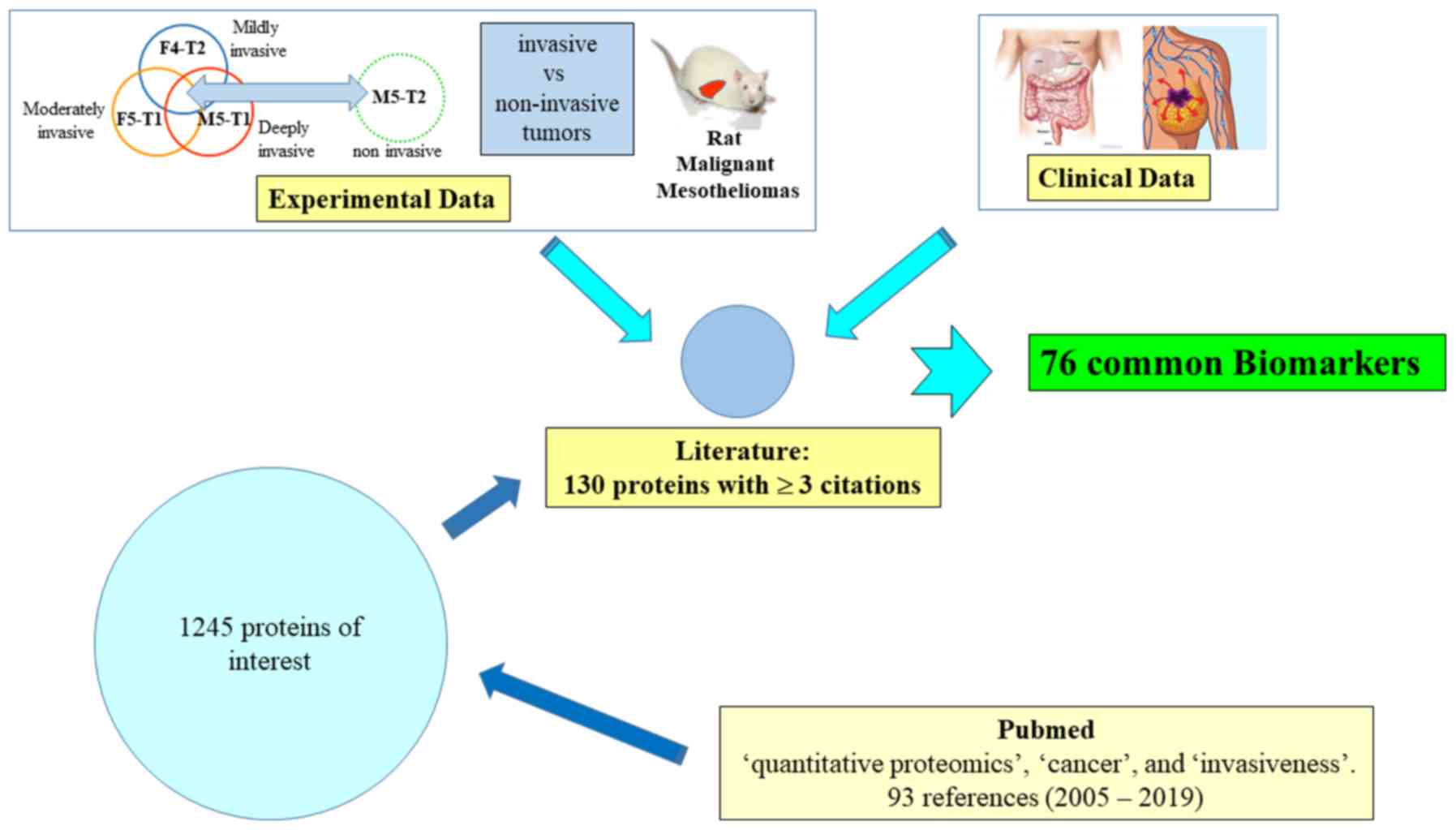
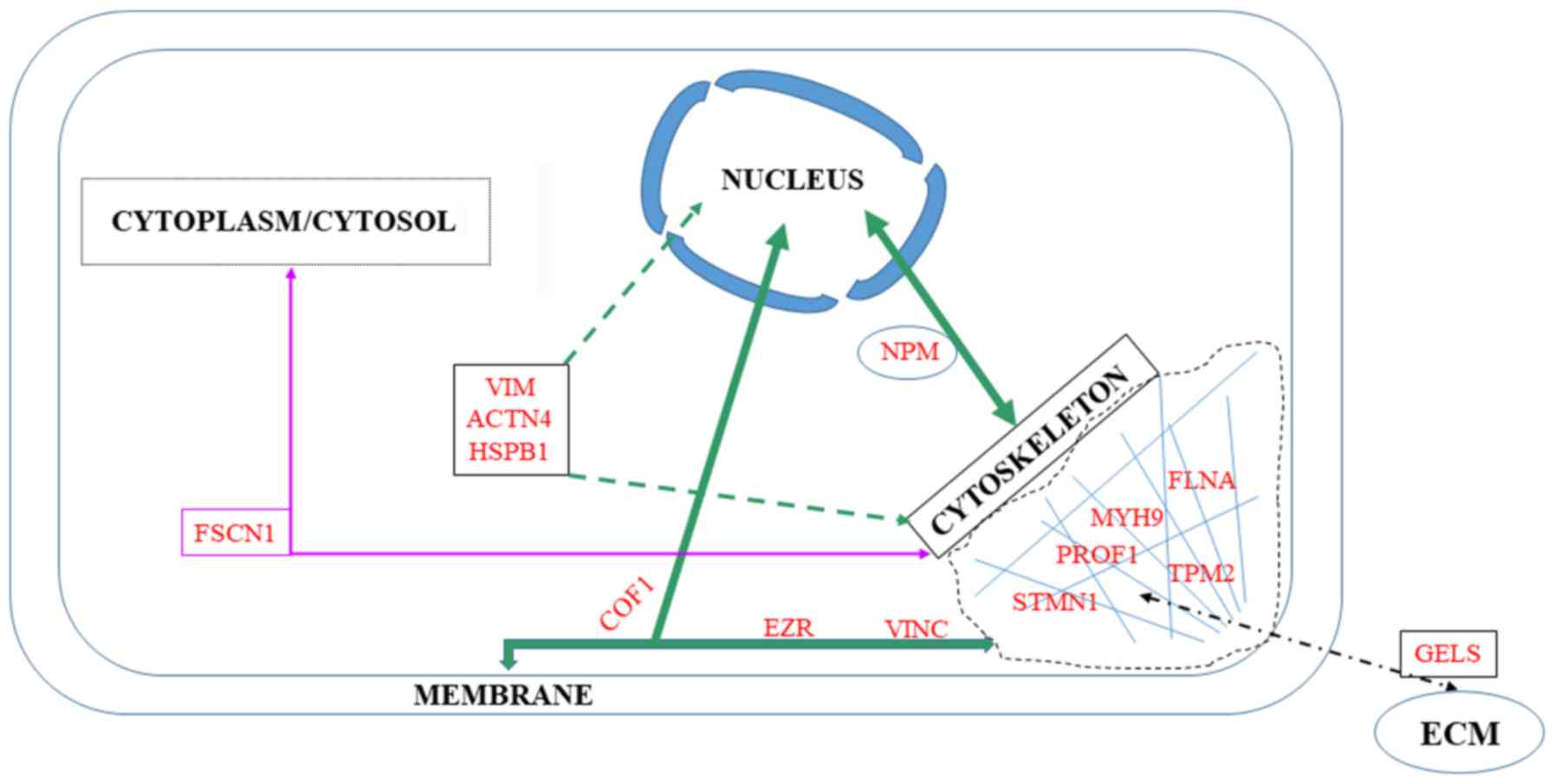
|
1
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber
RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn H-J, André F,
Baselga J, et al: Panel Members: Tailoring therapies - improving
the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International
Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer
2015. Ann Oncol. 26:1533–1546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang B, Wang J, Wang X, Zhu J, Liu Q, Shi
Z, Chambers MC, Zimmerman LJ, Shaddox KF, Kim S, et al: NCI CPTAC:
Proteogenomic characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 513:382–387. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johansson HJ, Socciarelli F, Vacanti NM,
Haugen MH, Zhu Y, Siavelis I, Fernandez-Woodbridge A, Aure MR,
Sennblad B, Vesterlund M, et al: Consortia Oslo Breast Cancer
Research Consortium (OSBREAC): Breast cancer quantitative proteome
and proteogenomic landscape. Nat Commun. 10:16002019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mann M: Quantitative proteomics? Nat
Biotechnol. 17:954–955. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Monti C, Zilocchi M, Colugnat I and
Alberio T: Proteomics turns functional. J Proteomics. 198:36–44.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Simpson RJ and Dorow DS: Cancer
proteomics: From signaling networks to tumor markers. Trends
Biotechnol. 19(Suppl): S40–S48. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cheung CHY and Juan HF: Quantitative
proteomics in lung cancer. J Biomed Sci. 24:372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geiger T and Geiger B: Towards elucidation
of functional molecular signatures of the adhesive-migratory
phenotype of malignant cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 20:146–152. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jazurek M, Ciesiolka A, Starega-Roslan J,
Bilinska K and Krzyzosiak WJ: Identifying proteins that bind to
specific RNAs - focus on simple repeat expansion diseases. Nucleic
Acids Res. 44:9050–9070. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abazova N and Krijgsveld J: Advances in
stem cell proteomics. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 46:149–155. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eubanks CG, Dayebgadoh G, Liu X and
Washburn MP: Unravelling the biology of chromatin in health and
cancer using proteomic approaches. Expert Rev Proteomics.
14:905–915. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gómez-Serrano M, Camafeita E, Loureiro M
and Peral B: Mitoproteomics: Tackling mitochondrial dysfunction in
human disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:14359342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suwakulsiri W, Rai A, Chen M, Greening DW
and Simpson RJ: Proteomic profiling reveals key cancer progression
modulators in shed microvesicles released from isogenic human
primary and metastatic colorectal cancer cell lines. Biochim
Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 1867:1401712019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li Z, Li N, Shen L and Fu J: Quantitative
proteomic analysis identifies MAPK15 as a potential regulator of
radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Front Oncol.
8:5482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gillet L, Navarro P, Tate S, Röst H,
Selevsek N, Reiter L, Bonner R and Aebersold R: Targeted data
extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent
acquisition: a new concept for consistent and accurate proteome
analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:pp. O111.0167172012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ludwig C, Gillet L, Rosenberger G, Amon S,
Collins BC and Aebersold R: Data-independent acquisition-based
SWATH-MS for quantitative proteomics: A tutorial. Mol Syst Biol.
14:pp. e81262018, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krisp C and Molloy MP: SWATH mass
spectrometry for proteomics of non-depleted plasma. Methods Mol
Biol. 1619:373–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jamwal R, Barlock BJ, Adusumalli S,
Ogasawara K, Simons BL and Akhlaghi F: Multiplex and label-free
relative quantification approach for studying protein abundance of
drug metabolizing enzymes in human liver microsomes using SWATH-MS.
J Proteome Res. 16:4134–4143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Skotland T, Berge V, Sandvig K and
Llorente A: Exosomal proteins as prostate cancer biomarkers in
urine: From mass spectrometry discovery to immunoassay-based
validation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 98:80–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nader JS, Abadie J, Deshayes S, Boissard
A, Blandin S, Blanquart C, Boisgerault N, Coqueret O, Guette C,
Grégoire M, et al: Characterization of increasing stages of
invasiveness identifies stromal/cancer cell crosstalk in rat models
of mesothelioma. Oncotarget. 9:16311–16329. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Besson D, Pavageau A-H, Valo I, Bourreau
A, Bélanger A, Eymerit-Morin C, Moulière A, Chassevent A,
Boisdron-Celle M, Morel A, et al: A quantitative proteomic approach
of the different stages of colorectal cancer establishes OLFM4 as a
new nonmetastatic tumor marker. Mol Cell Proteomics. 10:0097122011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valo I, Raro P, Boissard A, Maarouf A,
Jézéquel P, Verriele V, Campone M, Coqueret O and Guette C: OLFM4
expression in ductal carcinoma in situ and in invasive breast
cancer cohorts by a SWATH-based proteomic approach. Proteomics.
19:pp. e18004462019, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Powell AA, Talasaz AH, Zhang H, Coram MA,
Reddy A, Deng G, Telli ML, Advani RH, Carlson RW, Mollick JA, et
al: Single cell profiling of circulating tumor cells:
Transcriptional heterogeneity and diversity from breast cancer cell
lines. PLoS One. 7:e337882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lukanidin E and Sleeman JP: Building the
niche: The role of the S100 proteins in metastatic growth. Semin
Cancer Biol. 22:216–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bresnick AR, Weber DJ and Zimmer DB: S100
proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:96–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shabani F, Farasat A, Mahdavi M and Gheibi
N: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9): A key protein between inflammation
and cancer. Inflamm Res. 67:801–812. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Björk P, Källberg E, Wellmar U, Riva M,
Olsson A, He Z, Törngren M, Liberg D, Ivars F and Leanderson T:
Common interactions between S100A4 and S100A9 defined by a novel
chemical probe. PLoS One. 8:pp. e630122013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fei F, Qu J, Zhang M, Li Y and Zhang S:
S100A4 in cancer progression and metastasis: A systematic review.
Oncotarget. 8:73219–73239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshimura H, Otsuka A, Michishita M,
Yamamoto M, Ashizawa M, Zushi M, Moriya M, Azakami D, Ochiai K,
Matsuda Y, et al: Expression and roles of S100A4 in anaplastic
cells of canine mammary carcinomas. Vet Pathol. 56:389–398. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y and Cao X: Characteristics and
significance of the pre-metastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 30:668–681.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hansen MT, Forst B, Cremers N, Quagliata
L, Ambartsumian N, Grum-Schwensen B, Klingelhöfer J, Abdul-Al A,
Herrmann P, Osterland M, et al: A link between inflammation and
metastasis: Serum amyloid A1 and A3 induce metastasis, and are
targets of metastasis-inducing S100A4. Oncogene. 34:424–435. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mahmood MQ, Ward C, Muller HK, Sohal SS
and Walters EH: Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A mutual association with
airway disease. Med Oncol. 34:452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu M, Liu J, Yang B, Gao X, Gao LL, Kong
QY, Zhang P and Li H: Inversed expression patterns of S100A4 and
E-cadherin in cervical cancers: Implication in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 300:pp.
2184–2191. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Roulois D, Deshayes S, Guilly MN, Nader
JS, Liddell C, Robard M, Hulin P, Ouacher A, Le Martelot V,
Fonteneau JF, et al: Characterization of preneoplastic and
neoplastic rat mesothelial cell lines: The involvement of TETs,
DNMTs, and 5-hydroxy-methylcytosine. Oncotarget. 7:34664–34687.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Donato R, Sorci G and Giambanco I: S100A6
protein: Functional roles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:2749–2760. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lyu X, Li H, Ma X, Li X, Gao Y, Ni D, Shen
D, Gu L, Wang B, Zhang Y, et al: High-level S100A6 promotes
metastasis and predicts the outcome of T1-T2stage in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 71:279–290. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Luo X, Sharff KA, Chen J, He T-C and Luu
HH: S100A6 expression and function in human osteosarcoma. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 466:2060–2070. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang J, Zhang K, Jiang X and Zhang J:
S100A6 as a potential serum prognostic biomarker and therapeutic
target in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2136–2144. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Popa SJ, Stewart SE and Moreau K:
Unconventional secretion of annexins and galectins. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 83:42–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gerke V, Creutz CE and Moss SE: Annexins:
Linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 6:449–461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qi H, Liu S, Guo C, Wang J, Greenaway FT
and Sun M-Z: Role of annexin A6 in cancer (Review). Oncol Lett.
10:1947–1952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Grewal T, Hoque M, Conway JRW, Reverter M,
Wahba M, Beevi SS, Timpson P, Enrich C and Rentero C: Annexin A6-A
multifunctional scaffold in cell motility. Cell Adhes Migr.
11:288–304. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sakwe AM, Koumangoye R, Guillory B and
Ochieng J: Annexin A6 contributes to the invasiveness of breast
carcinoma cells by influencing the organization and localization of
functional focal adhesions. Exp Cell Res. 317:823–837. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Keklikoglou I, Cianciaruso C, Güç E,
Squadrito ML, Spring LM, Tazzyman S, Lambein L, Poissonnier A,
Ferraro GB, Baer C, et al: Chemotherapy elicits pro-metastatic
extracellular vesicles in breast cancer models. Nat Cell Biol.
21:190–202. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koumangoye RB, Nangami GN, Thompson PD,
Agboto VK, Ochieng J and Sakwe AM: Reduced annexin A6 expression
promotes the degradation of activated epidermal growth factor
receptor and sensitizes invasive breast cancer cells to
EGFR-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Mol Cancer. 12:1672013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
García-Melero A, Reverter M, Hoque M,
Meneses-Salas E, Koese M, Conway JRW, Johnsen CH, Alvarez-Guaita A,
Morales-Paytuvi F, Elmaghrabi YA, et al: Annexin A6 and late
endosomal cholesterol modulate integrin recycling and cell
migration. J Biol Chem. 291:1320–1335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Widatalla SE, Korolkova OY, Whalen DS,
Goodwin JS, Williams KP, Ochieng J and Sakwe AM: Lapatinib-induced
annexin A6 upregulation as an adaptive response of triple-negative
breast cancer cells to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Carcinogenesis. 40:998–1009. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Leca J, Martinez S, Lac S, Nigri J, Secq
V, Rubis M, Bressy C, Sergé A, Lavaut M-N, Dusetti N, et al:
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived annexin A6+
extracellular vesicles support pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. J
Clin Invest. 126:4140–4156. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Whalen DS, Widatalla SE, Korolkova OY,
Nangami GS, Beasley HK, Williams SD, Virgous C, Lehmann BD, Ochieng
J and Sakwe AM: Implication of calcium activated RasGRF2 in Annexin
A6-mediated breast tumor cell growth and motility. Oncotarget.
10:133–151. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sheikh MH and Solito E: Annexin A1:
Uncovering the many talents of an old protein. Int J Mol Sci.
19:10452018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Babbin BA, Lee WY, Parkos CA, Winfree LM,
Akyildiz A, Perretti M and Nusrat A: Annexin I regulates SKCO-15
cell invasion by signaling through formyl peptide receptors. J Biol
Chem. 281:19588–19599. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Guo C, Liu S and Sun M-Z: Potential role
of Anxa1 in cancer. Future Oncol. 9:1773–1793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Swa HLF, Shaik AA, Lim LHK and Gunaratne
J: Mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics and integrative
network analysis accentuates modulating roles of annexin-1 in
mammary tumorigenesis. Proteomics. 15:408–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Okano M, Kumamoto K, Saito M, Onozawa H,
Saito K, Abe N, Ohtake T and Takenoshita S: Upregulated Annexin A1
promotes cellular invasion in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol
Rep. 33:1064–1070. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tu Y, Johnstone CN and Stewart AG: Annexin
A1 influences in breast cancer: Controversies on contributions to
tumour, host and immunoediting processes. Pharmacol Res.
119:278–288. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liao S-H, Zhao X-Y, Han Y-H, Zhang J, Wang
L-S, Xia L, Zhao K-W, Zheng Y, Guo M and Chen G-Q: Proteomics-based
identification of two novel direct targets of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 and their potential roles in migration/invasion of cancer
cells. Proteomics. 9:3901–3912. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu Y, Wang J, Xu Y, Xiao H, Li J and Wang
Z: Screening critical genes associated with malignant glioma using
bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep. 16:6580–6589. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kang H, Ko J and Jang S-W: The role of
annexin A1 in expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and invasion
of breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:188–194.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Grindheim AK, Saraste J and Vedeler A:
Protein phosphorylation and its role in the regulation of Annexin
A2 function. Biochim Biophys Acta, Gen Subj. 1861A:A2515–A2529.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Christensen MV, Høgdall CK, Jochumsen KM
and Høgdall EVS: Annexin A2 and cancer: A systematic review. Int J
Oncol. 52:5–18. 2018.
|
|
62
|
Maule F, Bresolin S, Rampazzo E, Boso D,
Della Puppa A, Esposito G, Porcù E, Mitola S, Lombardi G, Accordi
B, et al: Annexin 2A sustains glioblastoma cell dissemination and
proliferation. Oncotarget. 7:54632–54649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu Y, Li H, Ban Z, Nai M, Yang L, Chen Y
and Xu Y: Annexin A2 inhibition suppresses ovarian cancer
progression via regulating β-catenin/EMT. Oncol Rep. 37:3643–3650.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rocha MR, Barcellos-de-Souza P,
Sousa-Squiavinato ACM, Fernandes PV, de Oliveira IM, Boroni M and
Morgado-Diaz JA: Annexin A2 overexpression associates with
colorectal cancer invasiveness and TGF-β induced epithelial
mesenchymal transition via Src/ANXA2/STAT3. Sci Rep. 8:112852018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Yoneura N, Takano S, Yoshitomi H, Nakata
Y, Shimazaki R, Kagawa S, Furukawa K, Takayashiki T, Kuboki S,
Miyazaki M, et al: Expression of annexin II and stromal tenascin C
promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and correlates with
distant metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Med. 42:821–830.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang Q, Zhao Z, Ma Y, Wang H, Ma J, He X
and Zhang D: Combined expression of S100A4 and Annexin A2 predicts
disease progression and overall survival in patients with
urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 32:798–805. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang Q, Ye Z, Yang Q, He X, Wang H and
Zhao Z: Upregulated expression of annexin II is a prognostic marker
for patients with gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 10:1032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Korwar AM, Bhonsle HS, Chougale AD, Kote
SS, Gawai KR, Ghole VS, Koppikar CB and Kulkarni MJ: Analysis of
AGE modified proteins and RAGE expression in HER2/neu negative
invasive ductal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 419:490–494.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sheng SH and Zhu HL: Proteomic analysis of
pleural effusion from lung adenocarcinoma patients by shotgun
strategy. Clin Transl Oncol. 16:153–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ricciardelli C, Lokman NA, Ween MP and
Oehler MK: WOMEN IN CANCER THEMATIC REVIEW: Ovarian
cancer-peritoneal cell interactions promote extracellular matrix
processing. Endocr Relat Cancer. 23:T155–T168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
van den Brûle FA, Buicu C, Berchuck A,
Bast RC, Deprez M, Liu F-T, Cooper DNW, Pieters C, Sobel ME and
Castronovo V: Expression of the 67-kD laminin receptor, galectin-1,
and galectin-3 in advanced human uterine adenocarcinoma. Hum
Pathol. 27:1185–1191. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Camby I, Belot N, Rorive S, Lefranc F,
Maurage C-A, Lahm H, Kaltner H, Hadari Y, Ruchoux MM, Brotchi J, et
al: Galectins are differentially expressed in supratentorial
pilocytic astrocytomas, astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytomas and
glioblastomas, and significantly modulate tumor astrocyte
migration. Brain Pathol. 11:12–26. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Astorgues-Xerri L, Riveiro ME,
Tijeras-Raballand A, Serova M, Neuzillet C, Albert S, Raymond E and
Faivre S: Unraveling galectin-1 as a novel therapeutic target for
cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:307–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cousin JM and Cloninger MJ: The role of
galectin-1 in cancer progression, and synthetic multivalent systems
for the study of galectin-1. Int J Mol Sci. 17:15662016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Bhat R, Belardi B, Mori H, Kuo P, Tam A,
Hines WC, Le Q-T, Bertozzi CR and Bissell MJ: Nuclear
repartitioning of galectin-1 by an extracellular glycan switch
regulates mammary morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E4820–E4827. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shen K-H, Li C-F, Chien L-H, Huang C-H, Su
C-C, Liao AC and Wu T-F: Role of galectin-1 in urinary bladder
urothelial carcinoma cell invasion through the JNK pathway. Cancer
Sci. 107:1390–1398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chong Y, Tang D, Xiong Q, Jiang X, Xu C,
Huang Y, Wang J, Zhou H, Shi Y, Wu X, et al: Galectin-1 from
cancer-associated fibroblasts induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition through β1 integrin-mediated upregulation of Gli1 in
gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1752016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Chong Y, Tang D, Gao J, Jiang X, Xu C,
Xiong Q, Huang Y, Wang J, Zhou H, Shi Y, et al: Galectin-1 induces
invasion and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human gastric
cancer cells via non-canonical activation of the hedgehog signaling
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:83611–83626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang P-F, Li K-S, Shen YH, Gao P-T, Dong
Z-R, Cai J-B, Zhang C, Huang X-Y, Tian M-X, Hu Z-Q, et al:
Galectin-1 induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib
resistance by activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Qian D, Lu Z, Xu Q, Wu P, Tian L, Zhao L,
Cai B, Yin J, Wu Y, Staveley-O'Carroll KF, et al: Galectin-1-driven
upregulation of SDF-1 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes
pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 397:43–51. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Noda Y, Kishino M, Sato S, Hirose K, Sakai
M, Fukuda Y, Murakami S and Toyosawa S: Galectin-1 expression is
associated with tumour immunity and prognosis in gingival squamous
cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 70:126–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Song L, Tang JW, Owusu L, Sun M-Z, Wu J
and Zhang J: Galectin-3 in cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 431:185–191.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ajani JA, Estrella JS, Chen Q, Correa AM,
Ma L, Scott AW, Jin J, Liu B, Xie M, Sudo K, et al: Galectin-3
expression is prognostic in diffuse type gastric adenocarcinoma,
confers aggressive phenotype, and can be targeted by YAP1/BET
inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 118:52–61. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Ruvolo PP: Galectin 3 as a guardian of the
tumor microenvi-ronment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:427–437. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Cardoso AC, Andrade LN, Bustos SO and
Chammas R: Galectin-3 determines tumor cell adaptive strategies in
stressed tumor microenvironments. Front Oncol. 6:1272016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Mackay A, Jones C, Dexter T, Silva RL,
Bulmer K, Jones A, Simpson P, Harris RA, Jat PS, Neville AM, et al:
cDNA microarray analysis of genes associated with ERBB2 (HER2/neu)
overexpression in human mammary luminal epithelial cells. Oncogene.
22:2680–2688. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nomura T and Katunuma N: Involvement of
cathepsins in the invasion, metastasis and proliferation of cancer
cells. J Med Invest. 52:1–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Derocq D, Prébois C, Beaujouin M,
Laurent-Matha V, Pattingre S, Smith GK and Liaudet-Coopman E:
Cathepsin D is partly endocytosed by the LRP1 receptor and inhibits
LRP1-regulated intramembrane proteolysis. Oncogene. 31:3202–3212.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Dubey V and Luqman S: Cathepsin D as a
promising target for the discovery of novel anticancer agents. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 17:404–422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Brown KD: Transglutaminase 2 and NF-κB: An
odd couple that shapes breast cancer phenotype. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 137:329–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Yang P, Yu D, Zhou J, Zhuang S and Jiang
T: TGM2 interference regulates the angiogenesis and apoptosis of
colorectal cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Cycle.
18:1122–1134. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Eble JA and Niland S: The extracellular
matrix in tumor progression and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis.
36:171–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Garamszegi N, Garamszegi SP, Shehadeh LA
and Scully SP: Extracellular matrix-induced gene expression in
human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:319–329. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Giehl K and Menke A: Microenvironmental
regulation of E-cadherin-mediated adherens junctions. Front Biosci.
13:3975–3985. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yang S, Shin J, Park KH, Jeung H-C, Rha
SY, Noh SH, Yang WI and Chung HC: Molecular basis of the
differences between normal and tumor tissues of gastric cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1772:1033–1040. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liang Y, Diehn M, Bollen AW, Israel MA and
Gupta N: Type I collagen is overexpressed in medulloblastoma as a
component of tumor microenvironment. J Neurooncol. 86:133–141.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Montgomery H, Rustogi N, Hadjisavvas A,
Tanaka K, Kyriacou K and Sutton CW: Proteomic profiling of breast
tissue collagens and site-specific characterization of
hydroxyproline residues of collagen alpha-1-(I). J Proteome Res.
11:5890–5902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Mitsuhashi A, Goto H, Saijo A, Trung VT,
Aono Y, Ogino H, Kuramoto T, Tabata S, Uehara H, Izumi K, et al:
Fibrocyte-like cells mediate acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic
therapy with bevacizumab. Nat Commun. 6:87922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Rong L, Huang W, Tian S, Chi X, Zhao P and
Liu F: COL1A2 is a novel biomarker to improve clinical prediction
in human gastric cancer: Integrating bioinformatics and
meta-analysis. Pathol Oncol Res. 24:129–134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Yang X, Staren ED, Howard JM, Iwamura T,
Bartsch JE and Appert HE: Invasiveness and MMP expression in
pancreatic carcinoma. J Surg Res. 98:33–39. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Parmo-Cabañas M, Molina-Ortiz I,
Matías-Román S, García-Bernal D, Carvajal-Vergara X, Valle I,
Pandiella A, Arroyo AG and Teixidó J: Role of metalloproteinases
MMP-9 and MT1-MMP in CXCL12-promoted myeloma cell invasion across
basement membranes. J Pathol. 208:108–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ren F, Tang R, Zhang X, Madushi WM, Luo D,
Dang Y, Li Z, Wei K and Chen G: Overexpression of MMP family
members functions as prognostic biomarker for breast cancer
patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:pp.
e01355442015, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Liu H-Y, Gu W-J, Wang C-Z, Ji X-J and Mu
Y-M: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -2 and tissue inhibitor of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 in invasive pituitary adenomas: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control trials.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:pp. e39042016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Delassus GS, Cho H, Park J and Eliceiri
GL: New pathway links from cancer-progression determinants to gene
expression of matrix metalloproteinases in breast cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 217:739–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Franco-Barraza J, Valdivia-Silva JE,
Zamudio-Meza H, Castillo A, García-Zepeda EA, Benítez-Bribiesca L
and Meza I: Actin cytoskeleton participation in the onset of
IL-1beta induction of an invasive mesenchymal-like phenotype in
epithelial MCF-7 cells. Arch Med Res. 41:170–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Matsuura I, Lai C-Y and Chiang K-N:
Functional interaction between Smad3 and S100A4 (metastatin-1) for
TGF-beta-mediated cancer cell invasiveness. Biochem J. 426:327–335.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Oskarsson T: Extracellular matrix
components in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Breast.
22(Suppl 2): S66–S72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley
AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA, et
al: VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate
the pre-metastatic niche. Nature. 438:820–827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Topalovski M and Brekken RA: Matrix
control of pancreatic cancer: New insights into fibronectin
signaling. Cancer Lett. 381:252–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Liao Y-X, Zhang Z-P, Zhao J and Liu J-P:
Effects of fibronectin 1 on cell proliferation, senescence and
apoptosis of human glioma cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1382–1396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Sercu S, Zhang L and Merregaert J: The
extracellular matrix protein 1: Its molecular interaction and
implication in tumor progression. Cancer Invest. 26:375–384. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Bergamaschi A, Tagliabue E, Sørlie T,
Naume B, Triulzi T, Orlandi R, Russnes HG, Nesland JM, Tammi R,
Auvinen P, et al: Extracellular matrix signature identifies breast
cancer subgroups with different clinical outcome. J Pathol.
214:357–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Lal G, Hashimi S, Smith BJ, Lynch CF,
Zhang L, Robinson RA and Weigel RJ: Extracellular matrix 1 (ECM1)
expression is a novel prognostic marker for poor long-term survival
in breast cancer: A Hospital-based Cohort Study in Iowa. Ann Surg
Oncol. 16:2280–2287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lee KM, Nam K, Oh S, Lim J, Kim RK, Shim
D, Choi JH, Lee S-J, Yu J-H, Lee JW, et al: ECM1 regulates tumor
metastasis and CSC-like property through stabilization of
β-catenin. Oncogene. 34:6055–6065. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Chen H, Jia W and Li J: ECM1 promotes
migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing
epithelial-mesen-chymal transition. World J Surg Oncol. 14:1952016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Gómez-Contreras P, Ramiro-Díaz JM, Sierra
A, Stipp C, Domann FE, Weigel RJ and Lal G: Extracellular matrix 1
(ECM1) regulates the actin cytoskeletal architecture of aggressive
breast cancer cells in part via S100A4 and Rho-family GTPases. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 34:37–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
117
|
Gan L, Meng J, Xu M, Liu M, Qi Y, Tan C,
Wang Y, Zhang P, Weng W, Sheng W, et al: Extracellular matrix
protein 1 promotes cell metastasis and glucose metabolism by
inducing integrin β4/FAK/SOX2/HIF-1α signaling pathway in gastric
cancer. Oncogene. 37:744–755. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Troup S, Njue C, Kliewer EV, Parisien M,
Roskelley C, Chakravarti S, Roughley PJ, Murphy LC and Watson PH:
Reduced expression of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans,
lumican, and decorin is associated with poor outcome in
node-negative invasive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:207–214.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Vuillermoz B, Khoruzhenko A, D'Onofrio
M-F, Ramont L, Venteo L, Perreau C, Antonicelli F, Maquart F-X and
Wegrowski Y: The small leucine-rich proteoglycan lumican inhibits
melanoma progression. Exp Cell Res. 296:294–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Radwanska A, Litwin M, Nowak D, Baczynska
D, Wegrowski Y, Maquart F-X and Malicka-Blaszkiewicz M:
Overexpression of lumican affects the migration of human colon
cancer cells through up-regulation of gelsolin and filamentous
actin reorganization. Exp Cell Res. 318:2312–2323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Coulson-Thomas VJ, Coulson-Thomas YM,
Gesteira TF, Andrade de Paula CA, Carneiro CR, Ortiz V, Toma L, Kao
WW and Nader HB: Lumican expression, localization and antitumor
activity in prostate cancer. Exp Cell Res. 319:967–981. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
de Wit M, Carvalho B, Delis-van Diemen PM,
van Alphen C, Beliën JAM, Meijer GA and Fijneman RJA: Lumican and
versican protein expression are associated with colorectal
adenoma-to-carcinoma progression. PLoS One. 12:pp. e01747682017,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Farace C, Oliver JA, Melguizo C, Alvarez
P, Bandiera P, Rama AR, Malaguarnera G, Ortiz R, Madeddu R and
Prados J: Microenvironmental modulation of decorin and lumican in
Temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma and neuroblastoma cancer
stem-like cells. PLoS One. 10:pp. e01341112015, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Jeanne A, Untereiner V, Perreau C, Proult
I, Gobinet C, Boulagnon-Rombi C, Terryn C, Martiny L, Brézillon S
and Dedieu S: Lumican delays melanoma growth in mice and drives
tumor molecular assembly as well as response to matrix-targeted
TAX2 therapeutic peptide. Sci Rep. 7:77002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Gritsenko PG, Ilina O and Friedl P:
Interstitial guidance of cancer invasion. J Pathol. 226:185–199.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Ruan K, Bao S and Ouyang G: The
multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:2219–2230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Kim G-E, Lee JS, Park MH and Yoon JH:
Epithelial periostin expression is correlated with poor survival in
patients with invasive breast carcinoma. PLoS One. 12:pp.
e01876352017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Mino M, Kanno K, Okimoto K, Sugiyama A,
Kishikawa N, Kobayashi T, Ono J, Izuhara K, Kobayashi T, Ohigashi
T, et al: Periostin promotes malignant potential by induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic
cholangiocar-cinoma. Hepatol Commun. 1:1099–1109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Sid B, Sartelet H, Bellon G, El Btaouri H,
Rath G, Delorme N, Haye B and Martiny L: Thrombospondin 1: A
multifunctional protein implicated in the regulation of tumor
growth. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 49:245–258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Okada K, Hirabayashi K, Imaizumi T,
Matsuyama M, Yazawa N, Dowaki S, Tobita K, Ohtani Y, Tanaka M,
Inokuchi S, et al: Stromal thrombospondin-1 expression is a
prognostic indicator and a new marker of invasiveness in
intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Biomed
Res. 31:13–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Firlej V, Mathieu JRR, Gilbert C,
Lemonnier L, Nakhlé J, Gallou-Kabani C, Guarmit B, Morin A,
Prevarskaya N, Delongchamps NB, et al: Thrombospondin-1 triggers
cell migration and development of advanced prostate tumors. Cancer
Res. 71:7649–7658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Radziwon-Balicka A, Santos-Martinez MJ,
Corbalan JJ, O'Sullivan S, Treumann A, Gilmer JF, Radomski MW and
Medina C: Mechanisms of platelet-stimulated colon cancer invasion:
Role of clusterin and thrombospondin 1 in regulation of the
P38MAPK-MMP-9 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 35:324–332. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Joshi R, Goihberg E, Ren W, Pilichowska M
and Mathew P: Proteolytic fragments of fibronectin function as
matrikines driving the chemotactic affinity of prostate cancer
cells to human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells via the α5β1
integrin. Cell Adhes Migr. 11:305–315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Lebdai S, Verhoest G, Parikh H, Jacquet
SF, Bensalah K, Chautard D, Rioux Leclercq N, Azzouzi AR and Bigot
P: Identification and validation of TGFBI as a promising prognosis
marker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 33:pp.
69.e11–69.e18. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Nummela P, Lammi J, Soikkeli J, Saksela O,
Laakkonen P and Hölttä E: Transforming growth factor beta-induced
(TGFBI) is an anti-adhesive protein regulating the invasive growth
of melanoma cells. Am J Pathol. 180:1663–1674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Klamer SE, Kuijk CG, Hordijk PL, van der
Schoot CE, von Lindern M, van Hennik PB and Voermans C: BIGH3
modulates adhesion and migration of hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cells. Cell Adhes Migr. 7:434–449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Kontostathi G, Zoidakis J, Makridakis M,
Lygirou V, Mermelekas G, Papadopoulos T, Vougas K, Vlamis-Gardikas
A, Drakakis P, Loutradis D, et al: Cervical cancer cell line
secretome highlights the roles of transforming growth
factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3, peroxiredoxin-2, and NRF2 on
cervical carcinogenesis. BioMed Res Int. 2017:41807032017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Mathias RA, Wang B, Ji H, Kapp EA, Moritz
RL, Zhu HJ and Simpson RJ: Secretome-based proteomic profiling of
Ras-transformed MDCK cells reveals extracellular modulators of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Proteome Res. 8:2827–2837.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Lunter PC, van Kilsdonk JWJ, van Beek H,
Cornelissen IMHA, Bergers M, Willems PHGM, van Muijen GNP and Swart
GWM: Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM/CD166/MEMD),
a novel actor in invasive growth, controls matrix metalloproteinase
activity. Cancer Res. 65:8801–8808. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Ofori-Acquah SF and King JA: Activated
leukocyte cell adhesion molecule: A new paradox in cancer. Transl
Res. 151:122–128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Weidle UH, Eggle D, Klostermann S and
Swart GWM: ALCAM/CD166: Cancer-related issues. Cancer Genomics
Proteomics. 7:231–243. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
von Lersner A, Droesen L and Zijlstra A:
Modulation of cell adhesion and migration through regulation of the
immunoglobulin superfamily member ALCAM/CD166. Clin Exp Metastasis.
36:87–95. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Glentis A, Gurchenkov V and Matic
Vignjevic D: Assembly, heterogeneity, and breaching of the basement
membranes. Cell Adhes Migr. 8:236–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Pozzi A, Yurchenco PD and Iozzo RV: The
nature and biology of basement membranes. Matrix Biol. 57–58:1–11.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Randles MJ, Humphries MJ and Lennon R:
Proteomic definitions of basement membrane composition in health
and disease. Matrix Biol. 57–58:12–28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Fan X, Zhang C, Wang Y,
Zhang L, Zhang H, Wen T, Zhang K, Huo X, et al: NID1, a new
regulator of EMT required for metastasis and chemoresistance of
ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:33110–33121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Pedrola N, Devis L, Llauradó M, Campoy I,
Martinez-Garcia E, Garcia M, Muinelo-Romay L, Alonso-Alconada L,
Abal M, Alameda F, et al: Nidogen 1 and Nuclear Protein 1: Novel
targets of ETV5 transcription factor involved in endometrial cancer
invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis. 32:467–478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
McMahon B and Kwaan HC: The plasminogen
activator system and cancer. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb.
36:184–194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Durand MKV, Bødker JS, Christensen A,
Dupont DM, Hansen M, Jensen JK, Kjelgaard S, Mathiasen L, Pedersen
KE, Skeldal S, et al: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-I and tumour
growth, invasion, and metastasis. Thromb Haemost. 91:438–449. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Sitaram RT, Mallikarjuna P, Landström M
and Ljungberg B: Transforming growth factor-β promotes
aggressiveness and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:35917–35931. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Rabi ZA, Todorović-Raković N, Vujasinović
T, Milovanović J and Nikolić-Vukosavljević D: Markers of
progression and invasion in short term follow up of untreated
breast cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 15:745–754. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Rhone P, Ruszkowska-Ciastek B, Bielawski
K, Brkic A, Zarychta E, Góralczyk B, Roszkowski K and Rość D:
Comprehensive analysis of haemostatic profile depending on
clinicopathological determinants in breast cancer patients. Biosci
Rep. 38:BSR201716572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Li S, Wei X, He J, Tian X, Yuan S and Sun
L: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cancer research. Biomed
Pharmacother. 105:83–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ochieng J, Nangami G, Sakwe A, Moye C,
Alvarez J, Whalen D, Thomas P and Lammers P: Impact of Fetuin-A
(AHSG) on tumor progression and type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci.
19:22112018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
155
|
Nangami GN, Watson K, Parker-Johnson K,
Okereke KO, Sakwe A, Thompson P, Frimpong N and Ochieng J: Fetuin-A
(α2HS-glycoprotein) is a serum chemo-attractant that also promotes
invasion of tumor cells through Matrigel. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 438:660–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Watson K, Koumangoye R, Thompson P, Sakwe
AM, Patel T, Pratap S and Ochieng J: Fetuin-A triggers the
secretion of a novel set of exosomes in detached tumor cells that
mediate their adhesion and spreading. FEBS Lett. 586:3458–3463.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Niu L, Song X, Wang N, Xue L, Song X and
Xie L: Tumor-derived exosomal proteins as diagnostic biomarkers in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 110:433–442. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Adams GN, Rosenfeldt L, Frederick M,
Miller W, Waltz D, Kombrinck K, McElhinney KE, Flick MJ, Monia BP,
Revenko AS, et al: Colon cancer growth and dissemination relies
upon thrombin, stromal PAR-1, and fibrinogen. Cancer Res.
75:4235–4243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Honda K-I, Asada R, Kageyama K, Fukuda T,
Terada H, Yasui T, Sumi T, Koyama M, Ishiko O and Sugawa T: Protein
complex of fibrinogen gamma chain and complement factor H in
ovarian cancer patient plasma. Anticancer Res. 37:2861–2866.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Duan S, Gong B, Wang P, Huang H, Luo L and
Liu F: Novel prognostic biomarkers of gastric cancer based on gene
expression microarray: COL12A1, GSTA3, FGA and FGG. Mol Med Rep.
18:3727–3736. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zhang X, Wang F, Huang Y, Ke K, Zhao B,
Chen L, Liao N, Wang L, Li Q, Liu X, et al: FGG promotes migration
and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through activating
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Manag Res.
11:1653–1665. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Brakebusch C and Fässler R: beta 1
integrin function in vivo: Adhesion, migration and more. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 24:403–411. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Pan B, Guo J, Liao Q and Zhao Y: β1 and β3
integrins in breast, prostate and pancreatic cancer: A novel
implication (Review). Oncol Lett. 15:5412–5416. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Sun Q, Zhou C, Ma R, Guo Q, Huang H, Hao
J, Liu H, Shi R and Liu B: Prognostic value of increased
integrin-beta 1 expression in solid cancers: A meta-analysis.
OncoTargets Ther. 11:1787–1799. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Albrektsen T, Richter HE, Clausen JT and
Fleckner J: Identification of a novel integral plasma membrane
protein induced during adipocyte differentiation. Biochem J.
359:393–402. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Pessentheiner AR, Huber K, Pelzmann HJ,
Prokesch A, Radner FPW, Wolinski H, Lindroos-Christensen J, Hoefler
G, Rülicke T, Birner-Gruenberger R, et al: APMAP interacts with
lysyl oxidase-like proteins, and disruption of Apmap leads to
beneficial visceral adipose tissue expansion. FASEB J.
31:4088–4103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Gabriele C, Cantiello F, Nicastri A,
Crocerossa F, Russo GI, Cicione A, Vartolomei MD, Ferro M, Morgia
G, Lucarelli G, et al: High-throughput detection of low abundance
sialylated glycoproteins in human serum by TiO2
enrichment and targeted LC-MS/MS analysis: Application to a
prostate cancer sample set. Anal Bioanal Chem. 411:755–763. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Jiang S, Wang X, Song D, Liu X, Gu Y, Xu
Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Ye Q, Tong Z, et al: Cholesterol induces
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by
suppressing degradation of EGFR through APMAP. Cancer Res.
79:3063–3075. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Moriyama-Kita M, Endo Y, Yonemura Y,
Heizmann CW, Miyamori H, Sato H, Yamamoto E and Sasaki T: S100A4
regulates E-cadherin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 230:211–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Shin J, Song I-S, Pak JH and Jang S-W:
Upregulation of annexin A1 expression by butyrate in human melanoma
cells induces invasion by inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Tumour
Biol. 37:14577–14584. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Wong SHM, Fang CM, Chuah L-H, Leong CO and
Ngai SC: E-cadherin: Its dysregulation in carcinogenesis and
clinical implications. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 121:11–22. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Yu W, Wu J, Ning ZL, Liu QY and Quan RL:
High expression of peroxiredoxin 1 is associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker and poor prognosis in
gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 24:2259–2270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Kim S-Y: Cancer energy metabolism:
Shutting power off cancer factory. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:39–44.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Warburg O, Posener K and Negelein E: Über
den stoffwechsel der carcinomzelle. Biochem Zeitschr. 152:309–344.
1924.
|
|
175
|
Chen T, Huang Z, Tian Y, Wang H, Ouyang P,
Chen H, Wu L, Lin B and He R: Role of triosephosphate isomerase and
downstream functional genes on gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
38:1822–1832. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Lincet H and Icard P: How do glycolytic
enzymes favour cancer cell proliferation by nonmetabolic functions?
Oncogene. 34:3751–3759. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Lone SN, Maqbool R, Parray FQ and Ul
Hussain M: Triose-phosphate isomerase is a novel target of miR-22
and miR-28, with implications in tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol.
233:8919–8929. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:763–777. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Madigan AA, Rycyna KJ, Parwani AV, Datiri
YJ, Basudan AM, Sobek KM, Cummings JL, Basse PH, Bacich DJ and
O'Keefe DS: Novel nuclear localization of fatty acid synthase
correlates with prostate cancer aggressiveness. Am J Pathol.
184:2156–2162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wang H, Xi Q and Wu G: Fatty acid synthase
regulates invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer via Wnt
signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 5:1599–1606. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Wen S, Niu Y, Lee SO, Yeh S, Shang Z, Gao
H, Li Y, Chou F and Chang C: Targeting fatty acid synthase with
ASC-J9 suppresses proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer
cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:2278–2290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase (FASN) as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 21:1001–1016. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Zaidi N, Swinnen JV and Smans K:
ATP-citrate lyase: A key player in cancer metabolism. Cancer Res.
72:3709–3714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Cheng Y, Jia B, Wang Y and Wan S: miR-133b
acts as a tumor suppressor and negatively regulates ATP citrate
lyase via PPARγ in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 38:3220–3226. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Granchi C: ATP citrate lyase (ACLY)
inhibitors: An anti-cancer strategy at the crossroads of glucose
and lipid metabolism. Eur J Med Chem. 157:1276–1291. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Icard P and Lincet H: The reduced
concentration of citrate in cancer cells: An indicator of cancer
aggressiveness and a possible therapeutic target. Drug Resist
Updat. 29:47–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Nicolussi A, D'Inzeo S, Capalbo C,
Giannini G and Coppa A: The role of peroxiredoxins in cancer.
(Review) Mol Clin Oncol. 6:pp. 139–153. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Veal E, Jackson T and Latimer H: Role/s of
'Antioxidant' enzymes in ageing. Subcell Biochem. 90:425–450. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Hampton MB, Vick KA, Skoko JJ and Neumann
CA: Peroxiredoxin involvement in the initiation and progression of
human cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:591–608. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Kang SW, Lee S and Lee JHS:
Cancer-associated function of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin subtypes as a
survival gatekeeper. Antioxidants. 7:1612018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
191
|
Forshaw TE, Holmila R, Nelson KJ, Lewis
JE, Kemp ML, Tsang AW, Poole LB, Lowther WT and Furdui CM:
Peroxiredoxins in cancer and response to radiation therapies.
Antioxidants. 8:112019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
192
|
Kim E-K, Lee SY, Kim Y, Ahn S-M and Jang
HH: Peroxiredoxin 1 post-transcriptionally regulates snoRNA
expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 141:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Dayton TL, Jacks T and Vander Heiden MG:
PKM2, cancer metabolism, and the road ahead. EMBO Rep.
17:1721–1730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Méndez-Lucas A, Li X, Hu J, Che L, Song X,
Jia J, Wang J, Xie C, Driscoll PC, Tschaharganeh DF, et al: Glucose
catabolism in liver tumors induced by c-MYC can be sustained by
various PKM1/PKM2 ratios and pyruvate kinase activities. Cancer
Res. 77:4355–4364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Zhao Y, Butler EB and Tan M: Targeting
cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis.
4:pp. e5322013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Zhou W, Liotta LA and Petricoin EF: Cancer
metabolism and mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Cancer Lett.
356A. pp. A176–A183. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Cheng T-Y, Yang Y-C, Wang H-P, Tien Y-W,
Shun C-T, Huang H-Y, Hsiao M and Hua K-T: Pyruvate kinase M2
promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis
through phosphorylation and stabilization of PAK = 2 protein.
Oncogene. 37:1730–1742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Marchitti SA, Brocker C, Stagos D and
Vasiliou V: Non-P450 aldehyde oxidizing enzymes: The aldehyde
dehydrogenase superfamily. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol.
4:697–720. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Xu X, Chai S, Wang P, Zhang C, Yang Y,
Yang Y and Wang K: Aldehyde dehydrogenases and cancer stem cells.
Cancer Lett. 369:50–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Zhou C and Sun B: The prognostic role of
the cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in head and
neck squamous cell carcinomas: A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol.
50:1144–1148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Wei D, Peng J-J, Gao H, Zhang T, Tan Y and
Hu Y-H: ALDH1 expression and the prognosis of lung cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 24:780–788.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Li J, Zhang B, Yang YF, Jin J and Liu YH:
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 as a predictor of the neoadjuvant
chemotherapy response in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 97:pp. e120562018, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Dvorakova M, Nenutil R and Bouchal P:
Transgelins, cytoskeletal proteins implicated in different aspects
of cancer development. Expert Rev Proteomics. 11:149–165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Rao D, Kimler BF, Nothnick WB, Davis MK,
Fan F and Tawfik O: Transgelin: A potentially useful diagnostic
marker differentially expressed in triple-negative and
non-triple-negative breast cancers. Hum Pathol. 46:876–883. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Tan VY, Lewis SJ, Adams JC and Martin RM:
Association of fascin-1 with mortality, disease progression and
metastasis in carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
BMC Med. 11:522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Iancu-Rubin C and Atweh GF: p27(Kip1) and
stathmin share the stage for the first time. Trends Cell Biol.
15:346–348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Belletti B and Baldassarre G: Stathmin: A
protein with many tasks. New biomarker and potential target in
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:1249–1266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Biaoxue R, Hua L, Wenlong G and Shuanying
Y: Overexpression of stathmin promotes metastasis and growth of
malignant solid tumors: A systemic review and meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 7:78994–79007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Ding Z, Bae YH and Roy P: Molecular
insights on context-specific role of profilin-1 in cell migration.
Cell Adhes Migr. 6:442–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Alkam D, Feldman EZ, Singh A and Kiaei M:
Profilin1 biology and its mutation, actin(g) in disease. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 74:967–981. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
211
|
Jiang C, Ding Z, Joy M, Chakraborty S, Kim
SH, Bottcher R, Condeelis J, Singh S and Roy P: A balanced level of
profilin-1 promotes stemness and tumor-initiating potential of
breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 16:2366–2373. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang L, Zhang H and Zhang
Y: Profilin 1, negatively regulated by microRNA-19a-3p, serves as a
tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res
Pract. 215:499–505. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Nakamura F, Stossel TP and Hartwig JH: The
filamins: Organizers of cell structure and function. Cell Adhes
Migr. 5:160–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Savoy RM and Ghosh PM: The dual role of
filamin A in cancer: Can't live with (too much of) it, can't live
without it. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:R341–R356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Shao Q-Q, Zhang T-P, Zhao W-J, Liu Z-W,
You L, Zhou L, Guo J-C and Zhao Y-P: Filamin A: Insights into its
exact role in cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 22:245–252. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
216
|
Wang Y, Liu S, Zhang Y and Yang J: Myosin
heavy chain 9: Oncogene or tumor suppressor gene? Med Sci Monit.
25:888–892. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Desouza-Armstrong M, Gunning PW and Stehn
JR: Tumor suppressor tropomyosin Tpm2.1 regulates sensitivity to
apoptosis beyond anoikis characterized by changes in the levels of
intrinsic apoptosis proteins. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 74:233–248.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Ma Y, Xiao T, Xu Q, Shao X and Wang H:
iTRAQ-based quantitative analysis of cancer-derived secretory
proteome reveals TPM2 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of
colorectal cancer. Front Med. 10:278–285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Zhang J, Zhang J, Xu S, Zhang X, Wang P,
Wu H, Xia B, Zhang G, Lei B, Wan L, et al: Hypoxia-induced TPM2
methylation is associated with chemoresistance and poor prognosis
in breast cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:692–705. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Shin H, Kim D and Helfman DM: Tropomyosin
isoform Tpm2.1 regulates collective and amoeboid cell migration and
cell aggregation in breast epithelial cells. Oncotarget.
8:95192–95205. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Mitchell CB, Black B, Sun F, Chrzanowski
W, Cooper-White J, Maisonneuve B, Stringer B, Day B, Biro M and
O'Neill GM: Tropomyosin Tpm 2.1 loss induces glioblastoma spreading
in soft brain-like environments. J Neurooncol. 141:303–313. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Shishkin S, Eremina L, Pashintseva N,
Kovalev L and Kovaleva M: Cofilin-1 and other ADF/Cofilin
superfamily members in human malignant cells. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Gasparski AN, Ozarkar S and Beningo KA:
Transient mechanical strain promotes the maturation of invadopodia
and enhances cancer cell invasion in vitro. J Cell Sci.
130:1965–1978. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Tsai C-H, Lin L-T, Wang C-Y, Chiu Y-W,
Chou Y-T, Chiu S-J, Wang H-E, Liu R-S, Wu C-Y, Chan P-C, et al:
Over-expression of cofilin-1 suppressed growth and invasion of
cancer cells is associated with up-regulation of let-7 microRNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:851–861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Curto M and McClatchey AI: Ezrin...a
metastatic detERMinant? Cancer Cell. 5:113–114. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Haase G, Gavert N, Brabletz T and
Ben-Zé'ev A: The Wnt target gene L1 in colon cancer invasion and
metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 8:482016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
227
|
Cihan YB: Does ezrin play a predictive
role in cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy and/or
chemotherapy? Hum Pathol. 80:247–248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Mierke CT: The role of vinculin in the
regulation of the mechanical properties of cells. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 53:115–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Goldmann WH, Auernheimer V, Thievessen I
and Fabry B: Vinculin, cell mechanics and tumour cell invasion.
Cell Biol Int. 37:397–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Gao Y, Wang Z, Hao Q, Li W, Xu Y, Zhang J,
Zhang W, Wang S, Liu S, Li M, et al: Loss of ERα induces
amoeboid-like migration of breast cancer cells by downregulating
vinculin. Nat Commun. 8:144832017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
231
|
Colombo E, Alcalay M and Pelicci PG:
Nucleophosmin and its complex network: A possible therapeutic
target in hematological diseases. Oncogene. 30:2595–2609. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Andersen JS, Wilkinson CJ, Mayor T,
Mortensen P, Nigg EA and Mann M: Proteomic characterization of the
human centrosome by protein correlation profiling. Nature.
426:570–574. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Box JK, Paquet N, Adams MN, Boucher D,
Bolderson E, O'Byrne KJ and Richard DJ: Nucleophosmin: From
structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol Biol.
17:192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Werner MT, Zhao C, Zhang Q and Wasik MA:
Nucleophosmin- anaplastic lymphoma kinase: The ultimate oncogene
and therapeutic target. Blood. 129:823–831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Arrigo A-P: Mammalian HspB1 (Hsp27) is a
molecular sensor linked to the physiology and environment of the
cell. Cell Stress Chaperones. 22:517–529. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Xie Y-H, Li L-Y, He J-Z, Xu X-E, Liao L-D,
Zhang Q, Xie J-J, Xu L-Y and Li E-M: Heat shock protein family B
member 1 facilitates ezrin activation to control cell migration in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
112:79–87. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Honda K, Yamada T, Endo R, Ino Y, Gotoh M,
Tsuda H, Yamada Y, Chiba H and Hirohashi S: Actinin-4, a novel
actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility and cancer
invasion. J Cell Biol. 140:1383–1393. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Hayashida Y, Honda K, Idogawa M, Ino Y,
Ono M, Tsuchida A, Aoki T, Hirohashi S and Yamada T: E-cadherin
regulates the association between beta-catenin and actinin-4.
Cancer Res. 65:8836–8845. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Thomas DG and Robinson DN: The fifth
sense: Mechanosensory regulation of alpha-actinin-4 and its
relevance for cancer metastasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 71:68–74.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Yamaguchi H, Ito Y, Miura N, Nagamura Y,
Nakabo A, Fukami K, Honda K and Sakai R: Actinin-1 and actinin-4
play essential but distinct roles in invadopodia formation by
carcinoma cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 96:685–694. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Keeling MC, Flores LR, Dodhy AH, Murray ER
and Gavara N: Actomyosin and vimentin cytoskeletal networks
regulate nuclear shape, mechanics and chromatin organization. Sci
Rep. 7:52192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Battaglia RA, Delic S, Herrmann H and
Snider NT: Vimentin on the move: new developments in cell
migration. F1000 Res 7 (F1000 Faculty Rev). 17962018.
|
|
243
|
Rao J and Li N: Microfilament actin
remodeling as a potential target for cancer drug development. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 4:345–354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Piktel E, Levental I, Durnaś B, Janmey PA
and Bucki R: Plasma gelsolin: Indicator of inflammation and its
potential as a diagnostic tool and therapeutic target. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:25162018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
245
|
Krishnakumar S, Sundaram A, Abhyankar D,
Krishnamurthy V, Shanmugam MP, Gopal L, Sharma T and Biswas J:
Major histocompatibility antigens and antigen-processing molecules
in retinoblastoma. Cancer. 100:1059–1069. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Okayama A, Miyagi Y, Oshita F, Nishi M,
Nakamura Y, Nagashima Y, Akimoto K, Ryo A and Hirano H: Proteomic
analysis of proteins related to prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. J
Proteome Res. 13:4686–4694. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Ryan D, Carberry S, Murphy AC, Lindner AU,
Fay J, Hector S, McCawley N, Bacon O, Concannon CG, Kay EW, et al:
Calnexin, an ER stress-induced protein, is a prognostic marker and
potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. J Transl Med.
14:1962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Vogiatzi F, Brandt DT, Schneikert J, Fuchs
J, Grikscheit K, Wanzel M, Pavlakis E, Charles JP, Timofeev O, Nist
A, et al: Mutant p53 promotes tumor progression and metastasis by
the endoplasmic reticulum UDPase ENTPD5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E8433–E8442. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Chen Y, Ma D, Wang X, Fang J, Liu X, Song
J, Li X, Ren X, Li Q, Li Q, et al: Calnexin impairs the antitumor
immunity of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Cancer
Immunol Res. 7:123–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
250
|
Dudek J, Benedix J, Cappel S, Greiner M,
Jalal C, Müller L and Zimmermann R: Functions and pathologies of
BiP and its interaction partners. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:1556–1569.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Wang J, Lee J, Liem D and Ping P: HSPA5
Gene encoding Hsp70 chaperone BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Gene. 618:14–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Herroon MK, Rajagurubandara E, Diedrich
JD, Heath EI and Podgorski I: Adipocyte-activated oxidative and ER
stress pathways promote tumor survival in bone via upregulation of
Heme Oxygenase 1 and Survivin. Sci Rep. 8:402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Chen W, Do KC, Saxton B, Leng S, Filipczak
P, Tessema M, Belinsky SA and Lin Y: Inhibition of the hexosamine
biosynthesis pathway potentiates cisplatin cytotoxicity by
decreasing BiP expression in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol
Carcinog. 58:1046–1055. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Sauk JJ, Nikitakis N and Siavash H: Hsp47
a novel collagen binding serpin chaperone, autoantigen and
therapeutic target. Front Biosci. 10:107–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
255
|
Duarte BDP and Bonatto D: The heat shock
protein 47 as a potential biomarker and a therapeutic agent in
cancer research. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:2319–2328. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Vatolin S, Phillips JG, Jha BK, Govindgari
S, Hu J, Grabowski D, Parker Y, Lindner DJ, Zhong F, Distelhorst
CW, et al: Novel protein disulfide isomerase inhibitor with
anticancer activity in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 76:3340–3350.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Kuo T-F, Chen T-Y, Jiang S-T, Chen K-W,
Chiang Y-M, Hsu Y-J, Liu Y-J, Chen H-M, Yokoyama KK, Tsai K-C, et
al: Protein disulfide isomerase a4 acts as a novel regulator of
cancer growth through the procaspase pathway. Oncogene.
36:5484–5496. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Fucikova J, Kasikova L, Truxova I, Laco J,
Skapa P, Ryska A and Spisek R: Relevance of the chaperone-like
protein calreticulin for the biological behavior and clinical
outcome of cancer. Immunol Lett. 193:25–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Sheng W, Chen C, Dong M, Wang G, Zhou J,
Song H, Li Y, Zhang J and Ding S: Calreticulin promotes EGF-induced
EMT in pancreatic cancer cells via Integrin/EGFR-ERK/MAPK signaling
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 8:pp. e31472017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Schcolnik-Cabrera A, Oldak B, Juárez M,
Cruz-Rivera M, Flisser A and Mendlovic F: Calreticulin in
phagocytosis and cancer: Opposite roles in immune response
outcomes. Apoptosis. 24:245–255. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Wang C, Jin G, Jin H, Wang N, Luo Q, Zhang
Y, Gao D, Jiang K, Gu D, Shen Q, et al: Clusterin facilitates
metastasis by EIF3I/Akt/MMP13 signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2903–2916. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Shapiro B, Tocci P, Haase G, Gavert N and
Ben-Ze'ev A: Clusterin, a gene enriched in intestinal stem cells,
is required for L1-mediated colon cancer metastasis. Oncotarget.
6:34389–34401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Liu Y, Men C, Xu Y, Zhao K, Luo L, Dong D
and Yu Q: Clusterin promotes growth and invasion of clear cell
renal carcinoma cell by upregulation of S100A4 expression. Cancer
Biomark. 21:915–923. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Tew KD, Manevich Y, Grek C, Xiong Y, Uys J
and Townsend DM: The role of glutathione S-transferase P in
signaling pathways and S-glutathionylation in cancer. Free Radic
Biol Med. 51:299–313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Wang Z, He W, Yang G, Wang J, Wang Z,
Nesland JM, Holm R and Suo Z: Decreased expression of GST pi is
correlated with a poor prognosis in human esophageal squamous
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 10:3522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Zannis-Hadjopoulos M, Yahyaoui W and
Callejo M: 14-3-3 cruciform-binding proteins as regulators of
eukaryotic DNA replication. Trends Biochem Sci. 33:44–50. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
267
|
Bortner JD Jr, Das A, Umstead TM, Freeman
WM, Somiari R, Aliaga C, Phelps DS and El-Bayoumy K:
Down-regulation of 14-3-3 isoforms and annexin A5 proteins in lung
adenocarcinoma induced by the tobacco-specific nitrosamine NNK in
the A/J mouse revealed by proteomic analysis. J Proteome Res.
8:4050–4061. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Leal MF, Calcagno DQ, Demachki S,
Assumpção PP, Chammas R, Burbano RR and Smith MA: Clinical
implication of 14-3-3 epsilon expression in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1531–1537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Qiu Y, Zhou Z, Li Z, Lu L, Li L, Li X,
Wang X and Zhang M: Pretreatment 14-3-3 epsilon level is predictive
for advanced extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma therapeutic response to
asparaginase-based chemotherapy. Proteomics Clin Appl. 11:3–4.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
270
|
Bavelloni A, Piazzi M, Raffini M, Faenza I
and Blalock WL: Prohibitin 2: At a communications crossroads. IUBMB
Life. 67:239–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Mishra S and Nyomba BG: Prohibitin - At
the crossroads of obesity-linked diabetes and cancer. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 242:1170–1177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
272
|
Taniguchi K, Matsumura K, Kageyama S, Ii
H, Ashihara E, Chano T, Kawauchi A, Yoshiki T and Nakata S:
Prohibitin-2 is a novel regulator of p21WAF1/CIP1 induced by
depletion of γ-glutamylcyclotransferase. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 496:218–224. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Zhou Z, Ai H, Li K, Yao X, Zhu W, Liu L,
Yu C, Song Z, Bao Y, Huang Y, et al: Prohibitin 2 localizes in
nucleolus to regulate ribosomal RNA transcription and facilitate
cell proliferation in RD cells. Sci Rep. 8:14792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Shen Y, Gao Y, Yuan H, Cao J, Jia B, Li M,
Peng Y, Du X, Zhang J and Shi J: Prohibitin-2 negatively regulates
AKT2 expression to promote prostate cancer cell migration. Int J
Mol Med. 41:1147–1155. 2018.
|
|
275
|
Yan C, Gong L, Chen L, Xu M, Abou-Hamdan
H, Tang M, Désaubry L and Song Z: PHB2 (prohibitin 2) promotes
PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent mitophagy by the PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis.
Autophagy. 16:419–434. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
276
|
Jubran R, Kocsis J, Garam N, Maláti É,
Gombos T, Barabás L, Gráf L, Prohászka Z and Fishelson Z:
Circulating mitochondrial stress 70 protein/mortalin and cytosolic
Hsp70 in blood: Risk indicators in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
141:2329–2335. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Cruz IN, Coley HM, Kramer HB, Madhuri TK,
Safuwan NAM, Angelino AR and Yang M: Proteomics analysis of ovarian
cancer cell lines and tissues reveals drug resistance-associated
proteins. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 14:35–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
278
|
Niu X, Su L, Qi S, Gao Z, Zhang Q and
Zhang S: GRP75 modulates oncogenic Dbl-driven endocytosis derailed
via the CHIP-mediated ubiquitin degradation pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 9:9712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Chang HJ, Lee MR, Hong S-H, Yoo BC, Shin
Y-K, Jeong JY, Lim S-B, Choi HS, Jeong S-Y and Park J-G:
Identification of mitochondrial FoF1-ATP synthase involved in liver
metastasis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 98:1184–1191. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Kühlbrandt W: Structure and mechanisms of
F-type ATP synthases. Annu Rev Biochem. 88:515–549. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Liu J, Zhan X, Li M, Li G, Zhang P, Xiao
Z, Shao M, Peng F, Hu R and Chen Z: Mitochondrial proteomics of
nasopha-ryngeal carcinoma metastasis. BMC Med Genomics. 5:622012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
282
|
Chen W-L, Kuo K-T, Chou T-Y, Chen C-L,
Wang C-H, Wei Y-H and Wang L-S: The role of cytochrome c oxidase
subunit Va in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells: Association with
migration, invasion and prediction of distant metastasis. BMC
Cancer. 12:2732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Wang Y, Hu L, Zhang X, Zhao H, Xu H, Wei
Y, Jiang H, Xie C, Zhou Y and Zhou F: Downregulation of
mitochondrial single stranded DNA binding protein (SSBP1) induces
mitochondrial dysfunction and increases the radiosensitivity in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Cancer. 8:1400–1409. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Rajapakse A, Suraweera A, Boucher D, Naqi
A, O'Byrne K, Richard DJ and Croft LV: Redox Regulation in the Base
Excision Repair Pathway: Old and New Players as Cancer Therapeutic
Targets. Curr Med Chem. 27:1901–1921. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
285
|
Croft LV, Bolderson E, Adams MN, El-Kamand
S, Kariawasam R, Cubeddu L, Gamsjaeger R and Richard DJ: Human
single-stranded DNA binding protein 1 (hSSB1, OBFC2B), a critical
component of the DNA damage response. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
86:121–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
286
|
Bozlu M, Orhan D, Baltaci S, Yaman O,
Elhan AH, Tulunay O and Müftüoğlu YZ: The prognostic value of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki-67 and nucleolar organizer
region in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Int Urol
Nephrol. 33:59–66. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Maeda K, Chung Y-S, Onoda N, Ogawa M, Kato
Y, Nitta A, Arimoto Y, Kondo Y, Arakawa T and Sowa M: Association
of tumor cell proliferation with lymph node metastasis in early
gastric cancer. Oncology. 53:1–5. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Ma S, Yang J, Li J and Song J: The
clinical utility of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen
expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:7405–7412. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
289
|
Wang L, Kong W, Liu B and Zhang X:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen promotes cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by up-regulating STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 104:595–602. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
290
|
Kato K, Kawashiri S, Yoshizawa K, Kitahara
H, Okamune A, Sugiura S, Noguchi N and Yamamoto E: Expression form
of p53 and PCNA at the invasive front in oral squamous cell
carcinoma: Correlation with clinicopathological features and
prognosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 40:693–698. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Dahl JA and Collas P: Q2ChIP, a quick and
quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, unravels
epigenetic dynamics of developmentally regulated genes in human
carcinoma cells. Stem Cells. 25:1037–1046. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
Mahen R, Hattori H, Lee M, Sharma P,
Jeyasekharan AD and Venkitaraman AR: A-type lamins maintain the
positional stability of DNA damage repair foci in mammalian nuclei.
PLoS One. 8:pp. e618932013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Sakthivel KM and Sehgal P: A novel role of
lamins from genetic disease to cancer biomarkers. Oncol Rev.
10:3092016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Kim J-K, Louhghalam A, Lee G, Schafer BW,
Wirtz D and Kim D-H: Nuclear lamin A/C harnesses the perinuclear
apical actin cables to protect nuclear morphology. Nat Commun.
8:21232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
295
|
Taheri F, Isbilir B, Müller G, Krieger JW,
Chirico G, Langowski J and Tóth K: Random motion of chromatin is
influenced by lamin A interconnections. Biophys J. 114:2465–2472.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
296
|
Zuo L, Zhao H, Yang R, Wang L, Ma H, Xu X,
Zhou P and Kong L: Lamin A/C might be involved in the EMT
signalling pathway. Gene. 663:51–64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
297
|
Dmello C, Srivastava SS, Tiwari R,
Chaudhari PR, Sawant S and Vaidya MM: Multifaceted role of keratins
in epithelial cell differentiation and transformation. J Biosci.
44:332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Sharma P, Alsharif S, Fallatah A and Chung
BM: Intermediate filaments as effectors of cancer development and
metastasis: A focus on keratins, vimentin, and nestin. Cells.
8:4972019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
299
|
Awe JA, Saranchuk J, Drachenberg D and Mai
S: Filtration-based enrichment of circulating tumor cells from all
prostate cancer risk groups. Urol Oncol. 35:300–309. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Erlandsson A, Forssell-Aronsson E, Seidal
T and Bernhardt P: Binding of TS1, an anti-keratin 8 antibody, in
small-cell lung cancer after 177Lu-DOTA-Tyr3-octreotate treatment:
A histological study in xenografted mice. EJNMMI Res. 1:192011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
301
|
Sawant S, Vaidya M, Chaukar D, Gangadaran
P, Singh AK, Rajadhyax S, Kannan S, Kane S, Pagare S and Kannan R:
Clinicopathological features and prognostic implications of loss of
K5 and gain of K1, K8 and K18 in oral potentially malignant lesions
and squamous cell carcinomas: An immunohistochemical analysis.
Edorium J Tumor Biol. 1:1–22. 2014.
|
|
302
|
Alam H, Kundu ST, Dalal SN and Vaidya MM:
Loss of keratins 8 and 18 leads to alterations in
α6β4-integrin-mediated signalling and decreased neoplastic
progression in an oral-tumour-derived cell line. J Cell Sci.
124:2096–2106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
303
|
Sun L and Fang J: Epigenetic regulation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:4493–4515.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
304
|
Zhou B-R and Bai Y: Chromatin structures
condensed by linker histones. Essays Biochem. 63:75–87. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
Sridharan R, Gonzales-Cope M, Chronis C,
Bonora G, McKee R, Huang C, Patel S, Lopez D, Mishra N, Pellegrini
M, et al: Proteomic and genomic approaches reveal critical
functions of H3K9 methylation and heterochromatin protein-1γ in
reprogramming to pluripotency. Nat Cell Biol. 15:872–882. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
306
|
Tzivion G, Gupta VS, Kaplun L and Balan V:
14-3-3 proteins as potential oncogenes. Semin Cancer Biol.
16:203–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
307
|
Kurpińska A, Suraj J, Bonar E, Zakrzewska
A, Stojak M, Sternak M, Jasztal A and Walczak M: Proteomic
characterization of early lung response to breast cancer metastasis
in mice. Exp Mol Pathol. 107:129–140. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
308
|
Kawahara T, Hotta N, Ozawa Y, Kato S, Kano
K, Yokoyama Y, Nagino M, Takahashi T and Yanagisawa K: Quantitative
proteomic profiling identifies DPYSL3 as pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma-associated molecule that regulates cell adhesion and
migration by stabilization of focal adhesion complex. PLoS One.
8:e796542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
309
|
Matsunuma R, Chan DW, Kim B-J, Singh P,
Han A, Saltzman AB, Cheng C, Lei JT, Wang J, Roberto da Silva L, et
al: DPYSL3 modulates mitosis, migration, and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in claudin-low breast cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E11978–E11987. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
310
|
Yang Y, Jiang Y, Xie D, Liu M, Song N, Zhu
J, Fan J and Zhu C: Inhibition of cell-adhesion protein DPYSL3
promotes metastasis of lung cancer. Respir Res. 19:412018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
311
|
Zarogoulidis P, Tsakiridis K, Karapantzou
C, Lampaki S, Kioumis I, Pitsiou G, Papaiwannou A,
Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Huang H, Kesisis G, et al: Use of proteins as
biomarkers and their role in carcinogenesis. J Cancer. 6:9–18.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
312
|
Frauchiger AL, Dummer R and Mangana J:
Serum S100B levels in melanoma. Methods Mol Biol. 1929:691–700.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Yang T, Cheng J, You J, Yan B, Liu H and
Li F: S100B promotes chemoresistance in ovarian cancer stem cells
by regulating p53. Oncol Rep. 40:1574–1582. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
314
|
Darlix A, Lamy P-J, Lopez-Crapez E,
Braccini AL, Firmin N, Romieu G, Thezenas S and Jacot W: Serum HER2
extra-cellular domain, S100β and CA 15-3 levels are independent
prognostic factors in metastatic breast cancer patients. BMC
Cancer. 16:4282016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
315
|
Gao H, Zhang IY, Zhang L, Song Y, Liu S,
Ren H, Liu H, Zhou H, Su Y, Yang Y, et al: S100B suppression alters
polarization of infiltrating myeloid-derived cells in gliomas and
inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 439:91–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
316
|
Sadeghi M, Ordway B, Rafiei I, Borad P,
Fang B, Koomen JL, Zhang C, Yoder S, Johnson J and Damaghi M:
Integrative analysis of breast cancer cells reveals an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition role in adaptation to acidic
microenvironment. Front Oncol. 10:3042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Pampalakis G, Zingkou E, Sidiropoulos KG,
Diamandis EP, Zoumpourlis V, Yousef GM and Sotiropoulou G:
Biochemical pathways mediated by KLK6 protease in breast cancer.
Mol Oncol. 13:2329–2343. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
318
|
Seguella L, Capuano R, Pesce M, Annunziata
G, Pesce M, de Conno B, Sarnelli G, Aurino L and Esposito G: S100B
protein stimulates proliferation and angiogenic mediators release
through RAGE/pAkt/mTOR pathway in human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:32402019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
319
|
Méndez O, Peg V, Salvans C, Pujals M,
Fernández Y, Abasolo I, Pérez J, Matres A, Valeri M, Gregori J, et
al: Extracellular HMGA1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:6367–6382. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
320
|
Wu X-J, Chen Y-Y, Gong C-C and Pei D-S:
The role of high-mobility group protein box 1 in lung cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 119:6354–6365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
321
|
Sharma AK, Sharma VR, Gupta GK, Ashraf GM
and Kamal MA: Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), glutathione
and breast cancer: Factors, mechanism and therapeutic
interventions. Curr Drug Metab. 20:65–71. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
322
|
Schröter D and Höhn A: Role of advanced
glycation end products in carcinogenesis and their therapeutic
implications. Curr Pharm Des. 24:5245–5251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
323
|
Palanissami G and Paul SFD: RAGE and its
ligands: Molecular interplay between glycation, inflammation, and
hallmarks of cancer - a review. Horm Cancer. 9:295–325. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
324
|
Ahmad S, Khan H, Siddiqui Z, Khan MY,
Rehman S, Shahab U, Godovikova T, Silnikov V and Moinuddin: AGEs,
RAGEs and s-RAGE; friend or foe for cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
49:44–55. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
325
|
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler
TW, Yamamoto M and Biswal S: Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes
induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by
oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res. 62:5196–5203.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
326
|
Sova M and Saso L: Design and development
of Nrf2 modulators for cancer chemoprevention and therapy: A
review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 12:3181–3197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
327
|
Taguchi K and Yamamoto M: The KEAP1-NRF2
system in cancer. Front Oncol. 7:852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
328
|
Rojo de la Vega M, Chapman E and Zhang DD:
NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell. 34:21–43. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
329
|
Lignitto L, LeBoeuf SE, Homer H, Jiang S,
Askenazi M, Karakousi TR, Pass HI, Bhutkar AJ, Tsirigos A,
Ueberheide B, et al: Nrf2 activation promotes lung cancer
metastasis by inhibiting the degradation of Bach1. Cell.
178:316–329e18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
330
|
Wiel C, Le Gal K, Ibrahim MX, Jahangir CA,
Kashif M, Yao H, Ziegler DV, Xu X, Ghosh T, Mondal T, et al: BACH1
stabilization by antioxidants stimulates lung cancer metastasis.
Cell. 178:330–345e22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
331
|
Ryoo IG, Choi BH, Ku S-K and Kwak M-K:
High CD44 expression mediates p62-associated NFE2L2/NRF2 activation
in breast cancer stem cell-like cells: Implications for cancer stem
cell resistance. Redox Biol. 17:246–258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|