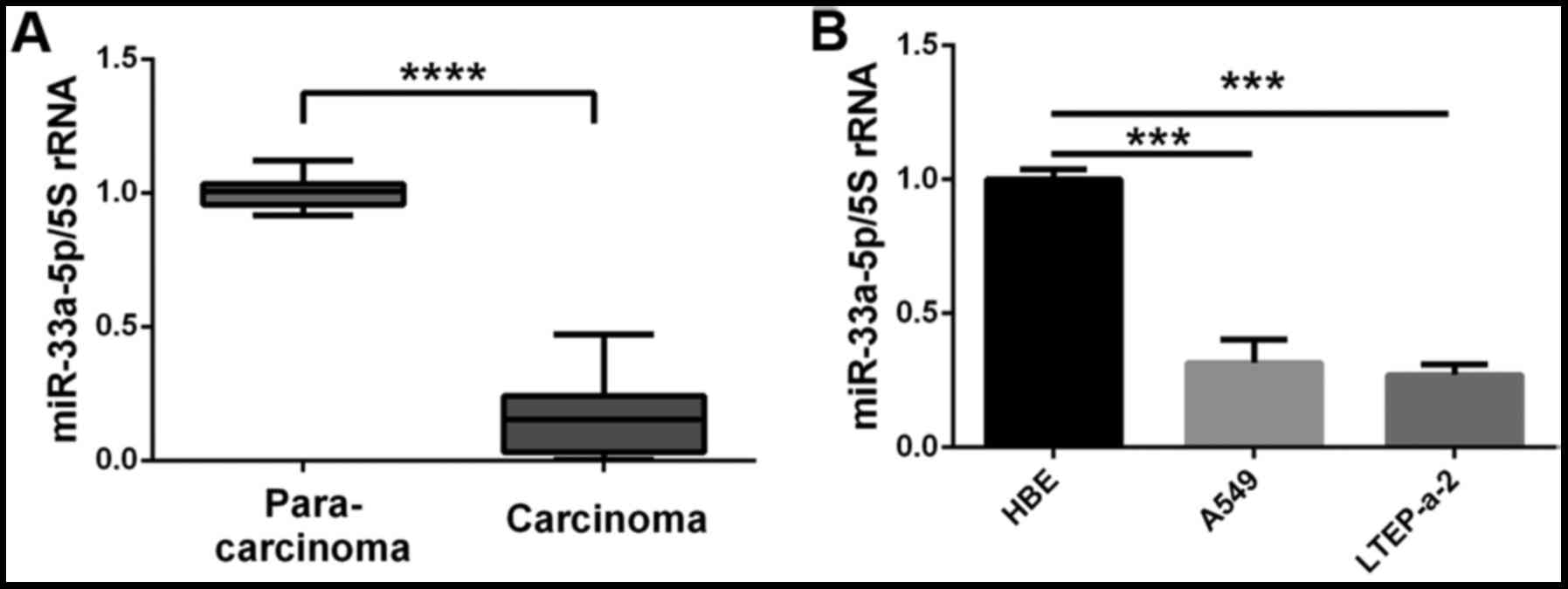
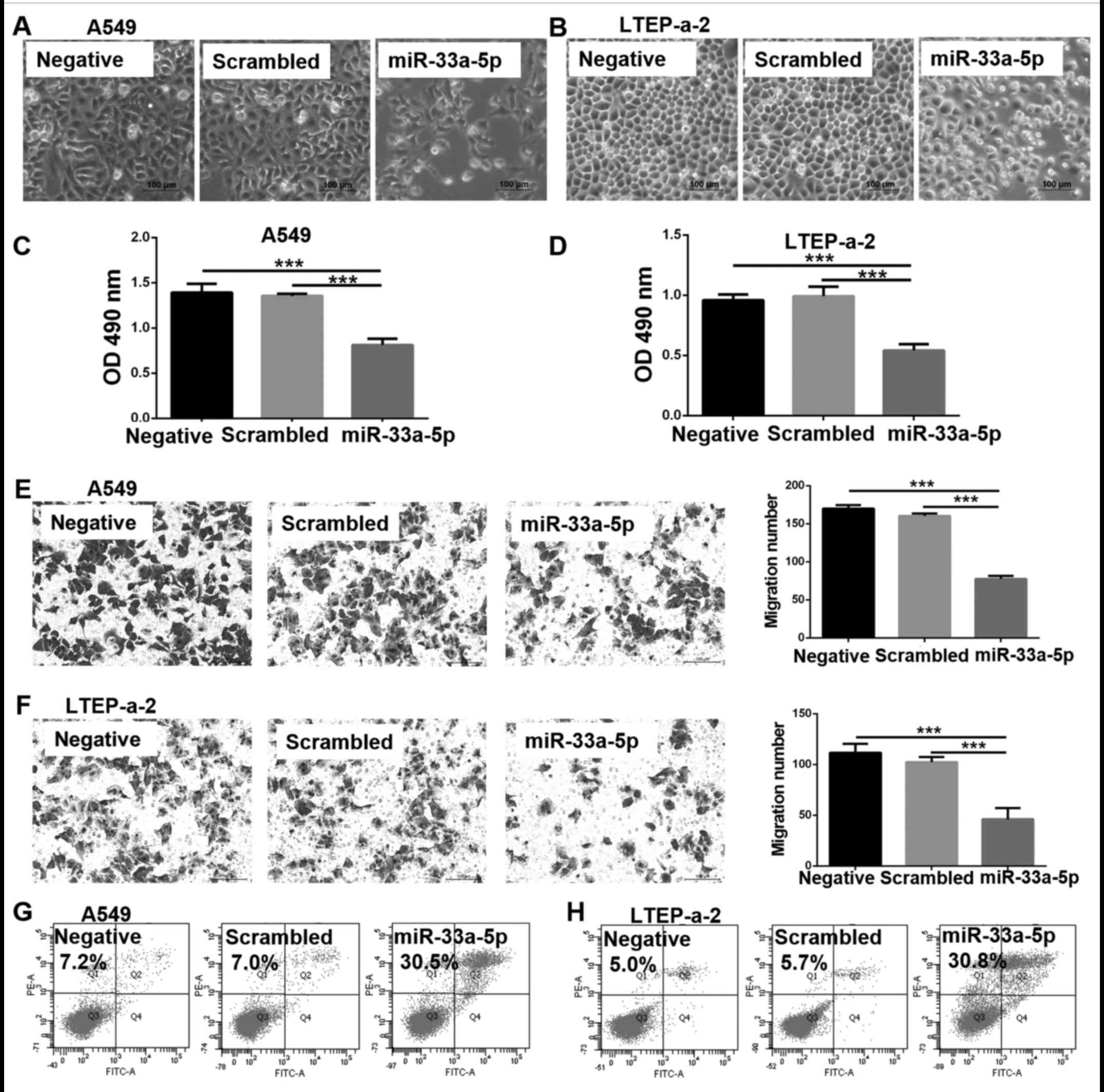
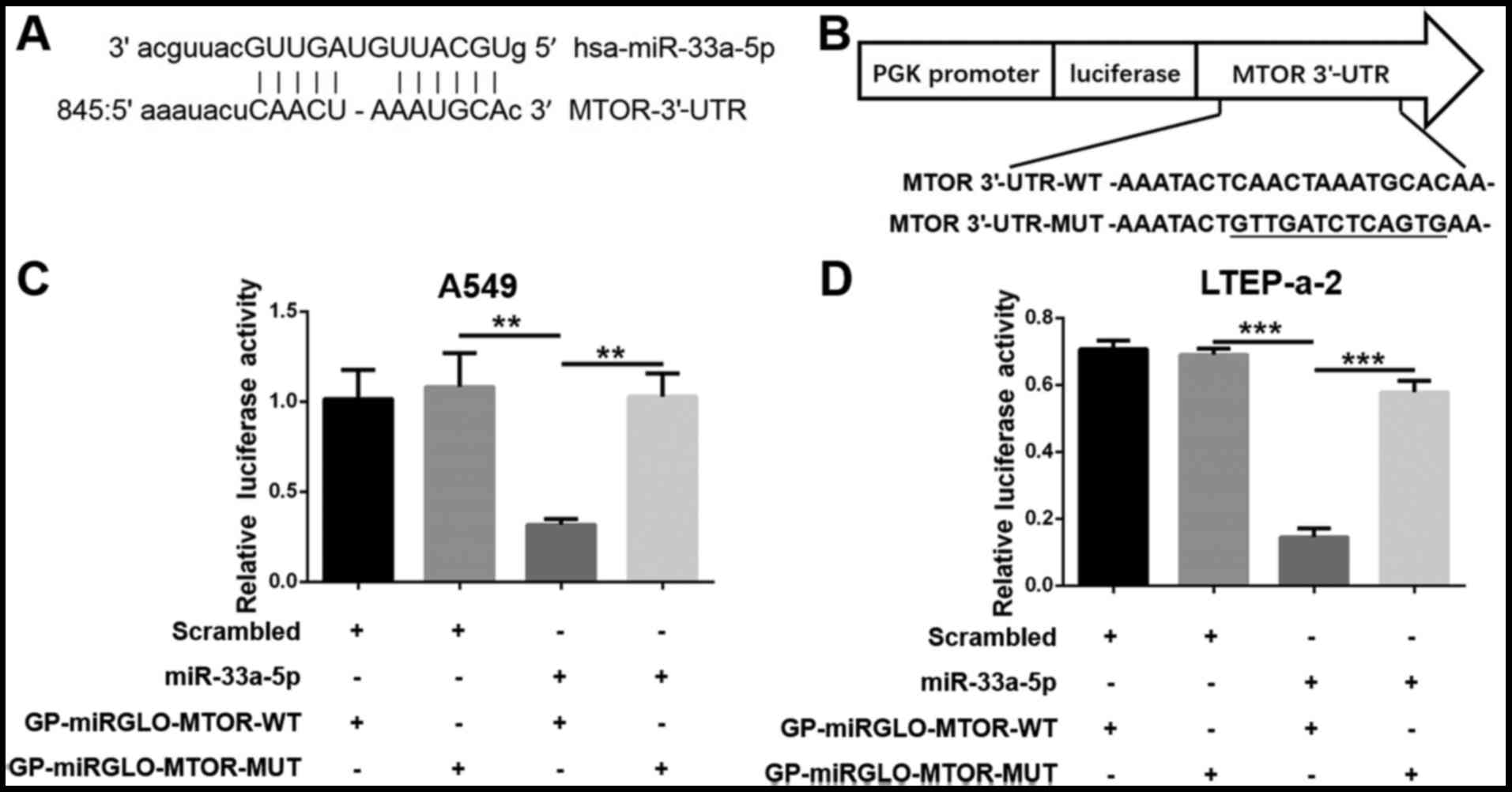
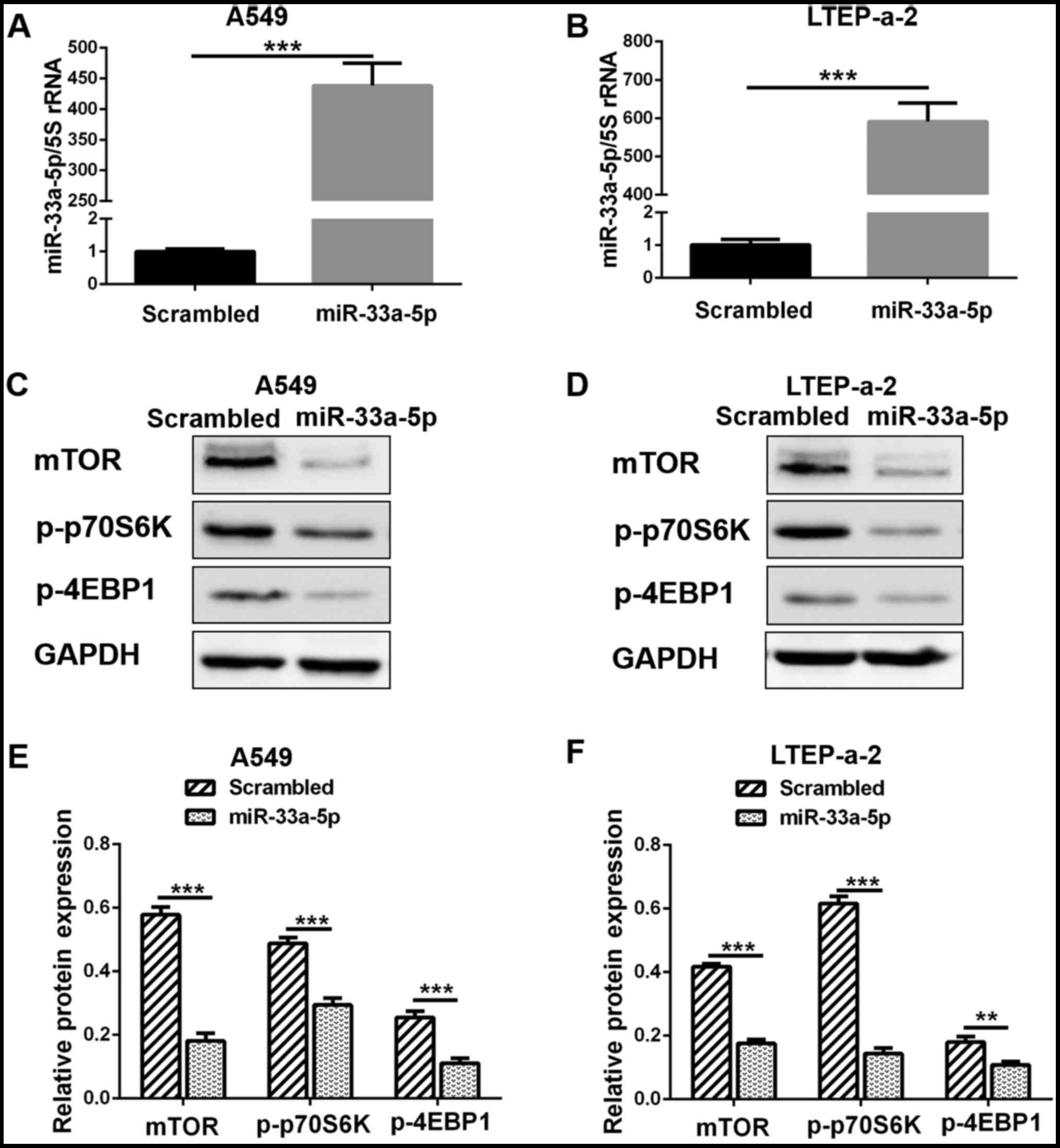
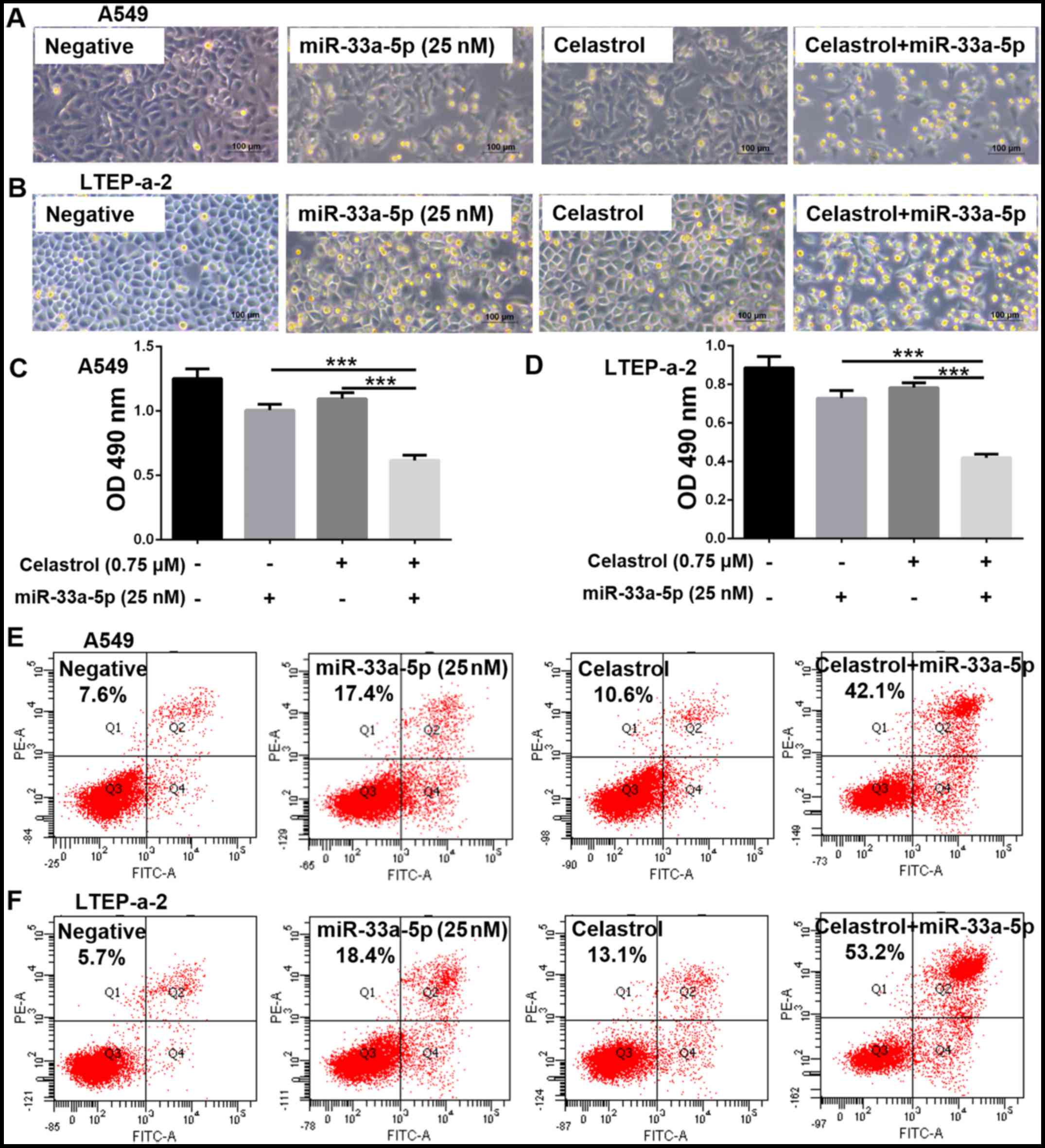
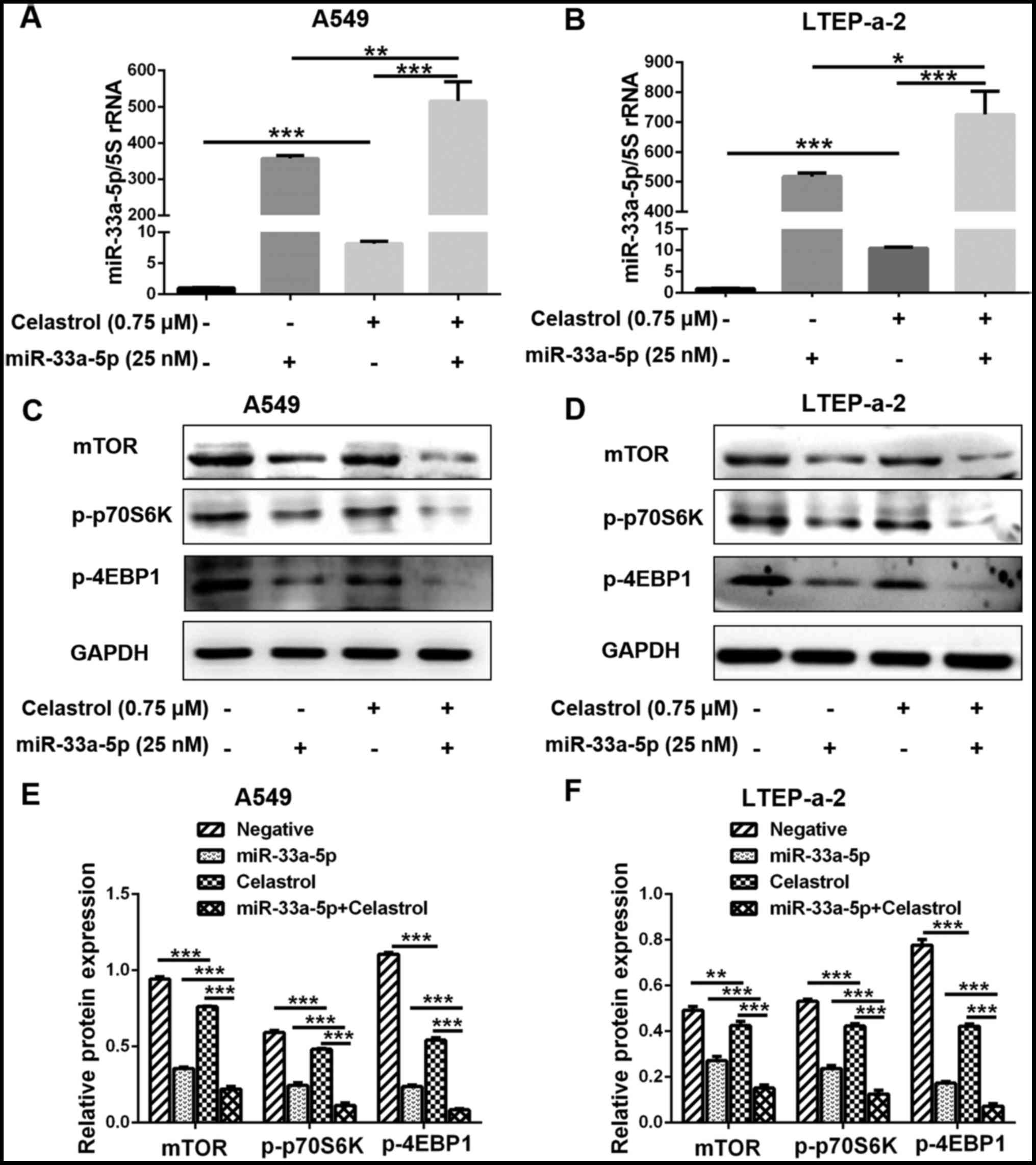
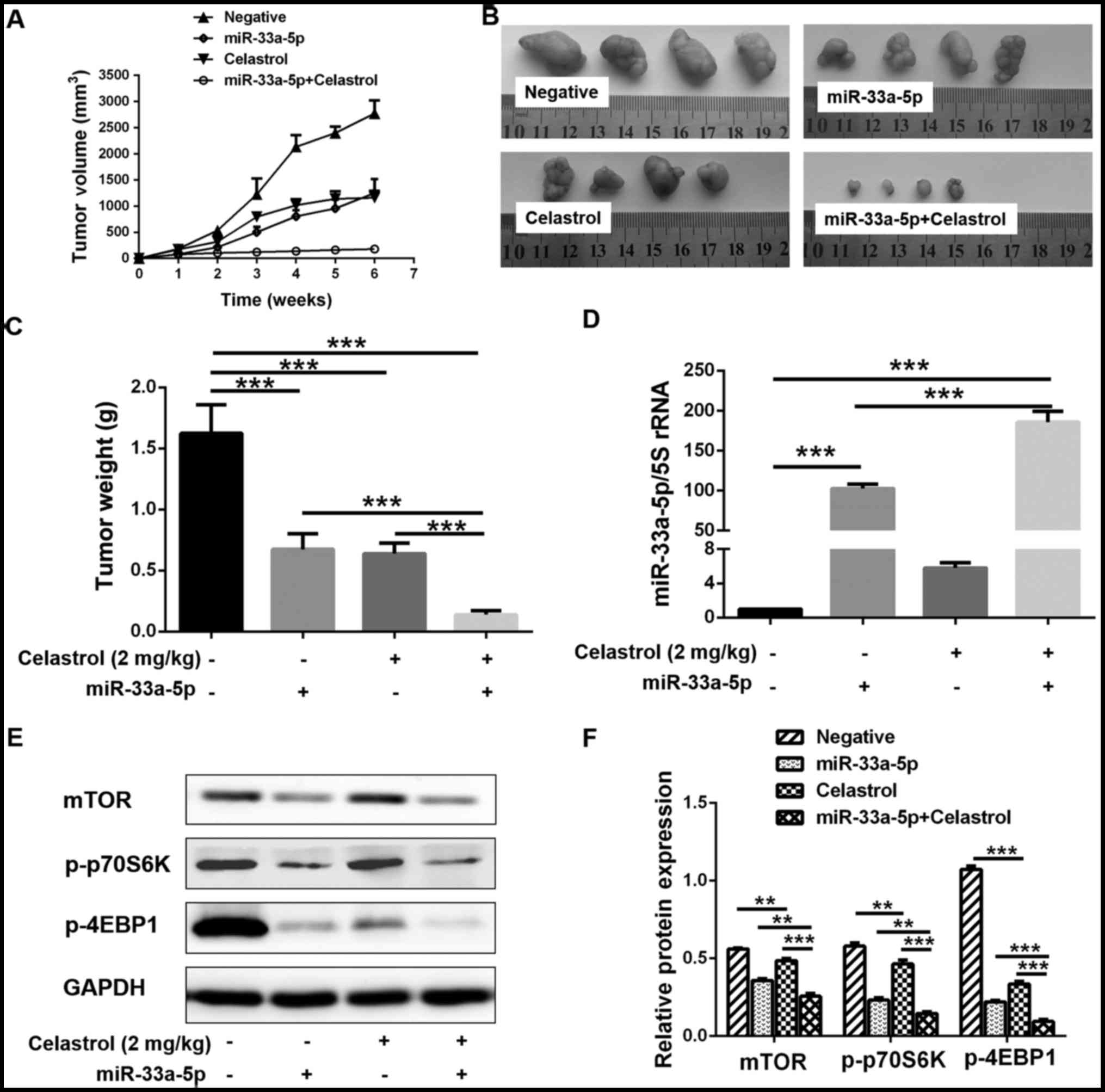
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Akerley W, Bazhenova
LA, Borghaei H, Camidge DR, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA,
Demmy TL, et al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 1. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 12:1738–1761. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tan CS, Gilligan D and Pacey S: Treatment
approaches for EGFR-inhibitor-resistant patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 16:e447–e459. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Lin Y, Huang Z
and Luo Q: MiR-33a suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and
metastasis by targeting ADAM9 and ROS1. Protein Cell. 6:881–889.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pu M, Li C, Qi X, Chen J, Wang Y, Gao L,
Miao L and Ren J: MiR-1254 suppresses HO-1 expression through seed
region-dependent silencing and non-seed interaction with TFAP2A
transcript to attenuate NSCLC growth. PLoS Genet. 13:e10068962017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo X, Zhu Y and Hong X, Zhang M, Qiu X,
Wang Z, Qi Z and Hong X: miR-181d and c-myc-mediated inhibition of
CRY2 and FBXL3 reprograms metabolism in colorectal cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e29582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Azmi AS, Li Y, Muqbil I, Aboukameel A,
Senapedis W, Baloglu E, Landesman Y, Shacham S, Kauffman MG, Philip
PA, et al: Exportin 1 (XPO1) inhibition leads to restoration of
tumor suppressor miR-145 and consequent suppression of pancreatic
cancer cell proliferation and migration. Oncotarget. 8:82144–82155.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Z, Sun F, Hong Y, Liu Y, Fen M, Yin K,
Ge X, Wang F, Chen X and Guan W: MEG2 is regulated by miR-181a-5p
and functions as a tumour suppressor gene to suppress the
proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
16:1332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li Y,
Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE and Näär AM: MicroRNA-33 and the
SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis.
Science. 328:1566–1569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mao M, Lei H, Liu Q, Chen Y, Zhao L, Li Q,
Luo S, Zuo Z, He Q, Huang W, et al: Effects of miR-33a-5P on
ABCA1/G1-mediated cholesterol efflux under inflammatory stress in
THP-1 macrophages. PLoS One. 9:e1097222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang L, Yang J, Li J, Shen X, Le Y, Zhou
C, Wang S, Zhang S, Xu D and Gong Z: MircoRNA-33a inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis and could be a
prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep.
5:136772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Xia F, Ma L, Shan J, Shen J, Yang Z,
Liu J, Cui Y, Bian X, Bie P, et al: MicroRNA-122 sensitizes HCC
cancer cells to adri-amycin and vincristinethrough modulating
expression of MDR and inducing cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett.
310:160–169. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu X, Li Y, Xie C, Yin X, Liu Y, Cao Y,
Fang Y, Lin X, Xu Y, Xu W, et al: miR-145 sensitizes ovarian cancer
cells to paclitaxel by targeting Sp1 and Cdk6. Int J Cancer.
135:1286–1296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang R, Gu X, Dai W, Ye J, Lu F, Chai Y,
Fan G, Gonzalez FJ, Duan G and Qi Y: A lipidomics investigation
into the intervention of celastrol in experimental colitis. Mol
Biosyst. 12:1436–1444. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L, Li Y, Ren J, Zhu C, Fu J, Lin D
and Qiu Y: Celastrol attenuates inflammatory and neuropathic pain
mediated by cannabinoid receptor type 2. Int J Mol Sci.
15:13637–13648. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu L, Bai W, Li S, Zhang Y, Han Y, Gu Y,
Meng G, Xie L, Wang J, Xiao Y, et al: Celastrol prevents
atherosclerosis via inhibiting LOX-1 and oxidative stress. PLoS
One. 8:e654772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang W, He W, Li PP, Song SS, Yuan PF, Lu
JT and Wei W: Protective effects of celastrol on
diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats and its
mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 784:173–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shao L, Zhou Z, Cai Y, Castro P, Dakhov O,
Shi P, Bai Y, Ji H, Shen W and Wang J: Celastrol suppresses tumor
cell growth through targeting an AR-ERG-NF-κB pathway in
TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene expressing prostate cancer. PLoS One.
8:e583912013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang HS, Kim JY, Lee JH, Lee BW, Park KH,
Shim KH, Lee MK and Seo KI: Celastrol isolated from Tripterygium
regelii induces apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and
-independent pathways in human breast cancer cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:527–532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) methods. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang X, Chen S and Wang Y: Honokiol
up-regulates prostacyclin synthease protein expression and inhibits
endothelial cell apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 554:1–7. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Labak CM, Wang PY, Arora R, Guda MR,
Asuthkar S, Tsung AJ and Velpula KK: Glucose transport: Meeting the
metabolic demands of cancer, and applications in glioblastoma
treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1599–1608. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang R, Zhang C, Liu G, Gu R and Wu H:
MicroRNA-101 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in
osteosarcoma cells by targeting ROCK1. Am J Cancer Res. 7:88–97.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baranwal and Alahari SK: miRNA control of
tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 126:1283–1290.
2010.
|
|
25
|
Li H, Chen H, Wang H, Dong Y, Yin M, Zhang
L and Wei J: MicroRNA-374a promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation by targeting mitogen-inducible gene-6 (MIG-6). Oncol
Res. Jul 21–2017.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Bu J, Liu X, Wang W, Mai W, Lv B,
Zou J, Mo X, Li X, Wang J, et al: miR-133b suppresses metastasis by
targeting HOXA9 in human colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:63935–63948. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu Y, Qin T, Li J, Wang L, Zhang Q, Jiang
Z and Mao J: MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits invasion and angiogenesis
through targeting VEGF-A in breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
24:386–392. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Zhou X, Shan B, Han J, Wang F, Fan
X, Lv Y, Chang L and Liu W: Downregulation of microRNA-33a promotes
cyclin-dependent kinase 6, cyclin D1 and PIM1 expression and
gastric cancer cell proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 12:6491–6500. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang W, Zhang L, Xian Y and Yu Z:
MicroRNA-33a promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by
targeting PPARα in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Ther Med.
13:2507–2514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei F, Ma C, Zhou T, Dong X, Luo Q, Geng
L, Ding L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Li N, et al: Exosomes derived from
gemcitabine-resistant cells transfer malignant phenotypic traits
via delivery of miRNA-222-3p. Mol Cancer. 16:1322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li JA, Wang YD, Wang K, Wang ZL, Jia DY,
Yang BY and Xiong CB: Downregulation of miR-214-3p may contribute
to pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis via targeting STAT6. BioMed
Res Int. 2017:85249722017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Perl A: mTOR activation is a biomarker and
a central pathway to autoimmune disorders, cancer, obesity, and
aging. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1346:33–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lekmine F, Uddin S, Sassano A, Parmar S,
Brachmann SM, Majchrzak B, Sonenberg N, Hay N, Fish EN and
Platanias LC: Activation of the p70 S6 kinase and phosphorylation
of the 4E-BP1 repressor of mRNA translation by type I interferons.
J Biol Chem. 278:27772–27780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mi C, Ma J, Wang KS, Zuo HX, Wang Z, Li
MY, Piao LX, Xu GH, Li X, Quan ZS, et al: Imperatorin suppresses
proliferation and angiogenesis of human colon cancer cell by
targeting HIF-1α via the mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 and MAPK pathways. J
Ethnopharmacol. 203:27–38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karatas OF, Wang J, Shao L, Ozen M, Zhang
Y, Creighton CJ and Ittmann M: miR-33a is a tumor suppressor
microRNA that is decreased in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
8:60243–60256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tian F, Wei H, Tian H, Qiu Y and Xu J:
miR-33a is downregulated in melanoma cells and modulates cell
proliferation by targeting PCTAIRE1. Oncol Lett. 11:2741–2746.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS and Hsu
YL: MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung
cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3756–3766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo J, Mei Y, Li K, Huang X and Yang H:
Downregulation of miR-17-92a cluster promotes autophagy induction
in response to celastrol treatment in prostate cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:804–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li H, Li Y, Liu D, Sun H and Liu J:
miR-224 is critical for celastrol-induced inhibition of migration
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:448–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lu W, Hu Y, Ma Q, Zhou L, Jiang L, Li Z,
Zhao S, Xu Y, Shi W, Li S, et al: miR-223 increases gallbladder
cancer cell sensitivity to docetaxel by downregulating STMN1.
Oncotarget. 7:62364–62376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen LG, Xia YJ and Cui Y: Upregulation of
miR-101 enhances the cytotoxic effect of anticancer drugs through
inhibition of colon cancer cell proliferation. Oncol Rep.
38:100–108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Asukai K, Kawamoto K, Eguchi H, Konno M,
Asai A, Iwagami Y, Yamada D, Asaoka T, Noda T, Wada H, et al:
Micro-RNA-130a-3p regulates gemcitabine resistance via PPARG in
cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:2344–2352. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|