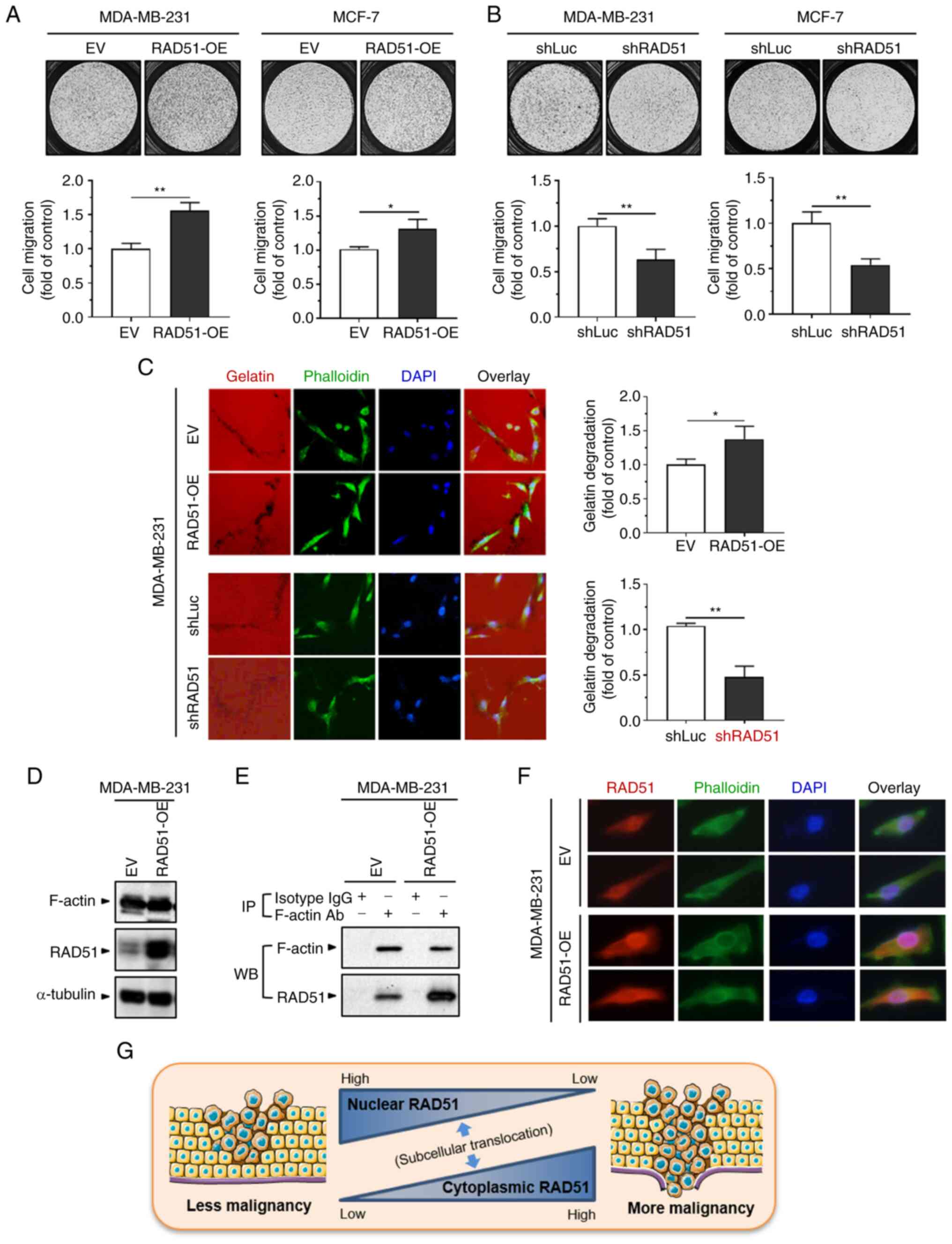
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moo TA, Sanford R, Dang C and Morrow M:
Overview of breast cancer therapy. PET Clin. 13:339–354. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trayes KP and Cokenakes SEH: Breast cancer
treatment. Am Fam Physician. 104:171–178. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martinez-Perez C, Turnbull AK, Ekatah GE,
Arthur LM, Sims AH, Thomas JS and Dixon JM: Current treatment
trends and the need for better predictive tools in the management
of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Treat Rev.
55:163–172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fahad Ullah M: Breast cancer: Current
perspectives on the disease status. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1152:51–64.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Giridhar KV and Liu MC: Available and
emerging molecular markers in the clinical management of breast
cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 19:919–928. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nickoloff JA: Targeting replication stress
response pathways to enhance genotoxic chemo- and radiotherapy.
Molecules. 27:47362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Z, Jia R, Wang L, Yang Q, Hu X, Fu Q,
Zhang X, Li W and Ren Y: The emerging roles of Rad51 in cancer and
its potential as a therapeutic target. Front Oncol. 12:9355932022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MG, Lee KS and Nam KS: The association
of changes in RAD51 and survivin expression levels with the proton
beam sensitivity of Capan-1 and Panc-1 human pancreatic cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 54:744–752. 2019.
|
|
10
|
Connell PP, Jayathilaka K, Haraf DJ,
Weichselbaum RR, Vokes EE and Lingen MW: Pilot study examining
tumor expression of RAD51 and clinical outcomes in human head
cancers. Int J Oncol. 28:1113–1119. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Luzhna L, Golubov A, Ilnytskyy S, Chekhun
VF and Kovalchuk O: Molecular mechanisms of radiation resistance in
doxorubicin-resistant breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
42:1692–1708. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maacke H, Opitz S, Jost K, Hamdorf W,
Henning W, Krüger S, Feller AC, Lopens A, Diedrich K, Schwinger E
and Stürzbecher HW: Over-expression of wild-type Rad51 correlates
with histological grading of invasive ductal breast cancer. Int J
Cancer. 88:907–913. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu J, Wang N and Wang YJ: XRCC3 and RAD51
expression are associated with clinical factors in breast cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e721042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiegmans AP, Al-Ejeh F, Chee N, Yap PY,
Gorski JJ, Da Silva L, Bolderson E, Chenevix-Trench G, Anderson R,
Simpson PT, et al: Rad51 supports triple negative breast cancer
metastasis. Oncotarget. 5:3261–3272. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Soderlund K, Skoog L, Fornander T and
Askmalm MS: The BRCA1/BRCA2/Rad51 complex is a prognostic and
predictive factor in early breast cancer. Radiother Oncol.
84:242–251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sosinska-Mielcarek K, Duchnowska R,
Winczura P, Badzio A, Majewska H, Lakomy J, Pęksa R, Pieczyńska B,
Radecka B, Dębska S, et al: Immunohistochemical prediction of brain
metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer: The role of
Rad51. Breast. 22:1178–1183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alshareeda AT, Negm OH, Aleskandarany MA,
Green AR, Nolan C, TigHhe PJ, Madhusudan S, Ellis IO and Rakha EA:
Clinical and biological significance of RAD51 expression in breast
cancer: A key DNA damage response protein. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
159:41–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chiu WC, Fang PT, Lee YC, Wang YY, Su YH,
Hu SC, Chen YK, Tsui YT, Kao YH, Huang MY and Yuan SF: DNA Repair
Protein Rad51 induces tumor growth and metastasis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma via a p38/Akt-Dependent pathway. Ann Surg
Oncol. 27:2090–2101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yuan SS, Hou MF, Hsieh YC, Huang CY, Lee
YC, Chen YJ and Lo S: Role of MRE11 in cell proliferation, tumor
invasion, and DNA repair in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
104:1485–1502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Lu LL, Wen D, Liu DL, Dong LL, Gao
DM, Bian XY, Zhou J, Fan J and Wu WZ: MiR-612 regulates invadopodia
of hepatocellular carcinoma by HADHA-mediated lipid reprogramming.
J Hematol Oncol. 13:122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee MY, Huang CH, Kuo CJ, Lin CL, Lai WT
and Chiou SH: Clinical proteomics identifies urinary CD14 as a
potential biomarker for diagnosis of stable coronary artery
disease. PLoS One. 10:e01171692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cottrell JS: Protein identification using
MS/MS data. J Proteomics. 74:1842–1851. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nedeljkovic M and Damjanovic A: Mechanisms
of chemotherapy resistance in triple-negative breast cancer-how we
can rise to the challenge. Cells. 8:9572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Prihantono and Faruk M: Breast cancer
resistance to chemotherapy: When should we suspect it and how can
we prevent it? Ann Med Surg. 70:1027932021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Holliday DL and Speirs V: Choosing the
right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res.
13:2152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guney Eskiler G, Sahin E, Deveci Ozkan A,
Cilingir Kaya OT and Kaleli S: Curcumin induces DNA damage by
mediating homologous recombination mechanism in triple negative
breast cancer. Nutr Cancer. 72:1057–1066. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gildemeister OS, Sage JM and Knight KL:
Cellular redistribution of Rad51 in response to DNA damage: Novel
role for Rad51C. J Biol Chem. 284:31945–31952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mladenov E, Anachkova B and Tsaneva I:
Sub-nuclear localization of Rad51 in response to DNA damage. Genes
Cells. 11:513–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dugina VB, Shagieva GS and Kopnin PB:
Biological role of actin isoforms in mammalian cells. Biochemistry.
84:583–592. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bunnell TM, Burbach BJ, Shimizu Y and
Ervasti JM: β-Actin specifically controls cell growth, migration,
and the G-actin pool. Mol Biol Cell. 22:4047–4058. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suresh R and Diaz RJ: The remodelling of
actin composition as a hallmark of cancer. Transl Oncol.
14:1010512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gourley C, Balmana J, Ledermann JA, Serra
V, Dent R, Loibl S, Pujade-Lauraine E and Boulton SJ: Moving from
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition to targeting DNA repair and
DNA damage response in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 37:2257–2269.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Honrado E, Osorio A, Palacios J, Milne RL,
Sánchez L, Díez O, Cazorla A, Syrjakoski K, Huntsman D, Heikkilä P,
et al: Immunohistochemical expression of DNA repair proteins in
familial breast cancer differentiate BRCA2-associated tumors. J
Clin Oncol. 23:7503–7511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Klein HL: The consequences of Rad51
overexpression for normal and tumor cells. DNA Repair. 7:686–693.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gachechiladze M, Skarda J, Soltermann A
and Joerger M: RAD51 as a potential surrogate marker for DNA repair
capacity in solid malignancies. Int J Cancer. 141:1286–1294. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stodtmann S, Nuthalapati S, Eckert D,
Kasichayanula S, Joshi R, Bach BA, Mensing S, Menon R and Xiong H:
A population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of veliparib, a PARP
inhibitor, across phase 1/2/3 trials in cancer patients. J Clin
Pharmacol. 61:1195–1205. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wiegmans AP, Yap PY, Ward A, Lim YC and
Khanna KK: Differences in expression of key DNA damage repair genes
after epigenetic-Induced BRCAness dictate synthetic lethality with
PARP1 inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2321–2331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoneda T, Williams PJ, Hiraga T, Niewolna
M and Nishimura R: A bone-seeking clone exhibits different
biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast
cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J Bone
Miner Res. 16:1486–1495. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Woditschka S, Evans L, Duchnowska R, Reed
LT, Palmieri D, Qian Y, Badve S, Sledge G Jr, Gril B, Aladjem MI,
et al: DNA double-strand break repair genes and oxidative damage in
brain metastasis of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
106:dju1452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J and Xu B: Targeted therapeutic
options and future perspectives for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 4:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nam S, Chang HR, Jung HR, Gim Y, Kim NY,
Grailhe R, Seo HR, Park HS, Balch C, Lee J, et al: A pathway-based
approach for identifying biomarkers of tumor progression to
trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 356:880–890.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Negrini S, Gorgoulis VG and Halazonetis
TD: Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:220–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schild D and Wiese C: Overexpression of
RAD51 suppresses recombination defects: A possible mechanism to
reverse genomic instability. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:1061–1070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Chen CC, Feng W, Lim PX, Kass EM and Jasin
M: Homology-directed repair and the role of BRCA1, BRCA2, and
related proteins in genome integrity and cancer. Annu Rev Cancer
Biol. 2:313–336. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Scully R, Xie A and Nagaraju G: Molecular
functions of BRCA1 in the DNA damage response. Cancer Biol Ther.
3:521–527. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Plo I, Laulier C, Gauthier L, Lebrun F,
Calvo F and Lopez BS: AKT1 inhibits homologous recombination by
inducing cytoplasmic retention of BRCA1 and RAD51. Cancer Res.
68:9404–9412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yuan SS, Lee SY, Chen G, Song M, Tomlinson
GE and Lee EY: BRCA2 is required for ionizing radiation-induced
assembly of Rad51 complex in vivo. Cancer Res. 59:3547–3551.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Davies AA, Masson JY, McIlwraith MJ,
Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Venkitaraman AR and West SC: Role of BRCA2
in control of the RAD51 recombination and DNA repair protein. Mol
Cell. 7:273–282. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suwaki N, Klare K and Tarsounas M: RAD51
paralogs: Roles in DNA damage signalling, recombinational repair
and tumorigenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 22:898–905. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jeyasekharan AD, Liu Y, Hattori H,
Pisupati V, Jonsdottir AB, Rajendra E, Lee M, Sundaramoorthy E,
Schlachter S, Kaminski CF, et al: A cancer-associated BRCA2
mutation reveals masked nuclear export signals controlling
localization. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:1191–1198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Paul A and Paul S: The breast cancer
susceptibility genes (BRCA) in breast and ovarian cancers. Front
Biosci. 19:605–618. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhao W, Wiese C, Kwon Y, Hromas R and Sung
P: The BRCA tumor suppressor network in chromosome damage repair by
homologous recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 88:221–245. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Paterson EK and Courtneidge SA:
Invadosomes are coming: New insights into function and disease
relevance. FEBS J. 285:8–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Izdebska M, Zielinska W, Grzanka D and
Gagat M: The role of actin dynamics and actin-binding proteins
expression in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its
association with cancer progression and evaluation of possible
therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int. 2018:45783732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nersesian S, Williams R, Newsted D, Shah
K, Young S, Evans PA, Allingham JS and Craig AW: Effects of
modulating actin dynamics on HER2 cancer cell motility and
metastasis. Sci Rep. 8:172432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
van Wijk LM, Nilas AB, Vrieling H and
Vreeswijk MPG: RAD51 as a functional biomarker for homologous
recombination deficiency in cancer: A promising addition to the HRD
toolbox? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 22:185–199. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|