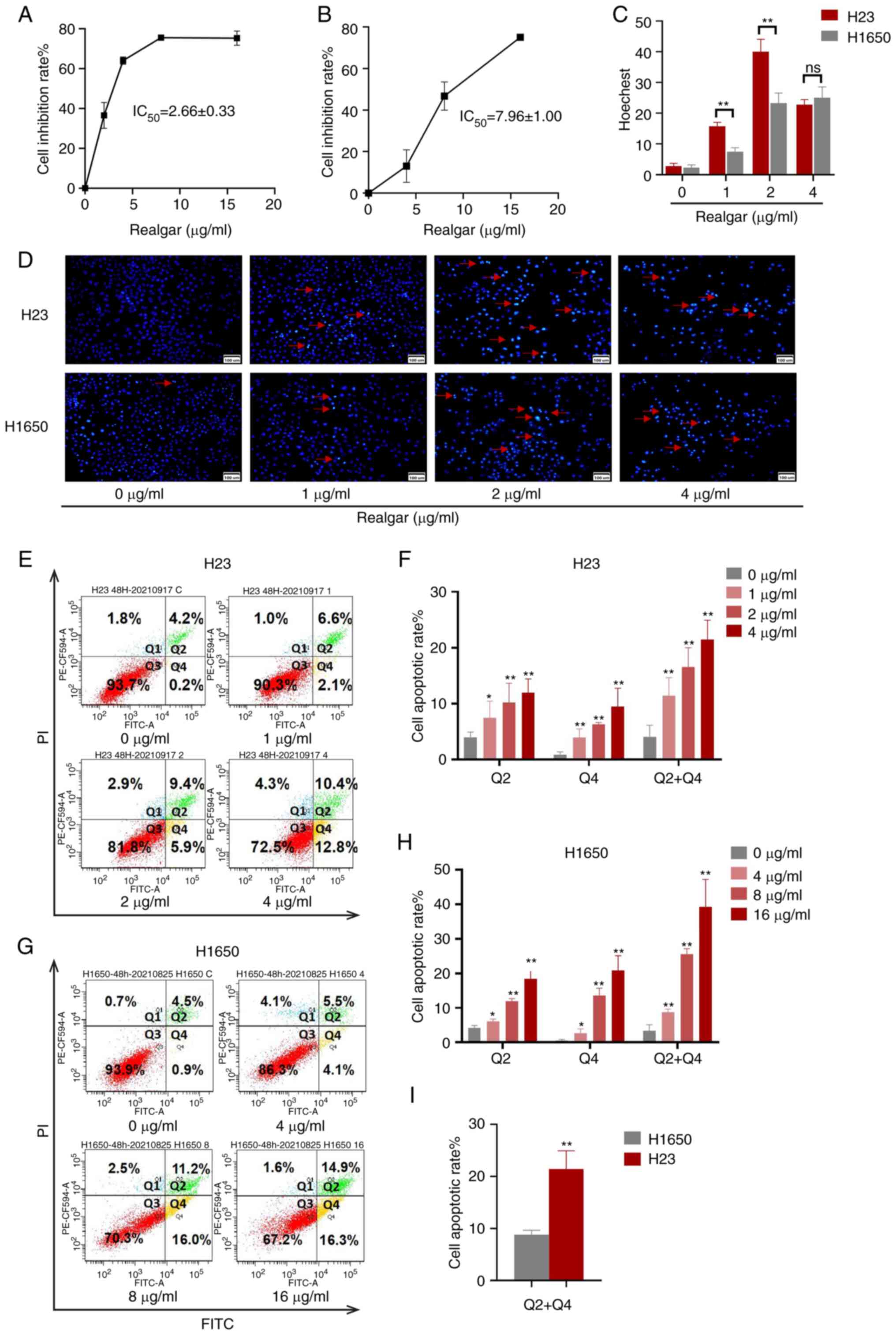
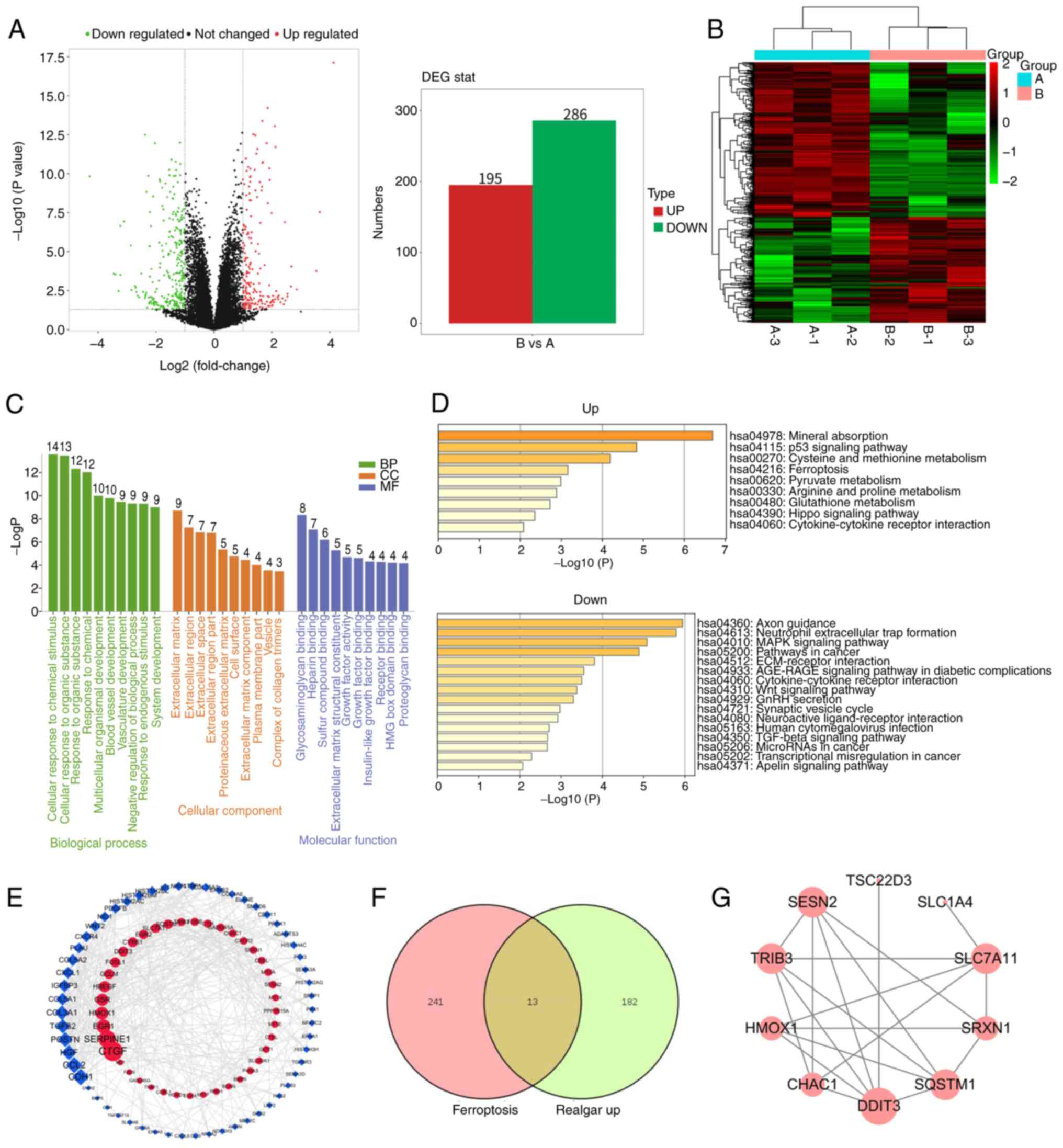
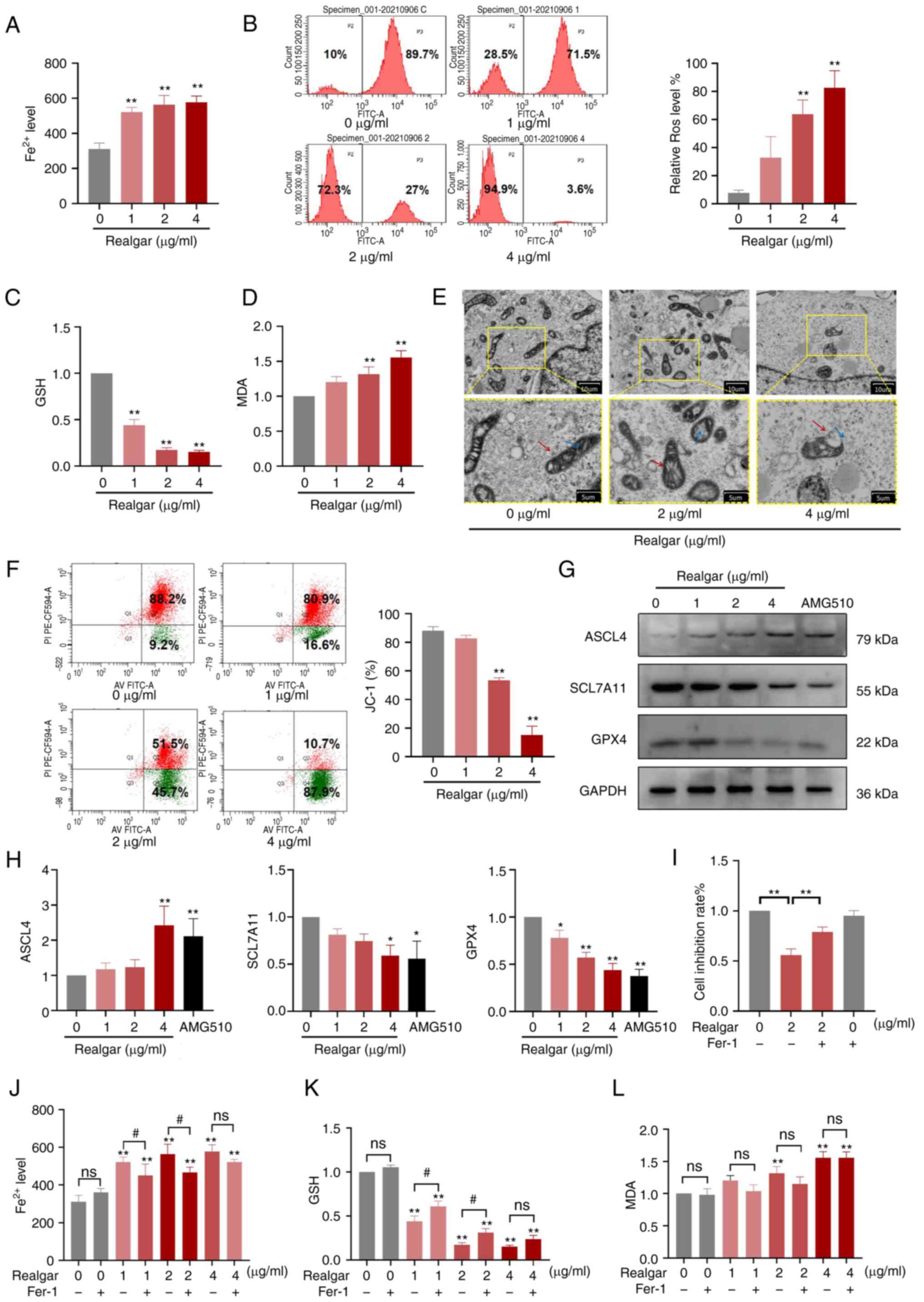
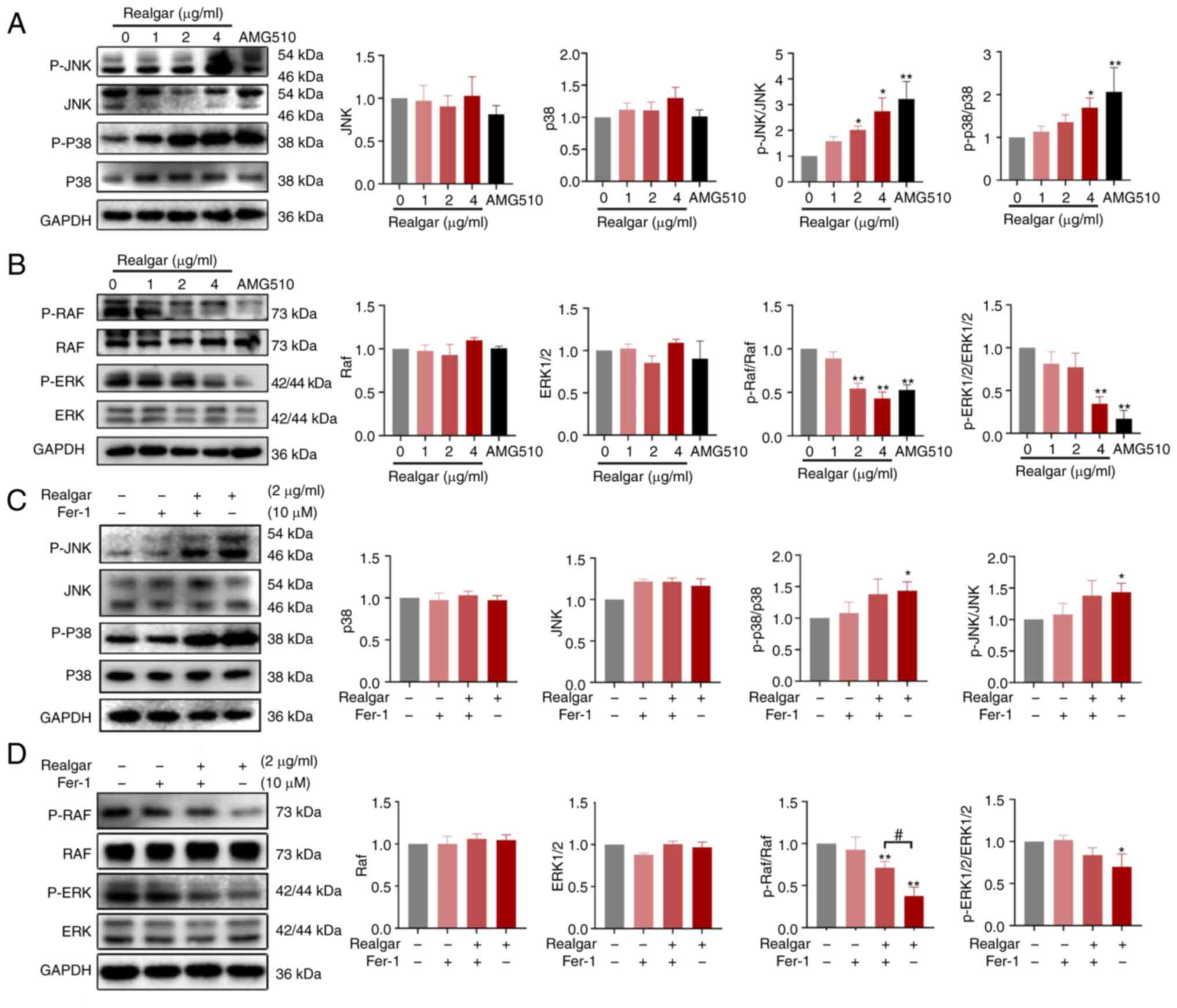
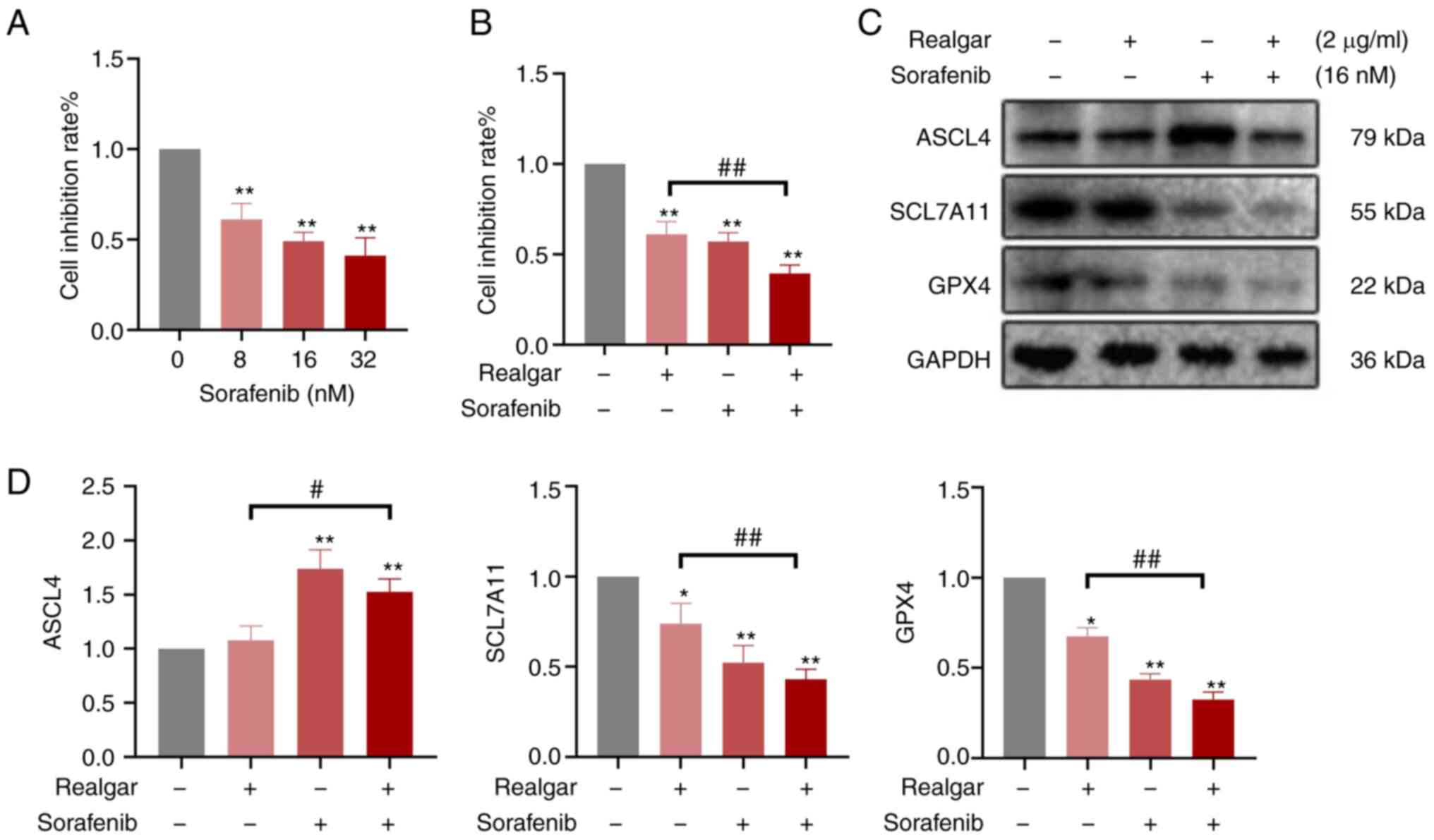
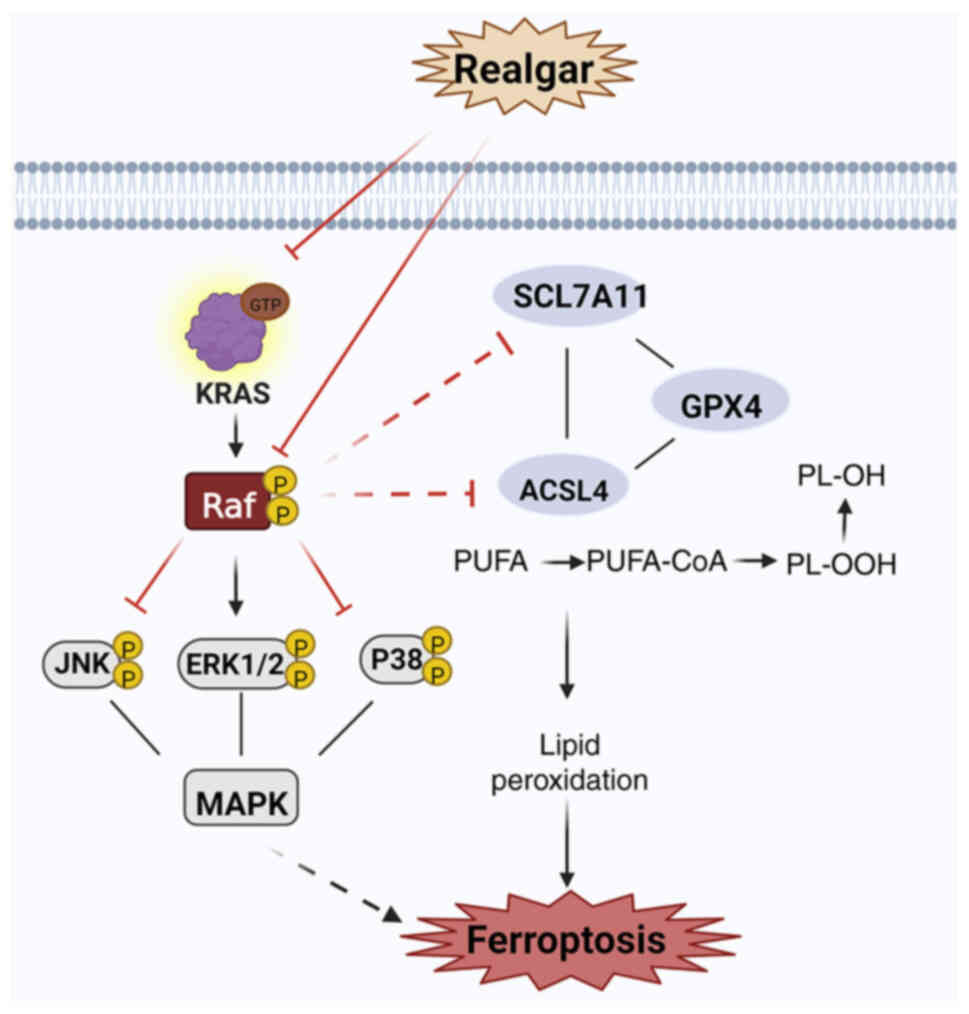
|
1
|
Huang J, Deng Y, Tin MS, Lok V, Ngai CH,
Zhang L, Lucero-Prisno DE III, Xu W, Zheng ZJ, Elcarte E, et al:
Distribution, risk factors, and temporal trends for lung cancer
incidence and mortality: A global analysis. Chest. 161:1101–1111.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryan MB and Corcoran RB: Therapeutic
strategies to target RAS-mutant cancers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
15:709–720. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagasaka M, Li Y, Sukari A, Ou SI,
Al-Hallak MN and Azmi AS: KRAS G12C game of thrones, which direct
KRAS inhibitor will claim the iron throne? Cancer Treat Rev.
84:1019742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rodak O, Peris-Díaz MD, Olbromski M,
Podhorska-Okołów M and Dzięgiel P: Current landscape of non-small
cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, histological classification,
targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel).
13:47052021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Skoulidis F, Li BT, Dy GK, Price TJ,
Falchook GS, Wolf J, Italiano A, Schuler M, Borghaei H, Barlesi F,
et al: Sotorasib for lung cancers with KRAS G12C-mutation. N Engl J
Med. 384:2371–2381. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ryan MB, Coker O, Sorokin A, Fella K,
Barnes H, Wong E, Kanikarla P, Gao F, Zhang Y, Zhou L, et al:
KRASG12C-independent feedback activation of wild-type
RAS constrains KRASG12C inhibitor efficacy. Cell Rep.
39:1109932022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xiaoxia X, Jing S, Dongbin X, Yonggang T,
Jingke Z, Yanying Z and Hulai W: Realgar nanoparticles inhibit
migration, invasion and metastasis in a mouse model of breast
cancer by suppressing matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis.
Curr Drug Deliv. 17:148–158. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Zhou GB, Liu P, Song JH, Liang Y,
Yan XJ, Xu F, Wang BS, Mao JH, Shen ZX, et al: Dissection of
mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula realgar-indigo naturalis as
an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:4826–4831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu DP, Qiu JY, Jiang B, Wang Q, Liu KY,
Liu YR and Chen SS: Tetra-arsenic tetra-sulfide for the treatment
of acute promyelocytic leukemia: A pilot report. Blood.
99:3136–3143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang SL, Guo AX, Xiang Y, Wand XB, Lin HX
and Fu L: Clinical study on the treatment of acute promyelocytic
leukemia with composite indigo naturalis tablets. Chin J Hematol.
16:26–28. 1995.
|
|
13
|
Shi G and Shan G: Effects of yellow loquat
on changes in immune function, hemorheology and coagulation
function in patients with lung cancer. China Tradit Chin Med Sci
Technol. 20:115–116. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Yang FR, Zhao YF, Hu XW, Liu ZK, Yu XD, Li
CY, Li XR and Li HJ: Nano-realgar suppresses lung cancer stem cell
growth by repressing metabolic reprogramming. Gene. 788:1456662021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu D, Zhi D, Zhou T, Yu Q, Wan F, Bai Y
and Li H: Realgar bioleaching solution is a less toxic arsenic
agent in suppressing the Ras/MAPK pathway in Caenorhabditis
elegans. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 35:292–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Drosten M and Barbacid M: Targeting the
MAPK Pathway in KRAS-driven tumors. Cancer Cell. 37:543–550. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moore AR, Rosenberg SC, McCormick F and
Malek S: RAS-targeted therapies: Is the undruggable drugged? Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 19:533–552. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karoulia Z, Gavathiotis E and Poulikakos
PI: New perspectives for targeting RAF kinase in human cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 17:676–691. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karnoub AE and Weinberg RA: Ras oncogenes:
Split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:517–531. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leevers SJ, Paterson HF and Marshall CJ:
Requirement for Ras in Raf activation is overcome by targeting Raf
to the plasma membrane. Nature. 369:411–414. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stokoe D, Macdonald SG, Cadwallader K,
Symons M and Hancock JF: Activation of Raf as a result of
recruitment to the plasma membrane. Science. 264:1463–1467. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng SB, Henry JR, Kaufman MD, Lu WP,
Smith BD, Vogeti S, Rutkoski TJ, Wise S, Chun L, Zhang Y, et al:
Inhibition of RAF isoforms and active dimers by LY3009120 leads to
anti-tumor activities in RAS or BRAF mutant cancers. Cancer Cell.
28:384–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Awad MM, Liu S, Rybkin II, Arbour KC,
Dilly J, Zhu VW, Johnson ML, Heist RS, Patil T, Riely GJ, et al:
Acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibition in cancer. N
Engl J Med. 384:2382–2393. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tanaka N, Lin JJ, Li C, Ryan MB, Zhang J,
Kiedrowski LA, Michel AG, Syed MU, Fella KA, Sakhi M, et al:
Clinical acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibition
through a novel KRAS switch-II pocket mutation and polyclonal
alterations converging on RAS-MAPK reactivation. Cancer Discov.
11:1913–1922. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E,
Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ, Wolpaw AJ, Smukste I, Peltier JM,
Boniface JJ, et al: RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death
involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature. 447:864–868.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 18:280–296. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen P, Li X, Zhang R, Liu S, Xiang Y,
Zhang M, Chen X, Pan T, Yan L, Feng J, et al: Combinative treatment
of β-elemene and cetuximab is sensitive to KRAS mutant colorectal
cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting
epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Theranostics. 10:5107–5119.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Balihodzic A, Prinz F, Dengler MA, Calin
GA, Jost PJ and Pichler M: Non-coding RNAs and ferroptosis:
Potential implications for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ.
29:1094–1106. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alemán MR, Santolaria F, Batista N, de La
Vega M, González-Reimers E, Milena A, Llanos M and Gómez-Sirvent
JL: Leptin role in advanced lung cancer. A mediator of the acute
phase response or a marker of the status of nutrition? Cytokine.
19:21–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M and Dong X:
Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv
Mater. 31:19041972019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gammella E, Buratti P, Cairo G and
Recalcati S: The transferrin receptor: The cellular iron gate.
Metallomics. 9:1367–1375. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Synthetic lethal
screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent,
nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells.
Chem Biol. 15:234–245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Yu C, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang
D: Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ.
28:1135–1148. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng S, Wu D, Li L, Liu T, Zhang T, Li J,
Yu Y, He M, Zhao YY, Han R and Xu Y: miR-324-3p reverses cisplatin
resistance by inducing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in lung
adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
549:54–60. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kukulj S, Jaganjac M, Boranic M, Krizanac
S, Santic Z and Poljak-Blazi M: Altered iron metabolism,
inflammation, transferrin receptors, and ferritin expression in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 27:268–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jaune-Pons E and Vasseur S: Role of amino
acids in regulation of ROS balance in cancer. Arch Biochem Biophys.
689:1084382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1): D605–D612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Nie Q, Hu Y, Yu X, Li X and Fang X:
Induction and application of ferroptosis in cancer therapy. Cancer
Cell Int. 22:122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu T, Ding W, Ji X, Ao X, Liu Y, Yu W and
Wang J: Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4900–4912. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun L, Dong H, Zhang W, Wang N, Ni N, Bai
X and Liu N: Lipid peroxidation, GSH depletion, and SLC7A11
inhibition are common causes of EMT and ferroptosis in A549 cells,
but different in specific mechanisms. DNA Cell Biol. 40:172–183.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang H, Liu C, Zhao Y and Gao G:
Mitochondria regulation in ferroptosis. Eur J Cell Biol.
99:1510582020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J, Minikes AM, Monian P,
Thompson CB and Jiang X: Role of mitochondria in ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 73:354–363.e3. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156:317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius
E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, Irmler M, Beckers J, Aichler M, Walch A,
et al: ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular
lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 13:91–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Su LJ, Zhang JH, Gomez H, Murugan R, Hong
X, Xu D, Jiang F and Peng ZY: Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid
peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019:50808432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chang WT, Bow YD, Fu PJ, Li CY, Wu CY,
Chang YH, Teng YN, Li RN, Lu MC, Liu YC and Chiu CC: A marine
terpenoid, heteronemin, induces both the apoptosis and ferroptosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involves the ROS and MAPK
pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:76890452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao J and Luo Z: Discovery of Raf family
is a milestone in deciphering the Ras-mediated intracellular
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 23:51582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu G, Song Y, Li C, Liu R, Chen Y, Yu L,
Huang Q, Zhu D, Lu C, Yu X, et al: Arsenic compounds: The wide
application and mechanisms applied in acute promyelocytic leukemia
and carcinogenic toxicology. Eur J Med Chem. 221:1135192021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin CC, Huang YK, Cho CF, Lin YS, Lo CC,
Kuo TT, Tseng GC, Cheng WC, Chang WC, Hsiao TH, et al: Targeting
positive feedback between BASP1 and EGFR as a therapeutic strategy
for lung cancer progression. Theranostics. 10:10925–10939. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cuenda A and Rousseau S: p38 MAP-kinases
pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1358–1375. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Huang CH, Lee YC, Chiou JT, Shi YJ, Wang
LJ and Chang LS: Arsenic trioxide-induced p38 MAPK and Akt mediated
MCL1 downregulation causes apoptosis of BCR-ABL1-positive leukemia
cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 397:1150132020.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu MF, Huang YH, Chiu LY, Cherng SH, Sheu
GT and Yang TY: Curcumin induces apoptosis of chemoresistant lung
cancer cells via ROS-regulated p38 MAPK phosphorylation = Arsenic
trioxide-induced p38 MAPK and Akt mediated MCL1 downregulation
causes apoptosis of BCR-ABL1-positive leukemia cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:82482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xiao X, Guo L, Dai W, Yan B, Zhang J, Yuan
Q, Zhou L, Shan L and Efferth Y: Green tea-derived theabrownin
suppresses human non-small cell lung carcinoma in xenograft model
through activation of not only p53 signaling but also MAPK/JNK
signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 291:1151672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu Z, Zhao M, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Zhang S,
Xu Y, Ren H, Su H, Wang H and Qiu X: Upregulation of KLHL17
promotes the proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung
cancer by activating the Ras/MAPK signaling pathway. Lab Invest.
Aug 17–2022.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH
and Park WH: The effect of MAPK inhibitors on arsenic
trioxide-treated Calu-6 lung cells in relation to cell death, ROS
and GSH levels. Anticancer Res. 29:3837–3844. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang X, Wu X, Wu X, Huang L, Song J, Yung
C, He Z and Li Y: The flavagline compound 1-(2-(dimethylamino)
acetyl)-rocaglaol induces apoptosis in K562 cells by regulating the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR, JAK2/STAT3, and MAPK pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther.
16:2545–2557. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Lee H, Lee HJ, Bae IJ, Kim JJ and Kim SH:
Inhibition of STAT3/VEGF/CDK2 axis signaling is critically involved
in the antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects of arsenic herbal
mixture PROS in non-small lung cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:101771–101783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu Z, Zhao Q, Zuo ZX, Yuan SQ, Yu K,
Zhang Q, Zhang X, Sheng H, Ju HQ, Cheng H, et al: Systematic
analysis of the aberrances and functional implications of
ferroptosis in cancer. iScience. 23:1013022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yong WP, Rha SY, Tan IB, Choo SP, Syn NL,
Koh V, Tan SH, Asuncion BR, Sundar R, So JB, et al: Real-time tumor
gene expression profiling to direct gastric cancer chemotherapy:
Proof-of-concept '3G' trial. Clin Cancer Res. 24:5272–5281. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lim JKM and Leprivier G: The impact of
oncogenic RAS on redox balance and implications for cancer
development. Cell Death Dis. 10:9552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lim JKM, Delaidelli A, Minaker SW, Zhang
HF, Colovic M, Yang H, Negri GL, von Karstedt S, Lockwood WW,
Schaffer P, et al: Cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT (SLC7A11)
facilitates oncogenic RAS transformation by preserving
intracellular redox balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:9433–9442.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Baek S, Choi CM, Ahn SH, Lee JW, Gong G,
Ryu JS, Oh SJ, Bacher-Stier C, Fels L, Koglin N, et al: Exploratory
clinical trial of (4S)-4-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)-L-glutamate for
imaging xC-transporter using positron emission tomography in
patients with non-small cell lung or breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:5427–5437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hu K, Li K, Lv J, Feng J, Chen J, Wu H,
Cheng F, Jiang W, Wang J, Pei H, et al: Suppression of the
SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant
lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Invest. 130:1752–1766. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Zhang N, Huang J, Xu M and Wang Y: LncRNA
T-UCR Uc.339/miR-339/SLC7A11 axis regulates the metastasis of
ferroptosis-induced lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer. 13:1945–1957.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu XY, Wei DG and Li RS: Capsaicin
induces ferroptosis of NSCLC by regulating SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling
in vitro. Sci Rep. 12:119962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gao H, Bai Y, Jia Y, Zhao Y, Kang R, Tang
D and Dai E: Ferroptosis is a lysosomal cell death process. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 503:1550–1556. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ma X, Yan W and He N: Lidocaine attenuates
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced inflammation, apoptosis and
ferroptosis in lung epithelial cells by regulating the p38 MAPK
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 25:1502022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Yang J, Mo J, Dai J, Ye C, Cen W, Zheng X,
Jiang L and Ye L: Cetuximab promotes RSL3-induced ferroptosis by
suppressing the Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway in KRAS mutant
colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12:10792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhu K, Zhu X, Sun S, Yang W, Liu S, Tang
Z, Zhang R, Li J, Shen T and Hei M: Inhibition of TLR4 prevents
hippocampal hypoxic-ischemic injury by regulating ferroptosis in
neonatal rats. Exp Neurol. 345:1138282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang Y, Zhang L, Yao C, Ma Y and Liu Y:
Epithelial membrane protein 1 promotes sensitivity to RSL3-induced
ferroptosis and intensifies gefitinib resistance in head and neck
cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:47506712022.PubMed/NCBI
|