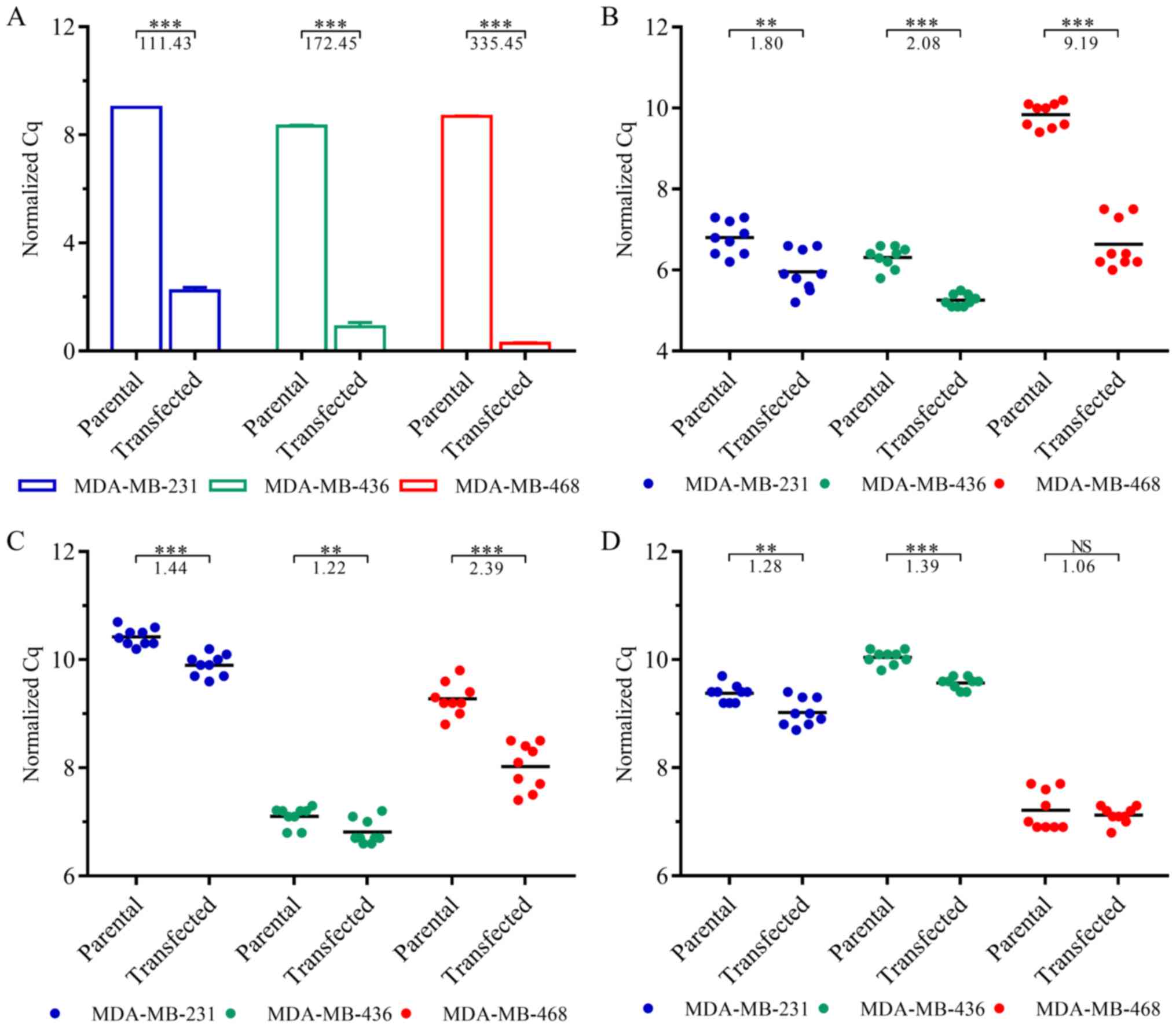
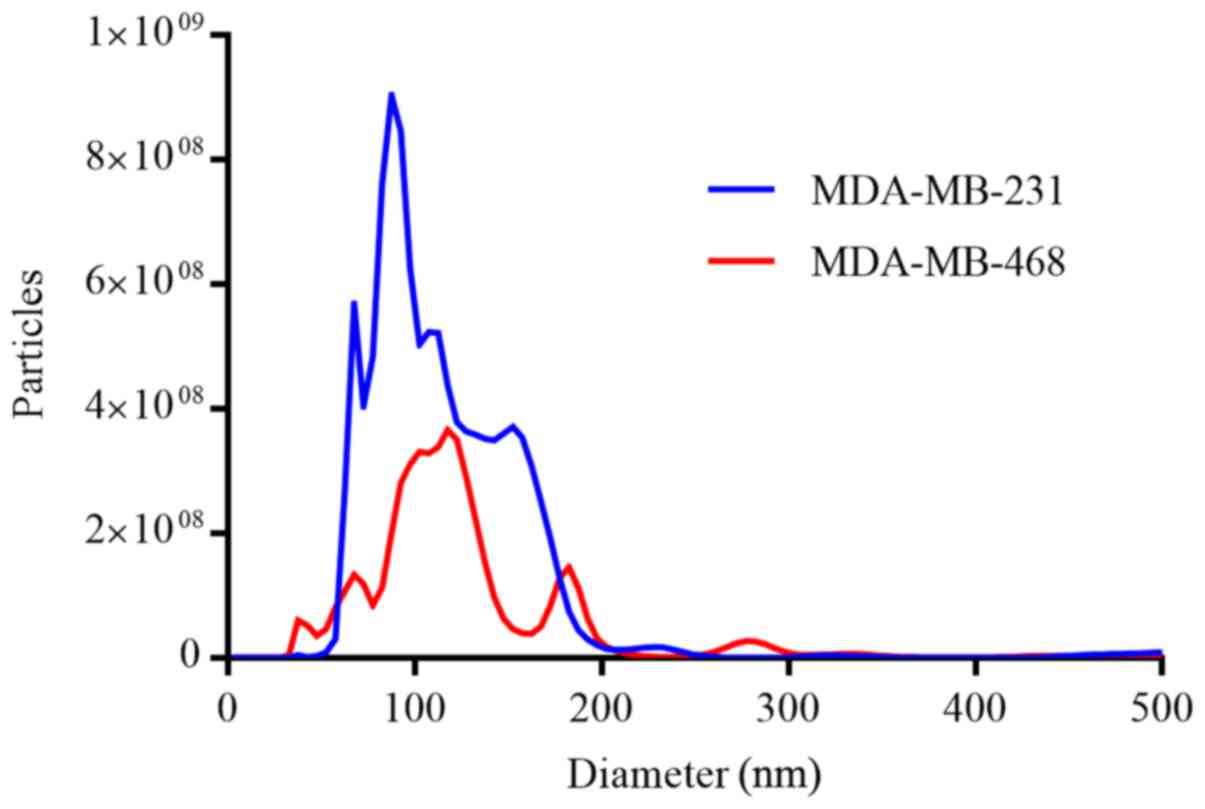
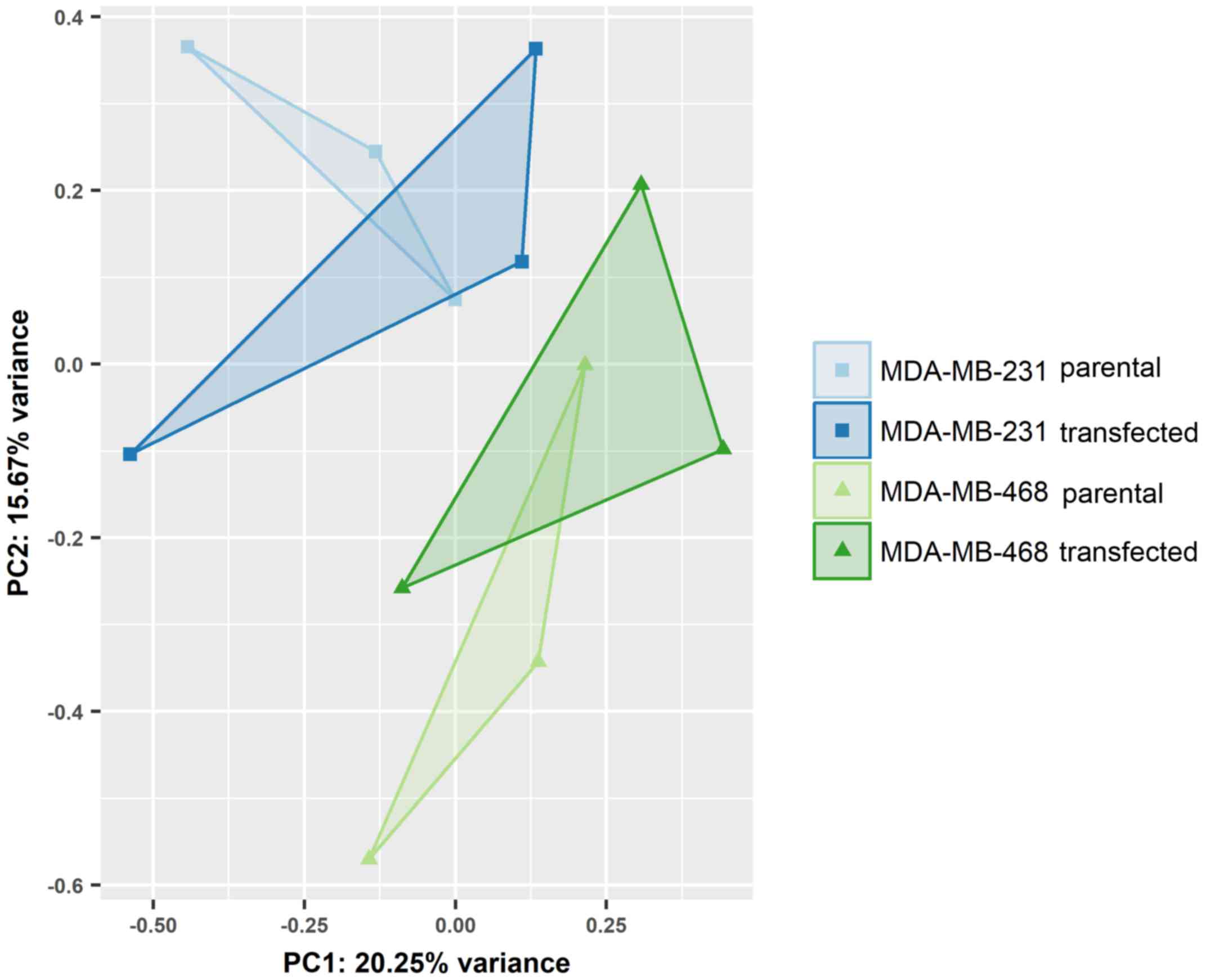
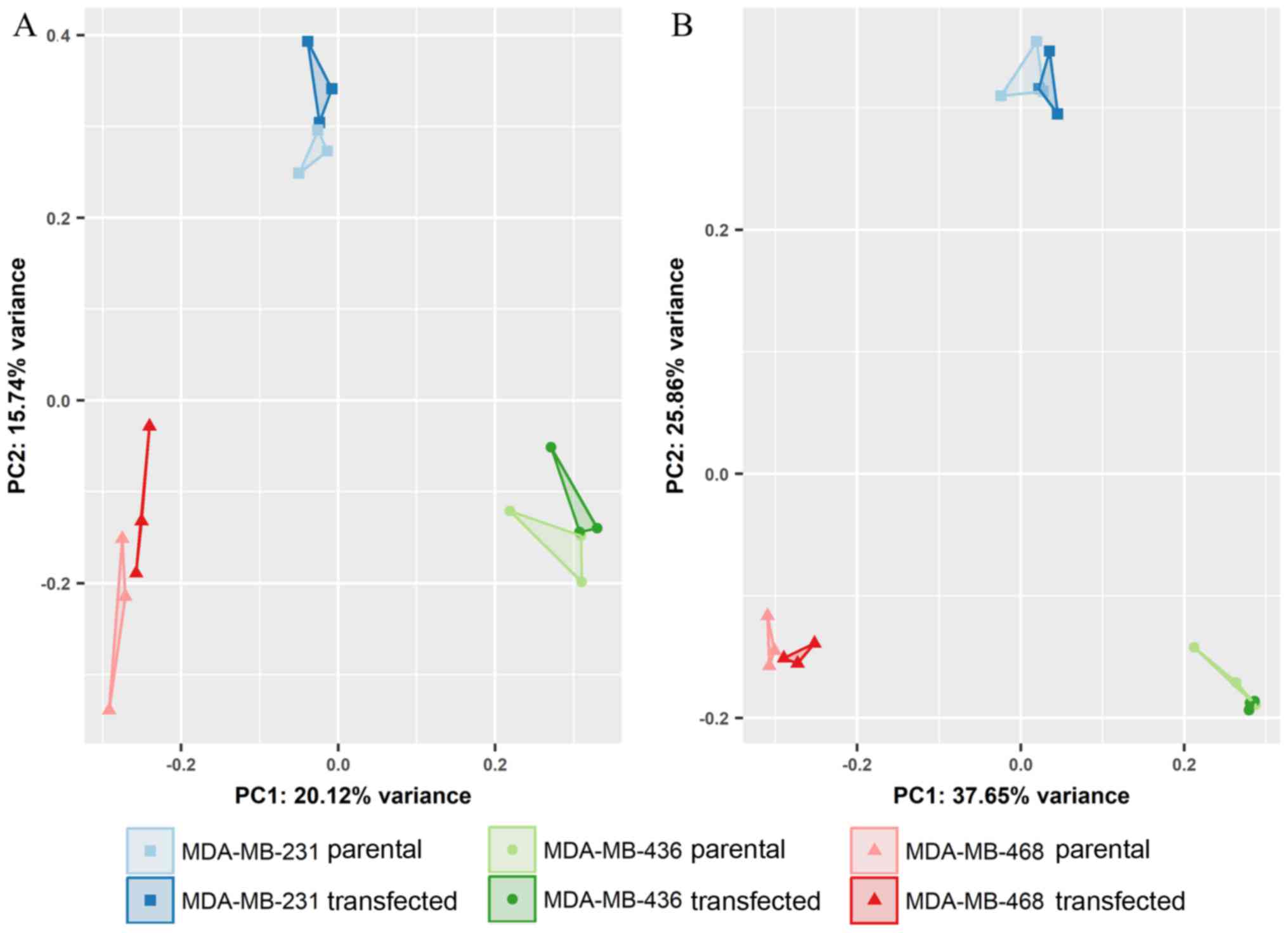
|
1
|
Ataollahi MR, Sharifi J, Paknahad MR and
Paknahad A: Breast cancer and associated factors: A review. J Med
Life. 8:6–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malvezzi M, Bertuccio P, Levi F, La
Vecchia C and Negri E: European cancer mortality predictions for
the year 2014. Ann Oncol. 25:1650–1656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wahba HA and El-Hadaad HA: Current
approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Biol Med. 12:106–116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yagata H, Kajiura Y and Yamauchi H:
Current strategy for triple-negative breast cancer: Appropriate
combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Breast Cancer.
18:165–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hurvitz S and Mead M: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Advancements in characterization and treatment
approach. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 28:59–69. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Sundahl N, Clarisse D, Bracke M, Offner F,
Berghe WV and Beck IM: Selective glucocorticoid receptor-activating
adjuvant therapy in cancer treatments. Oncoscience. 3:188–202.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Z, Lan X, Wu D, Sunkel B, Ye Z, Huang
J, Liu Z, Clinton SK, Jin VX and Wang Q: Ligand-dependent genomic
function of glucocorticoid receptor in triple-negative breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 6:83232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Skor MN, Wonder EL, Kocherginsky M, Goyal
A, Hall BA, Cai Y and Conzen SD: Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism
as a novel therapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:6163–6172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tessel MA, Krett NL and Rosen ST: Steroid
receptor and microRNA regulation in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol.
22:592–597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Devaney A, McNeill
RE, Davoren PA, Lemetre C, Benes V, Schmidt S, Blake J, Ball G, et
al: MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone
receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 11:R272009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang YY, Kuo WH, Hung JH, Lee CY, Lee YH,
Chang YC, Lin WC, Shen CY, Huang CS, Hsieh FJ, et al: Deregulated
microRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer revealed by deep
sequencing. Mol Cancer. 14:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cascione L, Gasparini P, Lovat F, Carasi
S, Pulvirenti A, Ferro A, Alder H, He G, Vecchione A, Croce CM, et
al: Integrated microRNA and mRNA signatures associated with
survival in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e559102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Falcone G, Felsani A and D'Agnano I:
Signaling by exosomal microRNAs in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harris DA, Patel SH, Gucek M, Hendrix A,
Westbroek W and Taraska JW: Exosomes released from breast cancer
carcinomas stimulate cell movement. PLoS One. 10:e01174952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
O'Brien K, Rani S, Corcoran C, Wallace R,
Hughes L, Friel AM, McDonnell S, Crown J, Radomski MW and
O'Driscoll L: Exosomes from triple-negative breast cancer cells can
transfer phenotypic traits representing their cells of origin to
secondary cells. Eur J Cancer. 49:1845–1859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh R, Pochampally R, Watabe K, Lu Z and
Mo YY: Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion
in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:2562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Li Q, Li J, Ma X, Xing J,
Rong S, Wu Z, Tian Y, Li J, et al: MiRNAs predict the prognosis of
patients with triple negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 12:e01700882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu LL, Zhao H, Ma TF, Ge F, Chen CS and
Zhang YP: Identification of valid reference genes for the
normalization of RT-qPCR expression studies in human breast cancer
cell lines treated with and without transient transfection. PLoS
One. 10:e01170582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Spornraft M, Kirchner B, Haase B, Benes V,
Pfaffl MW and Riedmaier I: Optimization of extraction of
circulating RNAs from plasma - enabling small RNA sequencing. PLoS
One. 9:e1072592014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Andrews S: FastQC: a quality control tool
for high throughput sequence data. http://www.citeulike.org/user/nailest/article/11583827.
Accessed Nov 21, 2017.
|
|
23
|
Kong Y: Btrim: A fast, lightweight adapter
and quality trimming program for next-generation sequencing
technologies. Genomics. 98:152–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Buschmann D, Haberberger A, Kirchner B,
Spornraft M, Riedmaier I, Schelling G and Pfaffl MW: Toward
reliable biomarker signatures in the age of liquid biopsies - how
to standardize the small RNA-Seq workflow. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:5995–6018. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Consortium RN; RNAcentral Consortium:
RNAcentral: An international database of ncRNA sequences. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43D:D123–D129. 2015.
|
|
26
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(D1): D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M and Salzberg
SL: Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences
to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10:R252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T,
Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G and Durbin R; 1000 Genome
Project Data Processing Subgroup: The Sequence Alignment/Map format
and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25:2078–2079. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Vandesompele J, Kubista M and Pfaffl MW:
Reference gene validation software for improved normalization.
Real-Time PCR: Current Technology and Applications. Logan J,
Edwards K and Saunders N: Caister Academic Press; London: pp.
47–64. 2009
|
|
31
|
Andersen CL, Jensen JL and Ørntoft TF:
Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR
data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes
suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data
sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
'walking' the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES and Golub
TR: A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors.
Nat Genet. 33:49–54. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu NZ and Cidlowski JA: Glucocorticoid
receptor isoforms generate transcription specificity. Trends Cell
Biol. 16:301–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reeder A, Attar M, Nazario L, Bathula C,
Zhang A, Hochbaum D, Roy E, Cooper KL, Oesterreich S, Davidson NE,
et al: Stress hormones reduce the efficacy of paclitaxel in triple
negative breast cancer through induction of DNA damage. Br J
Cancer. 112:1461–1470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McNamara KM, Kannai A and Sasano H:
Possible roles for glucocorticoid signalling in breast cancer. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. S0303-7207(17)30358-1. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu W, Pew T, Zou M, Pang D and Conzen SD:
Glucocorticoid receptor-induced MAPK phosphatase-1 (MPK-1)
expression inhibits paclitaxel-associated MAPK activation and
contributes to breast cancer cell survival. J Biol Chem.
280:4117–4124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Maiyar AC, Phu PT, Huang AJ and Firestone
GL: Repression of glucocorticoid receptor transactivation and DNA
binding of a glucocorticoid response element within the
serum/glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (sgk) gene promoter
by the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Mol Endocrinol. 11:312–329.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ayroldi E and Riccardi C:
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ): A new important
mediator of glucocorticoid action. FASEB J. 23:3649–3658. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK,
Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF,
Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, et al: Argonaute2 complexes
carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles
in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5003–5008. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM,
Shamburek RD and Remaley AT: MicroRNAs are transported in plasma
and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat
Cell Biol. 13:423–433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Puimège L, Van Hauwermeiren F, Steeland S,
Van Ryckeghem S, Vandewalle J, Lodens S, Dejager L, Vandevyver S,
Staelens J, Timmermans S, et al: Glucocorticoid-induced
microRNA-511 protects against TNF by down-regulating TNFR1. EMBO
Mol Med. 7:1004–1017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Smith LK, Tandon A, Shah RR, Mav D,
Scoltock AB and Cidlowski JA: Deep sequencing identification of
novel glucocorticoid-responsive miRNAs in apoptotic primary
lymphocytes. PLoS One. 8:e783162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang ZH, Liang YB, Tang H, Chen ZB, Li ZY,
Hu XC and Ma ZF: Dexamethasone down-regulates the expression of
microRNA-155 in the livers of septic mice. PLoS One. 8:e805472013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mathe A, Scott RJ and Avery-Kiejda KA:
MiRNAs and other epigenetic changes as biomarkers in triple
negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:28347–28376. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Vrekoussis T,
Kafousi M, Spandidos DA and Stathopoulos EN: MicroRNA expression
analysis in triple-negative (ER, PR and Her2/neu) breast cancer.
Cell Cycle. 10:507–517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rainer J, Ploner C, Jesacher S, Ploner A,
Eduardoff M, Mansha M, Wasim M, Panzer-Grümayer R, Trajanoski Z,
Niederegger H, et al: Glucocorticoid-regulated microRNAs and
mirtrons in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 23:746–752.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shao Y, Gu W, Ning Z, Song X, Pei H and
Jiang J: Evaluating the prognostic value of microRNA-203 in solid
tumors based on a meta-analysis and the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)
Datasets. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1468–1480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
He S, Zhang G, Dong H, Ma M and Sun Q:
miR-203 facilitates tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
fibroblast growth factor 2 in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
9:6203–6210. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liang Y, Yang W, Zhu Y and Yuan Y:
Prognostic role of microRNA-203 in various carcinomas: Evidence
from a meta-analysis involving 13 studies. Springerplus.
5:15382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ding X, Park SI, McCauley LK and Wang CY:
Signaling between transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and
transcription factor SNAI2 represses expression of microRNA miR-203
to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis.
J Biol Chem. 288:10241–10253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C and Shi Y:
MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Z, Zhang B, Li W, Fu L, Fu L, Zhu Z
and Dong JT: Epigenetic silencing of miR-203 upregulates SNAI2 and
contributes to the invasiveness of malignant breast cancer cells.
Genes Cancer. 2:782–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Laxman N, Rubin CJ, Mallmin H, Nilsson O,
Tellgren-Roth C and Kindmark A: Second generation sequencing of
microRNA in human bone cells treated with parathyroid hormone or
dexamethasone. Bone. 84:181–188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Choi C, Kwon J, Lim S and Helfman DM:
Integrin β1, myosin light chain kinase and myosin IIA are required
for activation of PI3K-AKT signaling following MEK inhibition in
metastatic triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:63466–63487. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cui WJ, Liu Y, Zhou XL, Wang FZ, Zhang XD
and Ye LH: Myosin light chain kinase is responsible for high
proliferative ability of breast cancer cells via anti-apoptosis
involving p38 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:725–732. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sundararajan V, Gengenbacher N, Stemmler
MP, Kleemann JA, Brabletz T and Brabletz S: The ZEB1/miR-200c
feedback loop regulates invasion via actin interacting proteins
MYLK and TKS5. Oncotarget. 6:27083–27096. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lawrence RT, Perez EM, Hernández D, Miller
CP, Haas KM, Irie HY, Lee SI, Blau CA and Villén J: The proteomic
landscape of triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Reports.
11:630–644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|