|
1
|
Melan K, Janky E, Macni J, Ulric-Gervaise
S, Dorival MJ, Veronique-Baudin J and Joachim C: Epidemiology and
survival of cervical cancer in the French West-Indies: Data from
the Martinique Cancer Registry (2002-2011). Glob Health Action.
10:13373412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vu M, Yu J, Awolude OA and Chuang L:
Cervical cancer worldwide. Curr Probl Cancer. 42:457–465. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé
S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J and Bray F: Estimates of incidence and
mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet
Glob Health. 8:e191–e203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe Estimates
for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen PA, Jhingran A, Oaknin A and Denny
L: Cervical cancer. Lancet. 393:169–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li H, Wu X and Cheng X: Advances in
diagnosis and treatment of metastatic cervical cancer. J Gynecol
Oncol. 27:e432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reddy BA, van der Knaap JA, Bot AG,
Mohd-Sarip A, Dekkers DH, Timmermans MA, Martens JW, Demmers JA and
Verrijzer CP: Nucleotide biosynthetic enzyme GMP synthase is a
TRIM21-controlled relay of p53 stabilization. Mol Cell. 53:458–470.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van der Knaap JA, Kozhevnikova E,
Langenberg K, Moshkin YM and Verrijzer CP: Biosynthetic enzyme GMP
synthetase cooperates with ubiquitin-specific protease 7 in
transcriptional regulation of ecdysteroid target genes. Mol Cell
Biol. 30:736–744. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
van der Knaap JA, Kumar BR, Moshkin YM,
Langenberg K, Krijgsveld J, Heck AJ, Karch F and Verrijzer CP: GMP
synthetase stimulates histone H2B deubiquitylation by the
epigenetic silencer USP7. Mol Cell. 17:695–707. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Zhang Z, Ma Y, Lu J, Zhao H, Wang
S, Tan J and Li B: Prognostic values of GMPS, PR, CD40, and p21 in
ovarian cancer. PeerJ. 7:e63012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang P, Li X, He Q, Zhang L, Song K, Yang
X, He Q, Wang Y, Hong X, Ma J, et al: TRIM21–SERPINB5. aids GMPS
repression to protect nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells from
radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biomed Sci. 27:302020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multi-dimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Wawrzyniak JA, Bagati
A, Marvin EK, Ackroyd J, Moparthy S, Bshara W, Fink EE, Foley CE,
Morozevich GE, et al: Pharmacological targeting of guanosine
monophosphate synthase suppresses melanoma cell invasion and
tumorigenicity. Cell Death Differ. 22:1858–1864. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
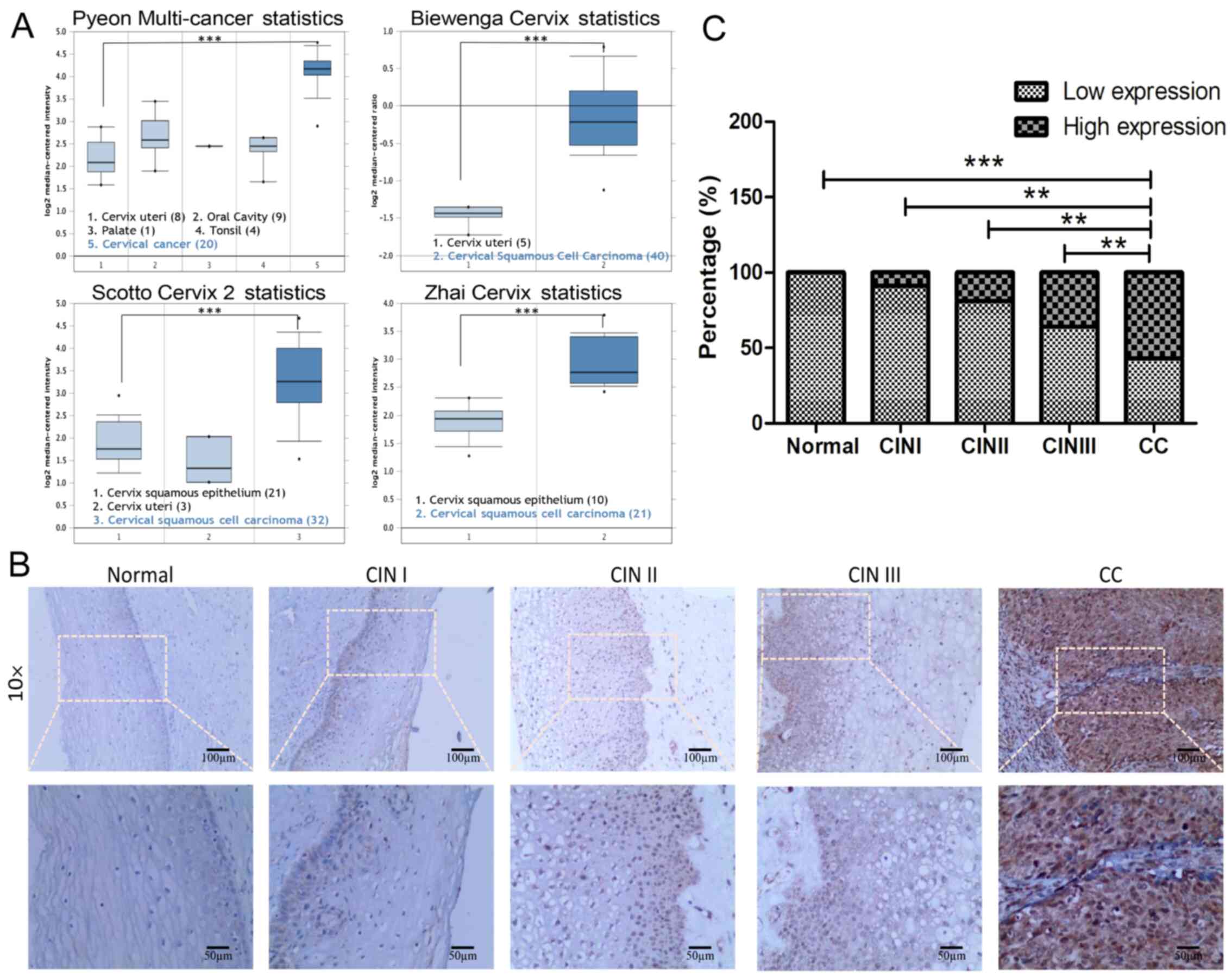
Pyeon D, Newton MA, Lambert PF, den Boon
JA, Sengupta S, Marsit CJ, Woodworth CD, Connor JP, Haugen TH,
Smith EM, et al: Fundamental differences in cell cycle deregulation
in human papillomavirus-positive and human papillomavirus-negative
head/neck and cervical cancers. Cancer Res. 67:4605–4619. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biewenga P, Buist MR, Moerland PD, Ver
Loren van Themaat E, van Kampen AH, ten Kate FJ and Baas F: Gene
expression in early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
108:520–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scotto L, Narayan G, Nandula SV,
Arias-Pulido H, Subramaniyam S, Schneider A, Kaufmann AM, Wright
JD, Pothuri B, Mansukhani M, et al: Identification of copy number
gain and overexpressed genes on chromosome arm 20q by an
integrative genomic approach in cervical cancer: Potential role in
progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:755–765. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhai Y, Kuick R, Nan B, Ota I, Weiss SJ,
Trimble CL, Fearon ER and Cho KR: Gene expression analysis of
preinvasive and invasive cervical squamous cell carcinomas
identifies HOXC10 as a key mediator of invasion. Cancer Res.
67:10163–10172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
National Research Council: Institute for
Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press; Washington, DC: pp.
80–83. 1996
|
|
21
|
FIGO staging for carcinoma of the vulva,
cervix, and corpus uteri(the official organ of the International
Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics). Int J Gynaecol Obstet.
125:97–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kozhevnikova EN, van der Knaap JA,
Pindyurin AV, Ozgur Z, van Ijcken WF, Moshkin YM and Verrijzer CP:
Metabolic enzyme IMPDH is also a transcription factor regulated by
cellular state. Mol Cell. 47:133–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wawrzyniak JA, Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Bshara
W, Mannava S, Ackroyd J, Bagati A, Omilian AR, Im M, Fedtsova N,
Miecznikowski JC, et al: A purine nucleotide biosynthesis enzyme
guanosine monophosphate reductase is a suppressor of melanoma
invasion. Cell Rep. 5:493–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C,
Garufi A and D'Orazi G: Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function
and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic
strategies. Aging (Albany NY). 8:603–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baig S, Seevasant I, Mohamad J, Mukheem A,
Huri HZ and Kamarul T: Potential of apoptotic pathway-targeted
cancer therapeutic research: Where do we stand? Cell Death Dis.
7:e20582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fulda S: Targeting apoptosis for
anticancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 31:84–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Giménez-Bonafé P, Tortosa A and
Pérez-Tomás R: Overcoming drug resistance by enhancing apoptosis of
tumor cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 9:320–340. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Avalle L, Camporeale A, Camperi A and Poli
V: STAT3 in cancer: A double edged sword. Cytokine. 98:42–50. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Banerjee K and Resat H: Constitutive
activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int J Cancer.
138:2570–2578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Galoczova M, Coates P and Vojtesek B:
STAT3, stem cells, cancer stem cells and p63. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
23:122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buettner R, Mora LB and Jove R: Activated
STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for
therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 8:945–954.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer–new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Decker T and Kovarik P: Transcription
factor activity of STAT proteins: Structural requirements and
regulation by phosphorylation and interacting proteins. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 55:1535–1546. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chatterjee K, Das P, Chattopadhyay NR, Mal
S and Choudhuri T: The interplay between Epstein-Bar virus (EBV)
with the p53 and its homologs during EBV associated malignancies.
Heliyon. 5:e026242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sullivan KD, Galbraith MD, Andrysik Z and
Espinosa JM: Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell
Death Differ. 25:133–143. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Ma Y, Wright GM, Huang
M, Irby R, Briggs J, Karras J, Cress WD, Pardoll D, et al: Role of
Stat3 in regulating p53 expression and function. Mol Cell Biol.
25:7432–7440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|