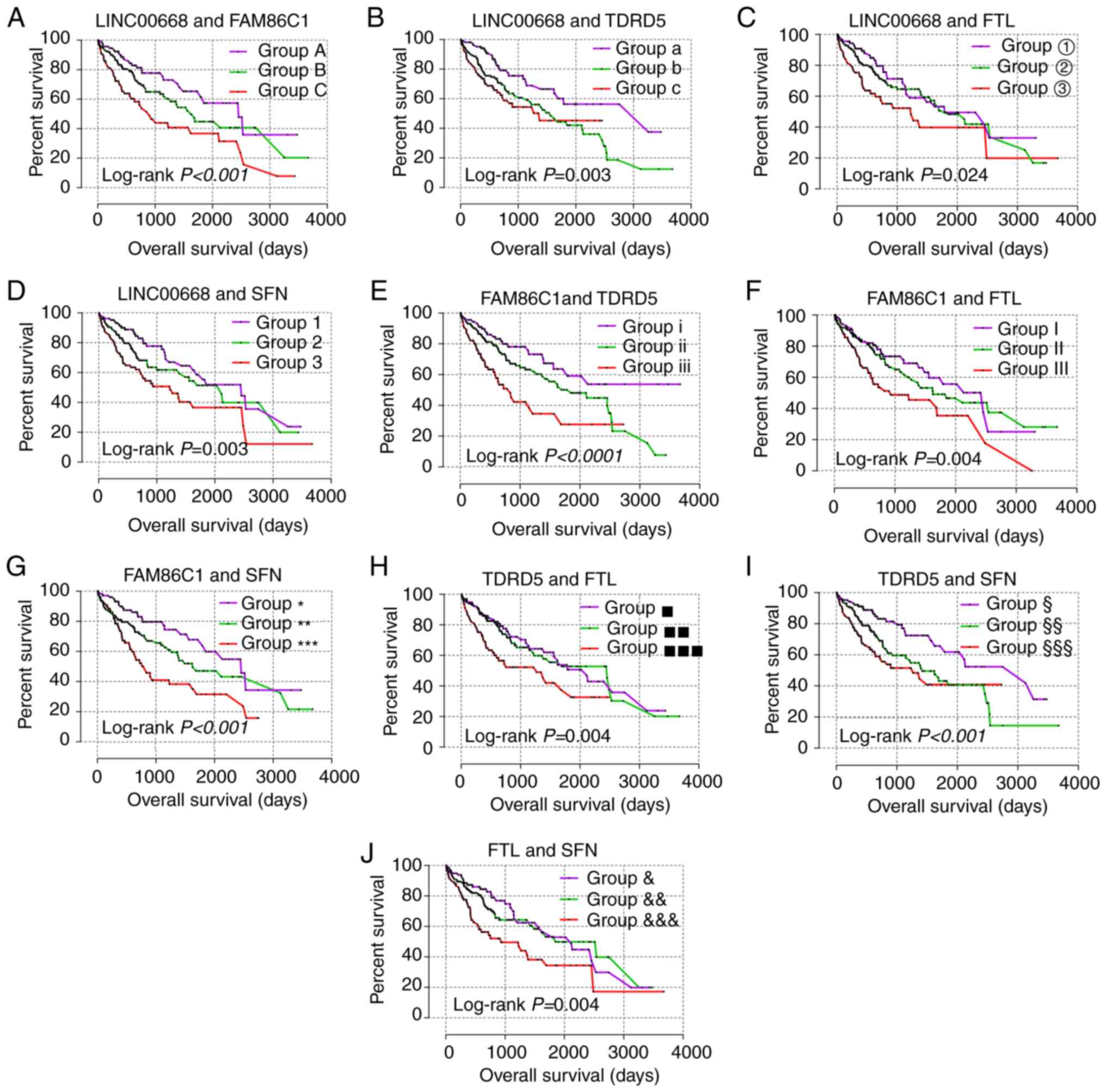
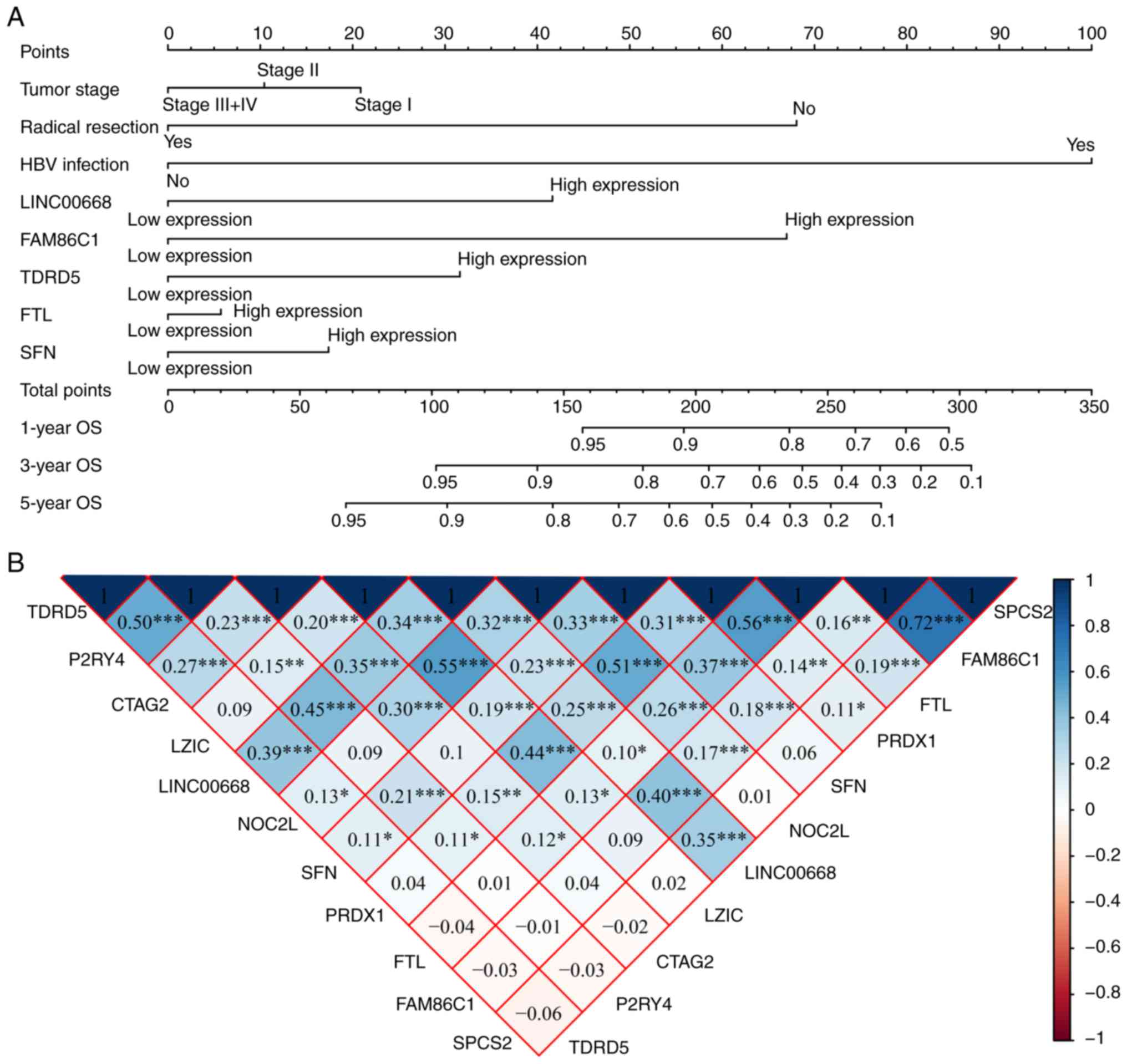
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Testino G, Leone S, Patussi V, Scafato E
and Borro P: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnosis and proposal of
treatment. Minerva Med. 107:413–426. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li S, Huang Y, Huang Y, Fu Y, Tang D, Kang
R, Zhou R and Fan XG: The long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 modulates
HCC cell proliferation through miR-200a-dependent HMGB1/RAGE
regulation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gomaa AI, Khan SA, Toledano MB, Waked I
and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology,
risk factors and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 14:4300–4308.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F,
Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP and Odenthal M: MicroRNA gene
expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:1223–1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Llovet JM: Liver cancer: Time to evolve
trial design after everolimus failure. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
11:506–507. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanaka S and Arii S: Molecular targeted
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in the current and potential
next strategies. J Gastroenterol. 46:289–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C and Kapranov P:
The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet.
31:239–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Devaux Y, Zangrando J, Schroen B, Creemers
EE, Pedrazzini T, Chang CP, Dorn GW II, Thum T and Heymans S;
Cardiolinc network: Long noncoding RNAs in cardiac development and
ageing. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:415–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma L, Bajic VB and Zhang Z: On the
classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 10:925–933. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Penny GD, Kay GF, Sheardown SA, Rastan S
and Brockdorff N: Requirement for Xist in X chromosome
inactivation. Nature. 379:131–137. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Hedge VL, Kirkham
L, Farzaneh F and Williams GT: Growth arrest in human T-cells is
controlled by the non-coding RNA growth-arrest-specific transcript
5 (GAS5). J Cell Sci. 121:939–946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huo X, Han S, Wu G, Latchoumanin O, Zhou
G, Hebbard L, George J and Qiao L: Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs
(lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for
tumori-genesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells.
Mol Cancer. 16:1652017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: Regulation of
apoptosis by long non-coding RNA GAS5 in breast cancer cells:
Implications for chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
145:359–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pickard MR, Mourtada-Maarabouni M and
Williams GT: Long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates apoptosis in
prostate cancer cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1613–1623.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiaoguang Z, Meirong L, Jingjing Z,
Ruishen Z, Qing Z and Xiaofeng T: Long noncoding RNA CPS1-IT1
suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in human lung cancer.
Oncol Res. 25:373–380. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang M, Wang W, Li T, Yu X, Zhu Y, Ding
F, Li D and Yang T: Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 predicts a poor
prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 80:73–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao B, Xu H, Ai X, Adalat Y, Tong Y,
Zhang J and Yang S: Expression profiles of long noncoding RNAs in
lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 11:5383–5390. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao L, Cao H, Chi W, Meng W, Cui W, Guo W
and Wang B: Expression profile analysis identifies the long
non-coding RNA landscape and the potential carcinogenic functions
of LINC00668 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 687:47–55.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang E, Yin D, Han L, He X, Si X, Chen W,
Xia R, Xu T, Gu D, De W, et al: E2F1-induced upregulation of long
noncoding RNA LINC00668 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer
and promotes cell proliferation through epigenetically silencing of
CKIs. Oncotarget. 7:23212–23226. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paci P, Colombo T and Farina L:
Computational analysis identifies a sponge interaction network
between long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs in human breast
cancer. BMC Syst Biol. 8:832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liao Q, Liu C, Yuan X, Kang S, Miao R,
Xiao H, Zhao G, Luo H, Bu D, Zhao H, et al: Large-scale prediction
of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding-non-coding gene
co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3864–3878. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shaul YD, Yuan B, Thiru P, Nutter-Upham A,
McCallum S, Lanzkron C, Bell GW and Sabatini DM: MERAV: A tool for
comparing gene expression across human tissues and cell types.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D560–D566. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Montojo J, Zuberi K, Rodriguez H, Kazi F,
Wright G, Donaldson SL, Morris Q and Bader GD: GeneMANIA Cytoscape
plugin: Fast gene function predictions on the desktop.
Bioinformatics. 26:2927–2928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maass PG, Luft FC and Bähring S: Long
non-coding RNA in health and disease. J Mol Med (Berl). 92:337–346.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang G, Lu X and Yuan L: LncRNA: A link
between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:1097–1109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wong CM, Kai AK, Tsang FH and Ng IO:
Regulation of hepato-carcinogenesis by microRNAs. Front Biosci
(Elite Ed). 5:49–60. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ulitsky I and Bartel DP: lincRNAs:
Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell. 154:26–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagano T and Fraser P: No-nonsense
functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 145:178–181. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsai MC, Spitale RC and Chang HY: Long
intergenic noncoding RNAs: New links in cancer progression. Cancer
Res. 71:3–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A and
Calin GA: Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of
translational research? Oncogene. 31:4577–4587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang X, Huang Z, He Z and
Chen Y: Long non-coding RNA: A new player in cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 6:372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li J, Zhuang C, Liu Y, Chen M, Chen Y,
Chen Z, He A, Lin J, Zhan Y, Liu L, et al: Synthetic
tetracycline-controllable shRNA targeting long non-coding RNA
HOXD-AS1 inhibits the progression of bladder cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 35:992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu Y, Wang J, Qian J, Kong X, Tang J, Wang
Y, Chen H, Hong J, Zou W, Chen Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA GAPLINC
regulates CD44-dependent cell invasiveness and associates with poor
prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 74:6890–6902. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu X, Feng Y, Zhang D, Zhao SD, Hu Z,
Greshock J, Zhang Y, Yang L, Zhong X, Wang LP, et al: A functional
genomic approach identifies FAL1 as an oncogenic long noncoding RNA
that associates with BMI1 and represses p21 expression in cancer.
Cancer Cell. 26:344–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ,
Tao QF, Liu F, Pan W, Wang TT, Zhou CC, et al: A long noncoding RNA
activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:666–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cui M, Xiao Z, Wang Y, Zheng M, Song T,
Cai X, Sun B, Ye L and Zhang X: Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates
abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an
miR-9-mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 75:846–857.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang J, Zhuo H, Zhang X, Jiang R, Ji J,
Deng L, Qian X, Zhang F and Sun B: A novel biomarker Linc00974
interacting with KRT19 promotes proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang CZ: Long intergenic non-coding RNA
668 regulates VEGFA signaling through inhibition of miR-297 in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 489:404–412.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ding D, Liu J, Midic U, Wu Y, Dong K,
Melnick A, Latham KE and Chen C: TDRD5 binds piRNA precursors and
selectively enhances pachytene piRNA processing in mice. Nat
Commun. 9:1272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shen Y, Li X, Zhao B, Xue Y, Wang S, Chen
X, Yang J, Lv H and Shang P: Iron metabolism gene expression and
prognostic features of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem.
119:9178–9204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu Y, Zhu X, Zhu J, Liao S, Tang Q, Liu
K, Guan X, Zhang J and Feng Z: Identification of differential
expression of genes in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppression
subtractive hybridization combined cDNA microarray. Oncol Rep.
18:943–951. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang K, Xu X, Nie Y, Dai L, Wang P and
Zhang J: Identification of tumor-associated antigens by using SEREX
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 281:144–150. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brum AM, van de Peppel J, Nguyen L, Aliev
A, Schreuders-Koedam M, Gajadien T, van der Leije CS, van Kerkwijk
A, Eijken M, van Leeuwen JPTM and van der Eerden BCJ: Using the
Connectivity Map to discover compounds influencing human osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 233:4895–4906. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Busby J, Murray L, Mills K, Zhang SD,
Liberante F and Cardwell CR: A combined connectivity mapping and
pharmacoepidemiology approach to identify existing medications with
breast cancer causing or preventing properties. Pharmacoepidemiol
Drug Saf. 27:78–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Xiao SJ, Zhu XC, Deng H, Zhou WP, Yang WY,
Yuan LK, Zhang JY, Tian S, Xu L, Zhang L and Xia HM: Gene
expression profiling coupled with Connectivity Map database mining
reveals potential therapeutic drugs for Hirschsprung disease. J
Pediatr Surg. 53:1716–1721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|