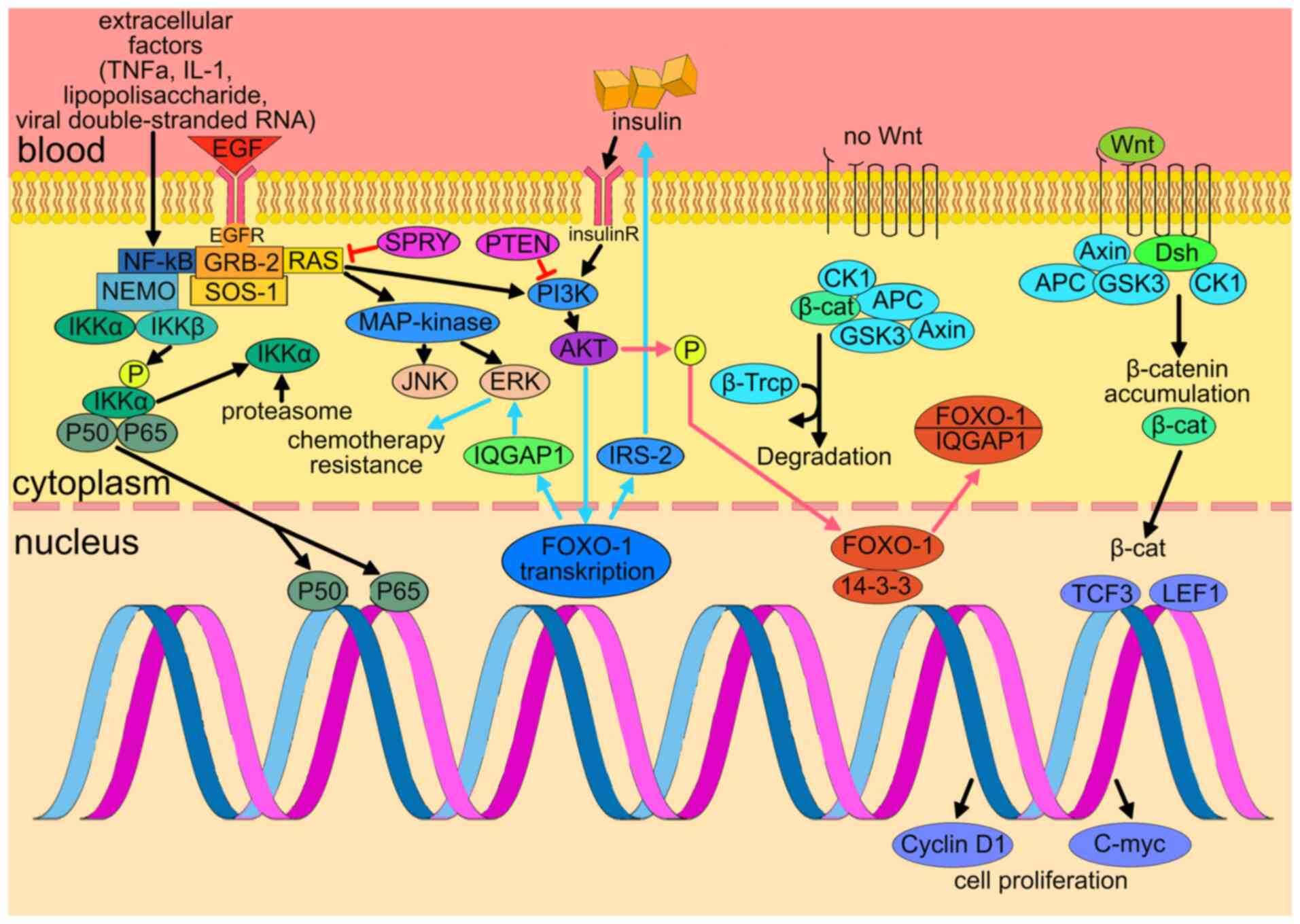
|
1
|
Darlix A, Zouaoui S, Rigau V, Bessaoud F,
Figarella-Branger D, Mathieu-Daudé H, Trétarre B, Bauchet F, Duffau
H, Taillandier L and Bauchet L: Epidemiology for primary brain
tumors: A nationwide population-based study. J Neurooncol.
131:525–546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tykocki T and Eltayeb M: Ten-year survival
in glioblastoma. A systematic review. J Clin Neurosci. 54:7–13.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Faleh TA and Juweid M: Epidemiology and
outcome of glioblastoma. Exon Publications. 143–153. 2017.
|
|
4
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ,
Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng HK, Pfister SM,
Reifenberger G, et al: The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the
central nervous system: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 23:1231–1251. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
World Health Organization: Histological
classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Lyon,
France: IARC; 2016
|
|
6
|
Zong H, Parada LF and Baker SJ: Cell of
origin for malignant gliomas and its implication in therapeutic
development. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:a0206102015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pombo Antunes AR, Scheyltjens I, Duerinck
J, Neyns B, Movahedi K and Van Ginderachter JA: Understanding the
glioblastoma immune microenvironment as basis for the development
of new immunotherapeutic strategies. Elife. 9:e521762020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khaddour K, Johanns TM and Ansstas G: The
landscape of novel therapeutics and challenges in glioblastoma
multiforme: Contemporary state and future directions.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 13:3892020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Stupp R, Taillibert S, Kanner A, Read W,
Steinberg D, Lhermitte B, Toms S, Idbaih A, Ahluwalia MS, Fink K,
et al: Effect of tumor-treating fields plus maintenance
temozolomide vs maintenance temozolomide alone on survival in
patients with glioblastoma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
318:2306–2316. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cloughesy TF, Brenner A, de Groot JF,
Butowski NA, Zach L, Campian JL, Ellingson BM, Freedman LS, Cohen
YC, Lowenton-Spier N, et al: A randomized controlled phase III
study of VB-111 combined with bevacizumab vs bevacizumab
monotherapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (GLOBE). Neuro
Oncol. 22:705–717. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nabors LB, Portnow J, Ahluwalia M,
Baehring J, Brem H, Brem S, Butowski N, Campian JL, Clark SW,
Fabiano AJ, et al: Central nervous system cancers, Version 3.2020,
NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 18:1537–1570. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lombardi G, De Salvo GL, Brandes AA, Eoli
M, Rudà R, Faedi M, Lolli I, Pace A, Daniele B, Pasqualetti F, et
al: Regorafenib compared with lomustine in patients with relapsed
glioblastoma (REGOMA): A multicentre, open-label, randomised,
controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:110–119. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Grothey A, Blay JY, Pavlakis N, Yoshino T
and Bruix J: Evolving role of regorafenib for the treatment of
advanced cancers. Cancer Treat Rev. 86:1019932020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Gittleman H, Patil N,
Waite K, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS statistical
report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2012-2016. Neuro Oncol. 21(Suppl
5): v1–v100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Levin VA, Leibel SA and Gutin PH:
Neoplasms of the central nervous system In: Cancer: Principles and
Practice of Oncology. 6th edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;
Philadelphia, PA: pp. 2100–2160. 2001
|
|
17
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al: Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and
adjuvant temozolo-mide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in
glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of
the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hanif F, Muzaffar K, Perveen K, Malhi SM
and Simjee ShU: Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of its
epidemiology and pathogenesis through clinical presentation and
treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:3–9. 2017.
|
|
19
|
Amirian ES, Ostrom QT, Armstrong GN, Lai
RK, Gu X, Jacobs DI, Jalali A, Claus EB, Barnholtz-Sloan JS,
Il'yasova D, et al: Aspirin, NSAIDs, and Glioma Risk: Original data
from the glioma international Case-Control study and a
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 28:555–562.
2019.
|
|
20
|
Scheurer ME, El-Zein R, Thompson PA,
Aldape KD, Levin VA, Gilbert MR, Weinberg JS and Bondy ML:
Long-term anti-inflam-matory and antihistamine medication use and
adult glioma risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:1277–1281.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dziurzynski K, Chang SM, Heimberger AB,
Kalejta RF, McGregor Dallas SR, Smit M, Soroceanu L and Cobbs CS;
HCMV and Gliomas Symposium: Consensus on the role of human
cytomegalovirus in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 14:246–255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Söderberg-Nauclér C, Rahbar A and
Stragliotto G: Survival in patients with glioblastoma receiving
valganciclovir. N Engl J Med. 369:985–986. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bei R, Marzocchella L and Turriziani M:
The use of temozolo-mide for the treatment of malignant tumors:
Clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms of action. Recent Pat
Anticancer Drug Discov. 5:172–187. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lacal PM, D'Atri S, Orlando L, Bonmassar E
and Graziani G: In vitro inactivation of human O6-alkylguanine DNA
alkyl-transferase by antitumor triazene compounds. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 279:416–422. 1996.
|
|
25
|
D'Atri S, Tentori L, Lacal PM, Graziani G,
Pagani E, Benincasa E, Zambruno G, Bonmassar E and Jiricny J:
Involvement of the mismatch repair system in temozolomide-induced
apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol. 54:334–341. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Baer JC, Freeman AA, Newlands ES, Watson
AJ, Rafferty JA and Margison GP: Depletion of O 6-alkylguanine-DNA
alkyltrans-ferase correlates with potentiation of temozolomide and
CCNU toxicity in human tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 67:1299–1302.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu W, Klockow JL, Zhang M, Lafortune F,
Chang E, Jin L, Wu Y and Daldrup-Link HE: Glioblastoma Multiforme
(GBM): An overview of current therapies and mechanisms of
resistance. Pharmacol Res. 17:1057802021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Grossmann P, Narayan V, Chang K, Rahman R,
Abrey L, Reardon DA, Schwartz LH, Wen PY, Alexander BM, Huang R and
Aerts HJWL: Quantitative imaging biomarkers for risk stratification
of patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab.
Neuro Oncol. 19:1688–1697. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen
T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen
R, et al: Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in
recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:4733–4740. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chinot OL, de La Motte Rouge T, Moore N,
Zeaiter A, Das A, Phillips H, Modrusan Z and Cloughesy T: AVAglio:
Phase 3 trial of bevacizumab plus temozolomide and radiotherapy in
newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Adv Ther. 28:334–340.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gilbert MR, Dignam J, Won M, Blumenthal
DT, Vogelbaum MA, AldapeHoward Colman KD, Chakravarti A, Jeraj R,
Armstrong TS, Scott Wefel J, et al: RTOG 0825: Phase III
double-blind placebo-controlled trial evaluating bevacizumab (Bev)
in patients (Pts) with newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM). J Clin
Oncol. 31:12013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Diaz RJ, Ali S, Qadir MG, De La Fuente MI,
Ivan ME and Komotar RJ: The role of bevacizumab in the treatment of
glio-blastoma. J Neurooncol. 133:455–467. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Taal W, Oosterkamp HM, Walenkamp AM,
Dubbink HJ, Beerepoot LV, Hanse MC, Buter J, Honkoop AH, Boerman D,
de Vos FY, et al: Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a
combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with
recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): A randomised controlled phase
2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:943–953. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Brandsma D and van den Bent MJ:
Pseudoprogression and pseu-doresponse in the treatment of gliomas.
Curr Opin Neurol. 22:633–638. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA,
Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert
MR, Lassman AB, et al: Updated response assessment criteria for
high-grade gliomas: Response assessment in Neuro-Oncology working
group. J Clin Oncol. 28:1963–1972. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Batchelor TT, Mulholland P, Neyns B,
Nabors LB, Campone M, Wick A, Mason W, Mikkelsen T, Phuphanich S,
Ashby LS, et al: Phase III randomized trial comparing the efficacy
of cediranib as monotherapy, and in combination with lomustine,
versus lomustine alone in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J
Clin Oncol. 31:32122013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
de Groot JF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Gilbert
MR, Cloughesy TF, Aldape K, Yao J, Jackson EF, Lieberman F, Robins
HI, et al: Phase II study of aflibercept in recurrent malignant
glioma: A North American Brain Tumor Consortium study. J Clin
Oncol. 29:2689–2995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Stupp R, Taillibert S, Kanner AA, Kesari
S, Steinberg DM, Toms SA, Taylor LP, Lieberman F, Silvani A, Fink
KL, et al: Maintenance therapy with tumor-treating fields plus
temozolomide vs temozolomide alone for glioblastoma: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA. 314:2535–2543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fabian D, Guillermo Prieto Eibl MDP,
Alnahhas I, Sebastian N, Giglio P, Puduvalli V, Gonzalez J and
Palmer JD: Treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) with the addition of
tumor-treating fields (TTF): A review. Cancers (Basel). 11:1742019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Brown TJ, Brennan MC, Li M, Church EW,
Brandmeir NJ, Rakszawski KL, Patel AS, Rizk EB, Suki D, Sawaya R
and Glantz M: Association of the extent of resection with survival
in glioblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol.
2:1460–1469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Noorbakhsh A, Tang JA, Marcus LP,
McCutcheon B, Gonda DD, Schallhorn CS, Talamini MA, Chang DC,
Carter BS and Chen CC: Gross-total resection outcomes in an elderly
population with glioblastoma: A SEER-based analysis. J Neurosurg.
120:31–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Eigenbrod S, Trabold R, Brucker D, Erös C,
Egensperger R, La Fougere C, Göbel W, Rühm A, Kretzschmar HA, Tonn
JC, et al: Molecular stereotactic biopsy technique improves
diagnostic accuracy and enables personalized treatment strategies
in glioma patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:1427–1440. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Stummer W, Tonn JC, Mehdorn HM, Nestler U,
Franz K, Goetz C, Bink A and Pichlmeier U; ALA-Glioma Study Group:
Counterbalancing risks and gains from extended resections in
malignant glioma surgery: A supplemental analysis from the
randomized 5-aminolevulinic acid glioma resection study. J
Neurosurg. 114:613–623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Berntsen EM, Gulati S, Solheim O, Kvistad
KA, Torp SH, Selbekk T, Unsgård G and Håberg AK: Functional
magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor tractography
incorporated into an intraoperative 3-dimensional ultrasound-based
neuronavigation system: Impact on therapeutic strategies, extent of
resection, and clinical outcome. Neurosurgery. 67:251–264. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ringel F, Pape H, Sabel M, Krex D, Bock
HC, Misch M, Weyerbrock A, Westermaier T, Senft C, Schucht P, et
al: Clinical benefit from resection of recurrent glioblastomas:
Results of a multicenter study including 503 patients with
recurrent glioblastomas undergoing surgical resection. Neuro Oncol.
18:96–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zuccarini M, Giuliani P, Ziberi S,
Carluccio M, Iorio PD, Caciagli F and Ciccarelli R: The role of Wnt
signal in glioblastoma development and progression: A possible new
pharmacological target for the therapy of this tumor. Genes
(Basel). 9:1052018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sigismund S, Avanzato D and Lanzetti L:
Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol Oncol. 12:3–20. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Xiao A, Brenneman B, Floyd D, Comeau L,
Spurio K, Olmez I, Lee J, Nakano I, Godlewski J, Bronisz A, et al:
Statins affect human glioblastoma and other cancers through TGF-β
inhibition. Oncotarget. 10:1716–1728. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Keunen O, Johansson M, Oudin A, Sanzey M,
Rahim SA, Fack F, Thorsen F, Taxt T, Bartos M, Jirik R, et al:
Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell
invasion in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:3749–3754.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A.
GeneCards. Weizmann institute of science. Retrieved December 15,
2021.
|
|
51
|
Albensi BC: What is nuclear factor kappa B
(NF-κB) doing in and to the mitochondrion? Front Cell Dev Biol.
7:1542019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Xia L, Tan S, Zhou Y, Lin J, Wang H, Oyang
L, Tian Y, Liu L, Su M, Wang H, et al: Role of the NFκB-signaling
pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 11:2063–2073. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Xia Y, Shen S and Verma IM: NF-κB, an
active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:823–830.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li X, Wu C, Chen N, Gu H, Yen A, Cao L,
Wang E and Wang L: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted
therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 7:33440–33450. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway-beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:5302010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Crespo I, Vital AL, Gonzalez-Tablas M,
Patino Mdel C, Otero A, Lopes MC, de Oliveira C, Domingues P, Orfao
A and Tabernero MD: Molecular and genomic alterations in
glioblastoma multiforme. Am J Pathol. 185:1820–1833. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Balça-Silva J, Matias D, Carmo AD,
Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Lopes MC and Moura-Neto V: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of glioblastoma malignancy: Implications in
resistance and therapeutic strategies. Semin Cancer Biol.
58:130–141. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Rajesh Y, Pal I, Banik P, Chakraborty S,
Borkar SA, Dey G, Mukherjee A and Mandal M: Insights into molecular
therapy of glioma: Current challenges and next generation
blueprint. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:591–613. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Cancer Genome Atlas and Research Network:
Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma
genes and core pathways. Nature. 455:1061–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hegi ME, Genbrugge E, Gorlia T, Stupp R,
Gilbert MR, Chinot OL, Nabors LB, Jones G, Van Criekinge W, Straub
J and Weller M: MGMT promoter methylation cutoff with safety margin
for selecting glioblastoma patients into trials omitting
temozolomide: A pooled analysis of four clinical trials. Clin
Cancer Res. 25:1809–1816. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Chai RC, Zhang KN, Chang YZ, Wu F, Liu YQ,
Zhao Z, Wang KY, Chang YH, Jiang T and Wang YZ: Systematically
characterize the clinical and biological significances of 1p19q
genes in 1p/19q non-codeletion glioma. Carcinogenesis.
40:1229–1239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wang Y, Li S, Chen L, You G, Bao Z, Yan W,
Shi Z, Chen Y, Yao K, Zhang W, et al: Glioblastoma with an
oligodendroglioma component: Distinct clinical behavior, genetic
alterations, and outcome. Neuro Oncol. 14:518–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Clark KH, Villano JL, Nikiforova MN,
Hamilton RL and Horbinski C: 1p/19q testing has no significance in
the workup of glioblastomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol.
39:706–717. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K,
Niu B, Lu C, Xie M, Zhang Q, McMichael JF, Wyczalkowski MA, et al:
Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types.
Nature. 502:333–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Brosh R and Rotter V: When mutants gain
new powers: News from the mutant p53 field. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:701–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos
B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ,
Berman SH, et al: Erratum: The somatic genomic landscape of
glioblastoma. Cell. 155:462–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Liu F, Huang J, Liu X, Cheng Q, Luo C and
Liu Z: CTLA-4 correlates with immune and clinical characteristics
of glioma. Cancer Cell Int. 20:72020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Garofano L, Migliozzi S, Oh YT, D'Angelo
F, Najac RD, Ko A, Frangaj B, Caruso FP, Yu K, Yuan J, et al:
Pathway-based clas-sification of glioblastoma uncovers a
mitochondrial subtype with therapeutic vulnerabilities. Nat Cancer.
2:141–156. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lu VM, O'Connor KP, Shah AH, Eichberg DG,
Luther EM, Komotar RJ and Ivan ME: The prognostic significance of
CDKN2A homozygous deletion in IDH-mutant lower-grade glioma and
glioblastoma: A systematic review of the contemporary literature. J
Neurooncol. 148:221–229. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
William D, Mokri P, Lamp N, Linnebacher M,
Classen CF, Erbersdobler A and Schneider B: Amplification of the
EGFR gene can be maintained and modulated by variation of EGF
concentrations in in vitro models of glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS
One. 12:e01852082017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Felsberg J, Hentschel B, Kaulich K,
Gramatzki D, Zacher A, Malzkorn B, Kamp M, Sabel M, Simon M,
Westphal M, et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor variant III
(EGFRvIII) positivity in EGFR-amplified glioblastomas: Prognostic
role and comparison between primary and recurrent tumors. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:6846–6855. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
An Z, Aksoy O, Zheng T, Fan QW and Weiss
WA: Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma:
Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. Oncogene. 37:1561–1575.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Xu H, Zong H, Ma C, Ming X, Shang M, Li K,
He X, Du H and Cao L: Epidermal growth factor receptor in
glioblastoma. Oncol Lett. 14:512–516. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
De S, Dermawan JK and Stark GR: EGF
receptor uses SOS1 to drive constitutive activation of NFκB in
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:11721–11726. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Talasila KM, Soentgerath A, Euskirchen P,
Rosland GV, Wang J, Huszthy PC, Prestegarden L, Skaftnesmo KO,
Sakariassen PØ, Eskilsson E, et al: EGFR wild-type amplification
and activation promote invasion and development of glioblastoma
independent of angiogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 125:683–698. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Katanasaka Y, Kodera Y, Kitamura Y,
Morimoto T, Tamura T and Koizumi F: Epidermal growth factor
receptor variant type III markedly accelerates angiogenesis and
tumor growth via inducing c-myc mediated angiopoietin-like 4
expression in malignant glioma. Mol Cancer. 12:312013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Sarkaria JN, Yang L, Grogan PT, Kitange
GJ, Carlson BL, Schroeder MA, Galanis E, Giannini C, Wu W, Dinca EB
and James CD: Identification of molecular characteristics
correlated with glioblastoma sensitivity to EGFR kinase inhibition
through use of an intracranial xenograft test panel. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1167–1174. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Cetintas VB and Batada NN: Is there a
causal link between PTEN deficient tumors and immunosuppressive
tumor microenvironment? J Transl Med. 18:452020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Raizer JJ, Abrey LE, Lassman AB, Chang SM,
Lamborn KR, Kuhn JG, Yung WK, Gilbert MR, Aldape KA, Wen PY, et al:
A phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant
gliomas and nonprogressive glioblastoma multiforme postradiation
therapy. Neuro Oncol. 12:95–103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I,
Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Lu KV, Yoshimoto K, Huang JH, Chute
DJ, et al: Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas
to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 353:2012–2024. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Chakravarti A, Wang M, Robins HI,
Lautenschlaeger T, Curran WJ, Brachman DG, Schultz CJ, Choucair A,
Dolled-Filhart M, Christiansen J, et al: RTOG 0211: A phase 1/2
study of radiation therapy with concurrent gefitinib for newly
diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phy.
85:1206–1211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Uhm JH, Ballman KV, Wu W, Giannini C,
Krauss JC, Buckner JC, James CD, Scheithauer BW, Behrens RJ, Flynn
PJ, et al: Phase II evaluation of gefitinib in patients with newly
diagnosed Grade 4 astrocytoma: Mayo/North central cancer treatment
group study N0074. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:347–353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Inda MM, Bonavia R, Mukasa A, Narita Y,
Sah DW, Vandenberg S, Brennan C, Johns TG, Bachoo R, Hadwiger P, et
al: Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant
EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev.
24:1731–1745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Mazzoleni S, Politi LS, Pala M, Cominelli
M, Franzin A, Sergi Sergi L, Falini A, De Palma M, Bulfone A,
Poliani PL and Galli R: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression
identifies functionally and molecularly distinct tumor-initiating
cells in human glioblastoma multiforme and is required for
gliomagenesis. Cancer Res. 70:7500–7513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Van Den Bent M, Eoli M, Sepulveda JM,
Smits M, Walenkamp A, Frenel JS, Franceschi E, Clement PM, Chinot
O, De Vos F, et al: INTELLANCE 2/EORTC 1410 randomized phase II
study of Depatux-M alone and with temozolomide vs temozolomide or
lomustine in recurrent EGFR amplified glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
22:684–693. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-kappaB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0000342009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Dresselhaus EC and Meffert MK: Cellular
specificity of NF-κB function in the nervous system. Front Immunol.
10:10432019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Friedmann-Morvinski D, Narasimamurthy R,
Xia Y, Myskiw C, Soda Y and Verma IM: Targeting NF-κB in
glioblastoma: A therapeutic approach. Sci Adv. 2:e15012922016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Wang H, Wang H, Zhang W, Huang HJ, Liao WS
and Fuller GN: Analysis of the activation status of Akt, NFkappaB,
and Stat3 in human diffuse gliomas. Lab Invest. 84:941–951. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Yang W, Xia Y, Cao Y, Zheng Y, Bu W, Zhang
L, You MJ, Koh MY, Cote G, Aldape K, et al: EGFR-induced and PKCε
monoubiquitylation-dependent NF-κB activation upregulates PKM2
expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 48:771–784. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Yap YS, McPherson JR, Ong CK, Rozen SG,
The BT, Lee AS and Callen DF: The NF1 gene revisited-from bench to
bedside. Oncotarget. 5:5873–5892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Schäfer C, Göder A, Beyer M, Kiweler N,
Mahendrarajah N, Rauch A, Nikolova T, Stojanovic N, Wieczorek M,
Reich TR, et al: Class I histone deacetylases regulate p53/NF-κB
crosstalk in cancer cells. Cell Signal. 29:218–225. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Zanotto-Filho A, Braganhol E, Schröder R,
de Souza LH, Dalmolin RJ, Pasquali MA, Gelain DP, Battastini AM and
Moreira JC: NFκB inhibitors induce cell death in glioblastomas.
Biochem Pharmacol. 81:412–424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Shinoda K, Kuboki S, Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M,
Kato A, Yoshitomi H, Furukawa K and Miyazaki M: Pin1 facilitates
NF-κ B activation and promotes tumour progression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 113:1323–1331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Medeiros M, Candido MF, Valera ET and
Brassesco MS: The multifaceted NF-kB: Are there still prospects of
its inhibition for clinical intervention in pediatric central
nervous system tumors? Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:6161–6200. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Phesse T, Flanagan D and Vincan E:
Frizzled7: A promising Achilles' Heel for targeting the Wnt
receptor complex to treat cancer. Cancers (Basel). 8:502016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Gao J, Liao Y, Qiu M and Shen W:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in neural stem cell homeostasis and
neurological diseases. Neuroscientist. 27:58–72. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Tang C, Guo J, Chen H, Yao CJ, Zhuang DX,
Wang Y, Tang WJ, Ren G, Yao Y, Wu JS, et al: Gene mutation
profiling of primary glioblastoma through multiple tumor biopsy
guided by 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:5327–5335. 2015.
|
|
99
|
Yun EJ, Kim S, Hsieh JT and Baek ST:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway induces autophagy-mediated
temozolomide-resistance in human glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
11:7712020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Tompa M, Kalovits F, Nagy A and Kalman B:
Contribution of the Wnt pathway to defining biology of
glioblastoma. Neuromolecular Med. 20:437–451. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Mori H, Yao Y, Learman BS, Kurozumi K,
Ishida J, Ramakrishnan SK, Overmyer KA, Xue X, Cawthorn WP, Reid
MA, et al: Induction of WNT11 by hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Sci
Rep. 6:215202016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Rampazzo E, Persano L, Pistollato F, Moro
E, Frasson C, Porazzi P, Della Puppa A, Bresolin S, Battilana G,
Indraccolo S, et al: Wnt activation promotes neuronal
differentiation of glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5002013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Liu C, Takada K and Di Z: Targeting
Wnt/β-catenin pathway for drug therapy. Med Drug Discovery.
8:1000662020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Diamond JR, Becerra C, Richards D, Mita A,
Osborne C, O'Shaughnessy J, Zhang C, Henner R, Kapoun AM, Xu L, et
al: Phase Ib clinical trial of the anti-frizzled antibody
vantictumab (OMP-18R5) plus paclitaxel in patients with locally
advanced or metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 184:53–62. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Selivanova LS, Volganova KS and Abrosimov
AY: Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations in
the tumors of human endocrine organs: Biological and prognostic
value. Arkh Patol. 78:62–69. 2016.In Russian. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Pekmezci M, Rice T, Molinaro AM, Walsh KM,
Decker PA, Hansen H, Sicotte H, Kollmeyer TM, McCoy LS, Sarkar G,
et al: Adult infiltrating gliomas with WHO 2016 integrated
diagnosis: Additional prognostic roles of ATRX and TERT. Acta
Neuropathol. 133:1001–1016. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Bell RJ, Rube HT, Xavier-Magalhães A,
Costa BM, Mancini A, Song JS and Costello JF: Understanding TERT
promoter mutations: A common path to immortality. Mol Cancer Res.
14:315–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Huang JJ, Lin MC, Bai YX, Jing DD, Wong
BC, Han SW, Lin J, Xu B, Huang CF and Kung HF: Ectopic expression
of a COOH-terminal fragment of the human telomerase reverse
transcriptase leads to telomere dysfunction and reduction of growth
and tumorigenicity in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 62:3226–3232.
2002.
|
|
109
|
Ng SS, Gao Y, Chau DH, Li GH, Lai LH,
Huang PT, Huang CF, Huang JJ, Chen YC, Kung HF and Lin MC: A novel
glioblastoma cancer gene therapy using AAV-mediated long-term
expression of human TERT C-terminal polypeptide. Cancer Gene Ther.
14:561–572. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Lavanya C, Sibin MK, Srinivas Bharath MM,
Manoj MJ, Venkataswamy MM, Bhat DI, Narasinga Rao KV and Chetan GK:
RNA interference mediated downregulation of human telomerase
reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in LN18 cells. Cytotechnology.
68:2311–2321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Li X, Qian X, Wang B, Xia Y, Zheng Y, Du
L, Xu D, Xing D, DePinho RA and Lu Z: Programmable base editing of
mutated TERT promoter inhibits brain tumour growth. Nat Cell Biol.
22:282–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Montalto G, Cervello M, Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Malaponte
G, Mazzarino MC, et al: Mutations and deregulation of
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascades which alter therapy
response. Oncotarget. 3:954–987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Zhao HF, Wang J, Shao W, Wu CP, Chen ZP,
To ST and Li WP: Recent advances in the use of PI3K inhibitors for
glioblastoma multiforme: Current preclinical and clinical
development. Mol Cancer. 16:1002017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Gymnopoulos M, Elsliger MA and Vogt PK:
Rare cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA show gain of function.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:5569–5574. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Höland K, Boller D, Hagel C, Dolski S,
Treszl A, Pardo OE, Cwiek P, Salm F, Leni Z, Shepherd PR, et al:
Targeting class IA PI3K isoforms selectively impairs cell growth,
survival, and migration in glioblastoma. PLoS One. 9:e941322014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Chen H, Mei L, Zhou L, Shen X, Guo C,
Zheng Y, Zhu H, Zhu Y and Huang L: PTEN restoration and PIK3CB
knockdown synergistically suppress glioblastoma growth in vitro and
in xenografts. J Neurooncol. 104:155–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Huang H, Regan KM, Wang F, Wang D, Smith
DI, van Deursen JM and Tindall DJ: Skp2 inhibits FOXO1 in tumor
suppression through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:1649–1654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Baretić D and Williams RL: PIKKs-the
solenoid nest where partners and kinases meet. Curr Opin Struct
Biol. 29:134–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, Guertin DA,
Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: Rictor, a
novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and
raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr
Biol. 14:1296–1302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Cornu M, Albert V and Hall MN: mTOR in
aging, metabolism, and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 23:53–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Lawlor MA and Alessi DR: PKB/Akt: A key
mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J
Cell Sci. 114:2903–2910. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Gini B, Zanca C, Guo D, Matsutani T, Masui
K, Ikegami S, Yang H, Nathanson D, Villa GR, Shackelford D, et al:
The mTOR kinase inhibitors, CC214-1 and CC214-2, preferentially
block the growth of EGFRvIII-activated glioblastomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:5722–5732. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Masri J, Bernath A, Martin J, Jo OD,
Vartanian R, Funk A and Gera J: mTORC2 activity is elevated in
gliomas and promotes growth and cell motility via overexpression of
rictor. Cancer Res. 67:11712–11720. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Agliano A, Balarajah G, Ciobota DM, Sidhu
J, Clarke PA, Jones C, Workman P, Leach MO and Al-Saffar NMS:
Pediatric and adult glioblastoma radiosensitization induced by
PI3K/mTOR inhibition causes early metabolic alterations detected by
nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Oncotarget. 8:47969–47983.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Chinnaiyan P, Won M, Wen PY, Rojiani AM,
Werner-Wasik M, Shih HA, Ashby LS, Michael Yu HH, Stieber VW,
Malone SC, et al: A randomized phase II study of everolimus in
combination with chemoradiation in newly diagnosed glioblas-toma:
Results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0913. Neuro Oncol. 20:666–673. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Reardon DA, Wen PY, Alfred Yung WK, Berk
L, Narasimhan N, Turner CD, Clackson T, Rivera VM and Vogelbaum MA:
Ridaforolimus for patients with progressive or recurrent malignant
glioma: A perisurgical, sequential, ascending-dose trial. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 69:849–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Wick W, Gorlia T, Bady P, Platten M, van
den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Steuve J, Brandes AA, Hamou MF, Wick A,
et al: Phase II study of radiotherapy and temsirolimus versus
radiochemotherapy with temozolomide in patients with newly
diagnosed glioblastoma without MGMT promoter hypermethylation
(EORTC 26082). Clin Cancer Res. 22:4797–4806. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
U.S National Library of Medincine (NIH):
NCT Neuro Master Match-N2M2 (NOA-20).
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03158389.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03158389.
Accessed May 18, 2017.
|
|
129
|
Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Okaniwa M, Yao Z,
Novotny CJ, McWhirter C, Banaji A, Won H, Wong W, Berger M, de
Stanchina E, et al: Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a
new-generation mTOR inhibitor. Nature. 534:272–276. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Babak S and Mason WP: mTOR inhibition in
glioblastoma: Requiem for a dream? Neuro Oncol. 20:584–585. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Zhang Y, Xia M, Jin K, Wang S, Wei H, Fan
C, Wu Y, Li X, Li X, Li G, et al: Function of the c-Met receptor
tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic
opportunities. Mol Cancer. 17:752018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Carvalho B, Lopes JM, Silva R, Peixoto J,
Leitão D, Soares P, Fernandes AC, Linhares P, Vaz R and Lima J: The
role of c-Met and VEGFR2 in glioblastoma resistance to bevacizumab.
Sci Rep. 11:60672021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
McCarty JH: Glioblastoma resistance to
anti-VEGF therapy: Has the challenge been MET? Clin Cancer Res.
19:1631–1633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Manneh Kopp RA, Sepúlveda-Sánchez JM,
Ruano Y, Toldos O, Pérez Núñez A, Cantero D, Hilario A, Ramos A, de
Velasco G, Sánchez-Gómez P and Hernández-Laín A: Correlation of
radiological and immunochemical parameters with clinical outcome in
patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with Bevacizumab. Clin
Transl Oncol. 21:1413–1423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Merchant M, Ma X, Maun HR, Zheng Z, Peng
J, Romero M, Huang A, Yang NY, Nishimura M, Greve J, et al:
Monovalent antibody design and mechanism of action of onartuzumab,
a MET antagonist with anti-tumor activity as a therapeutic agent.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E2987–E2996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Cloughesy T, Finocchiaro G, Belda-Iniesta
C, Recht L, Brandes AA, Pineda E, Mikkelsen T, Chinot OL, Balana C,
Macdonald DR, et al: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
multicenter phase II study of onartuzumab plus bevacizumab versus
placebo plus bevacizumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma:
Efficacy, safety, and hepatocyte growth factor and
O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase biomarker
analyses. J Clin Oncol. 35:343–351. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Garcia MM, Gil MJ, Losada E, Martin
Soberón MC, Mesia Barroso C, Foro P, Capellades J, Sarmiento B,
Bruna J, Verger E, et al: GEINO 1402: A phase Ib dose-escalation
study followed by an extension phase to evaluate safety and
efficacy of crizotinib in combination with temozolomide (TMZ) and
radiotherapy (RT) in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma
(GB. Ann Oncol. 30:v1472019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Guillemot F and Zimmer C: From cradle to
grave: The multiple roles of fibroblast growth factors in neural
development. Neuron. 71:574–588. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Frinchi M, Bonomo A, Trovato-Salinaro A,
Condorelli DF, Fuxe K, Spampinato MG and Mudò G: Fibroblast growth
factor-2 and its receptor expression in proliferating precursor
cells of the subventricular zone in the adult rat brain. Neurosci
Lett. 447:20–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Prat A,
Perez-Garcia J, Adamo B, Felip E, Cortes J, Iafrate AJ, Nuciforo P
and Tabernero J: Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway:
Opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann Oncol.
25:552–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Forbes SA, Beare D, Boutselakis H, Bamford
S, Bindal N, Tate J, Cole CG, Ward S, Dawson E, Ponting L, et al:
COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids
Res. 45:D777–D783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Hatlen MA, Schmidt-Kittler O, Sherwin CA,
Rozsahegyi E, Rubin N, Sheets MP, Kim JL, Miduturu C, Bifulco N,
Brooijmans N, et al: Acquired on-target clinical resistance
validates FGFR4 as a driver of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Discov. 9:1686–1695. 2019.
|
|
143
|
Kim RD, Sarker D, Meyer T, Yau T,
Macarulla T, Park JW, Choo SP, Hollebecque A, Sung MW, Lim HY, et
al: First-in-human phase I study of fisogatinib (BLU-554) validates
aberrant FGF19 signaling as a driver event in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 9:1696–1707. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Li W, Sparidans R, El-Lari M, Wang Y,
Lebre MC, Beijnen JH and Schinkel AH: P-glycoprotein (ABCB1/MDR1)
limits brain accumulation and Cytochrome P450-3A (CYP3A) restricts
oral availability of the novel FGFR4 inhibitor fisogatinib
(BLU-554). Int J Pharm. 573:1188422020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Sootome H, Fujita H, Ito K, Ochiiwa H,
Fujioka Y, Ito K, Miura A, Sagara T, Ito S, Ohsawa H, et al:
Futibatinib is a novel irreversible FGFR 1-4 inhibitor that shows
selective antitumor activity against FGFR-deregulated tumors.
Cancer Res. 80:4986–4997. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Singh D, Chan JM, Zoppoli P, Niola F,
Sullivan R, Castano A, Liu EM, Reichel J, Porrati P, Pellegatta S,
et al: Transforming fusions of FGFR and TACC genes in human
glioblastoma. Science. 337:1231–1235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Andre F, Ranson M, Dean E, Varga A, van
der Noll R, Stockman PK, Ghiorghiu D, Kilgour E, Smith PD,
Macpherson M, et al: Abstract LB-145: Results of a phase I study of
AZD4547, an inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR),
in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 73:LB–145.
2013.
|
|
148
|
Takahashi Y, Akahane T, Sawada T, Ikeda H,
Tempaku A, Yamauchi S, Nishihara H, Tanaka S, Nitta K, Ide W, et
al: Adult classical glioblastoma with a BRAF V600E mutation. World
J Surg Oncol. 13:1002015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Tosuner Z, Geçer MÖ, Hatiboğlu MA,
Abdallah A and Turna S: BRAF V600E mutation and BRAF VE1
immunoexpression profiles in different types of glioblastoma. Oncol
Lett. 16:2402–2408. 2018.
|
|
150
|
Raabe EH, Lim KS, Kim JM, Meeker A, Mao
XG, Nikkhah G, Maciaczyk J, Kahlert U, Jain D, Bar E, et al: BRAF
activation induces transformation and then senescence in human
neural stem cells: A pilocytic astrocytoma model. Clin Cancer Res.
17:3590–3599. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Behling F and Schittenhelm J: Oncogenic
BRAF alterations and their role in brain tumors. Cancers (Basel).
11:7942019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Cantwell-Dorris ER, O'Leary JJ and Sheils
OM: BRAFV600E: Implications for carcinogenesis and molecular
therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:385–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Nakajima N, Nobusawa S, Nakata S, Nakada
M, Yamazaki T, Matsumura N, Harada K, Matsuda H, Funata N, Nagai S,
et al: BRAF V600E, TERT promoter mutations and CDKN2A/B homozygous
deletions are frequent in epithelioid glioblastomas: A histological
and molecular analysis focusing on intratumoral heterogeneity.
Brain Pathol. 28:663–673. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Chapman PB, Robert C, Larkin J, Haanen JB,
Ribas A, Hogg D, Hamid O, Ascierto PA, Testori A, Lorigan PC, et
al: Vemurafenib in patients with BRAFV600 mutation-positive
metastatic melanoma: Final overall survival results of the
randomized BRIM-3 study. Ann Oncol. 28:2581–2587. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Burger MC, Ronellenfitsch MW, Lorenz NI,
Wagner M, Voss M, Capper D, Tzaridis T, Herrlinger U, Steinbach JP,
Stoffels G, et al: Dabrafenib in patients with recurrent, BRAF
V600E mutated malignant glioma and leptomeningeal disease. Oncol
Rep. 38:3291–3296. 2017.
|
|
156
|
Woo PYM, Lam TC, Pu JKS, Li LF, Leung RCY,
Ho JMK, Zhung JTF, Wong B, Chan TSK, Loong HHF and Ng HK:
Regression of BRAFV600E mutant adult glioblastoma after primary
combined BRAF-MEK inhibitor targeted therapy: A report of two
cases. Oncotarget. 10:3818–3826. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Schiff D and Sarkaria J: Dasatinib in
recurrent glioblastoma: Failure as a teacher. Neuro Oncol.
17:910–911. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Dumont RA, Hildebrandt I, Su H, Haubner R,
Reischl G, Czernin JG, Mischel PS and Weber WA: Noninvasive imaging
of alphaVbeta3 function as a predictor of the antimigratory and
anti-proliferative effects of dasatinib. Cancer Res. 69:3173–3179.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Galanis E, Anderson SK, Twohy EL, Carrero
XW, Dixon JG, Tran DD, Jeyapalan SA, Anderson DM, Kaufmann TJ,
Feathers RW, et al: A phase 1 and randomized, placebo-controlled
phase 2 trial of bevacizumab plus dasatinib in patients with
recurrent glioblastoma: Alliance/North Central Cancer Treatment
Group N0872. Cancer. 125:3790–3800. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Srivastava S, Jackson C, Kim T, Choi J and
Lim M: A characterization of dendritic cells and their role in
immunotherapy in glioblastoma: From preclinical studies to clinical
trials. Cancers. 11:5372019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Wen PY, Reardon DA, Armstrong TS,
Phuphanich S, Aiken RD, Landolfi JC, Curry WT, Zhu JJ, Glantz M,
Peereboom DM, et al: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled
phase II trial of dendritic cell vaccine ICT-107 in newly diagnosed
patients with glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 25:5799–5807. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Polson ES, Kuchler VB, Abbosh C, Ross EM,
Mathew RK, Beard HA, da Silva B, Holding AN, Ballereau S,
Chuntharpursat-Bon E, et al: KHS101 disrupts energy metabolism in
human glioblastoma cells and reduces tumor growth in mice. Sci
Transl Med. 10:eaar27182018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Gruslova A, Cavazos DA, Miller JR,
Breitbart E, Cohen YC, Bangio L, Yakov N, Soundararajan A, Floyd JR
and Brenner AJ: VB-111: A novel anti-vascular therapeutic for
glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol. 124:365–372. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Brenner AJ, Peters KB, Vredenburgh J,
Bokstein F, Blumenthal DT, Yust-Katz S, Peretz I, Oberman B,
Freedman LS, Ellingson BM, et al: Safety and efficacy of VB-111, an
anticancer gene therapy, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma:
Results of a phase I/II study. Neuro Oncol. 22:694–704. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Weller M, Butowski N, Tran DD, Recht LD,
Lim M, Hirte H, Ashby L, Mechtler L, Goldlust SA, Iwamoto F, et al:
Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed,
EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomized,
double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:1373–1385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Reardon DA, Desjardins A, Vredenburgh JJ,
O'Rourke DM, Tran DD, Fink KL, Nabors LB, Li G, Bota DA, Lukas RV,
et al: Rindopepimut with bevacizumab for patients with relapsed
EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ReACT): Results of a double-blind
randomized phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res. 26:1586–1594. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Heimberger AB, Archer GE, Crotty LE,
McLendon RE, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Bigner DD and Sampson JH:
Dendritic cells pulsed with a tumor-specific peptide induce
long-lasting immunity and are effective against murine
intrace-rebral melanoma. Neurosurgery. 50:158–166. 2002.
|
|
168
|
Filley AC, Henriquez M and Dey M:
Recurrent glioma clinical trial, CheckMate-143: The game is not
over yet. Oncotarget. 8:91779–91794. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J,
Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington K, Kasper S, Vokes EE,
Even C, et al: Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 375:1856–1867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Reardon DA, Brandes AA, Omuro A,
Mulholland P, Lim M, Wick A, Baehring J, Ahluwalia MS, Roth P, Bähr
O, et al: Effect of nivolumab vs bevaci-zumab in patients with
recurrent glioblastoma: The CheckMate 143 phase 3 randomized
clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 6:1003–1010. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Sampson JH, Padula Omuro AM, Preusser M,
Lim M, Butowski NA, Cloughesy TF, Strauss LC, Latek RR, Paliwal P,
Weller M and Reardon DA: A randomized, phase 3, open-label study of
nivolumab versus temozolomide (TMZ) in combination with
radiotherapy (RT) in adult patients (pts) with newly diagnosed,
O-6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-unmethylated
glioblastoma (GBM): CheckMate-498. J Clin Oncol. 34:TPS20792016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Reardon DA, Nayak L, Peters KB, Clarke JL,
Jordan JT, De Groot JF, Nghiemphu PL, Kaley TJ, Colman H, Gaffey
SC, et al: Phase II study of pembrolizumab or pembrolizumab plus
bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma (rGBM) patients. J Clin
Oncol. 36:20062018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Schalper KA, Rodriguez-Ruiz ME, Diez-Valle
R, López-Janeiro A, Porciuncula A, Idoate MA, Inogés S, de Andrea
C, López-Diaz de Cerio A, Tejada S, et al: Neoadjuvant nivolumab
modifies the tumor immune microenvironment in resectable
glioblastoma. Nat Med. 25:470–476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Cloughesy TF, Mochizuki AY, Orpilla JR,
Hugo W, Lee AH, Davidson TB, Wang AC, Ellingson BM, Rytlewski JA,
Sanders CM, et al: Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a
survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in
recurrent glioblastoma. Nat Med. 25:477–486. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Li R, Pourpak A and Morris SW: Inhibition
of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine
kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach. J Med Chem.
52:4981–5004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Chakravarti A, Loeffler JS and Dyson NJ:
Insulin-like growth factor receptor I mediates resistance to
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in primary human
glioblastoma cells through continued activation of phosphoinositide
3-kinase signaling. Cancer Res. 62:200–207. 2002.
|
|
177
|
Zhou X, Shen F, Ma P, Hui H, Pei S, Chen
M, Wang Z, Zhou W and Jin B: GSK1838705A, an IGF-1R inhibitor,
inhibits glioma cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth in
vivo. Mol Med Rep. 12:5641–5646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Osher E and Macaulay VM: Therapeutic
targeting of the IGF axis. Cells. 8:8952019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Janes PW, Vail ME, Gan HK and Scott AM:
Antibody targeting of eph receptors in cancer. Pharmaceuticals.
13:882020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Anderton M, van der Meulen E, Blumenthal
MJ and Schäfer G: The role of the Eph receptor family in
tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel). 13:2062021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Binda E, Visioli A, Giani F, Lamorte G,
Copetti M, Pitter KL, Huse JT, Cajola L, Zanetti N, DiMeco F, et
al: The EphA2 receptor drives self-renewal and tumorigenicity in
stem-like tumor-propagating cells from human glioblastomas. Cancer
Cell. 22:765–780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Stanton C and Debinski
W: EphA2 as a novel molecular marker and target in glioblastoma
multiforme. Mol Cancer Res. 3:541–551. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Swords RT, Greenberg PL, Wei AH, Durrant
S, Advani AS, Hertzberg MS, Jonas BA, Lewis ID, Rivera G,
Gratzinger D, et al: KB004, a first in class monoclonal antibody
targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA3, in patients with
advanced hematologic malignancies: Results from a phase 1 study.
Leuk Res. 50:123–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Wade M, Li YC and Wahl GM: MDM2, MDMX and
p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:83–96.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Avci NG, Ebrahimzadeh-Pustchi S, Akay YM,
Esquenazi Y, Tandon N, Zhu JJ and Akay M: NF-κB inhibitor with
Temozolomide results in significant apoptosis in glioblastoma via
the NF-κB(p65) and actin cytoskeleton regulatory pathways. Sci Rep.
10:133522020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Beck S, Jin X, Sohn YW, Kim JK, Kim SH,
Yin J, Pian X, Kim SC, Nam DH, Choi YJ and Kim H: Telomerase
activity-independent function of TERT allows glioma cells to attain
cancer stem cell characteristics by inducing EGFR expression. Mol
Cells. 31:9–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Olympios N, Gilard V, Marguet F, Clatot F,
Di Fiore F and Fontanilles M: TERT promoter alterations in
glioblastoma: A systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 13:11472021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Metro G, Pierini T and La Starza R: TERT
Mutations in Glioma: ESMO Biomarker Factsheet. European Society for
Medical Oncology; Lugano: 2019, https://oncologypro.esmo.org/education-library/factsheets-on-biomarkers/tert-mutations-in-glioma.
Accessed January 25, 2019.
|