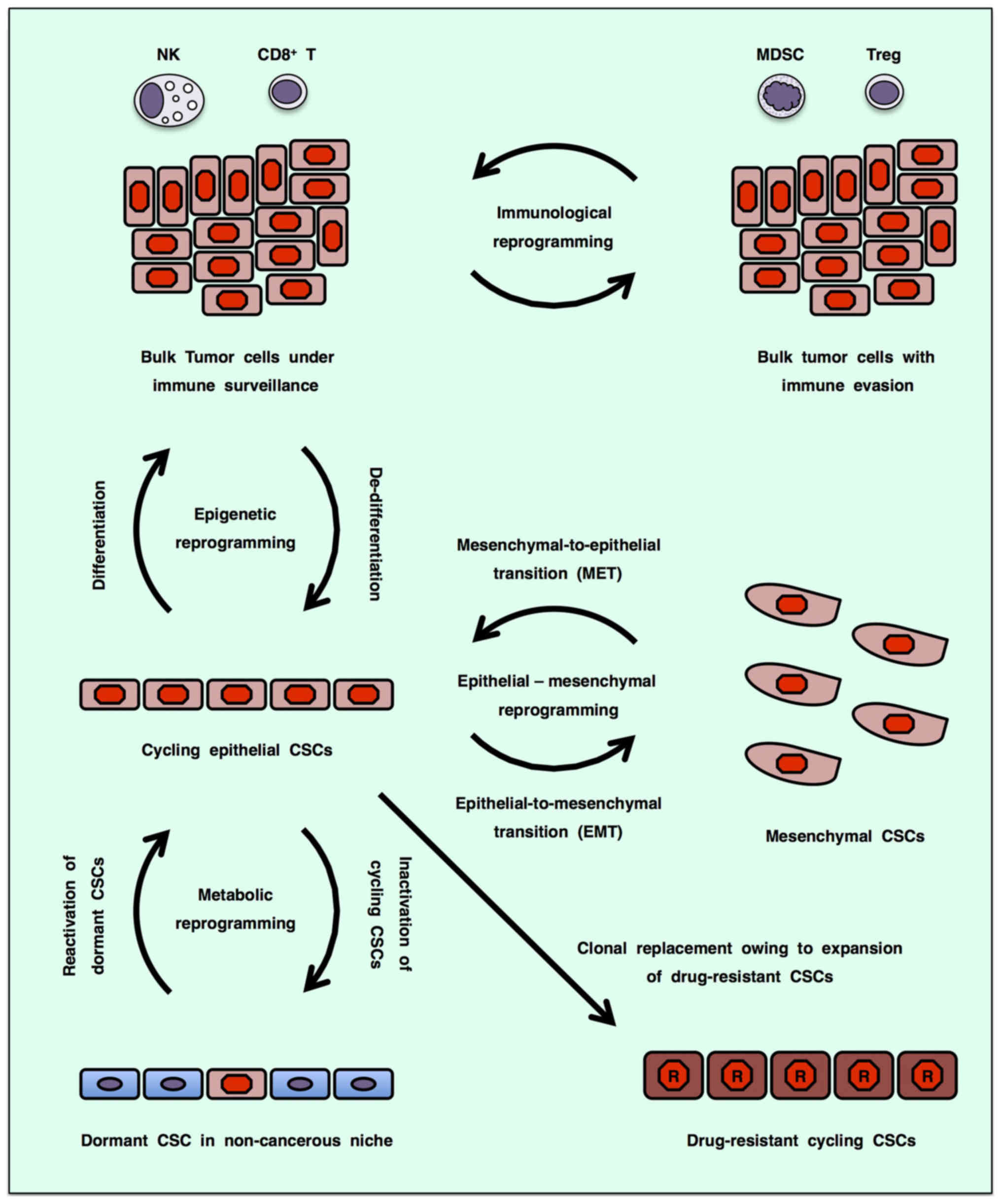
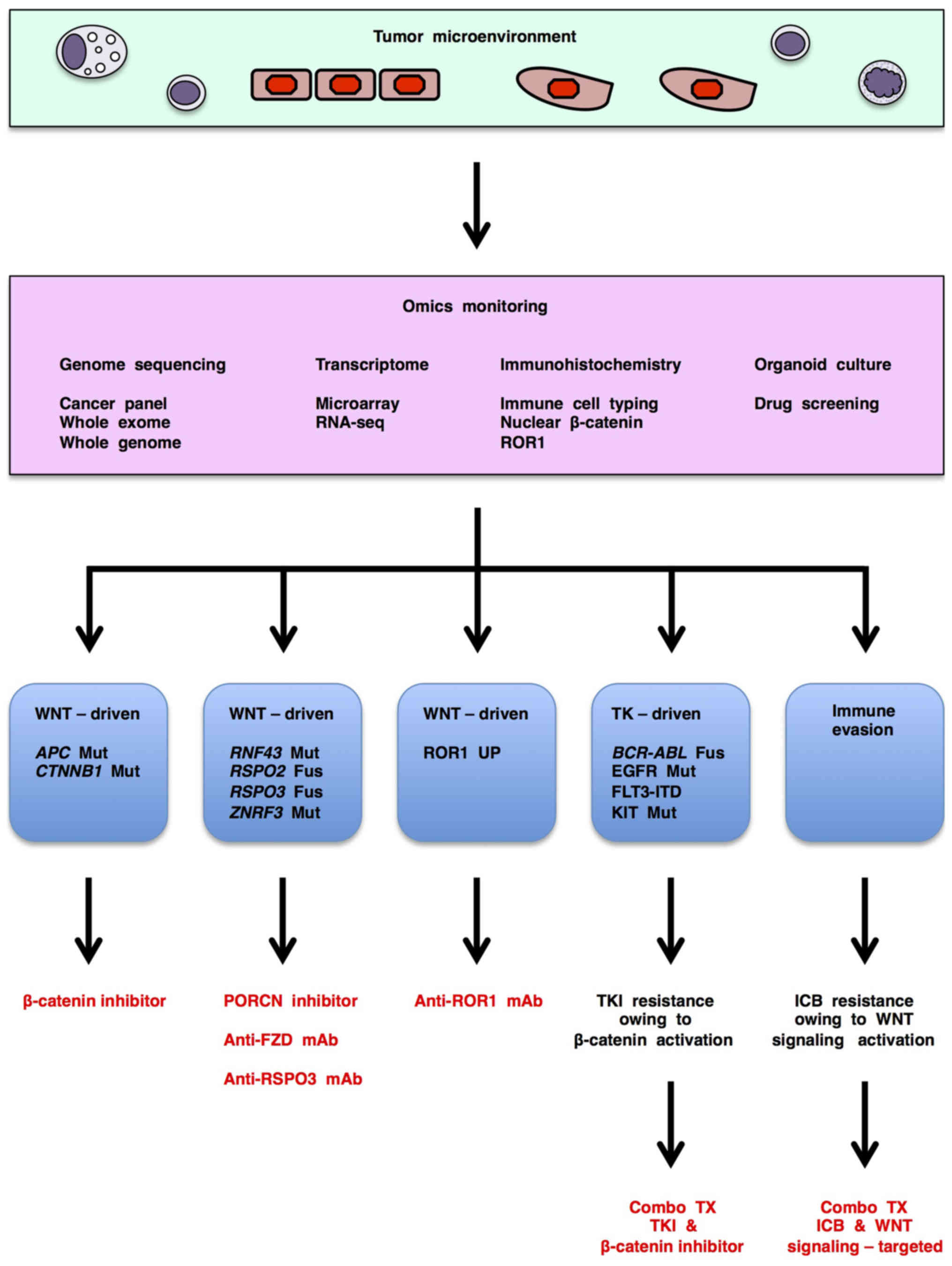
|
1
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Medema JP: Cancer stem cells: The
challenges ahead. Nat Cell Biol. 15:338–344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abbaszadegan MR, Bagheri V, Razavi MS,
Momtazi AA, Sahebkar A and Gholamin M: Isolation, identification,
and characterization of cancer stem cells: A review. J Cell
Physiol. 232:2008–2018. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Katoh M: Therapeutics targeting FGF
signaling network in human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
37:1081–1096. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Sousa e Melo F, Kurtova AV, Harnoss JM,
Kljavin N, Hoeck JD, Hung J, Anderson JE, Storm EE, Modrusan Z,
Koeppen H, et al: A distinct role for Lgr5(+) stem cells in primary
and metastatic colon cancer. Nature. 543:676–680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koury J, Zhong L and Hao J: Targeting
signaling pathways in cancer stem cells for cancer treatment. Stem
Cells Int. 2017:29258692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McDonald OG, Li X, Saunders T,
Tryggvadottir R, Mentch SJ, Warmoes MO, Word AE, Carrer A, Salz TH,
Natsume S, et al: Epigenomic reprogramming during pancreatic cancer
progression links anabolic glucose metabolism to distant
metastasis. Nat Genet. 49:367–376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tam WL and Weinberg RA: The epigenetics of
epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nat Med. 19:1438–1449.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schreiber RD, Old LJ and Smyth MJ: Cancer
immunoediting: Integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression
and promotion. Science. 331:1565–1570. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spranger S, Bao R and Gajewski TF:
Melanoma-intrinsic β-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour
immunity. Nature. 523:231–235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yamashita T, Ji J, Budhu A, Forgues M,
Yang W, Wang HY, Jia H, Ye Q, Qin LX, Wauthier E, et al:
EpCAM-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells are tumor-initiating
cells with stem/progenitor cell features. Gastroenterology.
136:1012–1024. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Todaro M, Gaggianesi M, Catalano V,
Benfante A, Iovino F, Biffoni M, Apuzzo T, Sperduti I, Volpe S,
Cocorullo G, et al: CD44v6 is a marker of constitutive and
reprogrammed cancer stem cells driving colon cancer metastasis.
Cell Stem Cell. 14:342–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirsch D, Barker N, McNeil N, Hu Y, Camps
J, McKinnon K, Clevers H, Ried T and Gaiser T: LGR5 positivity
defines stem-like cells in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:849–858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Van der Flier LG, Sabates-Bellver J, Oving
I, Haegebarth A, De Palo M, Anti M, Van Gijn ME, Suijkerbuijk S,
Van de Wetering M, Marra G, et al: The intestinal Wnt/TCF
signature. Gastroenterology. 132:628–632. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan KS, Janda CY, Chang J, Zheng GXY,
Larkin KA, Luca VC, Chia LA, Mah AT, Han A, Terry JM, et al:
Non-equivalence of Wnt and R-spondin ligands during Lgr5(+)
intestinal stem-cell self-renewal. Nature. 545:238–242. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hilkens J, Timmer NC, Boer M, Ikink GJ,
Schewe M, Sacchetti A, Koppens MAJ, Song JY and Bakker ERM: RSPO3
expands intestinal stem cell and niche compartments and drives
tumorigenesis. Gut. 66:1095–1105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Mani SK, Zhang H, Diab A, Pascuzzi PE,
Lefrançois L, Fares N, Bancel B, Merle P and Andrisani O:
EpCAM-regulated intra-membrane proteolysis induces a cancer stem
cell-like gene signature in hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes.
J Hepatol. 65:888–898. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: WNT signaling pathway
and stem cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4042–4045.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ranganathan P, Weaver KL and Capobianco
AJ: Notch signalling in solid tumours: A little bit of everything
but not all the time. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:338–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katoh M and Nakagama H: FGF receptors:
Cancer biology and therapeutics. Med Res Rev. 34:280–300. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lamb R, Bonuccelli G, Ozsvári B,
Peiris-Pagès M, Fiorillo M, Smith DL, Bevilacqua G, Mazzanti CM,
McDonnell LA, Naccarato AG, et al: Mitochondrial mass, a new
metabolic biomarker for stem-like cancer cells: Understanding
WNT/FGF-driven anabolic signaling. Oncotarget. 6:30453–30471. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Niehrs C: The complex world of WNT
receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:767–779. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN and
Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 25:254–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rada P, Rojo AI, Offergeld A, Feng GJ,
Velasco-Martín JP, González-Sancho JM, Valverde ÁM, Dale T,
Regadera J and Cuadrado A: WNT-3A regulates an Axin1/NRF2 complex
that regulates antioxidant metabolism in hepatocytes. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 22:555–571. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Acebron SP and Niehrs C:
β-catenin-independent roles of Wnt/LRP6 signaling. Trends Cell
Biol. 26:956–967. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Molecular genetics
and targeted therapy of WNT-related human diseases (Review). Int J
Mol Med. 40:587–606. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lui JH, Hansen DV and Kriegstein AR:
Development and evolution of the human neocortex. Cell. 146:18–36.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barker N: Adult intestinal stem cells:
Critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:19–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Van Camp JK, Beckers S, Zegers D and Van
Hul W: Wnt signaling and the control of human stem cell fate. Stem
Cell Rev. 10:207–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang K, Wang X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Nan G, Li
Y, Zhang F, Mohammed MK, Haydon RC, Luu HH, et al: The evolving
roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis:
Implications in targeted cancer therapies. Lab Invest. 96:116–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Qin L, Yin YT, Zheng FJ, Peng LX, Yang CF,
Bao YN, Liang YY, Li XJ, Xiang YQ, Sun R, et al: WNT5A promotes
stemness characteristics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells leading
to metastasis and tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6:10239–10252. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Webster MR, Kugel CH III and Weeraratna
AT: The Wnts of change: How Wnts regulate phenotype switching in
melanoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1856:244–251. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kumawat K and Gosens R: WNT-5A: Signaling
and functions in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:567–587.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Wang MT, Holderfield M, Galeas J,
Delrosario R, To MD, Balmain A and McCormick F: K-Ras promotes
tumorigenicity through suppression of non-canonical Wnt signaling.
Cell. 163:1237–1251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Plaks V, Kong N and Werb Z: The cancer
stem cell niche: How essential is the niche in regulating stemness
of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 16:225–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Katoh M: FGFR inhibitors: Effects on
cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 38:3–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bolli N, Avet-Loiseau H, Wedge DC, Van Loo
P, Alexandrov LB, Martincorena I, Dawson KJ, Iorio F, Nik-Zainal S,
Bignell GR, et al: Heterogeneity of genomic evolution and
mutational profiles in multiple myeloma. Nat Commun. 5:29972014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li S, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Chung SS,
Sanders MA, Hricik T, Rapaport F, Patel J, Dillon R, Vijay P, Brown
AL, et al: Distinct evolution and dynamics of epigenetic and
genetic heterogeneity in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med.
22:792–799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ, Wilson GA,
Jamal-Hanjani M, Constantin T, Salari R, Le Quesne J, Moore DA,
Veeriah S, Rosenthal R; TRACERx consortium; et al: PEACE
consortium: Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung
cancer evolution. Nature. 545:446–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tammela T, Sanchez-Rivera FJ, Cetinbas NM,
Wu K, Joshi NS, Helenius K, Park Y, Azimi R, Kerper NR, Wesselhoeft
RA, et al: A Wnt-producing niche drives proliferative potential and
progression in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 545:355–359. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mao Y, Keller ET, Garfield DH, Shen K and
Wang J: Stromal cells in tumor microenvironment and breast cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32:303–315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Son B, Lee S, Youn H, Kim E, Kim W and
Youn B: The role of tumor microenvironment in therapeutic
resistance. Oncotarget. 8:3933–3945. 2017.
|
|
47
|
Anderson KG, Stromnes IM and Greenberg PD:
Obstacles posed by the tumor microenvironment to T cell activity: A
case for synergistic therapies. Cancer Cell. 31:311–325. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Z, Liu P, Inuzuka H and Wei W: Roles
of F-box proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:233–247. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Katoh M, Hirai M, Sugimura T and Terada M:
Cloning, expression and chromosomal localization of Wnt-13, a novel
member of the Wnt gene family. Oncogene. 13:873–876.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Katoh M, Kirikoshi H, Terasaki H and
Shiokawa K: WNT2B2 mRNA, up-regulated in primary gastric cancer, is
a positive regulator of the WNT-β-catenin-TCF signaling pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 289:1093–1098. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jiang H, Li F, He C, Wang X, Li Q and Gao
H: Expression of Gli1 and Wnt2B correlates with progression and
clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4531–4538. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Steinhart Z, Pavlovic Z, Chandrashekhar M,
Hart T, Wang X, Zhang X, Robitaille M, Brown KR, Jaksani S,
Overmeer R, et al: Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal a Wnt-FZD5
signaling circuit as a druggable vulnerability of RNF43-mutant
pancreatic tumors. Nat Med. 23:60–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Seshagiri S, Stawiski EW, Durinck S,
Modrusan Z, Storm EE, Conboy CB, Chaudhuri S, Guan Y, Janakiraman
V, Jaiswal BS, et al: Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer.
Nature. 488:660–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Lessons from
hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 87:159–170. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mazzoni SM and Fearon ER: AXIN1 and AXIN2
variants in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 355:1–8. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chiche A, Moumen M, Romagnoli M, Petit V,
Lasla H, Jézéquel P, de la Grange P, Jonkers J, Deugnier MA,
Glukhova MA, et al: p53 deficiency induces cancer stem cell pool
expansion in a mouse model of triple-negative breast tumors.
Oncogene. 36:2355–2365. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Valenti G, Quinn HM, Heynen GJJE, Lan L,
Holland JD, Vogel R, Wulf-Goldenberg A and Birchmeier W: Cancer
stem cells regulate cancer-associated fibroblasts via activation of
Hedgehog signaling in mammary gland tumors. Cancer Res.
77:2134–2147. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Katoh M: WNT/PCP signaling pathway and
human cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 14:1583–1588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang Y and Mlodzik M: Wnt-Frizzled/planar
cell polarity signaling: Cellular orientation by facing the wind
(Wnt). Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 31:623–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Minegishi K, Hashimoto M, Ajima R, Takaoka
K, Shinohara K, Ikawa Y, Nishimura H, McMahon AP, Willert K, Okada
Y, et al: A Wnt5 activity asymmetry and intercellular signaling via
PCP proteins polarize node cells for left-right symmetry breaking.
Dev Cell. 40:439–452.e4. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu J and Mlodzik M: Wnt/PCP instructions
for cilia in left-right asymmetry. Dev Cell. 40:423–424. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang W, Runkle KB, Terkowski SM, Ekaireb
RI and Witze ES: Protein depalmitoylation is induced by Wnt5a and
promotes polarized cell behavior. J Biol Chem. 290:15707–15716.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nishimura T, Honda H and Takeichi M:
Planar cell polarity links axes of spatial dynamics in neural-tube
closure. Cell. 149:1084–1097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
De Marco P, Merello E, Piatelli G, Cama A,
Kibar Z and Capra V: Planar cell polarity gene mutations contribute
to the etiology of human neural tube defects in our population.
Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 100:633–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gödde NJ, Pearson HB, Smith LK and Humbert
PO: Dissecting the role of polarity regulators in cancer through
the use of mouse models. Exp Cell Res. 328:249–257. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Johnson R and Halder G: The two faces of
Hippo: Targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and
cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:63–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Zhang S, Chen L, Cui B, Chuang HY, Yu J,
Wang-Rodriguez J, Tang L, Chen G, Basak GW and Kipps TJ: ROR1 is
expressed in human breast cancer and associated with enhanced
tumor-cell growth. PLoS One. 7:e311272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Anastas JN, Kulikauskas RM, Tamir T, Rizos
H, Long GV, von Euw EM, Yang PT, Chen HW, Haydu L, Toroni RA, et
al: WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF
inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 124:2877–2890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yu J, Chen L, Cui B, Widhopf GF II, Shen
Z, Wu R, Zhang L, Zhang S, Briggs SP and Kipps TJ: Wnt5a induces
ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and
proliferation. J Clin Invest. 126:585–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Green JL, Kuntz SG and Sternberg PW: Ror
receptor tyrosine kinases: Orphans no more. Trends Cell Biol.
18:536–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lu W, Yamamoto V, Ortega B and Baltimore
D: Mammalian Ryk is a Wnt coreceptor required for stimulation of
neurite outgrowth. Cell. 119:97–108. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Petrova IM, Malessy MJ, Verhaagen J,
Fradkin LG and Noordermeer JN: Wnt signaling through the Ror
receptor in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. 49:303–315. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Debebe Z and Rathmell WK: Ror2 as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 150:143–148. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bicocca VT, Chang BH, Masouleh BK, Muschen
M, Loriaux MM, Druker BJ and Tyner JW: Crosstalk between ROR1 and
the Pre-B cell receptor promotes survival of t(1;19) acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 22:656–667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hojjat-Farsangi M, Moshfegh A,
Daneshmanesh AH, Khan AS, Mikaelsson E, Osterborg A and Mellstedt
H: The receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1 - an oncofetal antigen for
targeted cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 29:21–31. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Gentile A, Lazzari L, Benvenuti S,
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM: The ROR1 pseudokinase diversifies
signaling outputs in MET-addicted cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
135:2305–2316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yamaguchi T, Lu C, Ida L, Yanagisawa K,
Usukura J, Cheng J, Hotta N, Shimada Y, Isomura H, Suzuki M, et al:
ROR1 sustains caveolae and survival signalling as a scaffold of
cavin-1 and caveolin-1. Nat Commun. 7:100602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Li C, Wang S, Xing Z, Lin A, Liang K, Song
J, Hu Q, Yao J, Chen Z, Park PK, et al: A ROR1-HER3-lncRNA
signalling axis modulates the Hippo-YAP pathway to regulate bone
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 19:106–119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Dijksterhuis JP, Petersen J and Schulte G:
WNT/Frizzled signalling: receptor-ligand selectivity with focus on
FZD-G protein signalling and its physiological relevance: IUPHAR
Review 3. Br J Pharmacol. 171:1195–1209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Gong B, Shen W, Xiao W, Meng Y, Meng A and
Jia S: The Sec14-like phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins
Sec14l3/SEC14L2 act as GTPase proteins to mediate Wnt/Ca(2+)
signaling. eLife. 6:e263622017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Kim S, Nie H, Nesin V, Tran U, Outeda P,
Bai CX, Keeling J, Maskey D, Watnick T, Wessely O, et al: The
polycystin complex mediates Wnt/Ca(2+) signalling. Nat Cell Biol.
18:752–764. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno
N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Matsumoto K: The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade
functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:131–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Zhang M, Hagenmueller M, Riffel JH,
Kreusser MM, Bernhold E, Fan J, Katus HA, Backs J and Hardt SE:
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II couples Wnt
signaling with histone deacetylase 4 and mediates
dishevelled-induced cardiomyopathy. Hypertension. 65:335–344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Scholz B, Korn C, Wojtarowicz J, Mogler C,
Augustin I, Boutros M, Niehrs C and Augustin HG: Endothelial RSPO3
controls vascular stability and pruning through non-canonical
WNT/Ca(2+)/NFAT signaling. Dev Cell. 36:79–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang W, Snyder N, Worth AJ, Blair IA and
Witze ES: Regulation of lipid synthesis by the RNA helicase Mov10
controls Wnt5a production. Oncogenesis. 4:e1542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Miyamoto DT, Zheng Y, Wittner BS, Lee RJ,
Zhu H, Broderick KT, Desai R, Fox DB, Brannigan BW, Trautwein J, et
al: RNA-Seq of single prostate CTCs implicates noncanonical Wnt
signaling in antiandrogen resistance. Science. 349:1351–1356. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Blumenthal A, Ehlers S, Lauber J, Buer J,
Lange C, Goldmann T, Heine H, Brandt E and Reiling N: The Wingless
homolog WNT5A and its receptor Frizzled-5 regulate inflammatory
responses of human mononuclear cells induced by microbial
stimulation. Blood. 108:965–973. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang L, Steele I, Kumar JD, Dimaline R,
Jithesh PV, Tiszlavicz L, Reisz Z, Dockray GJ and Varro A: Distinct
miRNA profiles in normal and gastric cancer myofibroblasts and
significance in Wnt signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 310:G696–G704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Aznar N, Midde KK, Dunkel Y, Lopez-Sanchez
I, Pavlova Y, Marivin A, Barbazán J, Murray F, Nitsche U, Janssen
KP, et al: Daple is a novel non-receptor GEF required for trimeric
G protein activation in Wnt signaling. eLife. 4:e070912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yu FX, Zhao B and Guan KL: Hippo pathway
in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell.
163:811–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hansen CG, Moroishi T and Guan KL: YAP and
TAZ: A nexus for Hippo signaling and beyond. Trends Cell Biol.
25:499–513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Hot B, Valnohova J, Arthofer E, Simon K,
Shin J, Uhlén M, Kostenis E, Mulder J and Schulte G: FZD10-Gα13
signalling axis points to a role of FZD10 in CNS angiogenesis. Cell
Signal. 32:93–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Takebe N, Miele L, Harris PJ, Jeong W,
Bando H, Kahn M, Yang SX and Ivy SP: Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and
Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 12:445–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kahn M: Wnt signaling in stem cells and
tumor stem cells. Semin Reprod Med. 33:317–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tai D, Wells K, Arcaroli J, Vanderbilt C,
Aisner DL, Messersmith WA and Lieu CH: Targeting the WNT signaling
pathway in cancer therapeutics. Oncologist. 20:1189–1198. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Gurney A, Axelrod F, Bond CJ, Cain J,
Chartier C, Donigan L, Fischer M, Chaudhari A, Ji M, Kapoun AM, et
al: Wnt pathway inhibition via the targeting of Frizzled receptors
results in decreased growth and tumorigenicity of human tumors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:11717–11722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Nielsen TO, Poulin NM and Ladanyi M:
Synovial sarcoma: Recent discoveries as a roadmap to new avenues
for therapy. Cancer Discov. 5:124–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Gong X, Azhdarinia A, Ghosh SC, Xiong W,
An Z, Liu Q and Carmon KS: LGR5-targeted antibody-drug conjugate
eradicates gastrointestinal tumors and prevents recurrence. Mol
Cancer Ther. 15:1580–1590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Damelin M, Bankovich A, Bernstein J, Lucas
J, Chen L, Williams S, Park A, Aguilar J, Ernstoff E, Charati M, et
al: A PTK7-targeted antibody-drug conjugate reduces tumorinitiating
cells and induces sustained tumor regressions. Sci Transl Med.
9:pii: eaag2611. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Zhang S, Cui B, Lai H, Liu G, Ghia EM,
Widhopf GF II, Zhang Z, Wu CC, Chen L, Wu R, et al: Ovarian cancer
stem cells express ROR1, which can be targeted for
anti-cancer-stem-cell therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:17266–17271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Storm EE, Durinck S, de Sousa e Melo F,
Tremayne J, Kljavin N, Tan C, Ye X, Chiu C, Pham T, Hongo JA, et
al: Targeting PTPRK-RSPO3 colon tumours promotes differentiation
and loss of stem-cell function. Nature. 529:97–100. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Berger C, Sommermeyer D, Hudecek M, Berger
M, Balakrishnan A, Paszkiewicz PJ, Kosasih PL, Rader C and Riddell
SR: Safety of targeting ROR1 in primates with chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 3:206–216. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
104
|
Le PN, McDermott JD and Jimeno A:
Targeting the Wnt pathway in human cancers: Therapeutic targeting
with a focus on OMP-54F28. Pharmacol Ther. 146:1–11. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Cheng Y, Phoon YP, Jin X, Chong SY, Ip JC,
Wong BW and Lung ML: Wnt-C59 arrests stemness and suppresses growth
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in mice by inhibiting the Wnt pathway
in the tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget. 6:14428–14439. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Poulsen A, Ho SY, Wang W, Alam J, Jeyaraj
DA, Ang SH, Tan ES, Lin GR, Cheong VW, Ke Z, et al: Pharmacophore
model for Wnt/Porcupine inhibitors and its use in drug design. J
Chem Inf Model. 55:1435–1448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Langton PF, Kakugawa S and Vincent JP:
Making, exporting, and modulating Wnts. Trends Cell Biol.
26:756–765. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
DeBruine ZJ, Ke J, Harikumar KG, Gu X,
Borowsky P, Williams BO, Xu W, Miller LJ, Xu HE and Melcher K:
Wnt5a promotes Frizzled-4 signalosome assembly by stabilizing
cysteine-rich domain dimerization. Genes Dev. 31:916–926. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Madan B, Ke Z, Harmston N, Ho SY, Frois
AO, Alam J, Jeyaraj DA, Pendharkar V, Ghosh K, Virshup IH, et al:
Wnt addiction of genetically defined cancers reversed by PORCN
inhibition. Oncogene. 35:2197–2207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan
CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, et al: Small
molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue
regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 5:100–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Proffitt KD, Madan B, Ke Z, Pendharkar V,
Ding L, Lee MA, Hannoush RN and Virshup DM: Pharmacological
inhibition of the Wnt acyltransferase PORCN prevents growth of
WNT-driven mammary cancer. Cancer Res. 73:502–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Agarwal P, Zhang B, Ho Y, Cook A, Li L,
Mikhail FM, Wang Y, McLaughlin ME and Bhatia R: Enhanced targeting
of CML stem and progenitor cells by inhibition of porcupine
acyltrans-ferase in combination with TKI. Blood. 129:1008–1020.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Liu C and Yu X: ADP-ribosyltransferases
and poly ADP-ribosylation. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 16:491–501. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kulak O, Chen H, Holohan B, Wu X, He H,
Borek D, Otwinowski Z, Yamaguchi K, Garofalo LA, Ma Z, et al:
Disruption of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and telomeric shortening are
inextricable consequences of tankyrase inhibition in human cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 35:2425–2435. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang W, Li N, Li X, Tran MK, Han X and
Chen J: Tankyrase inhibitors target YAP by stabilizing Angiomotin
family proteins. Cell Rep. 13:524–532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Nathubhai A, Haikarainen T, Koivunen J,
Murthy S, Koumanov F, Lloyd MD, Holman GD, Pihlajaniemi T, Tosh D,
Lehtiö L, et al: Highly potent and isoform selective dual site
binding Tankyrase/Wnt signaling inhibitors that increase cellular
glucose uptake and have antiproliferative activity. J Med Chem.
60:814–820. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Quackenbush KS, Bagby S, Tai WM,
Messersmith WA, Schreiber A, Greene J, Kim J, Wang G, Purkey A,
Pitts TM, et al: The novel tankyrase inhibitor (AZ1366) enhances
irinotecan activity in tumors that exhibit elevated tankyrase and
irinotecan resistance. Oncotarget. 7:28273–28285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Lau T, Chan E, Callow M, Waaler J, Boggs
J, Blake RA, Magnuson S, Sambrone A, Schutten M, Firestein R, et
al: A novel tankyrase small-molecule inhibitor suppresses APC
mutation-driven colorectal tumor growth. Cancer Res. 73:3132–3144.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Waaler J, Machon O, Tumova L, Dinh H,
Korinek V, Wilson SR, Paulsen JE, Pedersen NM, Eide TJ, Machonova
O, et al: A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt
signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in
conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 72:2822–2832. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Arqués O, Chicote I, Puig I, Tenbaum SP,
Argilés G, Dienstmann R, Fernández N, Caratù G, Matito J,
Silberschmidt D, et al: Tankyrase inhibition blocks Wnt/β-catenin
pathway and reverts resistance to PI3K and AKT inhibitors in the
treatment of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:644–656. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A,
Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner
S, et al: Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Schoumacher M, Hurov KE, Lehár J,
Yan-Neale Y, Mishina Y, Sonkin D, Korn JM, Flemming D, Jones MD,
Antonakos B, et al: Inhibiting Tankyrases sensitizes KRAS-mutant
cancer cells to MEK inhibitors via FGFR2 feedback signaling. Cancer
Res. 74:3294–3305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wang H, Lu B, Castillo J, Zhang Y, Yang Z,
McAllister G, Lindeman A, Reece-Hoyes J, Tallarico J, Russ C, et
al: Tankyrase inhibitor sensitizes lung cancer cells to endothelial
growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition via stabilizing
angiomotins and inhibiting YAP signaling. J Biol Chem.
291:15256–15266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Scarborough HA, Helfrich BA, Casás-Selves
M, Schuller AG, Grosskurth SE, Kim J, Tan AC, Chan DC, Zhang Z,
Zaberezhnyy V, et al: AZ1366: An inhibitor of tankyrase and the
canonical Wnt pathway that limits the persistence of non-small cell
lung cancer cells following EGFR inhibition. Clin Cancer Res.
23:1531–1541. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Pelay-Gimeno M, Glas A, Koch O and
Grossmann TN: Structure-based design of inhibitors of
protein-protein interactions: Mimicking peptide binding epitopes.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 54:8896–8927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hwang SY, Deng X, Byun S, Lee C, Lee SJ,
Suh H, Zhang J, Kang Q, Zhang T, Westover KD, et al: Direct
targeting of β-catenin by a small molecule stimulates proteasomal
degradation and suppresses oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell
Rep. 16:28–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Mahmoudi T, Li VS, Ng SS, Taouatas N,
Vries RG, Mohammed S, Heck AJ and Clevers H: The kinase TNIK is an
essential activator of Wnt target genes. EMBO J. 28:3329–3340.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Lee Y, Jung JI, Park KY, Kim SA and Kim J:
Synergistic inhibition effect of TNIK inhibitor KY-05009 and
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor dovitinib on IL-6-induced
proliferation and Wnt signaling pathway in human multiple myeloma
cells. Oncotarget. 8:41091–41101. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Tan Z, Chen L and Zhang S: Comprehensive
modeling and discovery of mebendazole as a novel TRAF2- and
NCK-interacting kinase inhibitor. Sci Rep. 6:335342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Fiskus W, Sharma S, Saha S, Shah B,
Devaraj SG, Sun B, Horrigan S, Leveque C, Zu Y, Iyer S, et al:
Pre-clinical efficacy of combined therapy with novel β-catenin
antagonist BC2059 and histone deacetylase inhibitor against AML
cells. Leukemia. 29:1267–1278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Trautmann M, Sievers E, Aretz S, Kindler
D, Michels S, Friedrichs N, Renner M, Kirfel J, Steiner S, Huss S,
et al: SS18-SSX fusion protein-induced Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a
therapeutic target in synovial sarcoma. Oncogene. 33:5006–5016.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Kim JY, Lee HY, Park KK, Choi YK, Nam JS
and Hong IS: CWP232228 targets liver cancer stem cells through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling: A novel therapeutic approach for liver
cancer treatment. Oncotarget. 7:20395–20409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Nagaraj AB, Joseph P, Kovalenko O, Singh
S, Armstrong A, Redline R, Resnick K, Zanotti K, Waggoner S and
DiFeo A: Critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in driving
epithelial ovarian cancer platinum resistance. Oncotarget.
6:23720–23734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Fang L, Zhu Q, Neuenschwander M, Specker
E, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Weis WI, von Kries JP and Birchmeier W: A
small-molecule antagonist of the β-catenin/TCF4 interaction blocks
the self-renewal of cancer stem cells and suppresses tumorigenesis.
Cancer Res. 76:891–901. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Sukhdeo K, Mani M, Zhang Y, Dutta J, Yasui
H, Rooney MD, Carrasco DE, Zheng M, He H, Tai YT, et al: Targeting
the β-catenin/TCF transcriptional complex in the treatment of
multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7516–7521. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Zhou H, Mak PY, Mu H, Mak DH, Zeng Z,
Cortes J, Liu Q, Andreeff M and Carter BZ: Combined inhibition of
β-catenin and Bcr-Abl synergistically targets tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-resistant blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia blasts
and progenitors in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia. Apr 18–2017.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Takada K, Zhu D, Bird GH, Sukhdeo K, Zhao
JJ, Mani M, Lemieux M, Carrasco DE, Ryan J, Horst D, et al:
Targeted disruption of the BCL9/β-catenin complex inhibits
oncogenic Wnt signaling. Sci Transl Med. 4:148ra1172012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Wang Q, Amato SP, Rubitski DM, Hayward MM,
Kormos BL, Verhoest PR, Xu L, Brandon NJ and Ehlers MD:
Identification of phosphorylation consensus sequences and
endogenous neuronal substrates of the psychiatric risk kinase TNIK.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 356:410–423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Coluccia AM, Vacca A, Duñach M, Mologni L,
Redaelli S, Bustos VH, Benati D, Pinna LA and Gambacorti-Passerini
C: Bcr-Abl stabilizes β-catenin in chronic myeloid leukemia through
its tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 26:1456–1466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Nakayama S, Sng N, Carretero J, Welner R,
Hayashi Y, Yamamoto M, Tan AJ, Yamaguchi N, Yasuda H, Li D, et al:
β-catenin contributes to lung tumor development induced by EGFR
mutations. Cancer Res. 74:5891–5902. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Kajiguchi T, Katsumi A, Tanizaki R, Kiyoi
H and Naoe T: Y654 of β-catenin is essential for FLT3/ITD-related
tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear localization of β-catenin. Eur
J Haematol. 88:314–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Jin B, Ding K and Pan J: Ponatinib induces
apoptosis in imatinib-resistant human mast cells by
dephosphorylating mutant D816V KIT and silencing β-catenin
signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1217–1230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Fernández-Sánchez ME, Barbier S, Whitehead
J, Béalle G, Michel A, Latorre-Ossa H, Rey C, Fouassier L, Claperon
A, Brullé L, et al: Mechanical induction of the tumorigenic
β-catenin pathway by tumour growth pressure. Nature. 523:92–95.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Zhao Y, Masiello D, McMillian M, Nguyen C,
Wu Y, Melendez E, Smbatyan G, Kida A, He Y, Teo JL, et al:
CBP/catenin antagonist safely eliminates drug-resistant
leukemiainitiating cells. Oncogene. 35:3705–3717. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Smyth MJ, Ngiow SF, Ribas A and Teng MW:
Combination cancer immunotherapies tailored to the tumour
microenvironment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 13:143–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Palucka AK and Coussens LM: The basis of
oncoimmunology. Cell. 164:1233–1247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zarour HM: Reversing T-cell dysfunction
and exhaustion in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1856–1864. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Elements of cancer
immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature. 541:321–330.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Inman BA, Longo TA, Ramalingam S and
Harrison MR: Atezolizumab: A PD-L1-blocking antibody for bladder
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:1886–1890. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Kim ES: Avelumab: First global approval.
Drugs. 77:929–937. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Syed YY: Durvalumab: First global
approval. Drugs. 77:1369–1376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Zaretsky JM, Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS,
Escuin-Ordinas H, Hugo W, Hu-Lieskovan S, Torrejon DY,
Abril-Rodriguez G, Sandoval S, Barthly L, et al: Mutations
associated with acquired resistance to PD-1 blockade in melanoma. N
Engl J Med. 375:819–829. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Shin DS, Zaretsky JM, Escuin-Ordinas H,
Garcia-Diaz A, Hu-Lieskovan S, Kalbasi A, Grasso CS, Hugo W,
Sandoval S, Torrejon DY, et al: Primary resistance to PD-1 blockade
mediated by JAK1/2 mutations. Cancer Discov. 7:188–201. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Anagnostou V, Smith KN, Forde PM, Niknafs
N, Bhattacharya R, White J, Zhang T, Adleff V, Phallen J, Wali N,
et al: Evolution of neoantigen landscape during immune checkpoint
blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 7:264–276.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Huang AC, Postow MA, Orlowski RJ, Mick R,
Bengsch B, Manne S, Xu W, Harmon S, Giles JR, Wenz B, et al: T-cell
invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1
response. Nature. 545:60–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Manguso RT, Pope HW, Zimmer MD, Brown FD,
Yates KB, Miller BC, Collins NB, Bi K, LaFleur MW, Juneja VR, et
al: In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer
immunotherapy target. Nature. 547:413–418. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Holtzhausen A, Zhao F, Evans KS, Tsutsui
M, Orabona C, Tyler DS and Hanks BA: Melanoma-derived Wnt5a
promotes local dendritic-cell expression of IDO and
immunotolerance: Opportunities for pharmacologic enhancement of
immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 3:1082–1095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Hugo W, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Song C, Moreno
BH, Hu-Lieskovan S, Berent-Maoz B, Pang J, Chmielowski B, Cherry G,
et al: Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to anti-PD-1
therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell. 165:35–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
D'Amico L, Mahajan S, Capietto AH, Yang Z,
Zamani A, Ricci B, Bumpass DB, Meyer M, Su X, Wang-Gillam A, et al:
Dickkopf-related protein 1 (Dkk1) regulates the accumulation and
function of myeloid derived suppressor cells in cancer. J Exp Med.
213:827–840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Fulciniti M, Tassone P, Hideshima T,
Vallet S, Nanjappa P, Ettenberg SA, Shen Z, Patel N, Tai YT,
Chauhan D, et al: Anti-DKK1 mAb (BHQ880) as a potential therapeutic
agent for multiple myeloma. Blood. 114:371–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Bendell JC, Murphy JE, Mahalingam D,
Halmos B, Sirard CA, Landau SB and Ryan DP: A Phase 1 study of
DKN-01, an anti-DKK1 antibody, in combination with paclitaxel in
patients with DKK1 relapsed or refractory esophageal cancer or
gastro-esophageal junction tumors. J Clin Oncol. 34(Suppl 4): pp.
S1112016, http://ascopubs.org/doi/abs/10.1200/jco.2016.34.4_suppl.111.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Camidge DR, Pao W and Sequist LV: Acquired
resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: Learning from lung cancer. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 11:473–481. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Pauli C, Hopkins BD, Prandi D, Shaw R,
Fedrizzi T, Sboner A, Sailer V, Augello M, Puca L, Rosati R, et al:
Personalized in vitro and in vivo cancer models to guide precision
medicine. Cancer Discov. 7:462–477. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Massard C, Michiels S, Ferté C, Le Deley
MC, Lacroix L, Hollebecque A, Verlingue L, Ileana E, Rosellini S,
Ammari S, et al: High-throughput genomics and clinical outcome in
hard-to-treat advanced cancers: Results of the MOSCATO 01 trial.
Cancer Discov. 7:586–595. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Rheinbay E, Parasuraman P, Grimsby J, Tiao
G, Engreitz JM, Kim J, Lawrence MS, Taylor-Weiner A,
Rodriguez-Cuevas S, Rosenberg M, et al: Recurrent and functional
regulatory mutations in breast cancer. Nature. 547:55–60. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
van de Wetering M, Francies HE, Francis
JM, Bounova G, Iorio F, Pronk A, van Houdt W, van Gorp J,
Taylor-Weiner A, Kester L, et al: Prospective derivation of a
living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients. Cell.
161:933–945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Merker SR, Weitz J and Stange DE:
Gastrointestinal organoids: How they gut it out. Dev Biol.
420:239–250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Zhang L, Adileh M, Martin ML, Klingler S,
White J, Ma X, Howe LR, Brown AM and Kolesnick R: Establishing
estrogen-responsive mouse mammary organoids from single Lgr5(+)
cells. Cell Signal. 29:41–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|