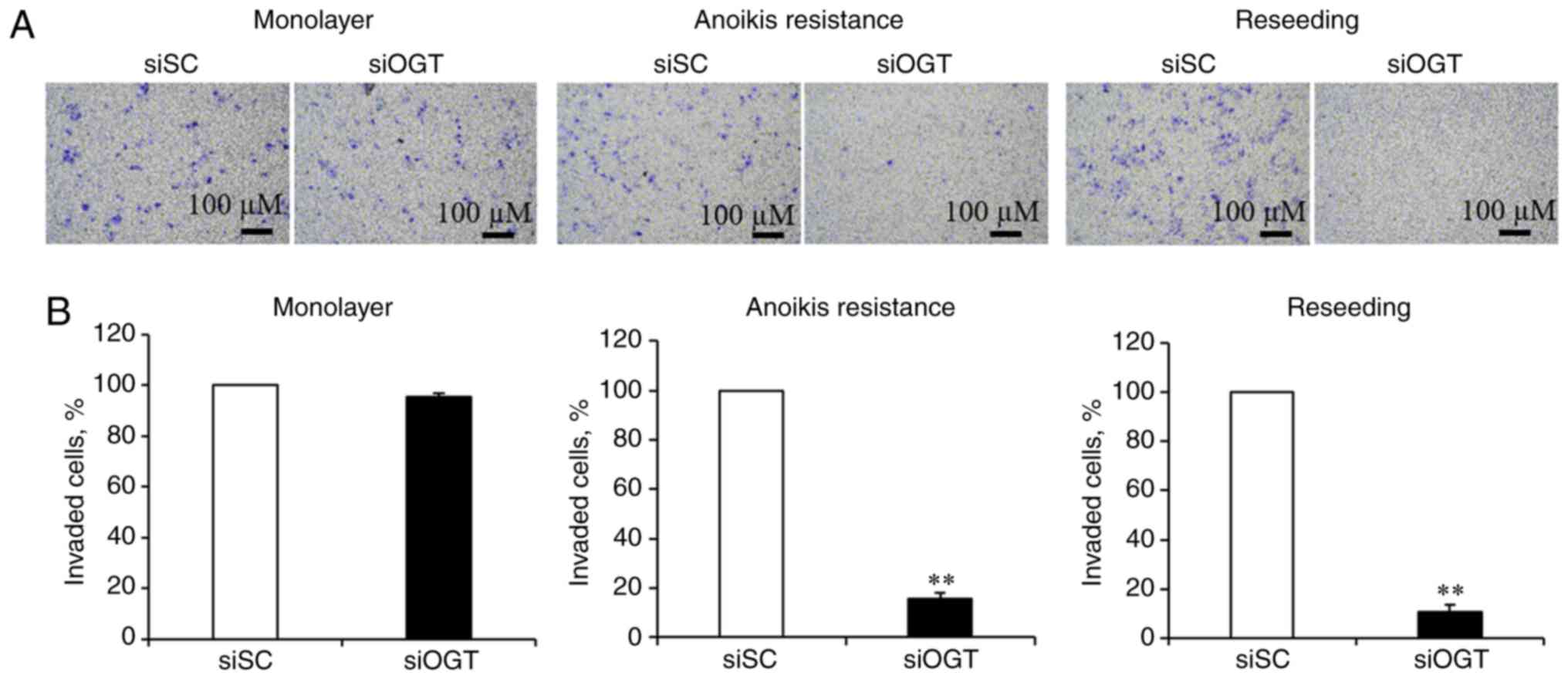
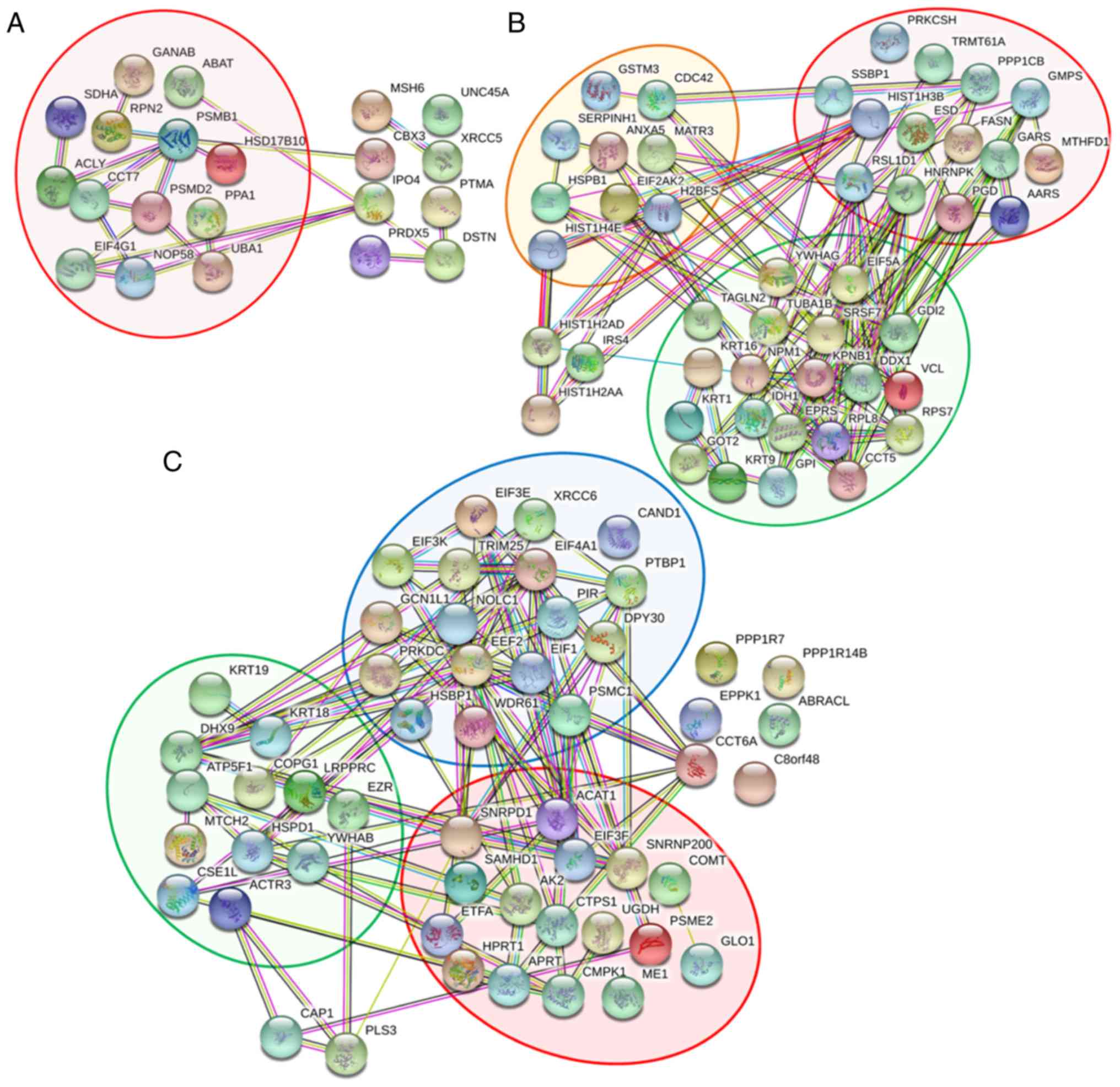
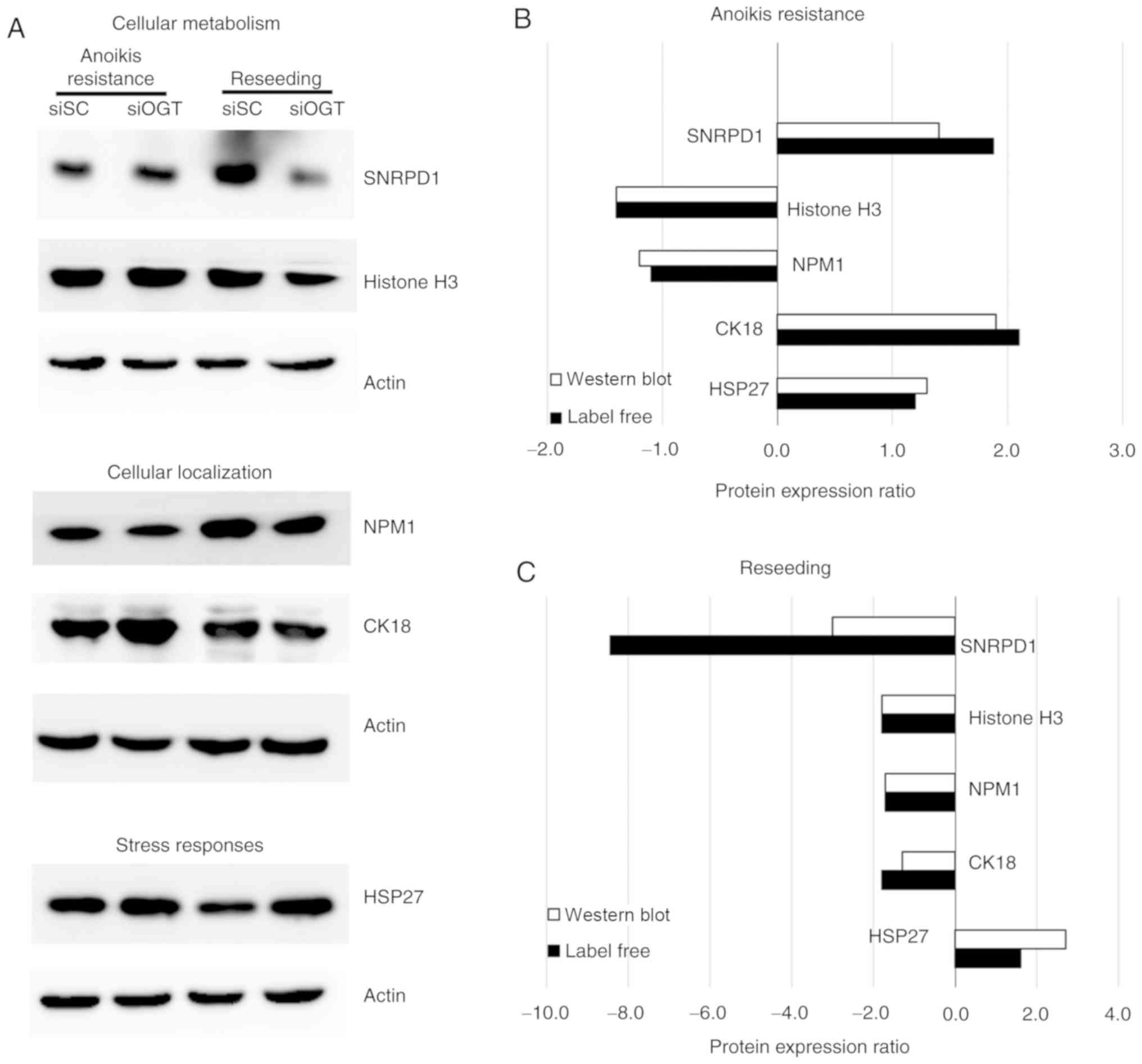
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Caplan L: Delay in breast cancer:
Implications for stage at diagnosis and survival. Front Public
Health. 2:872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hart GW, Housley MP and Slawson C: Cycling
of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins.
Nature. 446:1017–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kreppel LK, Blomberg MA and Hart GW:
Dynamic glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins. Cloning
and characterization of a unique O-GlcNAc transferase with multiple
tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem. 272:9308–9315. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao Y, Wells L, Comer FI, Parker GJ and
Hart GW: Dynamic O-glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins:
Cloning and characterization of a neutral, cytosolic
beta-N-acetylglucosa-minidase from human brain. J Biol Chem.
276:9838–9845. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanover JA, Chen W and Bond MR: O-GlcNAc
in cancer: An Oncometabolism-fueled vicious cycle. J Bioenerg
Biomembr. 50:155–173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chaiyawat P, Netsirisawan P, Svasti J and
Champattanachai V: Aberrant O-GIcNAcylated proteins: New
perspectives in breast and colorectal cancer. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 5:1932014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Champattanachai V, Netsirisawan P,
Chaiyawat P, Phueaouan T, Charoenwattanasatien R,
Chokchaichamnankit D, Punyarit P, Srisomsap C and Svasti J:
Proteomic analysis and abrogated expression of O-GlcNAcylated
proteins associated with primary breast cancer. Proteomics.
13:2088–2099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Phueaouan T, Chaiyawat P, Netsirisawan P,
Chokchaichamnankit D, Punyarit P, Srisomsap C, Svasti J and
Champattanachai V: Aberrant O-GlcNAc-modified proteins expressed in
primary colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:2929–2936. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Netsirisawan P, Chaiyawat P,
Chokchaichamnankit D, Lirdprapamongkol K, Srisomsap C, Svasti J and
Champattanachai V: Decreasing O-GlcNAcylation affects the malignant
transformation of MCF-7 cells via Hsp27 expression and its O-GlcNAc
modification. Oncol Rep. 40:2193–2205. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khongmanee A, Lirdprapamongkol K, Tit-oon
P, Chokchaichamnankit D, Svasti J and Srisomsap C: Proteomic
analysis reveals important role of 14-3-3sigma in anoikis
resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Proteomics. 13:3157–3166.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lirdprapamongkol K, Sakurai H, Kawasaki N,
Choo MK, Saitoh Y, Aozuka Y, Singhirunnusorn P, Ruchirawat S,
Svasti J and Saiki I: Vanillin suppresses in vitro invasion and in
vivo metastasis of mouse breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharm Sci.
25:57–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tit-Oon P, Chokchaichamnankit D,
Khongmanee A, Sawangareetrakul P, Svasti J and Srisomsap C:
Comparative secretome analysis of cholangiocarcinoma cell line in
three-dimensional culture. Int J Oncol. 45:2108–2116. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C,
Ivanyi I, Appel RD and Bairoch A: ExPASy: The proteomics server for
in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3784–3788. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kall L, Canterbury JD, Weston J, Noble WS
and MacCoss MJ: Semi-supervised learning for peptide identification
from shotgun proteomics datasets. Nat Methods. 4:923–925. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Donnell N, Zachara NE, Hart GW and Marth
JD: Ogt-dependent X-chromosome-linked protein glycosylation is a
requisite modification in somatic cell function and embryo
viability. Mol Cell Biol. 24:1680–1690. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gu Y, Mi W, Ge Y, Liu H, Fan Q, Han C,
Yang J, Han F, Lu X and Yu W: GlcNAcylation plays an essential role
in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:6344–6351. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lynch TP, Ferrer CM, Jackson SR, Shahriari
KS, Vosseller K and Reginato MJ: Critical role of O-Linked
beta-N-acetylglu-cosamine transferase in prostate cancer invasion,
angiogenesis, and metastasis. J Biol Chem. 287:11070–11081. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu Y, Xia Y, Wang J and Shi X:
O-GlcNAcylation promotes migration and invasion in human ovarian
cancer cells via the RhoA/ROCK/MLC pathway. Mol Med Rep.
15:2083–2089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang M, Xu B, Li X, Shang Y, Chu Y, Wang
W, Chen D, Wu N, Hu S, Zhang S, et al: O-GlcNAcylation promotes
colorectal cancer metastasis via the miR-101-O-GlcNAc/EZH2
regulatory feedback circuit. Oncogene. 38:301–316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Zhang H, Jiang X, Qian C, Liu Z and
Luo D: Factors involved in cancer metastasis: A better
understanding to 'seed and soil' hypothesis. Mol Cancer.
16:1762017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim YN, Koo KH, Sung JY, Yun UJ and Kim H:
Anoikis resistance: An essential prerequisite for tumor metastasis.
Int J Cell Biol. 2012:3068792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi HS, Choi BY, Cho YY, Mizuno H, Kang
BS, Bode AM and Dong Z: Phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10
is indispensable for neoplastic cell transformation. Cancer Res.
65:5818–5827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fong JJ, Nguyen BL, Bridger R, Medrano EE,
Wells L, Pan S and Sifers RN: β-N-Acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is a
novel regulator of mitosis-specific phosphorylations on histone H3.
J Biol Chem. 287:12195–12203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Phoomak C, Park D, Silsirivanit A,
Sawanyawisuth K, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Detarya M, Wongkham C,
Lebrilla CB and Wongkham S: O-GlcNAc-induced nuclear translocation
of hnRNP-K is associated with progression and metastasis of
chol-angiocarcinoma. Mol Oncol. 13:338–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Wong JCT, Hasan MR, Rahman M, Yu AC, Chan
SK, Schaeffer DF, Kennecke HF, Lim HJ, Owen D and Tai IT:
Nucleophosmin 1, upregulated in adenomas and cancers of the colon,
inhibits p53-mediated cellular senescence. Int J Cancer.
133:1567–1577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zeng D, Xiao YS, Zhu JL, Peng CY, Liang W
and Lin HY: Knockdown of nucleophosmin 1 suppresses proliferation
of triple-negative breast cancer cells through activating
CDH1/Skp2/p27kip1 pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 11:143–156. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qin FX, Shao HY, Chen XC, Tan S, Zhang HJ,
Miao ZY, Wang L, Hui-Chen and Zhang L: Knockdown of NPM1 by RNA
interference inhibits cells proliferation and induces apoptosis in
leukemic cell line. Int J Med Sci. 8:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kazemi Z, Chang HN, Haserodt S, McKen C
and Zachara NE: O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc)
regulates stress-induced heat shock protein expression in a
GSK-3beta-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 285:39096–39107. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hung CS, Huang CY, Lee CH, Chen WY, Huang
MT, Wei PL and Chang YJ: IGFBP2 plays an important role in heat
shock protein 27-mediated cancer progression and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 8:54978–54992. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cordonnier T, Bishop JL, Shiota M, Nip KM,
Thaper D, Vahid S, Heroux D, Gleave M and Zoubeidi A: Hsp27
regulates EGF/β-catenin mediated epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:E496–E507. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gibert B, Eckel B, Gonin V, Goldschneider
D, Fombonne J, Deux B, Mehlen P, Arrigo AP, Clézardin P and
Diaz-Latoud C: Targeting heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) interferes
with bone metastasis and tumour formation in vivo. Brit J Cancer.
107:63–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xiong XP, Vogler G, Kurthkoti K, Samsonova
A and Zhou R: SmD1 modulates the miRNA pathway independently of its
pre-mrna splicing function. PLoS Genet. 11:e10054752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z and Pützer BM: Spliceosomal protein E
regulates neoplastic cell growth by modulating expression of cyclin
E/CDK2 and G2/M checkpoint proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 12:2427–2438.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim YD, Lee J, Kim HS, Lee MO, Son MY, Yoo
CH, Choi JK, Lee SC and Cho YS: The unique spliceosome signature of
human pluripotent stem cells is mediated by SNRPA1, SNRPD1, and
PNN. Stem Cell Res. 22:43–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Quidville V, Alsafadi S, Goubar A, Commo
F, Scott V, Pioche-Durieu C, Girault I, Baconnais S, Le Cam E,
Lazar V, et al: Targeting the deregulated spliceosome core
machinery in cancer cells triggers mTOR blockade and autophagy.
Cancer Res. 73:2247–2258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hare SH and Harvey AJ: mTOR function and
therapeutic targeting in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 7:383–404.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu K, Liu P and Wei W: mTOR signaling in
tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:638–654. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian T, Li X and Zhang J: mTOR signaling
in cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:E7552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Malaguti P, Vari S, Cognetti F and Fabi A:
The Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in breast cancer:
Current evidence and future directions. Anticancer Res. 33:21–28.
2013.
|
|
45
|
Liu J, Li HQ, Zhou FX, Yu JW, Sun L and
Han ZH: Targeting the mTOR pathway in breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177108252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zaytseva YY, Valentino JD, Gulhati P and
Evers BM: mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 319:1–7.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gomez-Pinillos A and Ferrari AC: mTOR
signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 26:483–505. vii2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pópulo H, Lopes JM and Soares P: The mTOR
signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1886–1918.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|