|
1
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Goding Sauer A, Newman
LA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in
mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:439–448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sledge GW, Mamounas EP, Hortobagyi GN,
Burstein HJ, Goodwin PJ and Wolff AC: Past, present, and future
challenges in breast cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 32:1979–1986.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moiseenko F, Volkov N, Bogdanov A, Dubina
M and Moiseyenko V: Resistance mechanisms to drug therapy in breast
cancer and other solid tumors: An opinion. F1000Res. 6:2882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu W, Fu X, Yang Z, Li S, Cao Y, Li Q and
Luan J: Moderate intermittent negative pressure increases
invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cells.
Breast. 38:14–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sun L, Legood R, Dos-Santos-Silva I, Gaiha
SM and Sadique Z: Global treatment costs of breast cancer by stage:
A systematic review. PLoS One. 13:e02079932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
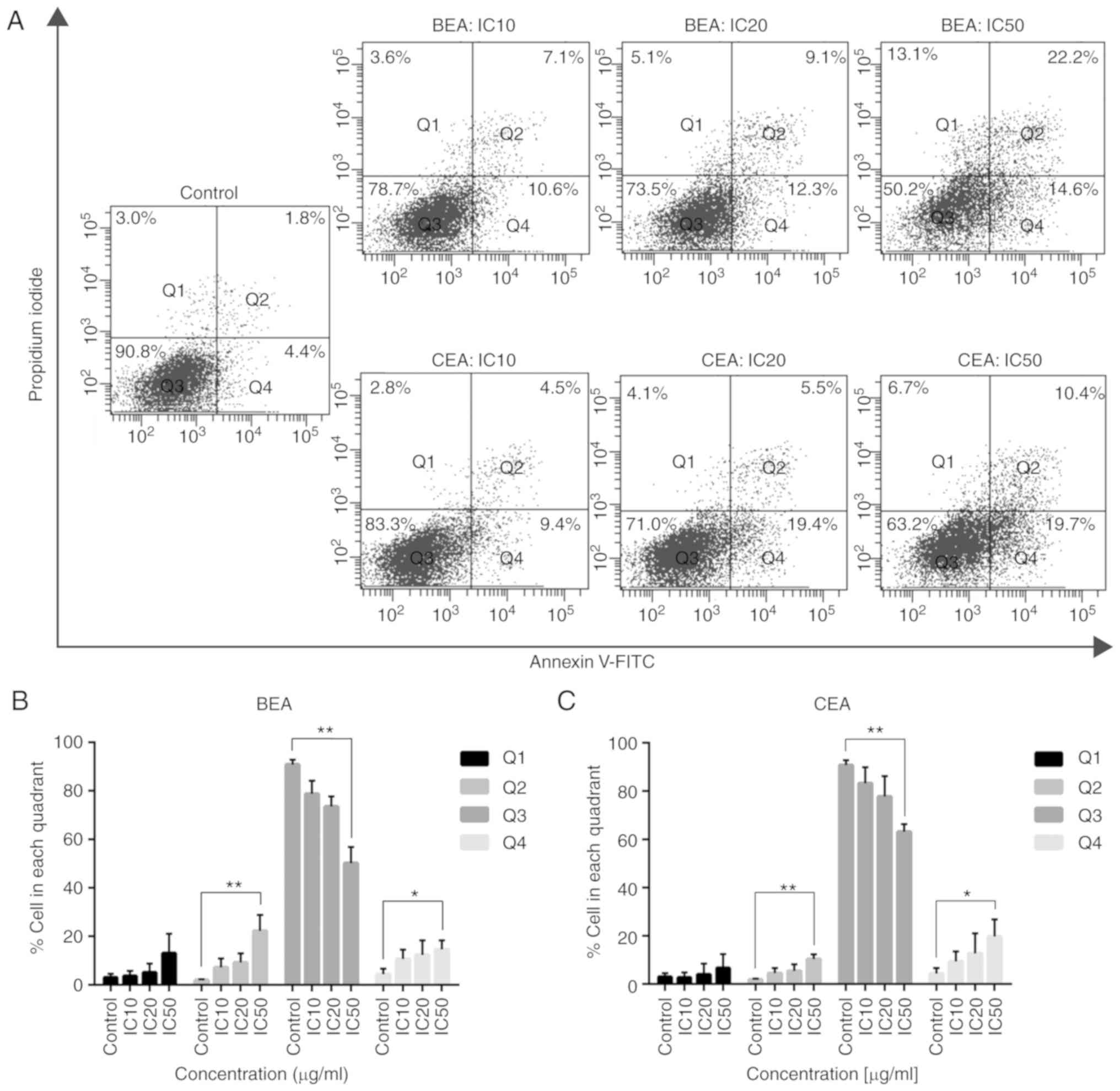
|
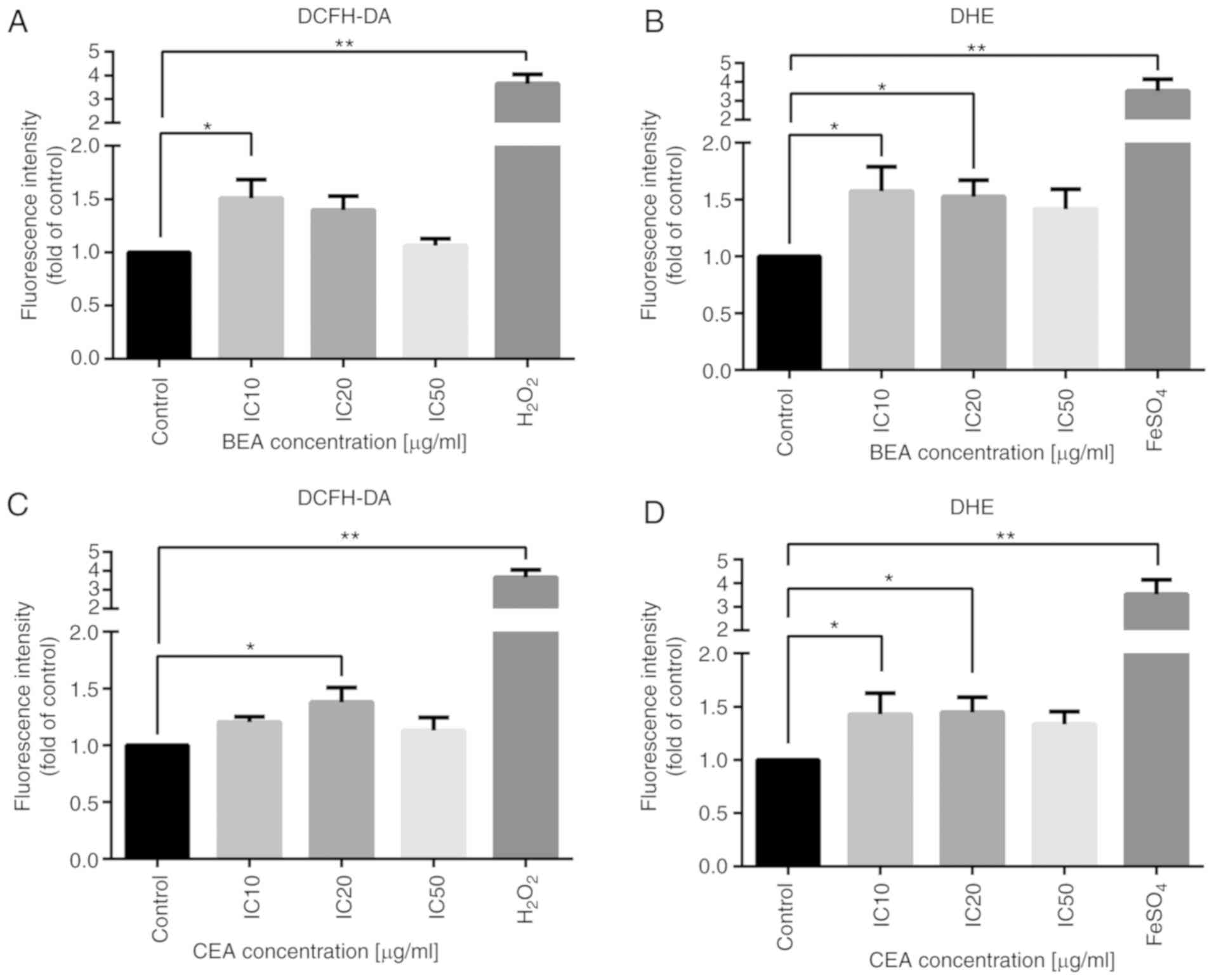
7
|
Chotchoungchatchai S, Saralamp P,
Jenjittikul T, Pornsiripongse S and Prathanturarug S: Medicinal
plants used with thai traditional medicine in modern healthcare
services: A case study in Kabchoeng Hospital, Surin Province,
Thailand. J Ethnopharmacol. 141:193–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boonyaratavej S, Tantayanontha S,
Kitchanachai P, Chaichantipyuth C, Chittawong V and Miles DH:
Trans-triacontyl-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamate, a new compound from
the thai plant bridelia ovata. J Nat Prod. 55:1761–1763. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Thongkorn N: Chemical constituents of the
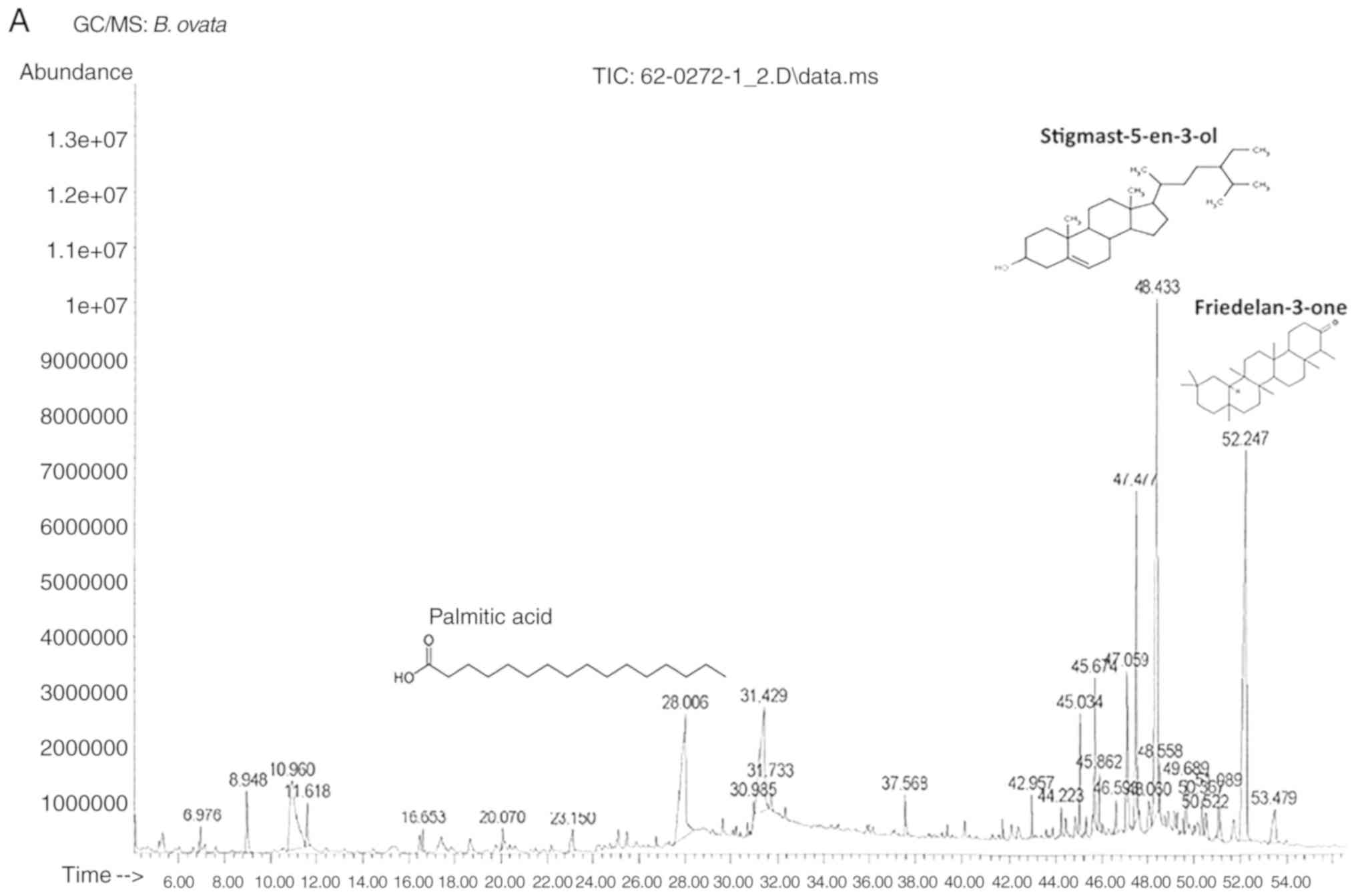
leaves of bridelia ovata decne (unpublished PhD thesis).
Chulalongkorn University; 1995
|
|
10
|
Baig H, Diskul-Na-Ayudthaya P, Weeraphan
C, Paricharttanakul M, Svasti J and Srisomsap C: Inhibitory effect
of bridelia ovata decne extract on HepG2 cell migration and
invasion stimulated by fibroblast-conditioned media. Naresuan
Phayao J. 1:6–10. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Sommit D, Petsom A, Ishikawa T and
Roengsumran S: Cytotoxic activity of natural labdanes and their
semi-synthetic modified derivatives from Croton oblongifolius.
Planta Med. 69:167–170. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
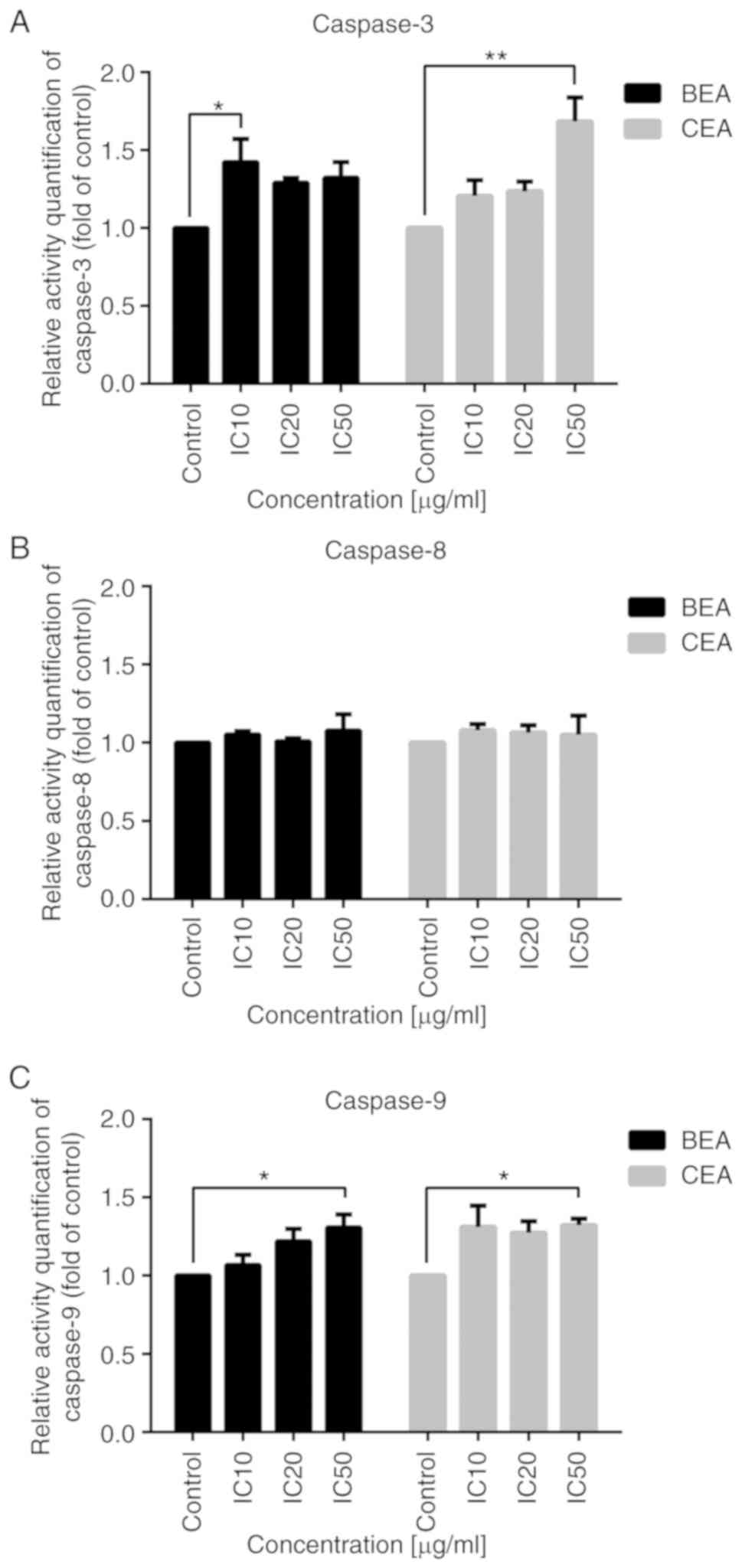
Ngamrojnavanich N, Sirimongkon S,
Roengsumran S, Petsom A and Kamimura H: Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase
activity by (-)-ent-Kaur-16-en-19-oic acid and its derivatives.
Planta Med. 69:555–556. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ahmed B, Alam T, Varshney M and Khan SA:
Hepatoprotective activity of two plants belonging to the Apiaceae
and the euphor-biaceae family. J Ethnopharmacol. 79:313–316. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Salatino A, Salatino MLF and Negri G:
Traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology of Croton species
(Euphorbiaceae). J Braz Chem Soc. 18:11–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Singh M, Pal M and Sharma RP: Biological
activity of the labdane diterpenes. Planta Med. 65:2–8. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takeshige Y, Kawakami S, Matsunami K,
Otsuka H, Lhieochaiphant D and Lhieochaiphant S: Oblongionosides
A-F, megastigmane glycosides from the leaves of Croton
oblongifolius Roxburgh. Phytochemistry. 80:132–136. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roengsumran S, Petsom A, Kuptiyanuwat N,
Vilaivan T, Ngamrojnavanich N, Chaichantipyuth C and Phuthong S:
Cytotoxic labdane diterpenoids from Croton oblongifolius.
Phytochemistry. 56:103–107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pudhom K and Sommit D: Clerodane
diterpenoids and a trisubstituted furan from Croton oblongifolius.
Phytochem Lett. 4:147–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Roengsumran S, Musikul K, Petsom A,
Vilaivan T, Sangvanich P, Pornpakakul S, Puthong S, Chaichantipyuth
C, Jaiboon N and Chaichit N: Croblongifolin, a new anticancer
clerodane from Croton oblongifolius. Planta Med. 68:274–277. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Youngsa-ad W, Ngamrojanavanich N, Mahidol
C, Ruchirawat S, Prawat H and Kittakoop P: Diterpenoids from the
roots of Croton oblongifolius. Planta Med. 73:1491–1494. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pudhom K, Vilaivan T, Ngamrojanavanich N,
Dechangvipart S, Sommit D, Petsom A and Roengsumran S:
Furanocembranoids from the stem bark of Croton oblongifolius. J Nat
Prod. 70:659–661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roengsumran S, Pornpakakul S, Muangsin N,
Sangvanich P, Nhujak T, Singtothong P, Chaichit N, Puthong S and
Petsom A: New halimane diterpenoids from Croton oblongifolius.
Planta Med. 70:87–89. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roengsumran S, Achayindee S, Petsom A,
Pudhom K, Singtothong P, Surachetapan C and Vilaivan T: Two new
cembranoids from Croton oblongifolius. J Nat Prod. 61:652–654.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roengsumran S, Singtothong P, Pudhom K,
Ngamrochanavanich N, Petsom A and Chaichantipyuth C:
Neocrotocembranal from Croton oblongifolius. J Nat Prod.
62:1163–1164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suwancharoen S, Tommeurd W, Phurat C,
Muangsin N and Pornpakakul S: Acanthoic acid. Acta Crystallogr Sect
E Struct Rep Online. 66:o15312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Renehan AG, Booth C and Potten CS: What is
apoptosis, and why is it important? BMJ. 322:1536–1538. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Favaloro B, Allocati N, Graziano V, Di
Ilio C and De Laurenzi V: Role of apoptosis in disease. Aging
(Albany N Y). 4:330–349. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Fathi N, Rashidi G, Khodadadi A, Shahi S
and Sharifi S: STAT3 and apoptosis challenges in cancer. Int J Biol
Macromol. 117:993–1001. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kumar R, Herbert PE and Warrens AN: An
introduction to death receptors in apoptosis. Int J Surg.
3:268–277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
O'Brien MA and Kirby R: Apoptosis: A
review of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways and
dysregulation in disease. J Veterinary Emergency Crit Care.
18:572–585. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schneider P and Tschopp J: Apoptosis
induced by death receptors. Pharm Acta Helv. 74:281–286. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chinnaiyan AM: The apoptosome: Heart and
soul of the cell death machine. Neoplasia. 1:5–15. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tait SW and Green DR: Mitochondria and
cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:621–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao K and Tait SWG: Apoptosis and cancer:
Force awakens, phantom menace, or both? Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
337:135–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong N, Liu X, Zhao T, Wang L, Li H, Zhang
S, Li X, Bai X, Zhang Y and Yang B: Apoptosis-inducing effects and
growth inhibitory of a novel chalcone, in human hepatic cancer
cells and lung cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:195–203.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J,
Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F, et al: A
collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of
functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell. 10:515–527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai X, Cheng H, Bai Z and Li J: Breast
cancer cell line classification and its relevance with breast tumor
subtyping. J Cancer. 8:3131–3141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen X and Thibeault S: Effect of DMSO
concentration, cell density and needle gauge on the viability of
cryopreserved cells in three dimensional hyaluronan hydrogel. Conf
Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013:6228–6231. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arega ED: Phytochemical studies of the
ethyl acetate extract of the fruit of piper capense. J Pharm Nat
Products. 4:148–152. 2018.
|
|
40
|
Obasi NL, Egbuonu ACC, Ukoha PO and
Ejikeme PM: Comparative phytochemical and antimicrobial screening
of some solvent extracts of Samanea saman (fabaceae or mimosaceae)
pods. Afr J Pure Appl Chem. 4:206–212. 2010.
|
|
41
|
Tiwari P, Kumar B, Kaur M, Kaur G and Kaur
H: Phytochemical screening and extraction: A review. Int Pharm Sci.
1:98–106. 2011.
|
|
42
|
Banjerdpongchai R, Yingyurn S and
Kongtawelert P: Sesamin induces human leukemic cell apoptosis via
mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways. World J
Oncol. 1:78–86. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wudtiwai B, Sripanidkulchai B,
Kongtawelert P and Banjerdpongchai R: Methoxyflavone derivatives
modulate the effect of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human leukemic
cell lines. J Hematol Oncol. 4:522011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khaw-on P and Banjerdpongchai R: Induction
of intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways in the human leukemic
MOLT-4 cell line by terpinen-4-ol. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:3073–3076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Khaw-On P, Pompimon W and Banjerdpongchai
R: Goniothalamin induces necroptosis and anoikis in human invasive
breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E39532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dikalov S, Griendling KK and Harrison DG:
Measurement of reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular studies.
Hypertension. 49:717–727. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao H, Kalivendi S, Zhang H, Joseph J,
Nithipatikom K, Vasquez-Vivar J and Kalyanaraman B: Superoxide
reacts with hydroethidine but forms a fluorescent product that is
distinctly different from ethidium: Potential implications in
intracellular fluorescence detection of superoxide. Free Radic Biol
Med. 34:1359–1368. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mitas M, Mikhitarian K, Walters C, Baron
PL, Elliott BM, Brothers TE, Robison JG, Metcalf JS, Palesch YY,
Zhang Z, et al: Quantitative real-time RT-PCR detection of breast
cancer micrometastasis using a multigene marker panel. Int J
Cancer. 93:162–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hanf A, Oelze M, Manea A, Li H, Munzel T
and Daiber A: The anti-cancer drug doxorubicin induces substantial
epigenetic changes in cultured cardiomyocytes. Chem Biol Interact.
313:1088342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wudtiwai B, Pitchakarn P and
Banjerdpongchai R: Alpha-mangostin, an active compound in Garcinia
mangostana, abrogates anoikis-resistance in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 53:222–232. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Badisa RB, Darling-Reed SF, Joseph P,
Cooperwood JS, Latinwo LM and Goodman CB: Selective cytotoxic
activities of two novel synthetic drugs on human breast carcinoma
MCF-7 cells. Anticancer Res. 29:2993–2996. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Prayong P, Barusrux S and Weerapreeyakul
N: Cytotoxic activity screening of some indigenous Thai plants.
Fitoterapia. 79:598–601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rivankar S: An overview of doxorubicin
formulations in cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:853–858.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kalogeris T, Bao Y and Korthuis RJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: A double edged sword in
ischemia/reperfusion vs. preconditioning Redox Biol. 2:702–714.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kalyanaraman B, Darley-Usmar V, Davies KJ,
Dennery PA, Forman HJ, Grisham MB, Mann GE, Moore K, Roberts LJ II
and Ischiropoulos H: Measuring reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
with fluorescent probes: Challenges and limitations. Free Radic
Biol Med. 52:1–6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2 family proteins
in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells. 3:697–707.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sousa GFd, Soares DCF, Mussel WdN, Pompeu
NFE, Silva GDdF, Vieira Filho SA and Duarte LP: Pentacyclic
triterpenes from branches of Maytenus robusta and in vitro
cytotoxic property against. J Braz Chem Soc. 25:1338–1345.
2014.
|
|
59
|
Martucciello S, Balestrieri ML, Felice F,
Estevam Cdos S, Sant'Ana AE, Pizza C and Piacente S: Effects of
triterpene derivatives from Maytenus rigida on VEGF-induced
Kaposi's sarcoma cell proliferation. Chem Biol Interact.
183:450–454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Balbinot RB, de Oliveira JAM, Bernardi DI,
Melo UZ, Zanqueta EB, Endo EH, Ribeiro FM, Volpato H, Figueiredo
MC, Back DF, et al: Structural characterization and biological
evaluation of 18-Nor-ent-labdane diterpenoids from grazielia
gaudichaudeana. Chem Biodivers. 16:e18006442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cavalcanti BC, Ferreira JR, Moura DJ, Rosa
RM, Furtado GV, Burbano RR, Silveira ER, Lima MA, Camara CA, Saffi
J, et al: Structure-mutagenicity relationship of kaurenoic acid
from Xylopia sericeae (Annonaceae). Mutat Res. 701:153–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cavalcanti BC, Bezerra Dp, Magalhaes HI,
Moraes MO, Lima MA, Silveira ER, Camara CA, Rao VS, Pessoa C and
Costa-Lotufo LV: Kauren-19-oic acid induces DNA damage followed by
apoptosis in human leukemia cells. J Appl Toxicol. 29:560–568.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cuca LE, Coy ED, Alarcon MA, Fernandez A
and Aristizabal FA: Cytotoxic effect of some natural compounds
isolated from Lauraceae plants and synthetic derivatives.
Biomedica. 31:335–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Cardoso PCDS, Rocha CAMD, Leal MF, Bahia
MO, Alcantara DDFA, Santos RAD, Gongalves NDS, Ambrosio SR,
Cavalcanti BC, Moreira-Nunes CA, et al: Effect of diterpenoid
kaurenoic acid on genotoxicity and cell cycle progression in
gastric cancer cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:772–780. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rocha SMMD, Cardoso PCDS, Bahia MO, Pessoa
CDO, Soares PC, Rocha SMD, Burbano RMR and Rocha CAMD: Effect of
the kaurenoic acid on genotoxicity and cell cycle progression in
cervical cancer cells lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 57:126–131. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fernandes VC, Pereira SI, Coppede J,
Martins JS, Rizo WF, Beleboni RO, Marins M, Pereira PS, Pereira AM
and Fachin AL: The epimer of kaurenoic acid from Croton
antisyphiliticus is cytotoxic toward B-16 and HeLa tumor cells
through apoptosis induction. Genet Mol Res. 12:1005–1011. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Fernando IPS, Sanjeewa KKA, Ann YS, Ko CI,
Lee SH, Lee WW and Jeon YJ: Apoptotic and antiproliferative effects
of Stigmast-5-en-3-ol from Dendronephthya gigantea on human
leukemia HL-60 and human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Toxicol In
Vitro. 52:297–305. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jian B, Zhang H, Han C and Liu J:
Anti-cancer activities of diterpenoids derived from Euphorbia
fischeriana steud. Molecules. 23:E3872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Petiwala SM and Johnson JJ: Diterpenes
from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis): Defining their potential
for anti-cancer activity. Cancer Lett. 367:93–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Suttiarporn P, Chumpolsri W,
Mahatheeranont S, Luangkamin S, Teepsawang S and Leardkamolkarn V:
Structures of phytosterols and triterpenoids with potential
anti-cancer activity in bran of black non-glutinous rice.
Nutrients. 7:1672–1687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Saleem M: Lupeol, a novel
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene. Cancer Lett.
285:109–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Weerapreeyakul N, Nonpunya A, Barusrux S,
Thitimetharoch T and Sripanidkulchai B: Evaluation of the
anticancer potential of six herbs against a hepatoma cell line.
Chin Med. 7:152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Reactive oxygen
species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol
Med. 48:749–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Redza-Dutordoir M and Averill-Bates DA:
Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen
species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2977–2992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
He H, Zang LH, Feng YS, Chen LX, Kang N,
Tashiro S, Onodera S, Qiu F and Ikejima T: Physalin A induces
apoptosis via p53-Noxa-mediated ROS generation, and autophagy plays
a protective role against apoptosis through p38-NF-kB survival
pathway in A375-S2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 148:544–555. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yu CC, Ko FY, Yu CS, Lin CC, Huang YP,
Yang JS, Lin JP and Chung JG: Norcantharidin triggers cell death
and DNA damage through S-phase arrest and ROS-modulated apoptotic
pathways in TSGH 8301 human urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 41:1050–1060. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Weinberg F, Ramnath N and Nagrath D:
Reactive oxygen species in the tumor microenvironment: An overview.
Cancers (Basel). 11:E11912019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Crompton M: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 341:233–249.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Griffith OW: Biologic and pharmacologic
regulation of mammalian glutathione synthesis. Free Radic Biol Med.
27:922–935. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Komonrit P and Banjerdpongchai R: Effect
of Pseuderanthemum palatiferum (Nees) radlk fresh leaf ethanolic
extract on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 regulated cell death.
Tumour Biol. 40:10104283188001822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kumari S, Badana AK, GMM GS and Malla R:
Reactive oxygen species: A key constituent in cancer survival.
Biomark Insights. 13:11772719187553912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kastenhuber ER and Lowe SW: Putting p53 in
context. Cell. 170:1062–1078. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Vousden KH and Lu X: Live or let die: The
cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:594–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T and Housman DE:
p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer
agents. Cell. 74:957–967. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shibue T, Suzuki S, Okamoto H, Yoshida H,
Ohba Y, Takaoka A and Taniguchi T: Differential contribution of
Puma and Noxa in dual regulation of p53-mediated apoptotic
pathways. EMBO J. 25:4952–4962. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Shibue T, Takeda K, Oda E, Tanaka H,
Murasawa H, Takaoka A, Morishita Y, Akira S, Taniguchi T and Tanaka
N: Integral role of Noxa in p53-mediated apoptotic response. Genes
Dev. 17:2233–2238. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhang LN, Li JY and Xu W: A review of the
role of Puma, Noxa and Bim in the tumorigenesis, therapy and drug
resistance of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther.
20:1–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
McIlwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5:a0086562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Saraste A and Pulkki K: Morphologic and
biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. 45:528–537.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Huttemann M, Pecina P, Rainbolt M,
Sanderson TH, Kagan VE, Samavati L, Doan JW and Lee I: The multiple
functions of cytochrome c and their regulation in life and death
decisions of the mammalian cell: From respiration to apoptosis.
Mitochondrion. 11:369–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Salvesen GS: Caspases and apoptosis.
Essays Biochem. 38:9–19. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|