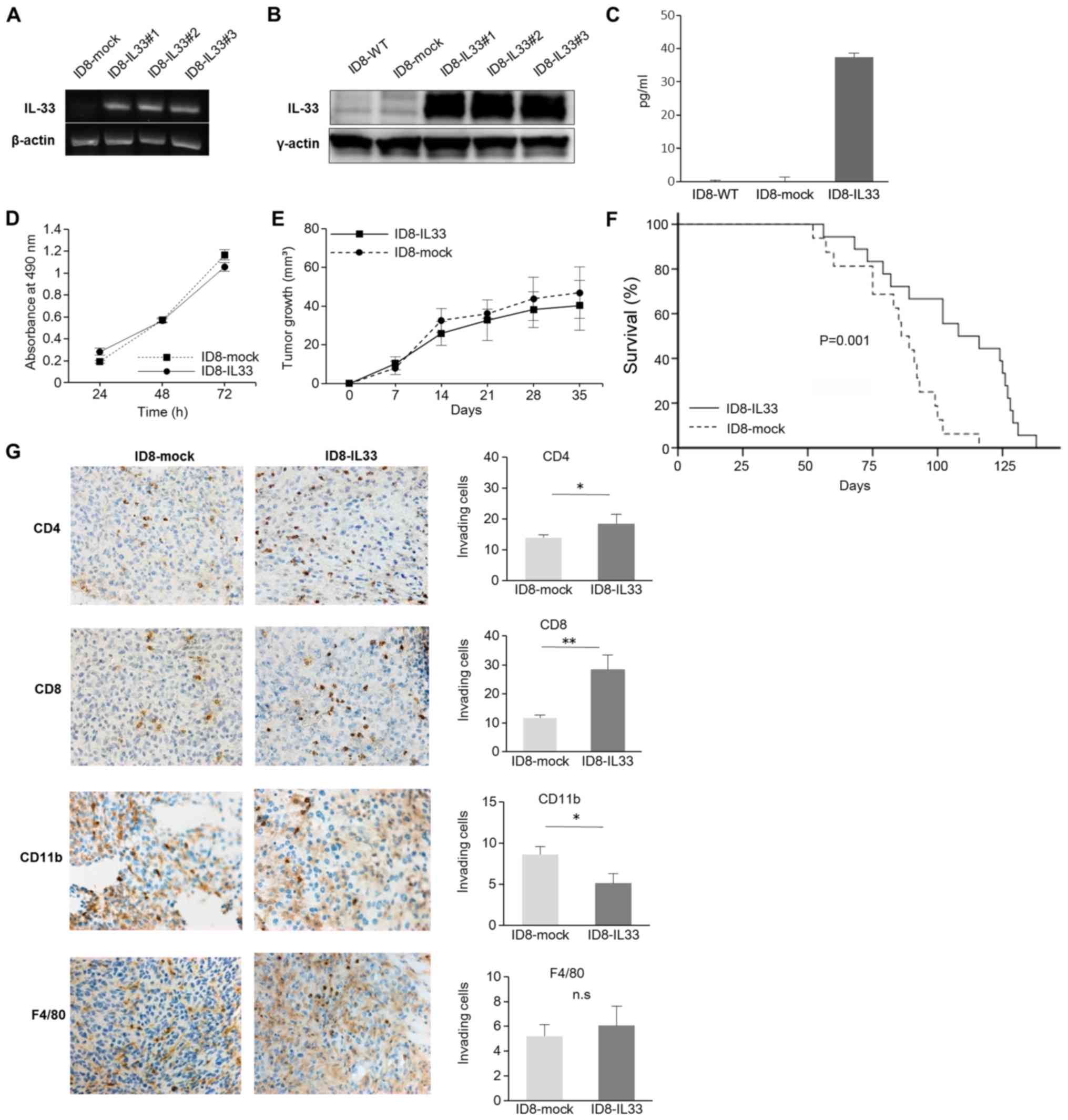
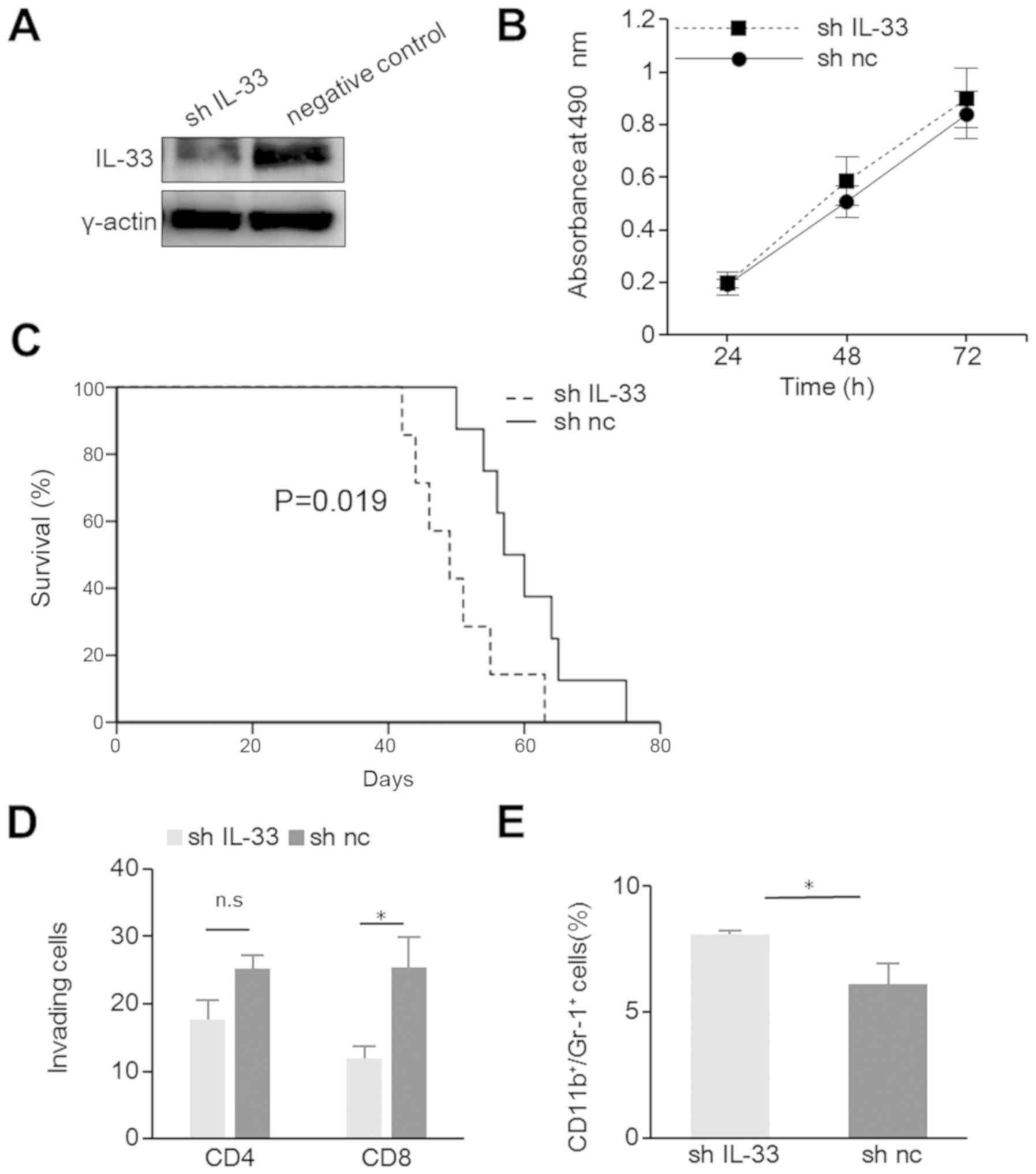
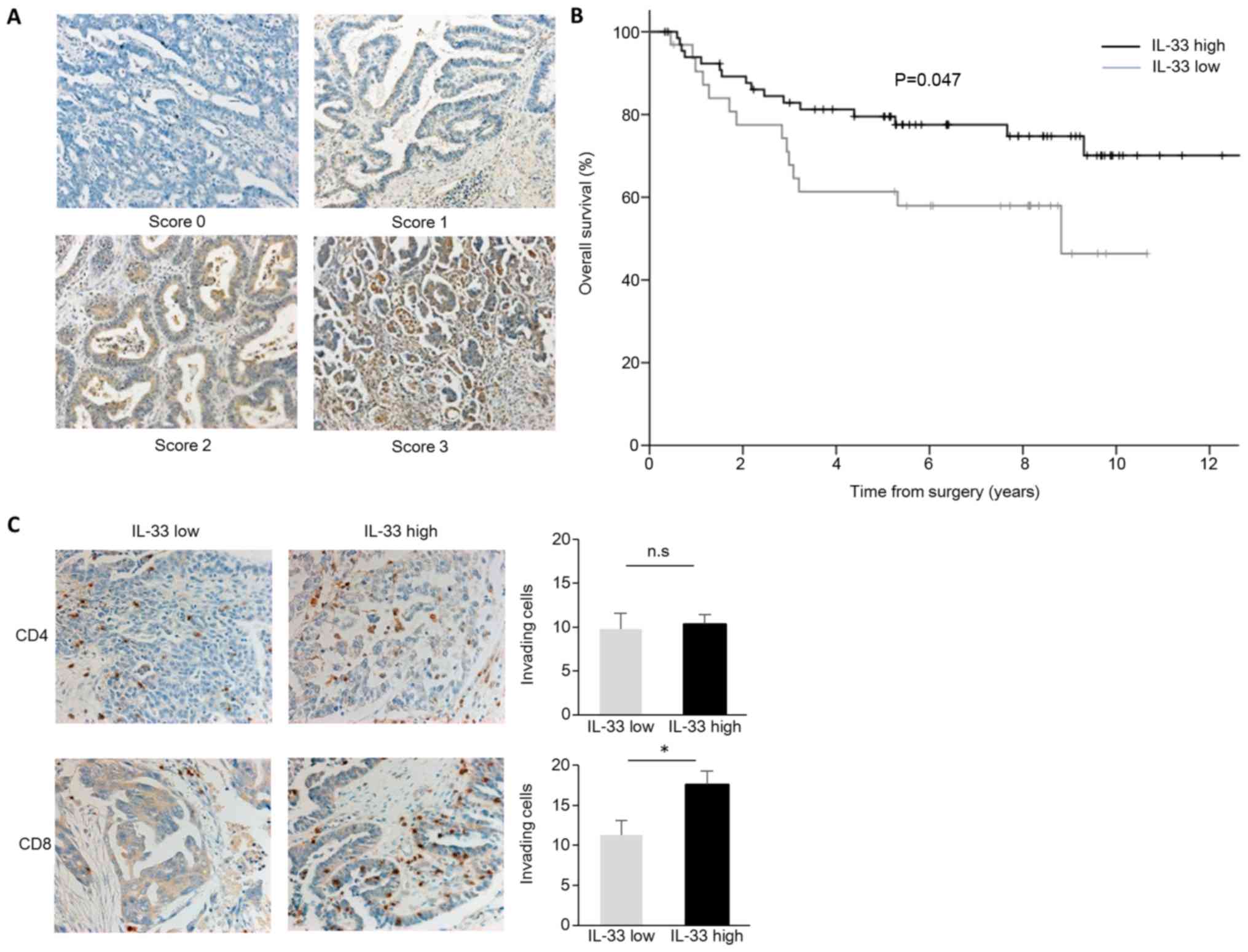
|
1
|
Ebell MH, Culp MB and Radke TJ: A
Systematic review of symptoms for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
Am J Prev Med. 50:384–394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Coleman RL, Monk BJ, Sood AK and Herzog
TJ: Latest research and treatment of advanced-stage epithelial
ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:211–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chae CS, Teran-Cabanillas E and
Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Dendritic cell rehab: New strategies to unleash
therapeutic immunity in ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
66:969–977. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki S, Sakata J, Utsumi F, Sekiya R,
Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Kikkawa F and Nakatsura T: Efficacy of
glypican-3-derived peptide vaccine therapy on the survival of
patients with refractory ovarian clear cell carcinoma.
OncoImmunology. 5:e12385422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu X, Cai H, Zhao L, Ning L and Lang J:
CAR-T cell therapy in ovarian cancer: From the bench to the
bedside. Oncotarget. 8:64607–64621. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Haraldsen G, Balogh J, Pollheimer J,
Sponheim J and Küchler AM: Interleukin-33 - cytokine of dual
function or novel alarmin? Trends Immunol. 30:227–233. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liew FY, Pitman NI and McInnes IB:
Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1
family. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:103–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y,
Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et
al: IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-asso-
ciated cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Saito H and
Nakae S: IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases.
Allergol Int. 59:143–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sattler S, Smits HH, Xu D and Huang FP:
The evolutionary role of the IL-33/ST2 system in host immune
defence. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 61:107–117. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Kewin P, Murphy G,
Russo RC, Stolarski B, Garcia CC, Komai-Koma M, Pitman N, Li Y,
Niedbala W, et al: IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+
T cells and promotes allergic-induced airway inflammation
independent of IL-4. J Immunol. 181:4780–4790. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Stolarski B, Kewin
P, Murphy G, Corrigan CJ, Ying S, Pitman N, Mirchandani A, Rana B,
van Rooijen N, et al: IL-33 amplifies the polarization of
alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway
inflammation. J Immunol. 183:6469–6477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pei C, Barbour M, Fairlie-Clarke KJ, Allan
D, Mu R and Jiang HR: Emerging role of interleukin-33 in autoimmune
diseases. Immunology. 141:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Wang S, Ding L, Liu SS, Wang C, Leng RX,
Chen GM, Fan YG, Pan HF and Ye DQ: IL-33: A potential therapeutic
target in autoimmune diseases. J Investig Med. 60:1151–1156. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, Denby L, Li
Y, Sattar N, Baker AH, McInnes IB and Liew FY: IL-33 reduces the
development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 205:339–346. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter
ER, McKenzie AN and Lee RT: IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical
biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J
Clin Invest. 117:1538–1549. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu XX, Hu Z, Shen X, Dong LY, Zhou WZ and
Hu WH: IL-33 promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and migration
via ST2 ERK1/2 pathway. Dig Dis Sci. 60:1265–1272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang P, Liu XK, Chu Z, Ye JC, Li KL,
Zhuang WL, Yang DJ and Jiang YF: Detection of interleukin-33 in
serum and carcinoma tissue from patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma and its clinical implications. J Int Med Res.
40:1654–1661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JY, Lim SC, Kim G, Yun HJ, Ahn SG and
Choi HS: Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes epithelial cell
transformation and breast tumorigenesis via upregulation of COT
activity. Oncogene. 34:4928–4938. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Shen JX, Hu JL, Huang WH and Zhang
GJ: Significance of interleukin-33 and its related cytokines in
patients with breast cancers. Front Immunol. 5:1412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O'Donnell C, Mahmoud A, Keane J, Murphy C,
White D, Carey S, O'Riordain M, Bennett MW, Brint E and Houston A:
An antitumorigenic role for the IL-33 receptor, ST2L, in colon
cancer. Br J Cancer. 114:37–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Akimoto M, Hayashi JI, Nakae S, Saito H
and Takenaga K: Interleukin-33 enhances programmed oncosis of
ST2L-positive low-metastatic cells in the tumour microenvironment
of lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 7:e20572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tong X, Barbour M, Hou K, Gao C, Cao S,
Zheng J, Zhao Y, Mu R and Jiang HR: Interleukin-33 predicts poor
prognosis and promotes ovarian cancer cell growth and metastasis
through regulating ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Mol Oncol.
10:113–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Saied EM and El-Etreby NM: The role and
prognostic value of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and
interleukin-33 (IL-33) in serous and mucinous epithelial ovarian
tumours. Ann Diagn Pathol. 27:62–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-ΔΔC(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Suzuki S, Terauchi M, Umezu T, Kajiyama H,
Shibata K, Nawa A and Kikkawa F: Identification and
characterization of cancer stem cells in ovarian yolk sac tumors.
Cancer Sci. 101:2179–2185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Villarreal DO, Wise MC, Walters JN,
Reuschel EL, Choi MJ, Obeng-Adjei N, Yan J, Morrow MP and Weiner
DB: Alarmin IL-33 acts as an immunoadjuvant to enhance
antigen-specific tumor immunity. Cancer Res. 74:1789–1800. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao K, Li X and Zhang L, Bai L, Dong W,
Gao K, Shi G, Xia X, Wu L and Zhang L: Transgenic expression of
IL-33 activates CD8(+) T cells and NK cells and inhibits tumor
growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Lett. 335:463–471. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao X, Wang X, Yang Q, Zhao X, Wen W, Li
G, Lu J, Qin W, Qi Y, Xie F, et al: Tumoral expression of IL-33
inhibits tumor growth and modifies the tumor microenvironment
through CD8+ T and NK cells. J Immunol. 194:438–445.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Millrud CR, Bergenfelz C and Leandersson
K: On the origin of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncotarget.
8:3649–3665. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Kolomeyevskaya N, Eng KH, Khan AN,
Grzankowski KS, Singel KL, Moysich K and Segal BH: Cytokine
profiling of ascites at primary surgery identifies an interaction
of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 in predicting reduced
progression-free survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 138:352–357. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morales JK, Kmieciak M, Knutson KL, Bear
HD and Manjili MH: GM-CSF is one of the main breast tumor-derived
soluble factors involved in the differentiation of
CD11b-GrL- bone marrow progenitor cells into
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
123:39–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu L, Deng Z, Peng Y, Han L, Liu J, Wang
L, Li B, Zhao J, Jiao S and Wei H: Ascites-derived IL-6 and IL-10
synergistically expand CD14+HLA-DR-/low
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in ovarian cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 8:76843–76856. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brickshawana A, Shapiro VS, Kita H and
Pease LR: Lineage(-) Sca1+c-Kit(-)CD25+ cells
are IL-33-responsive type 2 innate cells in the mouse bone marrow.
J Immunol. 187:5795–5804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mitsui H, Shibata K, Suzuki S, Umezu T,
Mizuno M, Kajiyama H and Kikkawa F: Functional interaction between
peritoneal mésothélial cells and stem cells of ovarian yolk sac
tumor (SC-OYST) in peritoneal dissemination. Gynecol Oncol.
124:303–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lau TS, Chan LK, Wong EC, Hui CW, Sneddon
K, Cheung TH, Yim SF, Lee JH, Yeung CS, Chung TK, et al: A loop of
cancer-stroma-cancer interaction promotes peritoneal metastasis of
ovarian cancer via TNFα-TGFα-EGFR. Oncogene. 36:3576–3587. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fujikake K, Kajiyama H, Yoshihara M,
Nishino K, Yoshikawa N, Utsumi F, Suzuki S, Niimi K, Sakata J,
Mitsui H, et al: A novel mechanism of neovascularization in
peritoneal dissemination via cancer-associated mesothelial cells
affected by TGF-β derived from ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep.
39:193–200. 2018.
|
|
38
|
Yokoi A, Yoshioka Y, Yamamoto Y, Ishikawa
M, Ikeda SI, Kato T, Kiyono T, Takeshita F, Kajiyama H, Kikkawa F,
et al: Malignant extracellular vesicles carrying MMP1 mRNA
facilitate peritoneal dissemination in ovarian cancer. Nat Commun.
8:144702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lohning M, Stroehmann A, Coyle AJ, Grogan
JL, Lin S, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Levinson D, Radbruch A and Kamradt
T: T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells,
independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10,
and important for Th2 effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:6930–6935. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu D, Chan WL, Leung BP, Huang F, Wheeler
R, Piedrahta D, Robinson JH and Liew FY: Selective expression of a
stable cell surface molecule on type 2 but not type 1 helper T
cells. J Exp Med. 187:787–794. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baumann C, Bonilla WV, Fröhlich A,
Helmstetter C, Peine M, Hegazy AN, Pinschewer DD and Löhning M:
T-bet- and STAT4-dependent IL-33 receptor expression directly
promotes antiviral Th1 cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:4056–4061. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bonilla WV, Fröhlich A, Senn K, Kallert S,
Fernandez M, Johnson S, Kreutzfeldt M, Hegazy AN, Schrick C, Fallon
PG, et al: The alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral
CD8+ T cell responses. Science. 335:984–989. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ribechini E, Greifenberg V, Sandwick S and
Lutz MB: Subsets, expansion and activation of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells. Med Microbiol Immunol (Berl). 199:273–281. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lim HX, Choi S, Cho D and Kim TS: IL-33
inhibits the differentiation and immunosuppressive activity of
granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing
mice. Immunol Cell Biol. 95:99–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Brunner SM, Rubner C, Kesselring R, Martin
M, Griesshammer E, Ruemmele P, Stempfl T, Teufel A, Schlitt HJ and
Fichtner-Feigl S: Tumor-infiltrating, interleukin-33-producing
effector-memory CD8(+) T cells in resected hepatocellular carcinoma
prolong patient survival. Hepatology. 61:1957–1967. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|