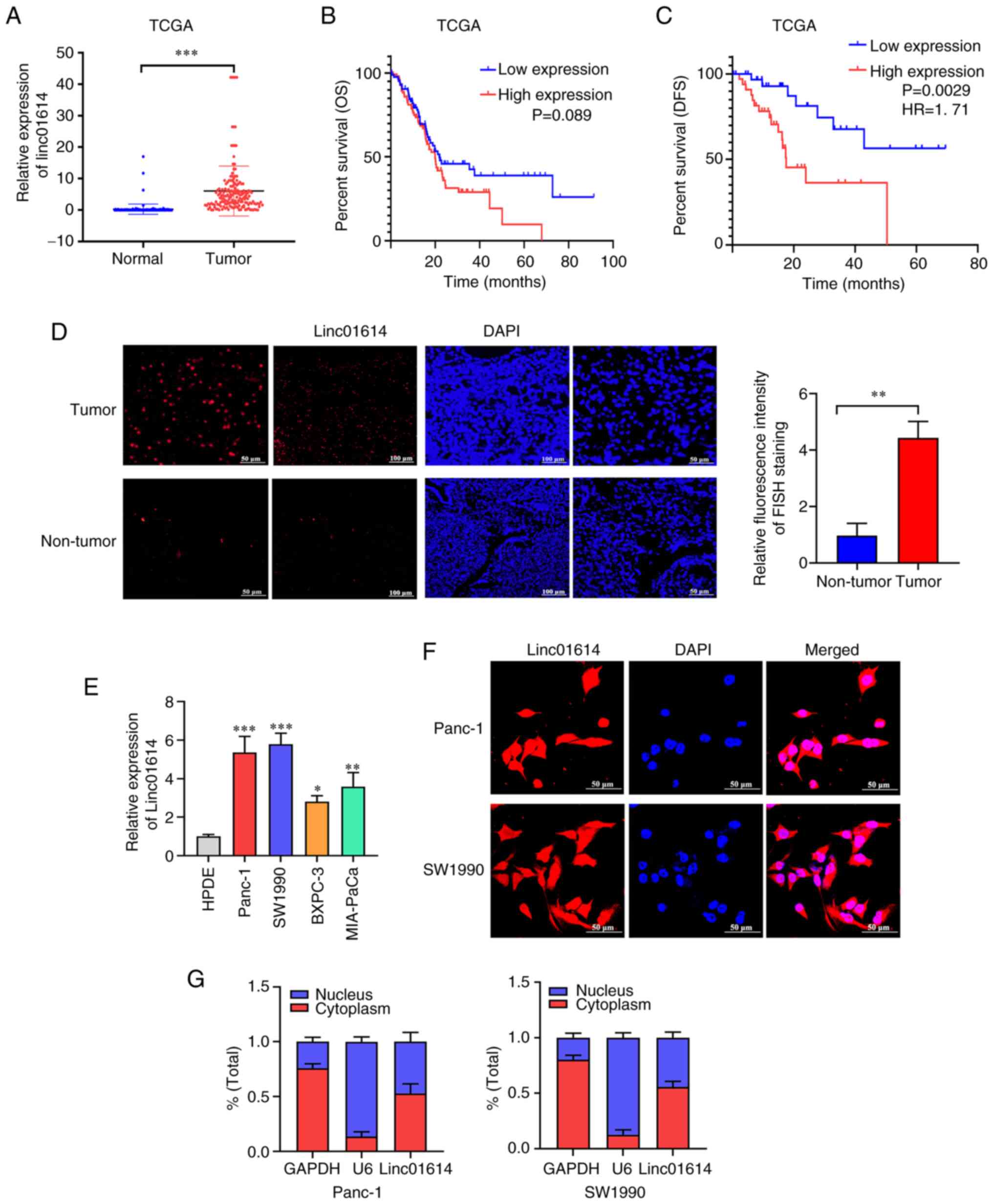
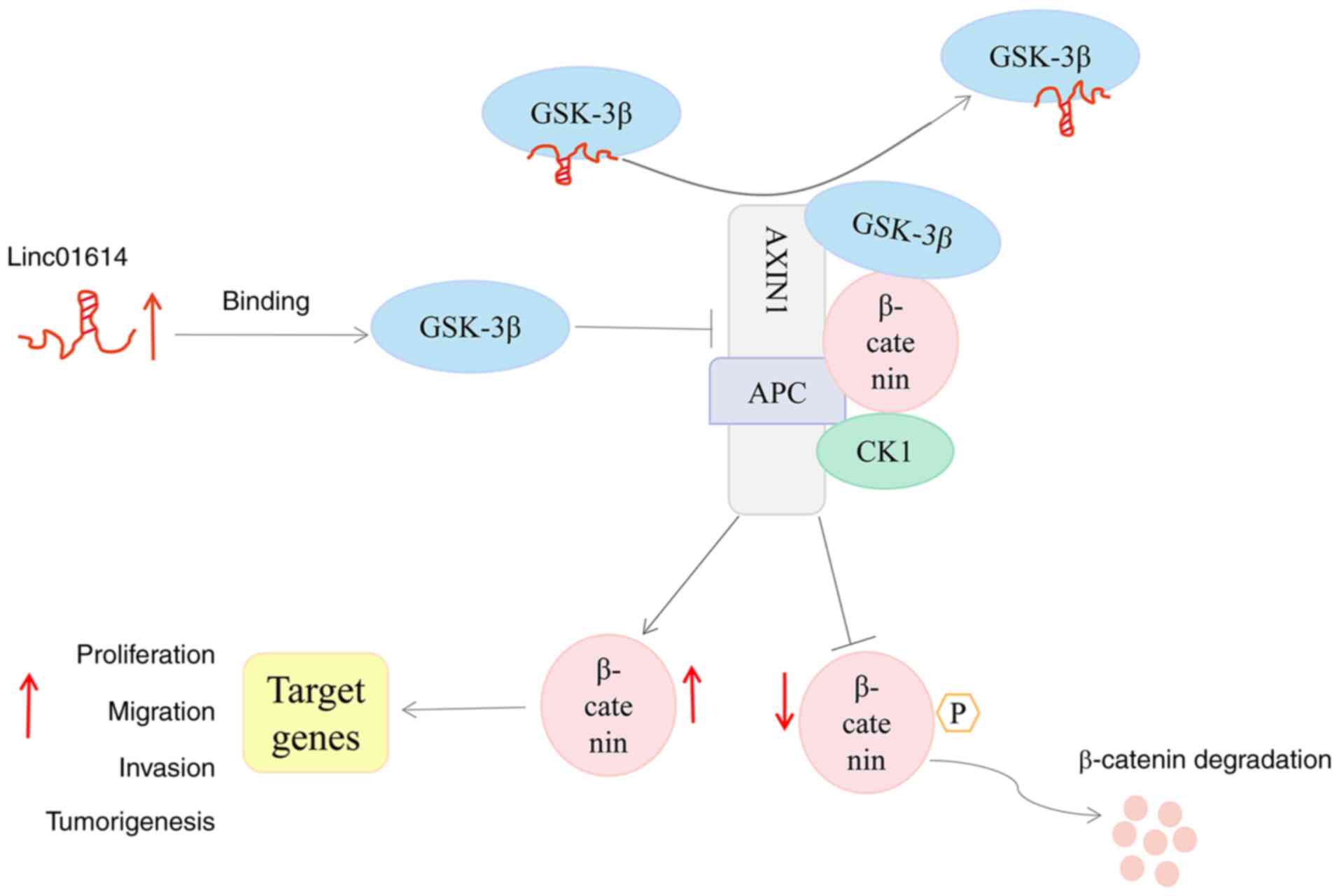
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
GBD 2017 Pancreatic Cancer Collaborators:
The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and
its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories,
1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease
study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:934–947. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herting CJ, Karpovsky I and Lesinski GB:
The tumor micro-environment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma:
Current perspectives and future directions. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
40:675–689. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ho WJ, Jaffee EM and Zheng L: The tumour
microenvironment in pancreatic cancer-clinical challenges and
opportunities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:527–540. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu S, Zhan N, Gao C, Xu P, Wang H, Wang
S, Piao S and Jing S: Long noncoding RNA CBR3-AS1 mediates
tumorigenesis and radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer
through redox and DNA repair by CBR3-AS1/miR-409-3p/SOD1 axis.
Cancer Lett. 526:1–11. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Tian Y, He J, Tian Y, Zhang G, Zhao
R, Zhu WJ and Gao P: Linc01133 contributes to gastric cancer growth
by enhancing YES1-dependent YAP1 nuclear translocation via sponging
miR-145-5p. Cell Death Dis. 13:512022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hu H, Wang Y, Ding X, He Y, Lu Z, Wu P,
Tian L, Yuan H, Liu D, Shi G, et al: Long non-coding RNA
XLOC_000647 suppresses progression of pancreatic cancer and
decreases epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced cell invasion
by down-regulating NLRP3. Mol Cancer. 17:182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh N, Ramnarine VR, Song JH, Pandey R,
Padi SK, Nouri M, Olive V, Kobelev M, Okumura K, Mccarthy D, et al:
The long noncoding RNA H19 regulates tumor plasticity in
neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 12:73492021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kopp F and Mendell JT: Functional
classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs.
Cell. 172:393–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gandhi M, Groß M, Holler JM, Coggins SA,
Patil N, Leupold JH, Munschauer M, Schenone M, Hartigan CR,
Allgayer H, et al: The lncRNA lincNMR regulates nucleotide
metabolism via a YBX1-RRM2 axis in cancer. Nat Commun. 11:32142020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pan S, Deng Y, Fu J, Zhang Y, Zhang Z and
Qin X: N6-methyladenosine upregulates miR181d5p in exosomes derived
from cancer associated fibroblasts to inhibit 5FU sensitivity by
targeting NCALD in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 60:142022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Cheng WY, Shi H, Huang S, Chen H,
Liu D, Xu W, Yu J and Wang J: Classifying gastric cancer using
FLORA reveals clinically relevant molecular subtypes and highlights
linc01614 as a biomarker for patient prognosis. Oncogene.
40:2898–2909. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vishnubalaji R, Shaath H, Elkord E and
Alajez NM: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcriptional landscape
in breast cancer identifies linc01614 as non-favorable prognostic
biomarker regulated by TGFβ and focal adhesion kinase (FAK)
signaling. Cell Death Discov. 5:1092019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu AN, Qu HJ, Yu CY and Sun P: Knockdown
of linc01614 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell progression by
up-regulating miR-217 and down-regulating FOXP1. J Cell Mol Med.
22:4034–4044. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun Y and Ling C: Analysis of the long
non-coding RNA linc01614 in non-small cell lung cancer. Medicine
(Baltimore). 98:e164372019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cai Q, Zhao X, Wang Y, Li S, Wang J, Xin Z
and Li F: linc01614 promotes osteosarcoma progression via
miR-520a-3p/SNX3 axis. Cell Signal. 83:1099852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang L, Chen Y, Peng X, Zhou Y, Jiang H,
Wang G and Zhuang W: Identification and validation of potential
pathogenic genes and prognostic markers in ESCC by integrated
bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet. 11:5210042020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aiello NM, Brabletz T, Kang Y, Nieto MA,
Weinberg RA and Stanger BZ: Upholding a role for EMT in pancreatic
cancer metastasis. Nature. 547:E7–E8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Wu H, Wang L, Zhang H, Lu J, Liang
Z and Liu T: Asporin promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion and
migration by regulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) through both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Cancer Lett.
398:24–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Tang T, Yang X, Qin P, Wang P,
Zhang H, Bai M, Wu R and Li F: Tumor-derived exosomal long
noncoding RNA LINC01133, regulated by Periostin, contributes to
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by silencing AXIN2. Oncogene.
40:3164–3179. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Cai H, Sun L, Zhan P, Chen M,
Zhang F, Ran Y and Wan J: LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell
marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and
predicts poor survival of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:2252018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu SL, Cai C, Yang ZY, Wu ZY, Wu XS, Wang
XF, Dong P and Gong W: DGCR5 is activated by PAX5 and promotes
pancreatic cancer via targeting miR-3163/TOP2A and activating
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 17:498–513. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Ram Makena M, Gatla H, Verlekar D,
Sukhavasi S, K Pandey M and C Pramanik K: Wnt/β-Catenin signaling:
The culprit in pancreatic carcinogenesis and therapeutic
resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 20:42422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tang N, Xu S, Song T, Qiu Y, He J and Fu
X: Zinc finger protein 91 accelerates tumour progression by
activating β-catenin signalling in pancreatic cancer. Cell Prolif.
54:e130312021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Heidt DG, Lee CJ, Yang H, Logsdon
CD, Zhang L, Fearon ER, Ljungman M and Simeone DM: Oncogenic
function of ATDC in pancreatic cancer through Wnt pathway
activation and beta-catenin stabilization. Cancer Cell. 15:207–219.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Zhou C, Liang Y, Zhou L, Yan Y, Liu N,
Zhang R, Huang Y, Wang M, Tang Y, Ali DW, et al: TSPAN1 promotes
autophagy flux and mediates cooperation between WNT-CTNNB1
signaling and autophagy via the MIR454-FAM83A-TSPAN1 axis in
pancreatic cancer. Autophagy. 17:3175–3195. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Kishida S, Yamamoto H, Ikeda S, Kishida M,
Sakamoto I, Koyama S and Kikuchi A: Axin, a negative regulator of
the wnt signaling pathway, directly interacts with adenomatous
polyposis coli and regulates the stabilization of beta-catenin. J
Biol Chem. 273:10823–10826. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seeling JM, Miller JR, Gil R, Moon RT,
White R and Virshup DM: Regulation of beta-catenin signaling by the
B56 subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Science. 283:2089–2091.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang M, Zhang S, Yang Z, Lin H, Zhu J,
Liu L, Wang W, Liu S, Liu W, Ma Y, et al: Self-recognition of an
inducible host lncRNA by RIG-I feedback restricts innate immune
response. Cell. 173:906–919. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu J, Shao T, Song M, Xie Y, Zhou J, Yin
J, Ding N, Zou H, Li Y and Zhang J: MIR22HG acts as a tumor
suppressor via TGFβ/SMAD signaling and facilitates immunotherapy in
colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:512020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cabili MN, Dunagin MC, Mcclanahan PD,
Biaesch A, Padovan-Merhar O, Regev A, Rinn JL and Raj A:
Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell
and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 16:202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
van Heesch S, van Iterson M, Jacobi J,
Boymans S, Essers PB, De Bruijn E, Hao W, Macinnes AW, Cuppen E and
Simonis M: Extensive localization of long noncoding RNAs to the
cytosol and mono- and polyribosomal complexes. Genome Biol.
15:R62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Sun M, Wang M, Feng M, Yang F, Li L,
Zhao J, Chang C, Dong H, Xie T, et al: Dysregulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling by protein kinases in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its therapeutic application. Cancer Sci.
112:1695–1706. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morris JP IV, Wang SC and Hebrok M: KRAS,
Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:683–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Han M, Wang S, Fritah S, Wang X, Zhou W,
Yang N, Ni S, Huang B, Chen A, Li G, et al: Interfering with long
non-coding RNA MIR22HG processing inhibits glioblastoma progression
through suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Brain.
143:512–530. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nyati KK, Hashimoto S, Singh SK, Tekguc M,
Metwally H, Liu YC, Okuzaki D, Gemechu Y, Kang S and Kishimoto T:
The novel long noncoding RNA AU021063, induced by IL-6/Arid5a
signaling, exacerbates breast cancer invasion and metastasis by
stabilizing Trib3 and activating the Mek/Erk pathway. Cancer Lett.
520:295–306. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu N, Jiang M, Liu H, Chu Y, Wang D, Cao
J, Wang Z, Xie X, Han Y and Xu B: LINC00941 promotes CRC metastasis
through preventing SMAD4 protein degradation and activating the
TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 28:219–232.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Xu M, Cui R, Ye L, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang
Q, Wang K, Dong C, Le W and Chen B: LINC00941 promotes glycolysis
in pancreatic cancer by modulating the Hippo pathway. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 26:280–294. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kimelman D and Xu W: beta-catenin
destruction complex: Insights and questions from a structural
perspective. Oncogene. 25:7482–7491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ryu HY, Kim LE, Jeong H, Yeo BK, Lee JW,
Nam H, Ha S, An HK, Park H, Jung S, et al: GSK3B induces autophagy
by phosphorylating ULK1. Exp Mol Med. 53:369–383. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park R, Coveler AL, Cavalcante L and Saeed
A: GSK-3β in pancreatic cancer: Spotlight on 9-ING-41, its
therapeutic potential and immune modulatory properties. Biology
(Basel). 10:6102021.
|
|
47
|
Zhang Z, Gao Q and Wang S: Kinase GSK3β
functions as a suppressor in colorectal carcinoma through the
FTO-mediated MZF1/c-Myc axis. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2655–2665. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Duda P, Akula SM, Abrams SL, Steelman LS,
Martelli AM, Cocco L, Ratti S, Candido S, Libra M, Montalto G, et
al: Targeting GSK3 and associated signaling pathways involved in
cancer. Cells. 9:11102020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Pecoraro C, Faggion B, Balboni B, Carbone
D, Peters GJ, Diana P, Assaraf YG and Giovannetti E: GSK3β as a
novel promising target to overcome chemoresistance in pancreatic
cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 58:1007792021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ying X, Jing L, Ma S, Li Q, Luo X, Pan Z,
Feng Y and Feng P: GSK3β mediates pancreatic cancer cell invasion
in vitro via the CXCR4/MMP-2 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 15:702015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mccubrey JA, Rakus D, Gizak A, Steelman
LS, Abrams SL, Lertpiriyapong K, Fitzgerald TL, Yang LV, Montalto
G, Cervello M, et al: Effects of mutations in Wnt/β-catenin,
hedgehog, Notch and PI3K pathways on GSK-3 activity-diverse effects
on cell growth, metabolism and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2942–2976. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ling J, Wang F, Liu C, Dong X, Xue Y, Jia
X, Song W and Li Q: FOXO1-regulated lncRNA LINC01197 inhibits
pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by restraining
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1792019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|