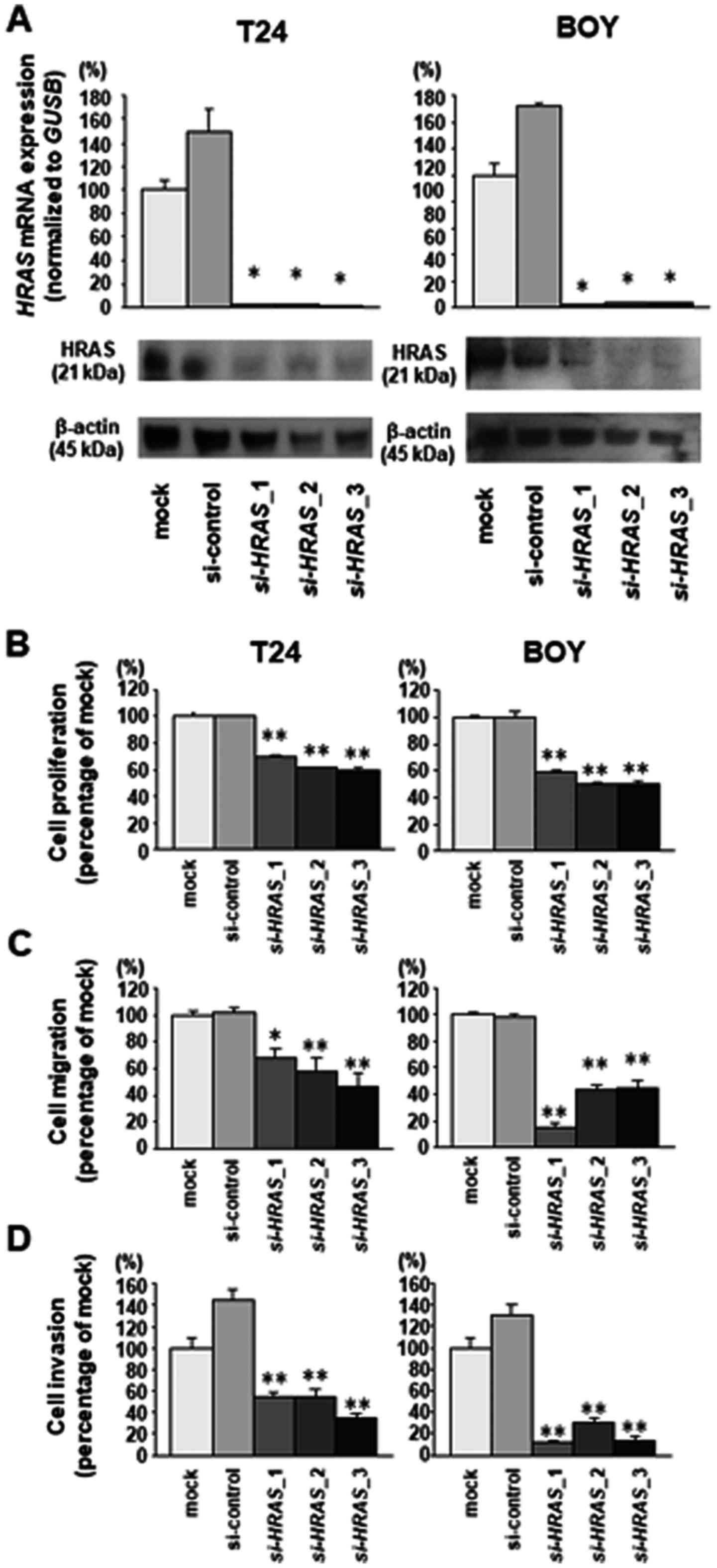
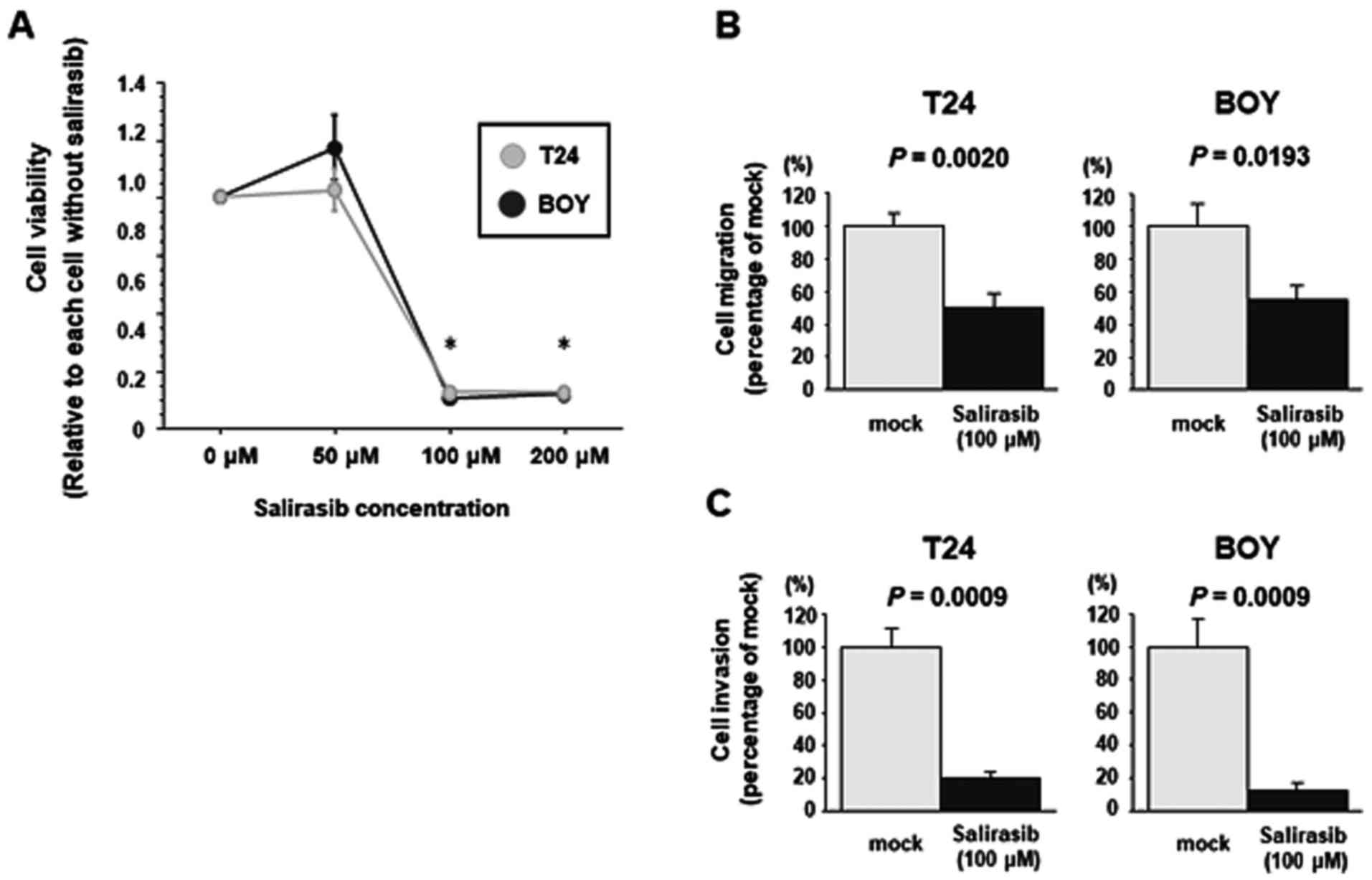
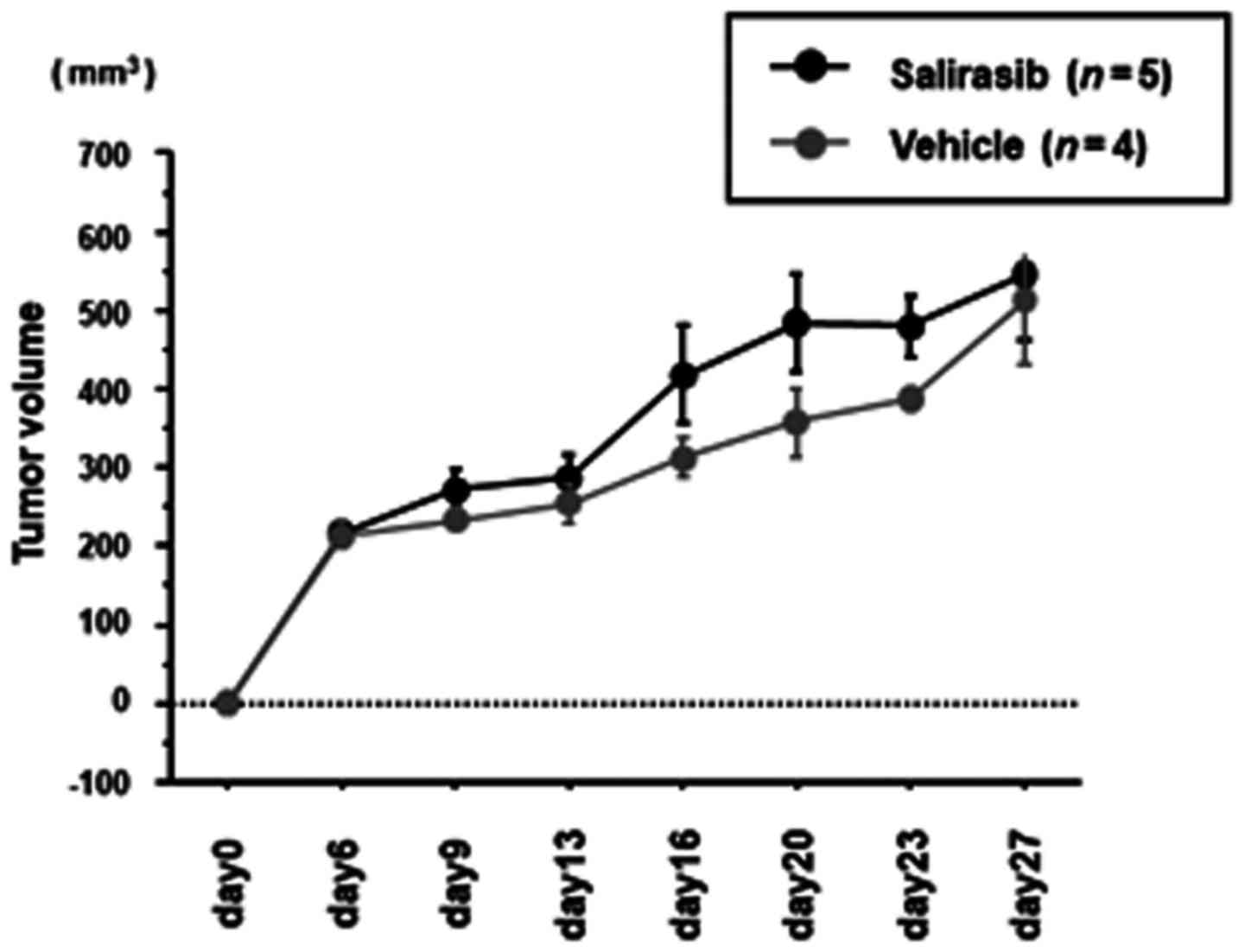
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abdollah F, Gandaglia G, Thuret R,
Schmitges J, Tian Z, Jeldres C, Passoni NM, Briganti A, Shariat SF,
Perrotte P, et al: Incidence, survival and mortality rates of
stage-specific bladder cancer in United States: A trend analysis.
Cancer Epidemiol. 37:219–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis
Collaboration: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 361:1927–1934. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pylayeva-Gupta Y, Grabocka E and Bar-Sagi
D: RAS oncogenes: Weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:761–774. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karnoub AE and Weinberg RA: Ras oncogenes:
Split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:517–531. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER,
McLellan MD, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Greulich H, Muzny DM, Morgan
MB, et al: Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 455:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kiaris H and Spandidos D: Mutations of ras
genes in human tumors (Review). Int J Oncol. 7:413–421.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baines AT, Xu D and Der CJ: Inhibition of
Ras for cancer treatment: The search continues. Future Med Chem.
3:1787–1808. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cox AD, Fesik SW, Kimmelman AC, Luo J and
Der CJ: Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible? Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 13:828–851. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elad G, Paz A, Haklai R, Marciano D, Cox A
and Kloog Y: Targeting of K-Ras 4B by S-trans, transfarnesyl
thiosalicylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1452:228–242. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weisz B, Giehl K, Gana-Weisz M, Egozi Y,
Ben-Baruch G, Marciano D, Gierschik P and Kloog Y: A new functional
Ras antagonist inhibits human pancreatic tumor growth in nude mice.
Oncogene. 18:2579–2588. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riely GJ, Johnson ML, Medina C, Rizvi NA,
Miller VA, Kris MG, Pietanza MC, Azzoli CG, Krug LM, Pao W, et al:
A phase II trial of Salirasib in patients with lung adenocarcinomas
with KRAS mutations. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1435–1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Badar T, Cortes JE, Ravandi F, O'Brien S,
Verstovsek S, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian H and Borthakur G: Phase
I study of S-trans, trans-farnesylthiosalicylic acid (salirasib), a
novel oral RAS inhibitor in patients with refractory hematologic
malignancies. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 15:433–438.e2. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bustinza-Linares E, Kurzrock R and
Tsimberidou AM: Salirasib in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Future Oncol. 6:885–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laheru D, Shah P, Rajeshkumar NV,
McAllister F, Taylor G, Goldsweig H, Le DT, Donehower R, Jimeno A,
Linden S, et al: Integrated preclinical and clinical development of
S-trans, trans-Farnesylthiosalicylic Acid (FTS, Salirasib) in
pancreatic cancer. Invest New Drugs. 30:2391–2399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Makovski V, Haklai R and Kloog Y:
Farnesylthiosalicylic acid (salirasib) inhibits Rheb in TSC2-null
ELT3 cells: A potential treatment for lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Int
J Cancer. 130:1420–1429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zundelevich A, Elad-Sfadia G, Haklai R and
Kloog Y: Suppression of lung cancer tumor growth in a nude mouse
model by the Ras inhibitor salirasib (farnesylthiosalicylic acid).
Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1765–1773. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsumoto M, Matsuzaki F, Oshikawa K,
Goshima N, Mori M, Kawamura Y, Ogawa K, Fukuda E, Nakatsumi H,
Natsume T, et al: A large-scale targeted proteomics assay resource
based on an in vitro human proteome. Nat Methods. 14:251–258. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li B and Dewey CN: RSEM: Accurate
transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a
reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:3232011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, Kunimoto R,
Chiyomaru T, Kawamoto K, Kawahara K, Toki K, Kawakami K, Nishiyama
K, et al: Identification of novel microRNA targets based on
microRNA signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:345–352.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H,
Kawakami K, Tatarano S, Nishiyama K, Nohata N, Seki N and Nakagawa
M: The tumoursuppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting
TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:808–818. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qing G, Skuli N, Mayes PA, Pawel B,
Martinez D, Maris JM and Simon MC: Combinatorial regulation of
neuroblastoma tumor progression by N-Myc and hypoxia inducible
factor HIF-1alpha. Cancer Res. 70:10351–10361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hong SS, Lee H and Kim KW: HIF-1alpha: A
valid therapeutic target for tumor therapy. Cancer Res Treat.
36:343–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hameiri-Grossman M, Porat-Klein A, Yaniv
I, Ash S, Cohen IJ, Kodman Y, Haklai R, Elad-Sfadia G, Kloog Y,
Chepurko E, et al: The association between let-7, RAS and HIF-1α in
Ewing Sarcoma tumor growth. Oncotarget. 6:33834–33848. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shih C and Weinberg RA: Isolation of a
transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line.
Cell. 29:161–169. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haliassos A, Liloglou T, Likourinas M,
Doumas C, Ricci N and Spandidos D: H-ras oncogene mutations in the
urine of patients with bladder-tumors - description of a
noninvasive method for the detection of neoplasia. Int J Oncol.
1:731–734. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X and Zhang Y: Bladder cancer and
genetic mutations. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:65–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kompier LC, Lurkin I, van der Aa MN, van
Rhijn BW, van der Kwast TH and Zwarthoff EC: FGFR3, HRAS, KRAS,
NRAS and PIK3CA mutations in bladder cancer and their potential as
biomarkers for surveillance and therapy. PLoS One. 5:e138212010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Beukers W, Hercegovac A and Zwarthoff EC:
HRAS mutations in bladder cancer at an early age and the possible
association with the Costello Syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet.
22:837–839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Pandith AA, Shah ZA, Khan NP, Baba KM,
Wani MS and Siddiqi MA: HRAS T81C polymorphism modulates risk of
urinary bladder cancer and predicts advanced tumors in ethnic
Kashmiri population. Urol Oncol. 31:487–492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Goldberg L, Israeli R and Kloog Y: FTS and
2-DG induce pancreatic cancer cell death and tumor shrinkage in
mice. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goldberg L, Ocherashvilli A, Daniels D,
Last D, Cohen ZR, Tamar G, Kloog Y and Mardor Y: Salirasib
(farnesyl thiosalicylic acid) for brain tumor treatment: A
convection-enhanced drug delivery study in rats. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3609–3616. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Charette N, De Saeger C, Lannoy V,
Horsmans Y, Leclercq I and Stärkel P: Salirasib inhibits the growth
of hepatocarcinoma cell lines in vitro and tumor growth in vivo
through ras and mTOR inhibition. Mol Cancer. 9:2562010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, Blascovich MA,
Bucher C, Verstovsek S, Wright JJ, Pilat SR, Cortes JE, Estey EH,
Giles FJ, et al: Phase I study of alternate-week administration of
tipifarnib in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:509–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lancet JE, Gojo I, Gotlib J, Feldman EJ,
Greer J, Liesveld JL, Bruzek LM, Morris L, Park Y, Adjei AA, et al:
A phase 2 study of the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib in
poor-risk and elderly patients with previously untreated acute
myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 109:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Welsch ME, Kaplan A, Chambers JM, Stokes
ME, Bos PH, Zask A, Zhang Y, Sanchez-Martin M, Badgley MA, Huang
CS, et al: Multivalent small-molecule Pan-RAS inhibitors. Cell.
168:878–889.e29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|