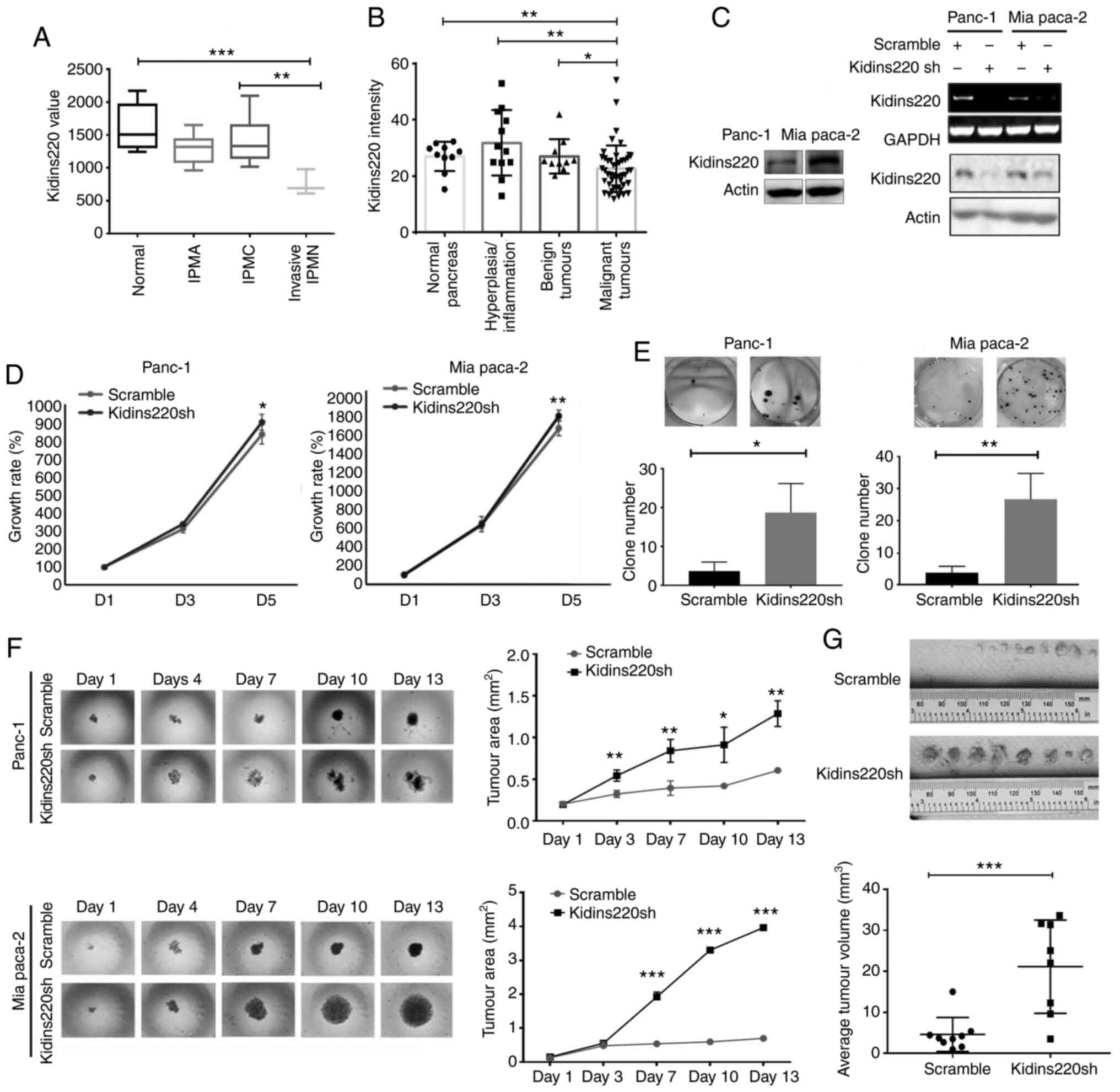
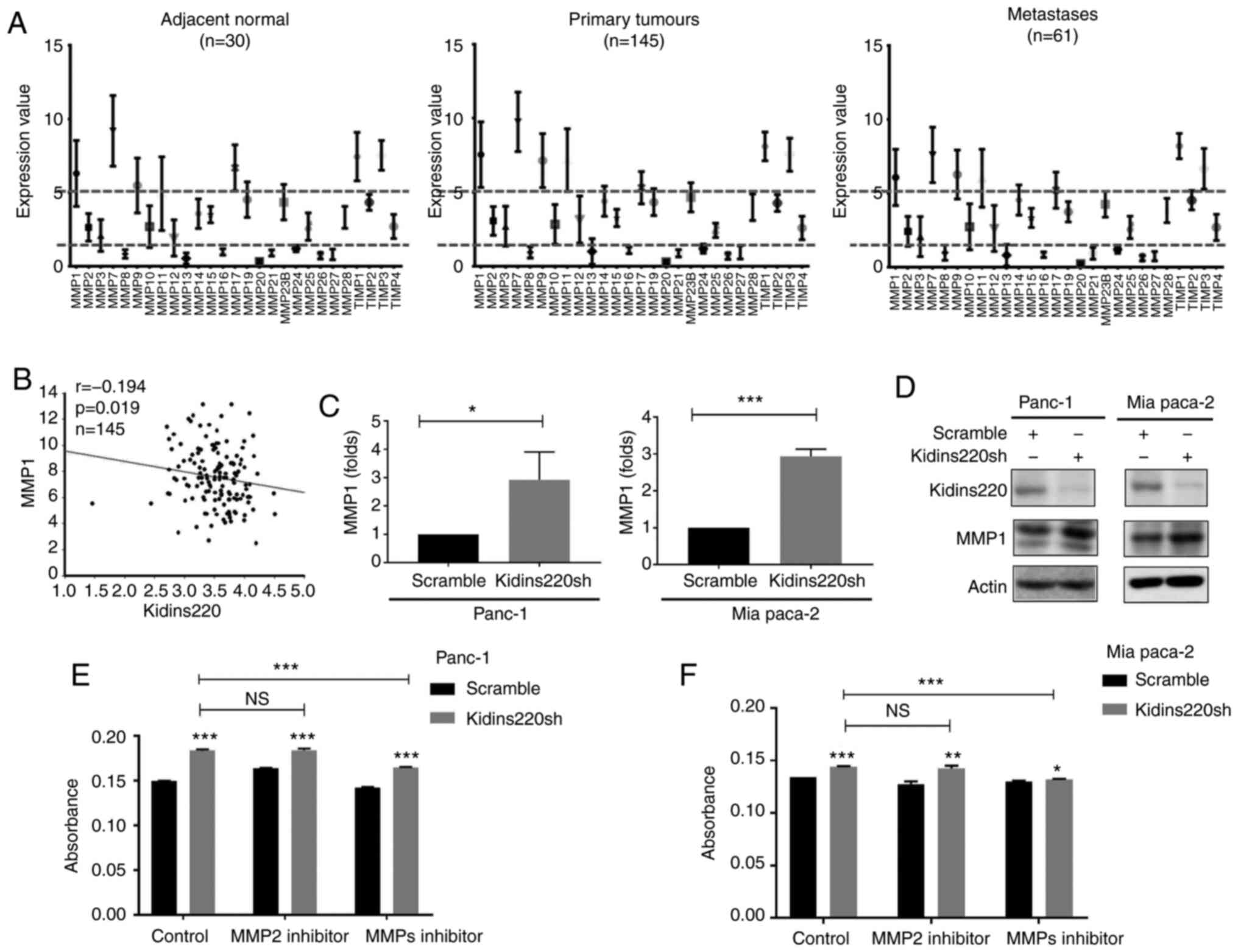
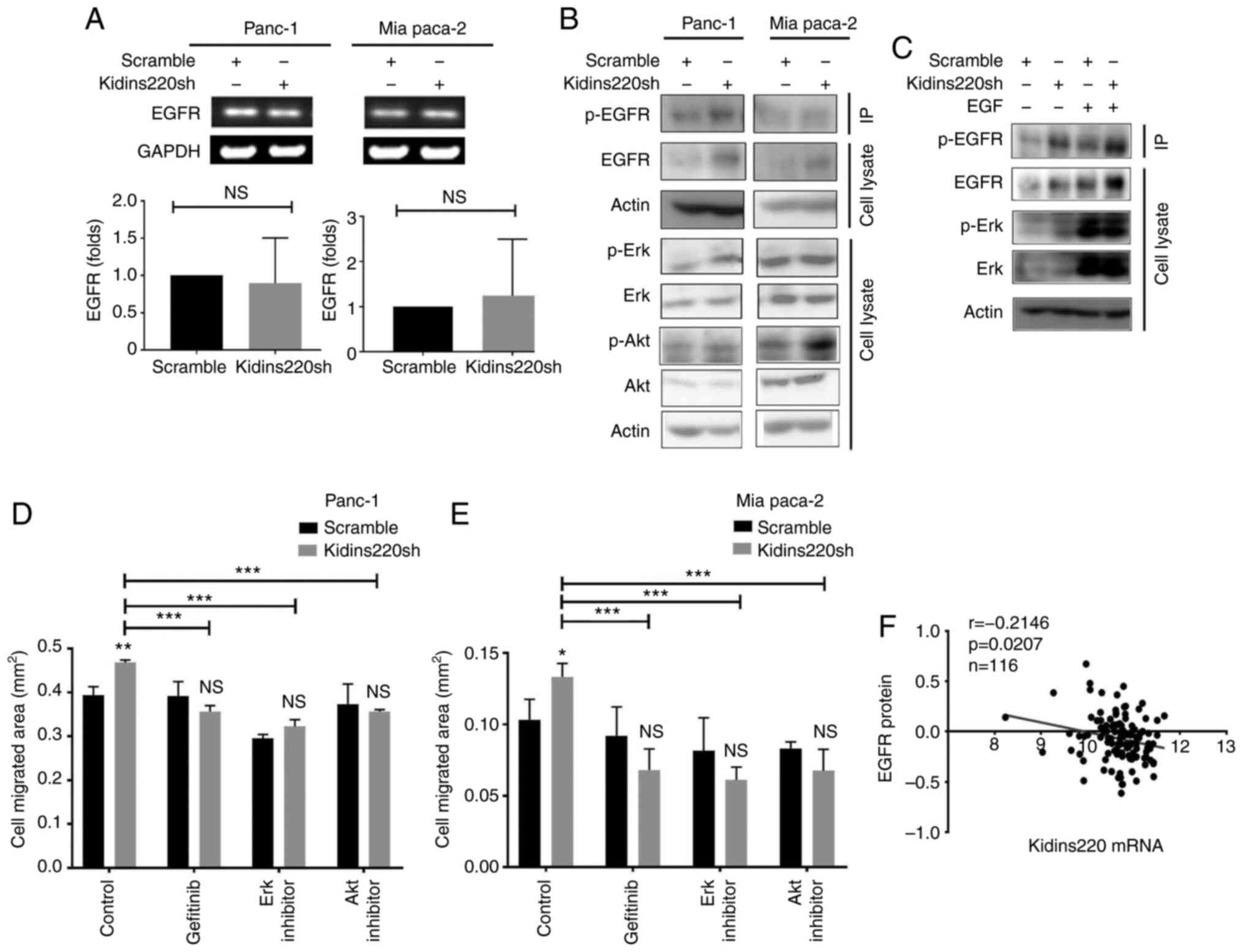
|
1
|
Scholz-Starke J and Cesca F: Stepping out
of the shade: Control of neuronal activity by the scaffold protein
Kidins220/ARMS. Front Cell Neurosci. 10:682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Neubrand VE, Cesca F, Benfenati F and
Schiavo G: Kidins220/ARMS as a functional mediator of multiple
receptor signalling pathways. J Cell Sci. 125:1845–1854. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cai S, Cai J, Jiang WG and Ye L: Kidins220
and tumour development: Insights into a complexity of cross-talk
among signalling pathways (review). Int J Mol Med. 40:965–971.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao YH, Hsu SM and Huang PH: ARMS
depletion facilitates UV irradiation induced apoptotic cell death
in melanoma. Cancer Res. 67:11547–11556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rogers DA and Schor NF: Kidins220/ARMS
depletion is associated with the neural-to Schwann-like transition
in a human neuroblastoma cell line model. Exp Cell Res.
319:660–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Shao N, Mao X, Zhu M, Fan W, Shen
Z, Xiao R, Wang C, Bao W, Xu X, et al: MiR-4638-5p inhibits
castration resistance of prostate cancer through repressing
Kidins220 expression and PI3K/AKT pathway activity. Oncotarget.
7:47444–47464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th edition.
Wiley-Blackwell; Chichester, West Sussex: pp. 132–135. 2009
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hiraoka N, Yamazaki-Itoh R, Ino Y,
Mizuguchi Y, Yamada T, Hirohashi S and Kanai Y: CXCL17 and ICAM2
are associated with a potential anti-tumor immune response in early
intraepithelial stages of human pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 140:310–321. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shostak K and Chariot A: EGFR and NF-κB:
Partners in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 21:385–393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung H, Shin JH, Park YS and Chang MS:
Ankyrin repeat-rich membrane spanning (ARMS)/Kidins220 scaffold
protein regulates neuroblastoma cell proliferation through p21. Mol
Cells. 37:881–887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao YH, Hsu SM, Yang HL, Tsai MS and
Huang PH: Upregulated ankyrin repeat-rich membrane spanning protein
contributes to tumour progression in cutaneous melanoma. Br J
Cancer. 104:982–988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okada Y, Eibl G, Guha S, Duffy JP, Reber
HA and Hines OJ: Nerve growth factor stimulates MMP-2 expression
and activity and increases invasion by human pancreatic cancer
cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 21:285–292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Diao DM, Song YC, Hou N, Xu HF, Wang JG
and Dang CX: Responses of pancreatic cancer cells to stimulations
by nerve growth factor and the role of Trk-A expression. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 32:296–300. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miknyoczki SJ, Lang D, Huang L,
Klein-Szanto AJ, Dionne CA and Ruggeri BA: Neurotrophins and Trk
receptors in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Expression
patterns and effects on in vitro invasive behavior. Int J Cancer.
81:417–427. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miknyoczki SJ, Chang H, Klein-Szanto A,
Dionne CA and Ruggeri BA: The Trk tyrosine kinase inhibitor CEP-701
(KT-5555) exhibits significant antitumor efficacy in preclinical
xenograft models of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 5:2205–2212. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shabbir M and Stuart R: Lestaurtinib, a
multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor: From bench to bedside.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:427–436. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miknyoczki SJ, Wan W, Chang H, Dobrzanski
P, Ruggeri BA, Dionne CA and Buchkovich K: The neurotrophin-trk
receptor axes are critical for the growth and progression of human
prostatic carcinoma and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma xenografts
in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1924–1931. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson MD, Stone B, Thibodeau BJ,
Baschnagel AM, Galoforo S, Fortier LE, Ketelsen B, Ahmed S, Kelley
Z, Hana A, et al: The significance of Trk receptors in pancreatic
cancer. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176922562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aristizabal Prada ET, Heinzle V, Knösel T,
Nölting S, Spöttl G, Maurer J, Spitzweg C, Angele M, Schmidt N,
Beuschlein F, et al: Tropomyosin receptor kinase: A novel target in
screened neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 25:547–560.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Renz BW, Takahashi R, Tanaka T, Macchini
M, Hayakawa Y, Dantes Z, Maurer HC, Chen X, Jiang Z, Westphalen CB,
et al: β2 adrenergic-neurotrophin feedforward loop promotes
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 33:75–90.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Desmet CJ and Peeper DS: The neurotrophic
receptor TrkB: A drug target in anti-cancer therapy? Cell Mol Life
Sci. 63:755–759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liou GY, Döppler H, Braun UB, Panayiotou
R, Scotti Buzhardt M, Radisky DC, Crawford HC, Fields AP, Murray
NR, Wang QJ, et al: Protein kinase D1 drives pancreatic acinar cell
reprogramming and progression to intraepithelial neoplasia. Nat
Commun. 6:62002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ochi N, Tanasanvimon S, Matsuo Y, Tong Z,
Sung B, Aggarwal BB, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E and Guha S:
Protein kinase D1 promotes anchorage-independent growth, invasion,
and angiogenesis by human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
226:1074–1081. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wille C, Köhler C, Armacki M, Jamali A,
Gössele U, Pfizenmaier K, Seufferlein T and Eiseler T: Protein
kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating
matrix metalloproteinases. Mol Biol Cell. 25:324–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Evans IM, Bagherzadeh A, Charles M,
Raynham T, Ireson C, Boakes A, Kelland L and Zachary IC:
Characterization of the biological effects of a novel protein
kinase D inhibitor in endothelial cells. Biochem J. 429:565–572.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harikumar KB, Kunnumakkara AB, Ochi N,
Tong Z, Deorukhkar A, Sung B, Kelland L, Jamieson S, Sutherland R,
Raynham T, et al: A novel small-molecule inhibitor of protein
kinase D blocks pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol
Cancer Ther. 9:1136–1146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li QQ, Hsu I, Sanford T, Railkar R, Balaji
N, Sourbier C, Vocke C, Balaji KC and Agarwal PK: Protein kinase D
inhibitor CRT0066101 suppresses bladder cancer growth in vitro and
xenografts via blockade of the cell cycle at G2/M. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 75:939–963. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD,
Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM,
Lachmann A, et al: Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment
analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W90–W97.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Makohon-Moore A and Iacobuzio-Donahue CA:
Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics from an evolutionary
perspective. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:553–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oliveira-Cunha M, Newman WG and
Siriwardena AK: Epidermal growth factor receptor in pancreatic
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 3:1513–1526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dong M, Nio Y, Guo KJ, Tamura K, Tian YL
and Dong YT: Epidermal growth factor and its receptor as prognostic
indicators in Chinese patients with pancreatic cancer. Anticancer
Res. 18:4613–4619. 1998.
|
|
34
|
Park SJ, Gu MJ, Lee DS, Yun SS, Kim HJ and
Choi JH: EGFR expression in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia
and ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8298–8304.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wee P and Wang Z: Epidermal growth factor
receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers (Basel).
9:522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Roy SK, Srivastava RK and Shankar S:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of
FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal. 5:102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Williams TM, Flecha AR, Keller P, Ram A,
Karnak D, Galbán S, Galbán CJ, Ross BD, Lawrence TS, Rehemtulla A
and Sebolt-Leopold J: Cotargeting MAPK and PI3K signaling with
concurrent radiotherapy as a strategy for the treatment of
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1193–1202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rogers DA and Schor NF: Kidins220/ARMS is
expressed in neuroblastoma tumors and stabilizes neurotrophic
signaling in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Pediatr Res.
74:517–524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim ST, Lim DH, Jang KT, Lim T, Lee J,
Choi YL, Jang HL, Yi JH, Baek KK, Park SH, et al: Impact of KRAS
mutations on clinical outcomes in pancreatic cancer patients
treated with first-line gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Mol Cancer
Ther. 10:1993–1999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee J, Jang KT, Ki CS, Lim T, Park YS, Lim
HY, Choi DW, Kang WK, Park K and Park JO: Impact of epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase mutations, EGFR gene
amplifications, and KRAS mutations on survival of pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 109:1561–1569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yeung KT and Yang J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol Oncol.
11:28–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hotz B, Arndt M, Dullat S, Bhargava S,
Buhr HJ and Hotz HG: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition:
Expression of the regulators snail, slug, and twist in pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4769–4776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nomura A, Majumder K, Giri B, Dauer P,
Dudeja V, Roy S, Banerjee S and Saluja AK: Inhibition of NF-kappa B
pathway leads to deregulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and neural invasion in pancreatic cancer. Lab Invest. 96:1268–1278.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Wada M, Miyamoto Y,
Fujimoto K, Lee JU, Doi R, Arii S and Imamura M: Involvement of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in invasion and metastasis of
pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 82:642–650. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bloomston M, Zervos EE and Rosemurgy AS
II: Matrix metalloproteinases and their role in pancreatic cancer:
A review of preclinical studies and clinical trials. Ann Surg
Oncol. 9:668–674. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huntington JT, Shields JM, Der CJ, Wyatt
CA, Benbow U, Slingluff CL Jr and Brinckerhoff CE: Overexpression
of collagenase 1 (MMP-1) is mediated by the ERK pathway in invasive
melanoma cells: role of BRAF mutation and fibroblast growth factor
signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:33168–33176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|