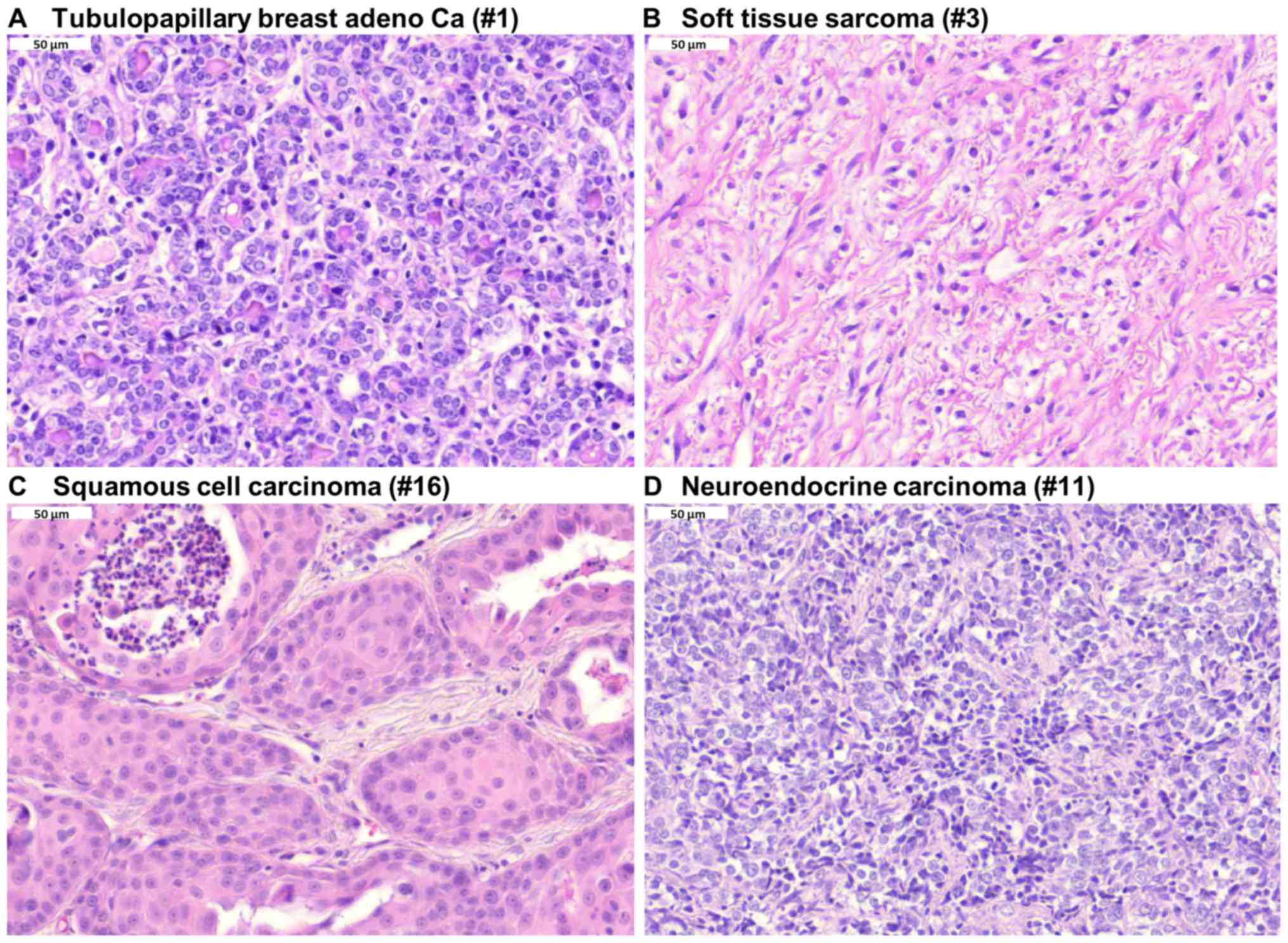
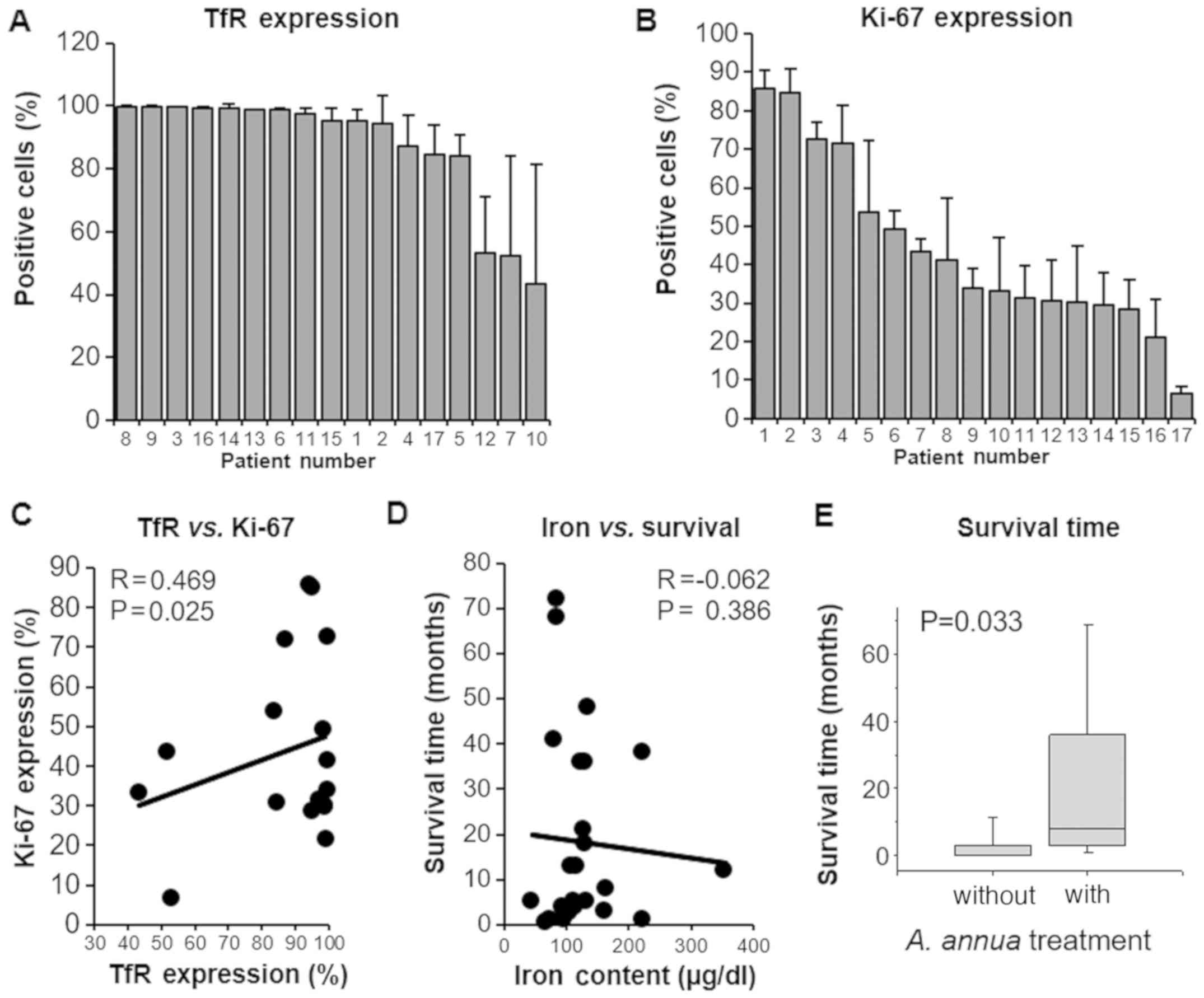
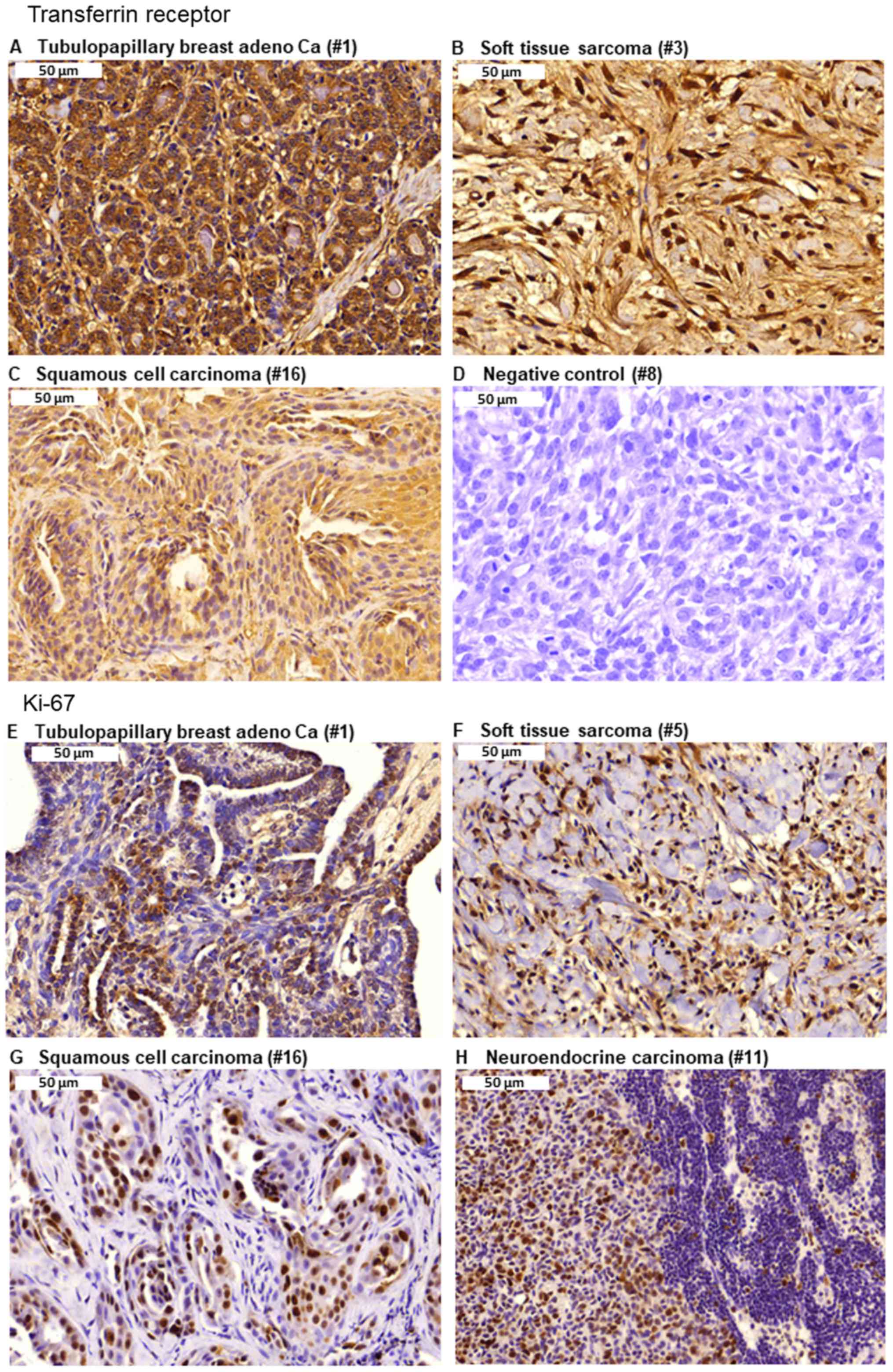
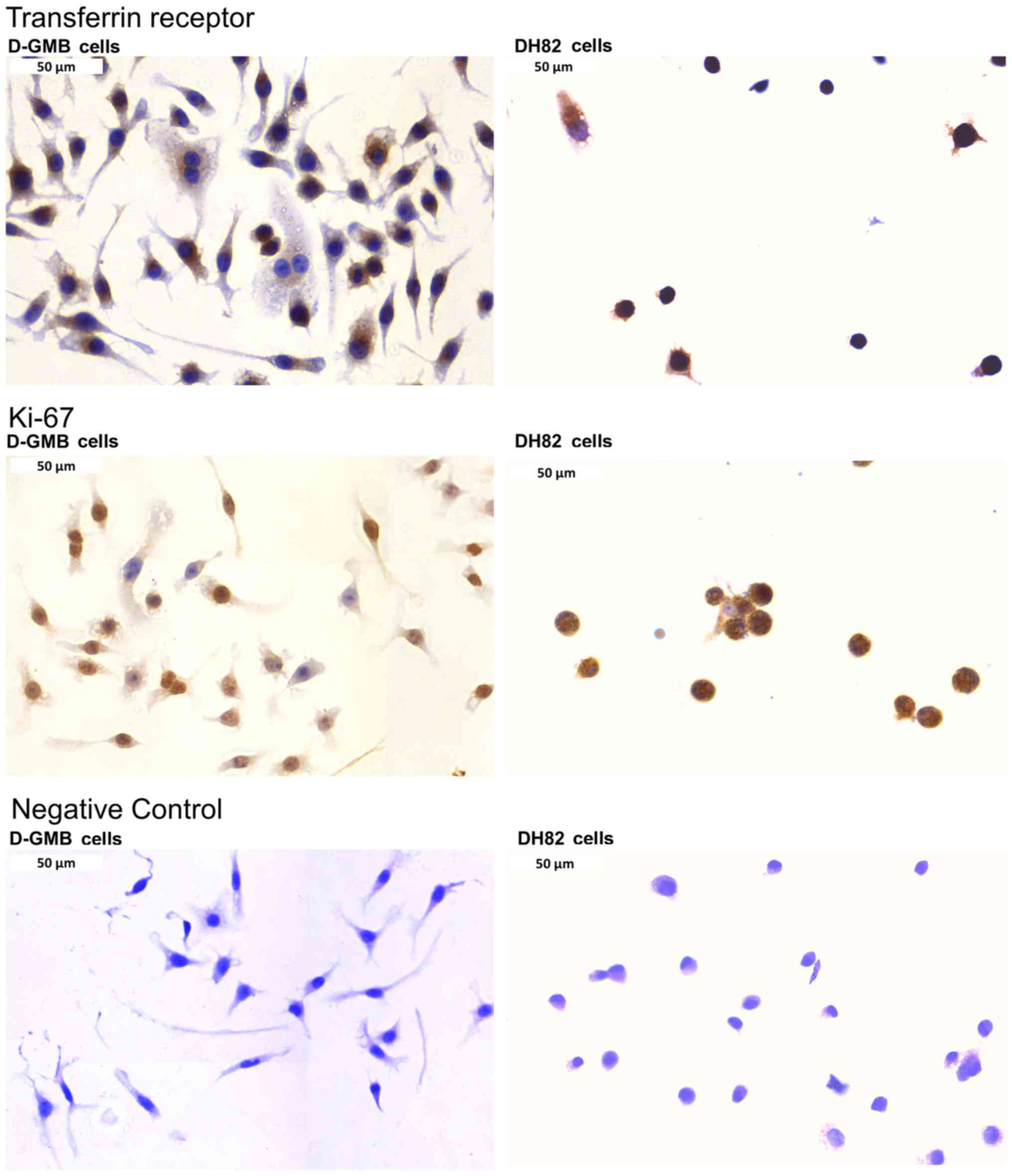
|
1
|
Talmadge JE, Singh RK, Fidler IJ and Raz
A: Murine models to evaluate novel and conventional therapeutic
strategies for cancer. Am J Pathol. 170:793–804. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jantscheff P, Beshay J, Lemarchand T,
Obodozie C, Schächtele C and Weber H: Mouse-derived isograft (MDI)
in vivo tumor models I Spontaneous sMDI models: Characterization
and cancer therapeutic approaches. Cancers (Basel). 11:112019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Choi JW, Yoon HY and Jeong SW: Clinical
outcomes of surgically managed spontaneous tumors in 114
client-owned dogs. Immune Netw. 16:116–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hellmén E, Bergström R, Holmberg L,
Spångberg IB, Hansson K and Lindgren A: Prognostic factors in
canine mammary tumors: A multivariate study of 202 consecutive
cases. Vet Pathol. 30:20–27. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marconato L: The staging and treatment of
multicentric high-grade lymphoma in dogs: A review of recent
developments and future prospects. Vet J. 188:34–38. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tuohy JL, Selmic LE, Worley DR, Ehrhart NP
and Withrow SJ: Outcome following curative-intent surgery for oral
melanoma in dogs: 70 cases (1998-2011). J Am Vet Med Assoc.
245:1266–1273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miller RL, Van Lelyveld S, Warland J,
Dobson JM and Foale RD: A retrospective review of treatment and
response of high-risk mast cell tumours in dogs. Vet Comp Oncol.
14:361–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Romano FR, Heinze CR, Barber LG, Mason JB
and Freeman LM: Association between body condition score and cancer
prognosis in dogs with lymphoma and osteosarcoma. J Vet Intern Med.
30:1179–1186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sarowitz BN, Davis GJ and Kim S: Outcome
and prognostic factors following curative-intent surgery for oral
tumours in dogs: 234 cases (2004 to 2014). J Small Anim Pract.
58:146–153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ettinger SN: Principles of treatment for
feline lymphoma. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 18:98–102. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morris J: Mammary tumours in the cat: Size
matters, so early intervention saves lives. J Feline Med Surg.
15:391–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zabielska-Koczywąs K, Wojtalewicz A and
Lechowski R: Current knowledge on feline injection-site sarcoma
treatment. Acta Vet Scand. 59:472017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Martano M, Iussich S, Morello E and
Buracco P: Canine oral fibrosarcoma: Changes in prognosis over the
last 30 years? Vet J. 241:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang D, Hedlund EM, Lim S, Chen F, Zhang
Y, Sun B and Cao Y: Antiangiogenic agents significantly improve
survival in tumor-bearing mice by increasing tolerance to
chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:4117–4122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tiwari A, Hadley JA, Hendricks GL III,
Elkin RG, Cooper T and Ramachandran R: Characterization of
ascites-derived ovarian tumor cells from spontaneously occurring
ovarian tumors of the chicken: Evidence for E-cadherin
upregulation. PLoS One. 8:e575822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod. 79:629–661.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tu Y: The discovery of artemisinin
(qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat Med. 17:1217–1220.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bridgford JL, Xie SC, Cobbold SA, Pasaje
CFA, Herrmann S, Yang T, Gillett DL, Dick LR, Ralph SA, Dogovski C,
et al: Artemisinin kills malaria parasites by damaging proteins and
inhibiting the proteasome. Nat Commun. 9:38012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Su XZ and Miller LH: The discovery of
artemisinin and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Sci
China Life Sci. 58:1175–1179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tu Y: Artemisinin-a gift from traditional
chinese medicine to the world (Nobel Lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed
Engl. 55:10210–10226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Daddy NB, Kalisya LM, Bagire PG, Watt RL,
Towler MJ and Weathers PJ: Artemisia annua dried leaf tablets
treated malaria resistant to ACT and i.v. artesunate: Case reports.
Phytomedicine. 32:37–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saeed ME, Krishna S, Greten HJ, Kremsner
PG and Efferth T: Antischistosomal activity of artemisinin
derivatives in vivo and in patients. Pharmacol Res. 110:216–226.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pérez del Villar L, Burguillo FJ,
López-Abán J and Muro A: Systematic review and meta-analysis of
artemisinin based therapies for the treatment and prevention of
schistosomiasis. PLoS One. 7:e458672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Naß J and Efferth T: The activity of
Artemisia spp. and their constituents against Trypanosomiasis.
Phytomedicine. 47:184–191. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Efferth T: Beyond malaria: The inhibition
of viruses by arte-misinin-type compounds. Biotechnol Adv.
36:1730–1737. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang W, Cen Y, Song Y, Li P, Qin R, Liu
C, Zhao Y, Zheng J and Zhou H: Artesunate attenuated progression of
atherosclerosis lesion formation alone or combined with
rosuvastatin through inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and
pro-inflammatory chemokines. Phytomedicine. 23:1259–1266. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Casteels T, Frogne T, Ingvorsen C,
Honore C, Courtney M, Huber KV, Schmitner N, Kimmel RA, Romanov RA,
et al: Artemisinins target GABAA receptor signaling and impair
alpha cell Identity. Cell. 168:86–100.e15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo Y, Fu W, Xin Y, Bai J, Peng H, Fu L,
Liu J, Li L, Ma Y and Jiang H: Antidiabetic and antiobesity effects
of artemether in db/db mice. BioMed Res Int. 2018:86395232018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Efferth T, Sauerbrey A, Olbrich A, Gebhart
E, Rauch P, Weber HO, Hengstler JG, Halatsch ME, Volm M, Tew KD, et
al: Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines.
Mol Pharmacol. 64:382–394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dell'Eva R, Pfeffer U, Vené R, Anfosso L,
Forlani A, Albini A and Efferth T: Inhibition of angiogenesis in
vivo and growth of Kaposi's sarcoma xenograft tumors by the
anti-malarial arte-sunate. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:2359–2366. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Efferth T: From ancient herb to modern
drug: Artemisia annua and artemisinin for cancer therapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 46:65–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abba ML, Patil N, Leupold JH, Saeed ME,
Efferth T and Allgayer H: Prevention of carcinogenesis and
metastasis by Artemisinin-type drugs. Cancer Lett. 429:11–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krusche B, Arend J and Efferth T:
Synergistic inhibition of angiogenesis by artesunate and captopril
in vitro and in vivo. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:4547832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Efferth T: Cancer combination therapy of
the sesquiterpenoid artesunate and the selective EGFR-tyrosine
kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Phytomedicine. 37:58–61. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Efferth T: Cancer combination therapies
with artemisinin-type drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 139:56–70. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hosoya K, Murahari S, Laio A, London CA,
Couto CG and Kisseberth WC: Biological activity of
dihydroartemisinin in canine osteosarcoma cell lines. Am J Vet Res.
69:519–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hosoya K, Couto CG, London CA, Kisseberth
WC, Phelps MA and Dalton JT: Comparison of high-dose intermittent
and low-dose continuous oral artemisinin in dogs with naturally
occurring tumors. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 50:390–395. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rutteman GR, Erich SA, Mol JA, Spee B,
Grinwis GC, Fleckenstein L, London CA and Efferth T: Safety and
efficacy field study of artesunate for dogs with non-resectable
tumours. Anticancer Res. 33:1819–1827. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berger TG, Dieckmann D, Efferth T, Schultz
ES, Funk JO, Baur A and Schuler G: Artesunate in the treatment of
metastatic uveal melanoma - first experiences. Oncol Rep.
14:1599–1603. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Michaelsen FW, Saeed ME, Schwarzkopf J and
Efferth T: Activity of Artemisia annua and artemisinin derivatives,
in prostate carcinoma. Phytomedicine. 22:1223–1231. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jansen FH, Adoubi I, JC KC, DE Cnodder T,
Jansen N, Tschulakow A and Efferth T: First study of oral
Artenimol-R in advanced cervical cancer: Clinical benefit,
tolerability and tumor markers. Anticancer Res. 31:4417–4422.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Krishna S, Ganapathi S, Ster IC, Saeed ME,
Cowan M, Finlayson C, Kovacsevics H, Jansen H, Kremsner PG, Efferth
T, et al: A randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled pilot
study of oral artesunate therapy for colorectal cancer.
EBioMedicine. 2:82–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
von Hagens C, Walter-Sack I, Goeckenjan M,
Osburg J, Storch-Hagenlocher B, Sertel S, Elsässer M, Remppis BA,
Edler L, Munzinger J, et al: Prospective open uncontrolled phase I
study to define a well-tolerated dose of oral artesunate as add-on
therapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer (ARTIC M33/2).
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 164:359–369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Breuer E and Efferth T: Treatment of
iron-loaded veterinary sarcoma by Artemisia annua. Nat Prod
Bioprospect. 4:113–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hegazy MF, Abdelfatah S, Hamed AR, Mohamed
TA, Elshamy AA, Saleh IA, Reda EH, Abdel-Azim NS, Shams KA, Sakr M,
et al: Cytotoxicity of 40 Egyptian plant extracts targeting
mechanisms of drug-resistant cancer cells. Phytomedicine.
59:1527712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chikazawa S, Hori Y, Kanai K, Ito N, Hoshi
F, Orino K, Watanabe K and Higuchi S: Factors influencing
measurement of serum iron concentration in dogs: Diurnal variation
and hyper-ferritinemia. J Vet Med Sci. 75:1615–1618. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Carpenter CE and Ward RE: Iron
determination by Ferrozine method. Food Analysis Laboratory Manual
Springer: Luxembourg: pp. 157–159. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Stoica G, Lungu G, Martini-Stoica H,
Waghela S, Levine J and Smith R III: Identification of cancer stem
cells in dog glioblastoma. Vet Pathol. 46:391–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wellman ML, Krakowka S, Jacobs RM and
Kociba GJ: A macrophage-monocyte cell line from a dog with
malignant histiocytosis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 24:223–229. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Alley MC, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Hursey ML,
Czerwinski MJ, Fine DL, Abbott BJ, Mayo JG, Shoemaker RH and Boyd
MR: Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell
lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res.
48:589–601. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rubinstein LV, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD,
Simon RM, Tosini S, Skehan P, Scudiero DA, Monks A and Boyd MR:
Comparison of in vitro anticancer-drug-screening data generated
with a tetra-zolium assay versus a protein assay against a diverse
panel of human tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1113–1118.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kuete V, Mbaveng AT, Sandjo LP, Zeino M
and Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and mode of action of a naturally
occurring naphthoquinone,
2-acetyl-7-methoxynaphtho[2,3-b]furan-4,9-quinone towards
multi-factorial drug-resistant cancer cells. Phytomedicine.
33:62–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
O'Brien J, Wilson I, Orton T and Pognan F:
Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for
the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur J Biochem.
267:5421–5426. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Saeed ME, Mertens R, Handgretinger R and
Efferth T: Identification of fatal outcome in a childhood
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient by protein expression profiling.
Int J Oncol. 53:1721–1731. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Blaskó G, Cordell GA and Lankin DC:
Definitive 1H-and 13C-NMR assignments of
artemisinin (Qinghaosu). J Nat Prod. 51:1273–1276. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Haynes RK, Cheu KW, N'Da D, Coghi P and
Monti D: Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin
anti-malarials: Part 1 - the 'carbon radical' and 'heme'
hypotheses. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 13:217–277. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Klonis N, Creek DJ and Tilley L: Iron and
heme metabolism in Plasmodium falciparum and the mechanism of
action of arte-misinins. Curr Opin Microbiol. 16:722–727. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Efferth T, Benakis A, Romero MR, Tomicic
M, Rauh R, Steinbach D, Häfer R, Stamminger T, Oesch F, Kaina B, et
al: Enhancement of cytotoxicity of artemisinins toward cancer cells
by ferrous iron. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:998–1009. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kelter G, Steinbach D, Konkimalla VB,
Tahara T, Taketani S, Fiebig HH and Efferth T: Role of transferrin
receptor and the ABC transporters ABCB6 and ABCB7 for resistance
and differentiation of tumor cells towards artesunate. PLoS One.
2:e7982007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Aulbert E, Disselhoff W, Sörje H, Schulz E
and Gericke D: Lysosomal accumulation of 67Ga - transferrin in
malignant tumors in relation to their growth rate. Eur J Cancer.
16:1217–1232. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sadava D, Phillips T, Lin C and Kane SE:
Transferrin overcomes drug resistance to artemisinin in human
small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 179:151–156. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhao F, Wang H, Kunda P, Chen X, Liu QL
and Liu T: Artesunate exerts specific cytotoxicity in
retinoblastoma cells via CD71. Oncol Rep. 30:1473–1482. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang Q, Wu S, Zhao X, Zhao C, Zhao H and
Huo L: Mechanisms of dihydroartemisinin and
dihydroartemisinin/holotransferrin cytotoxicity in t-cell lymphoma
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01373312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Judd W, Poodry CA and Strominger JL: Novel
surface antigen expressed on dividing cells but absent from
nondividing cells. J Exp Med. 152:1430–1435. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sutherland R, Delia D, Schneider C, Newman
R, Kemshead J and Greaves M: Ubiquitous cell-surface glycoprotein
on tumor cells is proliferation-associated receptor for
transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:4515–4519. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Trowbridge IS and Omary MB: Human cell
surface glycoprotein related to cell proliferation is the receptor
for transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 78:3039–3043. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gatter KC, Brown G, Trowbridge IS,
Woolston RE and Mason DY: Transferrin receptors in human tissues:
Their distribution and possible clinical relevance. J Clin Pathol.
36:539–545. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tortorella S and Karagiannis TC:
Transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis: A useful target for
cancer therapy. J Membr Biol. 247:291–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Luria-Pérez R, Helguera G and Rodríguez
JA: Antibody-mediated targeting of the transferrin receptor in
cancer cells. Bol Méd Hosp Infant México. 73:372–379. 2016.
|
|
71
|
Akbari B, Farajnia S, Ahdi Khosroshahi S,
Safari F, Yousefi M, Dariushnejad H and Rahbarnia L: Immunotoxins
in cancer therapy: Review and update. Int Rev Immunol. 36:207–219.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lai H, Sasaki T, Singh NP and Messay A:
Effects of arte-misinin-tagged holotransferrin on cancer cells.
Life Sci. 76:1267–1279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nakase I, Gallis B, Takatani-Nakase T, Oh
S, Lacoste E, Singh NP, Goodlett DR, Tanaka S, Futaki S, Lai H, et
al: Transferrin receptor-dependent cytotoxicity of
artemisinin-transferrin conjugates on prostate cancer cells and
induction of apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 274:290–298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Gong Y, Gallis BM, Goodlett DR, Yang Y, Lu
H, Lacoste E, Lai H and Sasaki T: Effects of transferrin conjugates
of artemisinin and artemisinin dimer on breast cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 33:123–132. 2013.
|
|
75
|
Zhong YR: Chemical constituents of
volatile oils of Artemisia annua. Zhong Yao Tong Bao. 8:31–32.
1983.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liao HW, Wang DY and Li XM: Studies on the
chemical constituents of essential oil of Hunan Artemisia annua.
Zhong Yao Cai. 29:562–564. 2006.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Efferth T, Herrmann F, Tahrani A and Wink
M: Cytotoxic activity of secondary metabolites derived from
Artemisia annua L. towards cancer cells in comparison to its
designated active constituent artemisinin. Phytomedicine.
18:959–969. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Guo L, Qiu Z, Huang L and
Qu X: Differences in chemical constituents of Artemisia annua L.
from different geographical regions in China. PLoS One.
12:e01830472017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Efferth T, Konkimalla VB, Wang YF,
Sauerbrey A, Meinhardt S, Zintl F, Mattern J and Volm M: Prediction
of broad spectrum resistance of tumors towards anticancer drugs.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:2405–2412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Volm M and Efferth T: Prediction of cancer
drug resistance and implications for personalized medicine. Front
Oncol. 5:2822015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Duffy MJ, Harbeck N, Nap M, Molina R,
Nicolini A, Senkus E and Cardoso F: Clinical use of biomarkers in
breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor
Markers (EGTM). Eur J Cancer. 75:284–298. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sun X and Kaufman PD: Ki-67: More than a
proliferation marker. Chromosoma. 127:175–186. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Scott CS, Ramsden W, Limbert HJ, Master PS
and Roberts BE: Membrane transferrin receptor (TfR) and nuclear
proliferation-associated Ki-67 expression in hemopoietic
malignancies. Leukemia. 2:438–442. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Soyer HP, Smolle J, Smolle-Juettner FM and
Kerl H: Proliferation antigens in cutaneous melanocytic tumors - an
immunohisto-chemical study comparing the transferrin receptor and
the Ki-67 antigen. Dermatologica. 179:3–9. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Wrba F, Chott A, Reiner A, Reiner G,
Markis-Ritzinger E and Holzner JH: Ki-67 immunoreactivity in breast
carcinomas in relation to transferrin receptor expression, estrogen
receptor status and morphological criteria. An immunohistochemical
study. Oncology. 46:255–259. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Prior R, Reifenberger G and Wechsler W:
Transferrin receptor expression in tumours of the human nervous
system: Relation to tumour type, grading and tumour growth
fraction. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 416:491–496.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kearsley JH, Furlong KL, Cooke RA and
Waters MJ: An immuno-histochemical assessment of cellular
proliferation markers in head and neck squamous cell cancers. Br J
Cancer. 61:821–827. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Chan KT, Choi MY, Lai KK, Tan W, Tung LN,
Lam HY, Tong DK, Lee NP and Law S: Overexpression of transferrin
receptor CD71 and its tumorigenic properties in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:1296–1304. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Motamedi M, Xu L and Elahi S: Correlation
of transferrin receptor (CD71) with Ki67 expression on stimulated
human and mouse T cells: The kinetics of expression of T cell
activation markers. J Immunol Methods. 437:43–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Darb-Esfahani S, Kolaschinski I, Trillsch
F, Mahner S, Concin N, Vergote I, Van Nieuwenhuysen E,
Achimas-Cadariu P, Glajzer J, Woopen H, et al: Morphology and
tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in high-stage, high-grade serous
ovarian carcinoma correlated with long-term survival.
Histopathology. 73:1002–1012. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lee JS, Won HS, Sun S, Hong JH and Ko YH:
Prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in gastric
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 97:e117692018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Shen M, Wang J and Ren X: New insights
into tumor-infiltrating B lymphocytes in breast cancer: Clinical
impacts and regulatory mechanisms. Front Immunol. 9:4702018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Uhl M, Schwab S and Efferth T: Fatal liver
and bone marrow toxicity by combination treatment of
dichloroacetate and arte-sunate in a glioblastoma multiforme
patient: Case report and review of the literature. Front Oncol.
6:2042016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Efferth T, Schöttler U, Krishna S,
Schmiedek P, Wenz F and Giordano FA: Answer to the comment of Hai
Lu et al. regarding 'Hepatotoxicity by combination treatment of
temozolomide, artesunate and Chinese herbs in a glioblastoma
multiforme patient: Case report and review of the literature. Arch
Toxicol (2016). Arch Toxicol. 91:2491–2492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Eigbibhalu UG, Albert Taiwo EO, Douglass
IA and Abimbola EA: Effect of selected anti-malarial drugs on the
blood chemistry and brain serotonin levels in male rabbits. Pak J
Pharm Sci. 26:125–129. 2013.
|
|
96
|
Zhu CY, Xu QH, Mao ZY and Lin N:
Application of three arte-misinin derivatives in neuropathic pain:
Evaluating co-curation of nociceptive and emotional syndromes in
spinal cord ligation mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 43:3058–3063.
2018.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Amos S, Chindo BA, Abbah J, Vongtau HO,
Edmond I, Binda L, Akah PA, Wambebe C and Gamaniel KS: Postsynaptic
dopamine (D(2))-mediated behavioural effects of high acute doses of
arte-misinin in rodents. Brain Res Bull. 62:255–260. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|