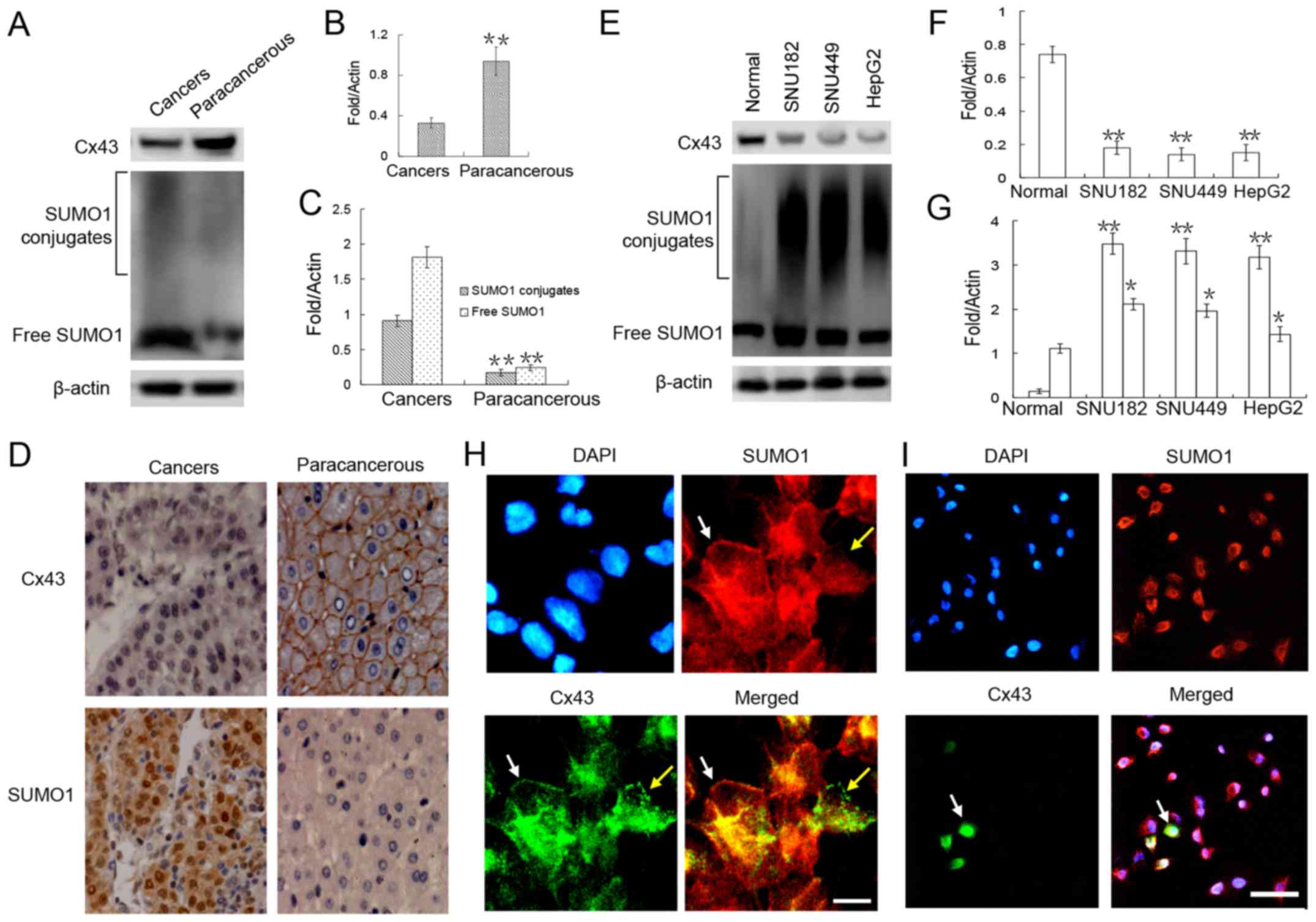
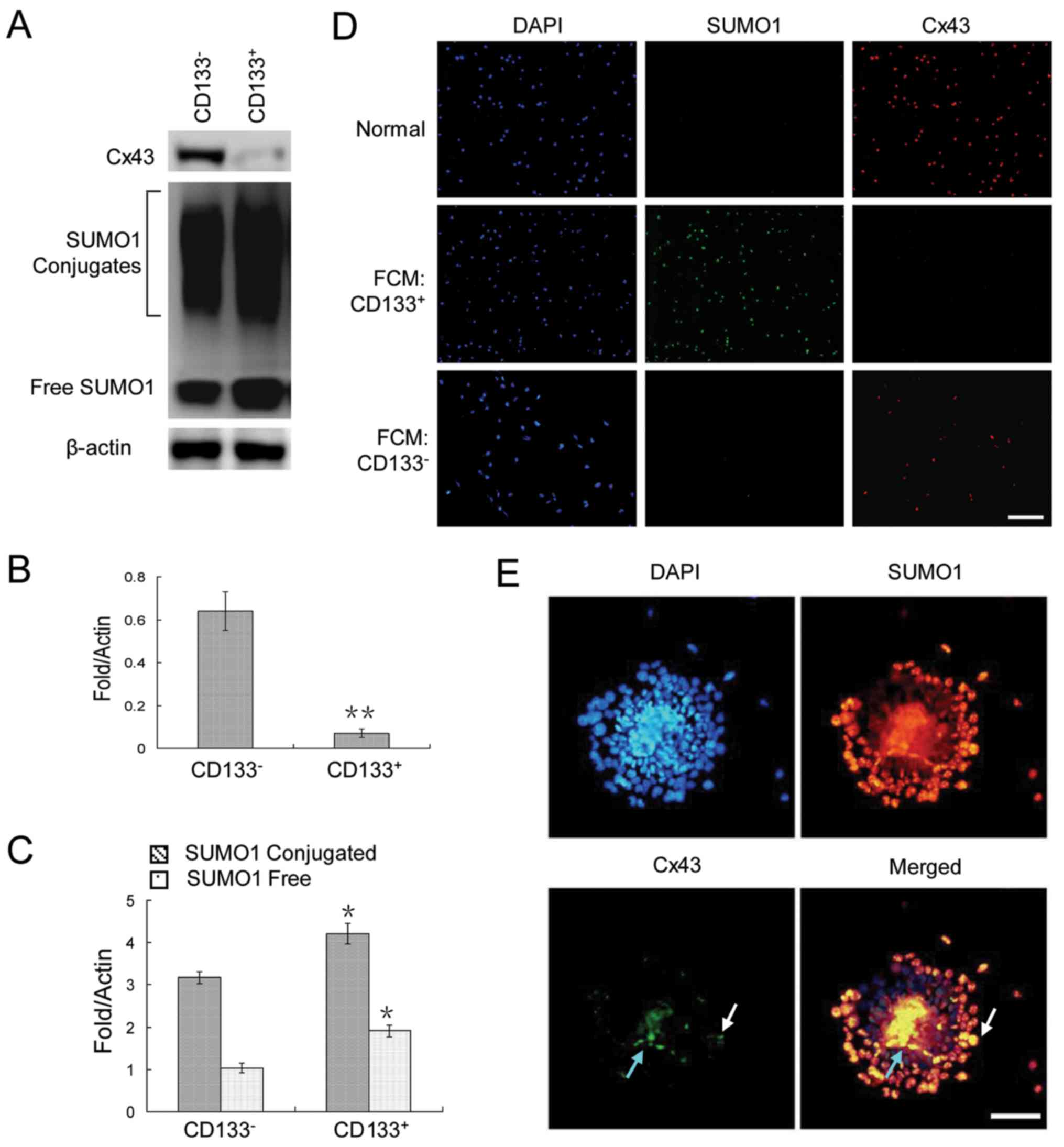
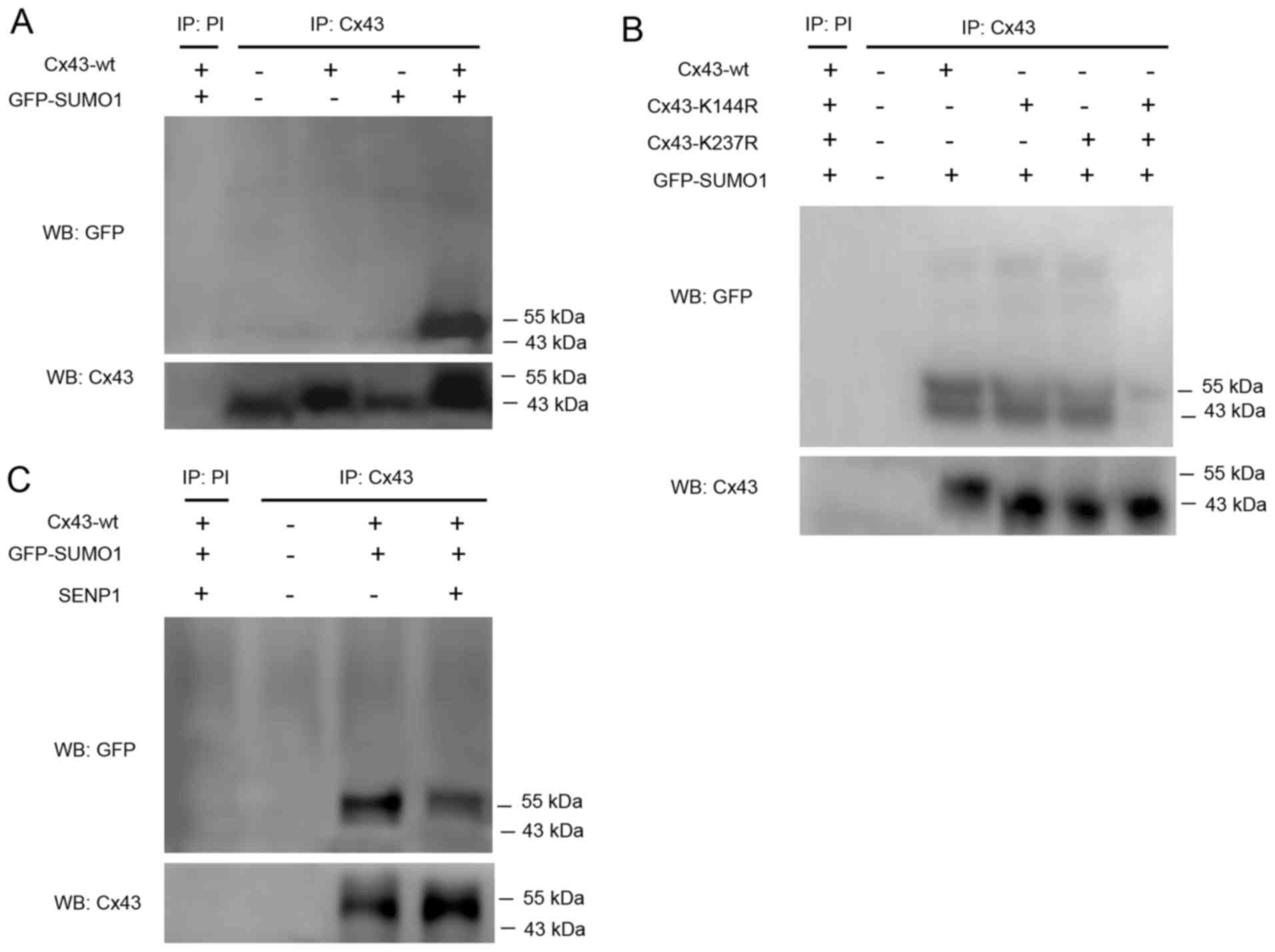
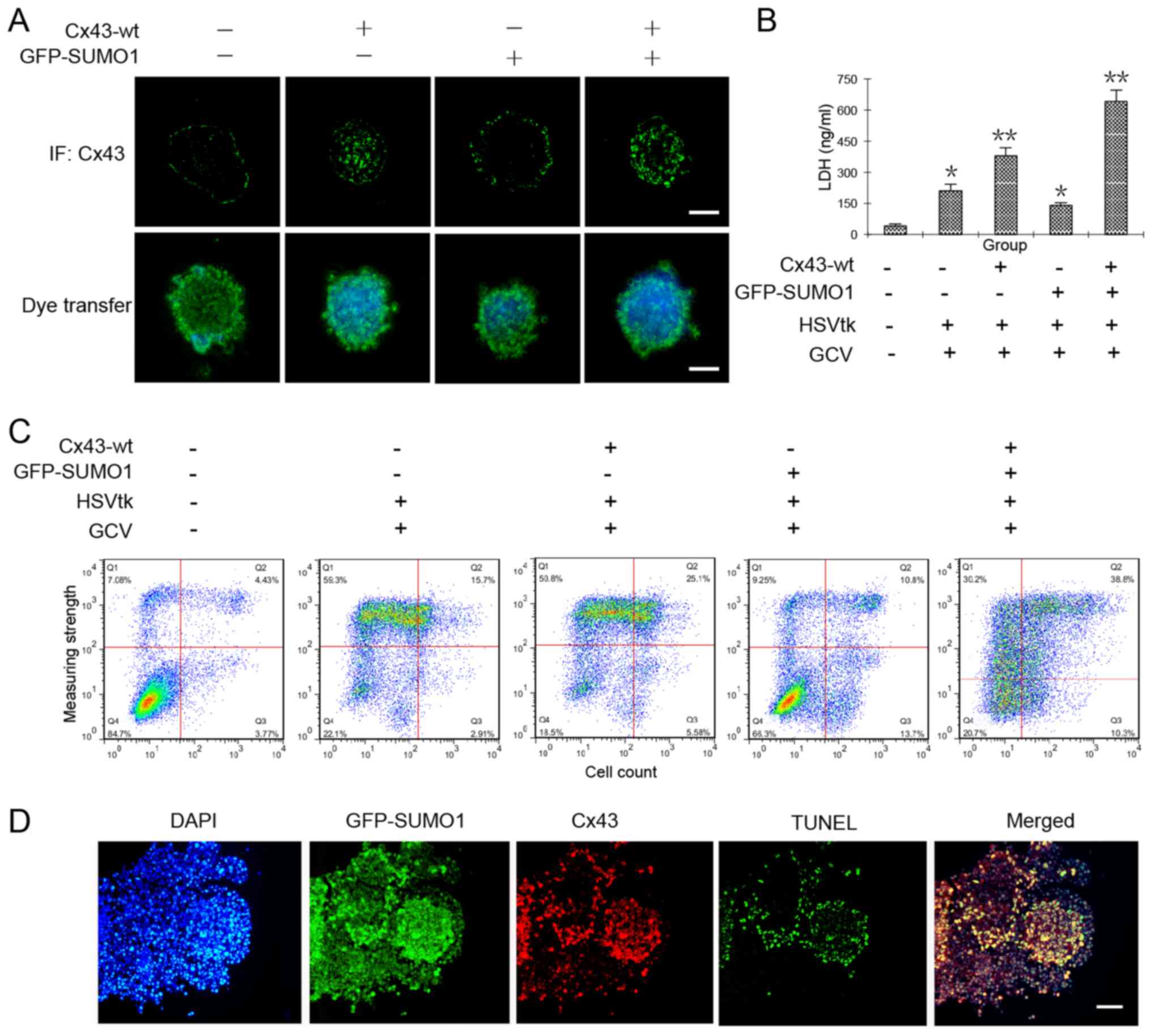
|
1
|
Kudo M, Trevisani F, Abou-Alfa GK and
Rimassa L: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic guidelines and
medical treatment. Liver Cancer. 6:16–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Z, Li Z, Ye Y, Xie L and Li W:
Oxidative stress and liver cancer: Etiology and therapeutic
targets. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:78915742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Castelli G, Pelosi E and Testa U: Liver
cancer: Molecular characterization, clonal evolution and cancer
stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 9:E1272017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Salem AI and Winslow ER: Current technical
aspects of oncological hepatic surgery. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 16:147–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim PT, Jang J, Fischer S, Greig PD,
Gallinger S, Wei AC, McGilivray IM, Cattral MS and Cleary SP: Liver
resection for multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
30(Suppl 4): 3552012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cong WM and Wu MC: New insights into
molecular diagnostic pathology of primary liver cancer: Advances
and challenges. Cancer Lett. 368:14–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Büttner N, Schmidt N and Thimme R:
Perspectives of immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Z
Gastroenterol. 54:1334–1342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nishida N, Kitano M, Sakurai T and Kudo M:
Molecular mechanism and prediction of sorafenib chemoresistance in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 33:771–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watson ME, Diepeveen LA, Stubbs KA and
Yeoh GC: Glycosylation-related diagnostic and therapeutic drug
target markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver
Dis. 24:349–357. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu K, Yang L, Huang Z, Zhao H, Wang J and
Xu S: A double suicide gene system driven by vascular endothelial
growth factor promoter selectively kills human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 11:3152–3160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Wang S, Guo X, Wei F, Yin J, Zang
Y, Li N and Chen D: Exogenous p53 and ASPP2 expression enhances
rAdV-TK/GCV-induced death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells lacking
functional p53. Oncotarget. 7:18896–18905. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JH, Kim KI, Lee KC, Lee YJ, Lee TS,
Chung WS, Lim SM and Kang JH: Assessment of α-fetoprotein targeted
HSV1-tk expression in hepatocellular carcinoma with in vivo
imaging. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 30:8–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Qin SK, Wu Q, Wang ZS, Zheng RS,
Tong XH, Liu H, Tao L and He XD: Connexin-dependent gap junction
enhancement is involved in the synergistic effect of sorafenib and
all-trans retinoic acid on HCC growth inhibition. Oncol Rep.
31:540–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Da Silva-Ferrada E, Ribeiro-Rodrigues TM,
Rodríguez MS and Girão H: Proteostasis and SUMO in the heart. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 79:443–450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bettermann K, Benesch M, Weis S and
Haybaeck J: SUMOylation in carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
316:113–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kjenseth A, Fykerud TA, Sirnes S, Bruun J,
Yohannes Z, Kolberg M, Omori Y, Rivedal E and Leithe E: The gap
junction channel protein connexin 43 is covalently modified and
regulated by SUMOylation. J Biol Chem. 287:15851–15861. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Z, Jiang Z, Huang J, Huang S, Li Y, Yu
S, Yu S and Liu X: miR-7 inhibits glioblastoma growth by
simultaneously interfering with the PI3K/ATK and Raf/MEK/ERK
pathways. Int J Oncol. 44:1571–1580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sin WC, Crespin S and Mesnil M: Opposing
roles of connexin43 in glioma progression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1818:2058–2067. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Grek CL, Rhett JM, Bruce JS, Ghatnekar GS
and Yeh ES: Connexin 43, breast cancer tumor suppressor: Missed
connections? Cancer Lett. 374:117–126. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leithe E: Regulation of connexins by the
ubiquitin system: Implications for intercellular communication and
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1865:133–146. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Khan IS and Ehtesham M: Isolation and
characterization of stem cells from human central nervous system
malignancies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 853:33–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mattoscio D and Chiocca S: SUMO pathway
components as possible cancer biomarkers. Future Oncol.
11:1599–1610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Amelio I, Landré V, Knight RA, Lisitsa A,
Melino G and Antonov AV: Polypharmacology of small molecules
targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome and ubiquitin-like systems.
Oncotarget. 6:9646–9656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang XJ and Chiang CM: Sumoylation in gene
regulation, human disease, and therapeutic action. F1000Prime Rep.
5:452013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bettermann K, Benesch M, Weis S and
Haybaeck J: SUMOylation in carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
316:113–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu Y, Guo Z, Wu H, Wang X, Yang L, Shi X,
Du J, Tang B, Li W, Yang L, et al: SUMOylation represses Nanog
expression via modulating transcription factors Oct4 and Sox2. PLoS
One. 7:e396062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei F, Schöler HR and Atchison ML:
Sumoylation of Oct4 enhances its stability, DNA binding, and
transactivation. J Biol Chem. 282:21551–21560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han X, Wang XL, Li Q, Dong XX, Zhang JS
and Yan QC: HIF-1α SUMOylation affects the stability and
transcriptional activity of HIF-1α in human lens epithelial cells.
Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 253:1279–1290. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gu J, Fan Y, Liu X, Zhou L, Cheng J, Cai R
and Xue S: SENP1 protects against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion
injury via a HIF1α-dependent pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 104:83–92.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maqbool R, Rashid R, Ismail R, Niaz S,
Chowdri NA and Hussain MU: The carboxy-terminal domain of connexin
43 (CT-Cx43) modulates the expression of p53 by altering miR-125b
expression in low-grade human breast cancers. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
38:443–451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fu Y, Shao ZM, He QZ, Jiang BQ, Wu Y and
Zhuang ZG: Hsa-miR-206 represses the proliferation and invasion of
breast cancer cells by targeting Cx43. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:2091–2104. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mauro V, Carette D, Pontier-Bres R,
Dompierre J, Czerucka D, Segretain D, Gilleron J and Pointis G: The
anti-mitotic drug griseofulvin induces apoptosis of human germ cell
tumor cells through a connexin 43-dependent molecular mechanism.
Apoptosis. 18:480–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|