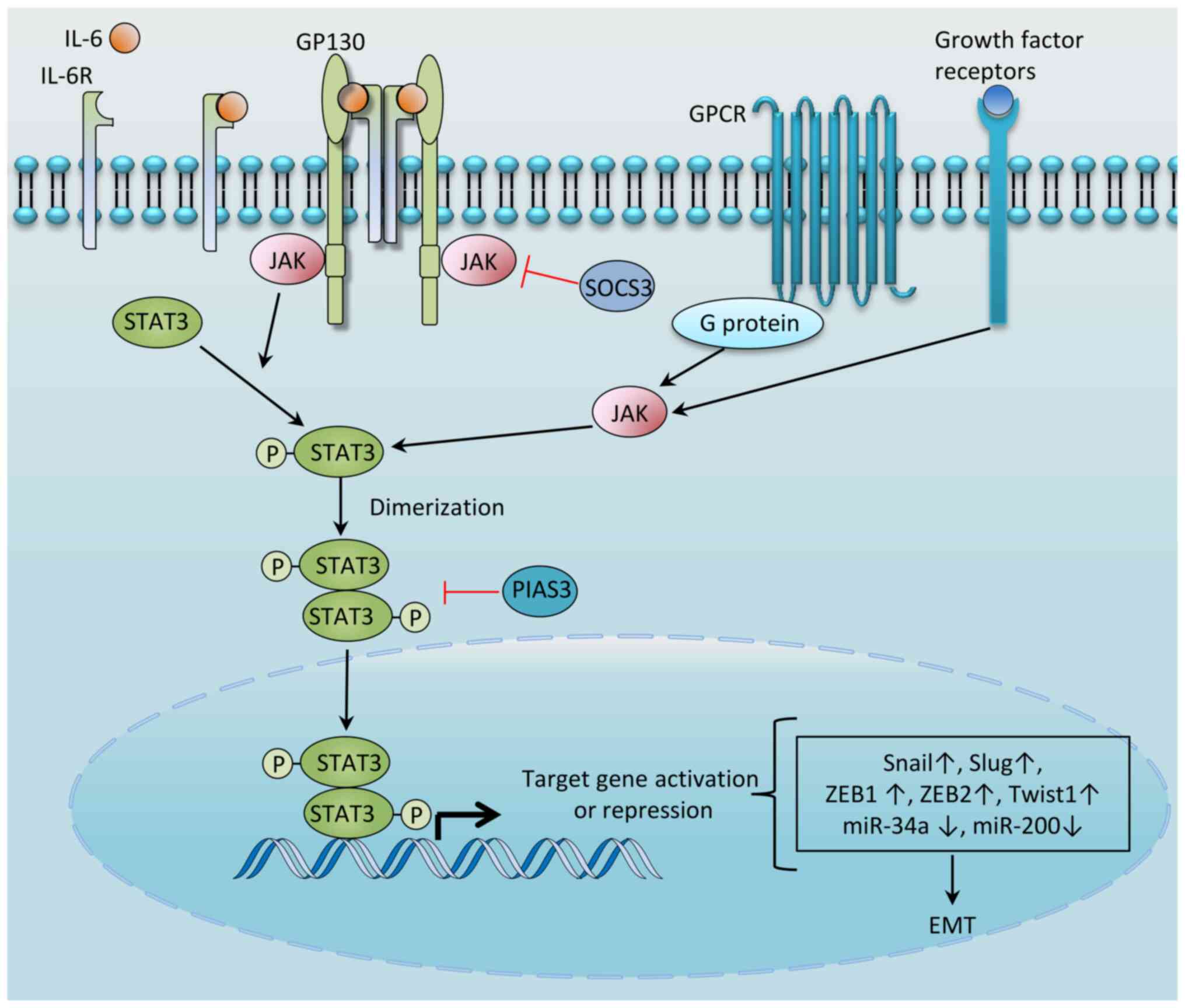
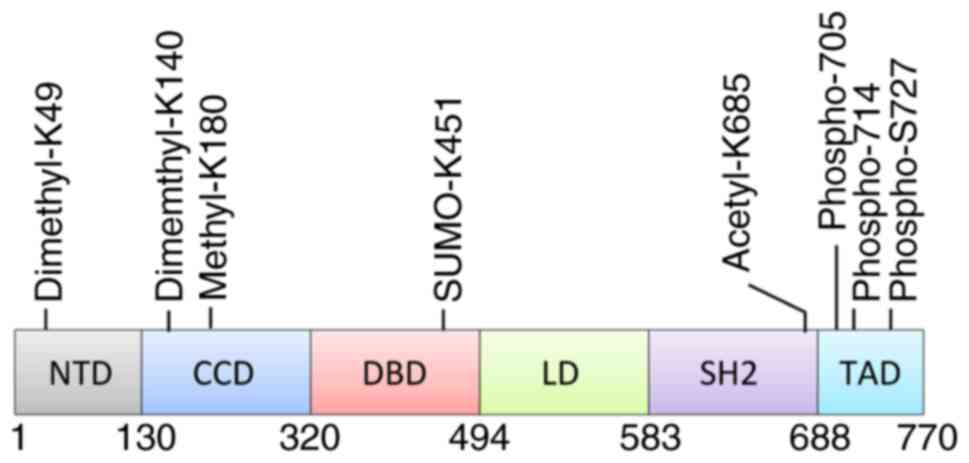
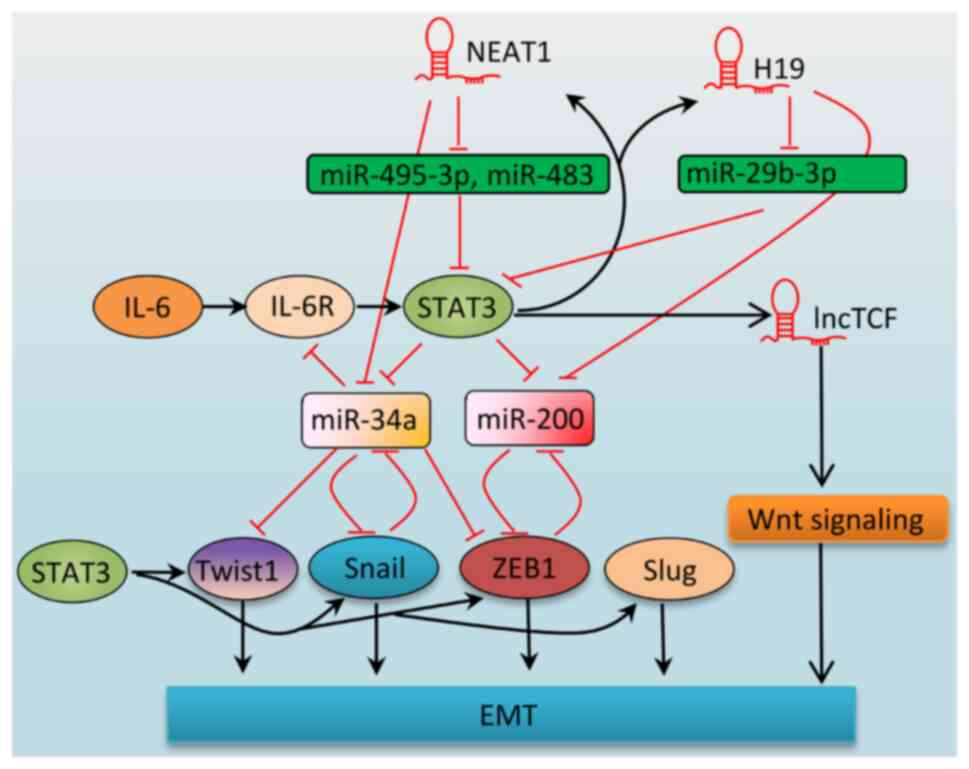
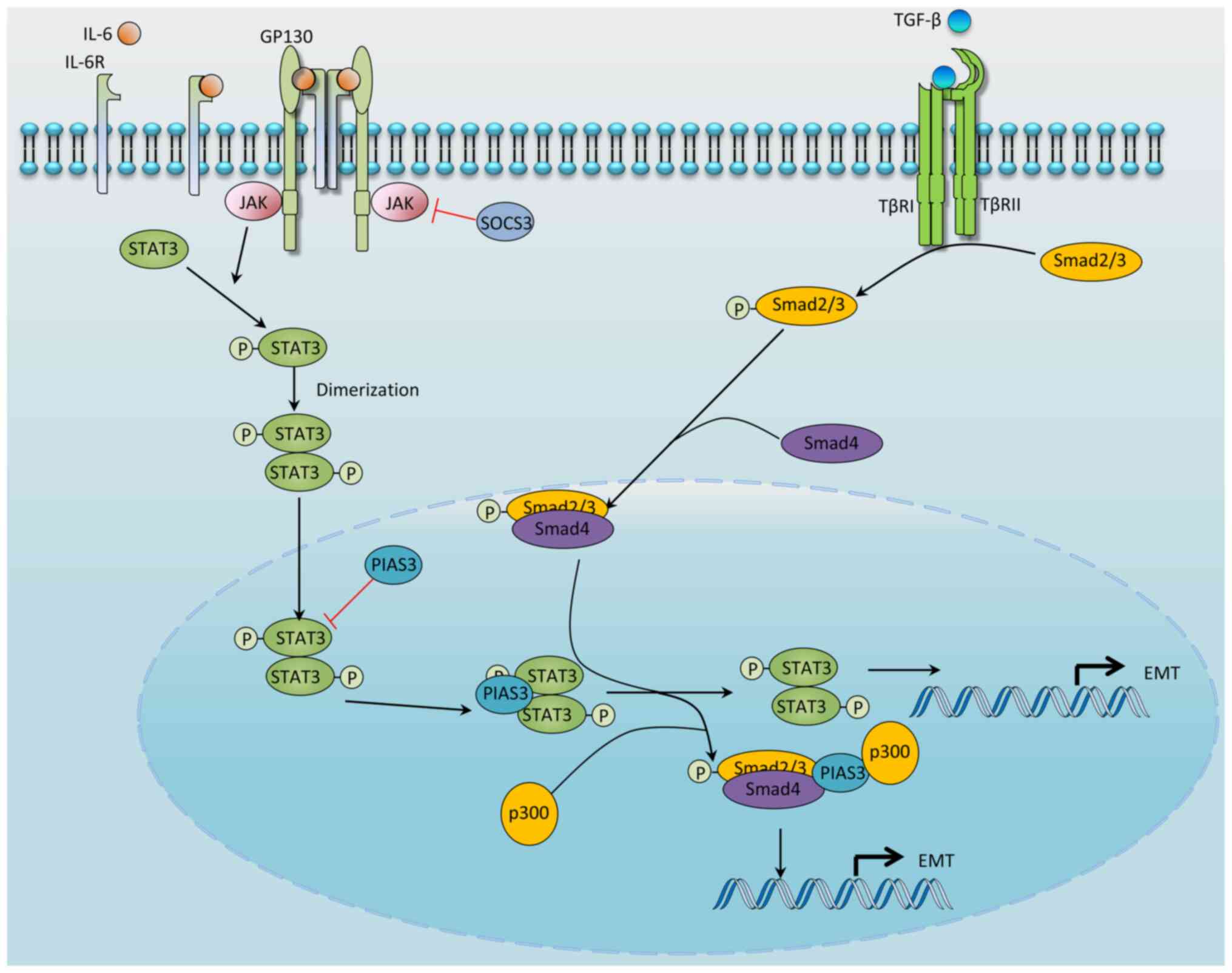
|
1
|
Philips RL, Wang Y, Cheon H, Kanno Y,
Gadina M, Sartorelli V, Horvath CM, Darnell JE Jr, Stark GR and
O'Shea JJ: The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to
do. Cell. 185:3857–3876. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson DE, O'Keefe RA and Grandis JR:
Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 15:234–248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huynh J, Chand A, Gough D and Ernst M:
Therapeutically exploiting STAT3 activity in cancer-using tissue
repair as a road map. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:82–96. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cimica V, Chen HC, Iyer JK and Reich NC:
Dynamics of the STAT3 transcription factor: Nuclear import
dependent on Ran and importin-β1. PLoS One. 6:e201882011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Garbers C, Aparicio-Siegmund S and
Rose-John S: The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: Recent advances
towards specific inhibition. Curr Opin Immunol. 34:75–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buchert M, Burns CJ and Ernst M: Targeting
JAK kinase in solid tumors: Emerging opportunities and challenges.
Oncogene. 35:939–951. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R and
Jove R: Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected
biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:736–746. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Diallo M and Herrera F: The role of
understudied post-translational modifications for the behavior and
function of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
FEBS J. 289:6235–6255. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Brabletz S, Schuhwerk H, Brabletz T and
Stemmler MP: Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO
J. 40:e1086472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hua W, Ten Dijke P, Kostidis S, Giera M
and Hornsveld M: TGFβ-induced metabolic reprogramming during
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
77:2103–2123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lai X, Li Q, Wu F, Lin J, Chen J, Zheng H
and Guo L: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metabolic
switching in cancer: Lessons from somatic cell reprogramming. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8:7602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Terry S, Savagner P, Ortiz-Cuaran S,
Mahjoubi L, Saintigny P, Thiery JP and Chouaib S: New insights into
the role of EMT in tumor immune escape. Mol Oncol. 11:824–846.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stemmler MP, Eccles RL, Brabletz S and
Brabletz T: Non-redundant functions of EMT transcription factors.
Nat Cell Biol. 21:102–112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo H, Zhuang K, Ding N, Hua R, Tang H, Wu
Y, Yuan Z, Li T and He S: High-fat diet induced cyclophilin B
enhances STAT3/lncRNA-PVT1 feedforward loop and promotes growth and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 13:8832022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akhmetkaliyev A, Alibrahim N, Shafiee D
and Tulchinsky E: EMT/MET plasticity in cancer and Go-or-Grow
decisions in quiescence: The two sides of the same coin? Mol
Cancer. 22:902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lambert AW and Weinberg RA: Linking EMT
programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev
Cancer. 21:325–338. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nieto MA, Huang RYJ, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng H and Kang Y: Multilayer control of
the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 33:1755–1763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RYJ and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vesuna F, van Diest P, Chen JH and Raman
V: Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene
expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
367:235–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, Wang HJ, Lan HY,
Yang WH, Huang CH, Kao SY, Tzeng CH, Tai SK, et al: Bmi1 is
essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:982–992. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shamir ER, Pappalardo E, Jorgens DM,
Coutinho K, Tsai WT, Aziz K, Auer M, Tran PT, Bader JS and Ewald
AJ: Twist1-induced dissemination preserves epithelial identity and
requires E-cadherin. J Cell Biol. 204:839–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F,
Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 induces
an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:2940–2947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rojas A, Liu G, Coleman I, Nelson PS,
Zhang M, Dash R, Fisher PB, Plymate SR and Wu JD: IL-6 promotes
prostate tumorigenesis and progression through autocrine
cross-activation of IGF-IR. Oncogene. 30:2345–2355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miao JW, Liu LJ and Huang J:
Interleukin-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in human
cervical carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 45:165–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shintani Y, Fujiwara A, Kimura T, Kawamura
T, Funaki S, Minami M and Okumura M: IL-6 secreted from
cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates chemoresistance in NSCLC by
increasing epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling. J Thorac
Oncol. 11:1482–1492. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baulida J, Diaz VM and Herreros AG:
Snail1: A transcriptional factor controlled at multiple levels. J
Clin Med. 8:7572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamashita S, Miyagi C, Fukada T, Kagara N,
Che YS and Hirano T: Zinc transporter LIVI controls
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in zebrafish gastrula organizer.
Nature. 429:298–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hogstrand C, Kille P, Ackland ML, Hiscox S
and Taylor KM: A mechanism for epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and anoikis resistance in breast cancer triggered by zinc channel
ZIP6 and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription
3). Biochem J. 455:229–237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang C, Yang G, Jiang T, Zhu G, Li H and
Qiu Z: The effects and mechanisms of blockage of STAT3 signaling
pathway on IL-6 inducing EMT in human pancreatic cancer cells in
vitro. Neoplasma. 58:396–405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–1867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peinado H, Quintanilla M and Cano A:
Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription
factor in epithelial cell lines: Mechanisms for epithelial
mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 278:21113–21123. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Saitoh M, Endo K, Furuya S, Minami M,
Fukasawa A, Imamura T and Miyazawa K: STAT3 integrates cooperative
Ras and TGF-β signals that induce Snail expression. Oncogene.
35:1049–1057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim M and Lim J, Yang Y, Lee M and Lim J:
N-myc downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2) suppresses the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells via
STAT3/Snail signaling. Cancer Lett. 354:33–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burton LJ, Smith BA, Smith BN, Loyd Q,
Nagappan P, McKeithen D, Wilder CL, Platt MO, Hudson T and
Odero-Marah VA: Muscadine grape skin extract can antagonize
Snail-cathepsin L-mediated invasion, migration and
osteoclastogenesis in prostate and breast cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1019–1027. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou JJ, Meng Z, He XY, Cheng D, Ye HL,
Deng XG and Chen RF: Hepatitis C virus core protein increases Snail
expression and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway in
hepatoma cells. Hepatol Res. 47:574–583. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu WH, Chen MT, Wang ML, Lee YY, Chiou
GY, Chien CS, Huang PI, Chen YW, Huang MC, Chiou SH, et al:
Cisplatin-selected resistance is associated with increased motility
and stem-like properties via activation of STAT3/Snail axis in
atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor cells. Oncotarget. 6:1750–1768.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liang H, Chen G, Li J and Yang F: Snail
expression contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma.
Am J Transl Res. 11:4277–4289. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dai X, Ahn KS, Wang LZ, Kim C,
Deivasigamni A, Arfuso F, Um JY, Kumar AP, Chang YC, Kumar D, et
al: Ascochlorin enhances the sensitivity of doxorubicin leading to
the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2966–2976. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xie Q, Zhu Z, He Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang
Y, Luo J, Peng T, Cheng F, Gao J, et al: A lactate-induced
Snail/STAT3 pathway drives GPR81 expression in lung cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1866:1655762020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kim E, Kim M, Woo DH, Shin Y, Shin J,
Chang N, Oh YT, Kim H, Rheey J, Nakano I, et al: Phosphorylation of
EZH2 activates STAT3 signaling via STAT3 methylation and promotes
tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Cell.
23:839–852. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao Y, Hu Z, Li J and Hu T: EZH2
exacerbates breast cancer by methylating and activating STAT3
directly. J Cancer. 12:5220–5230. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yuan K, Lei Y, Chen HN, Chen Y, Zhang T,
Li K, Xie N, Wang K, Feng X, Pu Q, et al: HBV-induced ROS
accumulation promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through Snail-mediated
epigenetic silencing of SOCS3. Cell Death Differ. 23:616–627. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim JY, Kim HJ, Jung CW, Lee TS, Kim EH
and Park MJ: CXCR4 uses STAT3-mediated slug expression to maintain
radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells: Emerges as a
potential prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. Cell Death Dis.
12:482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu S, Ye S and Lin X, Chen Y, Zhang Y,
Jing Z, Liu W, Chen W and Lin X and Lin X: Small hepatitis B virus
surface antigen promotes malignant progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma via endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced FGF19/JAK2/STAT3
signaling. Cancer Lett. 499:175–187. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chesnelong C, Hao X, Cseh O, Wang AY,
Luchman HA and Weiss S: SLUG directs the precursor state of human
brain tumor stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 11:16352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin JC, Tsai JT, Chao TY, Ma HI and Liu
WH: The STAT3/Slug axis enhances radiation-induced tumor invasion
and cancer stem-like properties in radioresistant glioblastoma.
Cancers (Basel). 10:5122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhou DD, Liu XF, Lu CW, Pant OP and Liu
XD: Long non-coding RNA PVT1: Emerging biomarker in digestive
system cancer. Cell Prolif. 50:e123982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dong L, Wang H, Gao Y, Wang S and Wang W:
Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes the proliferation, migration and
EMT process of ovarian cancer cells by regulating CTGF. Oncol Lett.
25:712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhao J, Wu J, Qin Y, Zhang W, Huang G and
Qin L: LncRNA PVT1 induces aggressive vasculogenic mimicry
formation through activating the STAT3/Slug axis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 43:863–876. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Barnes RM and Firulli AB: A twist of
insight-the role of Twist-family bHLH factors in development. Int J
Dev Biol. 53:909–924. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, Qin C and Xu J: Normal
and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying
molecular mechanisms. Cell Res. 22:90–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Ling X and Arlinghaus RB: Knockdown of
STAT3 expression by RNA interference inhibits the induction of
breast tumors in immunocompetent mice. Cancer Res. 65:2532–2536.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cheng GZ, Zhang WZ, Sun M, Wang Q, Coppola
D, Mansour M, Xu LM, Costanzo C, Cheng JQ and Wang LH: Twist is
transcriptionally induced by activation of STAT3 and mediates STAT3
oncogenic function. J Biol Chem. 283:14665–14673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, Cao X, Shih JY, Wei
Y, Abbruzzese JL, Hortobagyi GN and Hung MC: Epidermal growth
factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer
Res. 67:9066–9076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hsu KW, Hsieh RH, Huang KH, Fen-Yau Li A,
Chi CW, Wang TY, Tseng MJ, Wu KJ and Yeh TS: Activation of the
Notch1/STAT3/Twist signaling axis promotes gastric cancer
progression. Carcinogenesis. 33:1459–1467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim MS, Lee HS, Kim YJ, Lee DY, Kang SG
and Jin W: MEST induces Twist-1-mediated EMT through STAT3
activation in breast cancers. Cell Death Differ. 26:2594–2606.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang CH, Xu GL, Jia WD, Li JS, Ma JL, Ren
WH, Ge YS, Yu JH, Liu WB and Wang W: Activation of STAT3 signal
pathway correlates with twist and E-cadherin expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significance. J Surg
Res. 174:120–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cheng L, Zhou MY, Gu YJ, Chen L and Wang
Y: ZEB1: New advances in fibrosis and cancer. Mol Cell Biochem.
476:1643–1650. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Caramel J, Ligier M and Puisieux A:
Pleiotropic roles for ZEB1 in cancer. Cancer Res. 78:30–35. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lu R, Zhang YG and Sun J: STAT3 activation
in infection and infection-associated cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
451:80–87. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, Lin YW, Ren LL,
Wang YC, Su WY, Wang JL, Cui Y, Wang ZH and Fang JY: Roles of STAT3
and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human
colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:5819–5832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Avtanski DB, Nagalingam A, Bonner MY,
Arbiser JL, Saxena NK and Sharma D: Honokiol inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by
targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription
3/Zeb1/E-cadherin axis. Mol Oncol. 8:565–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu Z, Ma L, Sun Y, Yu W and Wang X:
Targeting STAT3 signaling overcomes gefitinib resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12:5612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Huang YH, Chen HK, Hsu YF, Chen HC, Chuang
CH, Huang SW and Hsu MJ: Src-FAK signaling mediates interleukin
6-induced HCT116 colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Int J Mol Sci. 24:66502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shi Q and Chen YG: Interplay between
TGF-beta signaling and receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor
development. Sci China Life Sci. 60:1133–1141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Derynck R and Budi EH: Specificity,
versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci Signal.
12:eaav51832019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Katsuno Y and Derynck R: Epithelial
plasticity, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and the TGF-β
family. Dev Cell. 56:726–746. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Itoh Y, Saitoh M and Miyazawa K:
Smad3-STAT3 crosstalk in pathophysiological contexts. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:82–90. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Sun CY, Nie J, Huang JP, Zheng GJ and Feng
B: Targeting STAT3 inhibition to reverse cisplatin resistance.
Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1091352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bowman T, Broome MA, Sinibaldi D, Wharton
W, Pledger WJ, Sedivy JM, Irby R, Yeatman T, Courtneidge SA and
Jove R: Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src
transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 98:7319–7324. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yu Y and Feng XH: TGF-β signaling in cell
fate control and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 61:56–63. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Horiguchi K, Shirakihara T, Nakano A,
Imamura T, Miyazono K and Saitoh M: Role of Ras signaling in the
induction of snail by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem.
284:245–253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Long J, Wang G, Matsuura I, He D and Liu
F: Activation of Smad transcriptional activity by protein inhibitor
of activated STAT3 (PIAS3). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:99–104.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
79
|
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S,
Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung
P, Zhang XH, et al: Dependency of colorectal cancer on a
TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation.
Cancer Cell. 22:571–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Abulaiti A, Shintani Y, Funaki S, Nakagiri
T, Inoue M, Sawabata N, Minami M and Okumura M: Interaction between
non-small-cell lung cancer cells and fibroblasts via enhancement of
TGF-β signaling by IL-6. Lung Cancer. 82:204–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu
Z, Zhao J and Zhang HT: JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 44:1643–1651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang B, Liu T, Wu JC, Luo SZ, Chen R, Lu
LG and Xu MY: STAT3 aggravates TGF-β1-induced hepatic
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration. Biomed
Pharmacother. 98:214–221. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Morris R, Butler L, Perkins A, Kershaw NJ
and Babon JJ: The Role of LNK (SH2B3) in the regulation of JAK-STAT
signalling in haematopoiesis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 15:242021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Ding LW, Sun QY, Lin DC, Chien W, Hattori
N, Dong XM, Gery S, Garg M, Doan NB, Said JW, et al: LNK (SH2B3):
Paradoxical effects in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 34:1463–1474.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Lv J, Yu W, Zhang Y, Cao X, Han L, Hu H
and Wang C: LNK promotes the growth and metastasis of triple
negative breast cancer via activating JAK/STAT3 and ERK1/2 pathway.
Cancer Cell Int. 20:1242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhong ZM, Chen X, Qi X, Wang XM, Li CY,
Qin RJ, Wang SQ, Liang J, Zeng MS and Sun CZ: Adaptor protein LNK
promotes anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell growth via 14-3-3 ε/γ
binding. Cancer Cell Int. 20:112020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Pan J, Peng R, Cheng N, Chen F and Gao B:
LNK protein: Low expression in human colorectal carcinoma and
relationship with tumor invasion. Biomed Pharmacother.
121:1094672020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Wang LN, Zhang ZT, Wang L, Wei HX, Zhang
T, Zhang LM, Lin H, Zhang H and Wang SQ: TGF-β1/SH2B3 axis
regulates anoikis resistance and EMT of lung cancer cells by
modulating JAK2/STAT3 and SHP2/Grb2 signaling pathways. Cell Death
Dis. 13:4722022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Dragomir MP, Knutsen E and Calin GA:
Classical and noncanonical functions of miRNAs in cancers. Trends
Genet. 38:379–394. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Bert AG and
Goodall GJ: MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Cycle. 7:3112–3118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hao J, Zhang Y, Deng M, Ye R, Zhao S, Wang
Y, Li J and Zhao Z: MicroRNA control of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer stem cells. Int J Cancer. 135:1019–1027. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang L, Liao Y and Tang L: MicroRNA-34
family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li WJ, Wang Y, Liu R, Kasinski AL, Shen H,
Slack FJ and Tang DG: MicroRNA-34a: Potent tumor suppressor, cancer
stem cell inhibitor, and potential anticancer therapeutic. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:6405872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Hünten S, Kaller
M, Menssen A, Götz U and Hermeking H: miR-34 and SNAIL form a
double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions. Cell Cycle. 10:4256–4271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Imani S, Wei C, Cheng J, Khan MA, Fu S,
Yang L, Tania M, Zhang X, Xiao X, Zhang X and Fu J: MicroRNA-34a
targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription
factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and
invasion. Oncotarget. 8:21362–21379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Huang G, Du MY, Zhu H, Zhang N, Lu ZW,
Qian LX, Zhang W, Tian X, He X and Yin L: MiRNA-34a reversed
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of
SMAD4 in NPC cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:217–224. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ma ZL, Hou PP, Li YL, Wang DT, Yuan TW,
Wei JL, Zhao BT, Lou JT, Zhao XT, Jin Y and Jin YX: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of non-small
cell lung cancer H1299 cell line by targeting TGFβR2. Tumour Biol.
36:2481–2490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Jiang L and Hermeking H: miR-34a and
miR-34b/c suppress intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
77:2746–2758. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Li B, Guo X, Li N, Chen Q, Shen J, Huang
X, Huang G and Wang F: WNT1, a target of miR-34a, promotes cervical
squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion by induction of
an E-P cadherin switch via the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 43:489–503. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hashimi ST, Fulcher JA, Chang MH, Gov L,
Wang S and Lee B: MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21
and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation
of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood. 114:404–414. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Si W, Li Y, Shao H, Hu R, Wang W, Zhang K
and Yang Q: MiR-34a inhibits breast cancer proliferation and
progression by targeting Wnt1 in Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Am J Med Sci. 352:191–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chen WY, Liu SY, Chang YS, Yin JJ, Yeh HL,
Mouhieddine TH, Hadadeh O, Abou-Kheir W and Liu YN: MicroRNA-34a
regulates WNT/TCF7 signaling and inhibits bone metastasis in
Ras-activated prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 6:441–457. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Wang X, Zhao Y, Lu Q, Fei X, Lu C, Li C
and Chen H: MiR-34a-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by targeting LEF1 and inactivation of the Hippo-YAP1/TAZ
signaling pathway. J Cancer. 11:3072–3081. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, Song B, Ma W, Lu Y,
Zhao L, Li J, Yang B and Li L: MicroRNA-34a suppresses the breast
cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1
pathway. Cancer Sci. 106:700–708. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Fan F, Zhuang J, Zhou P, Liu X and Luo Y:
MicroRNA-34a promotes mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis
in human lens epithelial cells by targeting Notch2. Oncotarget.
8:110209–110220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Kumarswamy R,
Scagliotti GV, Papotti M and Allgayer H: Regulation of Axl receptor
tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid
cancer. Oncogene. 30:2888–2899. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Marcucci F, Stassi G and De Maria R:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A new target in anticancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:311–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhang G, Wang M, Zhao H and Cui W:
Function of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:2726–2734. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Avtanski DB, Nagalingam A, Kuppusamy P,
Bonner MY, Arbiser JL, Saxena NK and Sharma D: Honokiol abrogates
leptin-induced tumor progression by inhibiting Wnt1-MTA1-β-catenin
signaling axis in a microRNA-34a dependent manner. Oncotarget.
6:16396–16410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Cavallari I, Ciccarese F, Sharova E, Urso
L, Raimondi V, Silic-Benussi M, D'Agostino DM and Ciminale V: The
miR-200 family of microRNAs: Fine tuners of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and circulating cancer biomarkers. Cancers (Basel).
13:58742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Peter ME: Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs:
Guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle.
8:843–852. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Feng X, Wang Z, Fillmore R and Xi Y:
MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett.
344:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
113
|
Georgakopoulos-Soares I, Chartoumpekis DV,
Kyriazopoulou V and Zaravinos A: EMT factors and metabolic pathways
in cancer. Front Oncol. 10:4992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N,
Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF and Goodall GJ: A double-negative
feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
68:7846–7854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer
O, Vincan E, Spaderna S and Brabletz T: A reciprocal repression
between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and
invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 9:582–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Guo L, Chen C, Shi M, Wang F, Chen X, Diao
D, Hu M, Yu M, Qian L and Guo N: Stat3-coordinated
Lin-28-let-7-HMGA2 and miR-200-ZEB1 circuits initiate and maintain
oncostatin M-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene.
32:5272–5282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wang Y, Guo W, Li Z, Wu Y, Jing C, Ren Y,
Zhao M, Kong L, Zhang C, Dong J, et al: Role of the EZH2/miR-200
axis in STAT3-mediated OSCC invasion. Int J Oncol. 52:1149–1164.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Pan YM, Wang CG, Zhu M, Xing R, Cui JT, Li
WM, Yu DD, Wang SB, Zhu W, Ye YJ, et al: STAT3 signaling drives
EZH2 transcriptional activation and mediates poor prognosis in
gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 15:792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Martínez-Fernández M, Dueñas M, Feber A,
Segovia C, García-Escudero R, Rubio C, López-Calderón FF,
Díaz-García C, Villacampa F, Duarte J, et al: A Polycomb-mir200
loop regulates clinical outcome in bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
6:42258–42275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Yang X, Chen Y and Chen L: The versatile
role of microRNA-30a in human cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem.
41:1616–1632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Zhang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Tu X, Zang Y, Zhu
J, Chen J, Dong L and Zhang J: miR-30 inhibits TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting
Snail1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:1100–1105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Wang Y, Wu C, Zhang C, Li Z, Zhu T, Chen
J, Ren Y, Wang X, Zhang L and Zhou X: TGF-β-induced STAT3
overexpression promotes human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
invasion and metastasis through malat1/miR-30a interactions. Cancer
Lett. 436:52–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Pfeffer SR, Yang CH and Pfeffer LM: The
role of miR-21 in cancer. Drug Dev Res. 76:270–277. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Singh A, Singh AK, Giri R, Kumar D, Sharma
R, Valis M, Kuca K and Garg N: The role of microRNA-21 in the onset
and progression of cancer. Future Med Chem. 13:1885–1906. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Yan LX, Liu YH, Xiang JW, Wu QN, Xu LB,
Luo XL, Zhu XL, Liu C, Xu FP, Luo DL, et al: PIK3R1 targeting by
miR-21 suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by reducing
PI3K/AKT signaling and reversing EMT, and predicts clinical outcome
of breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:471–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
129
|
Tang Y, Zhao Y, Ran J and Wang Y:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell metastasis in cervical cancer through
modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett.
19:3289–3295. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Su C, Cheng X, Li Y, Han Y, Song X, Yu D,
Cao X and Liu Z: MiR-21 improves invasion and migration of
drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell and transformation
of EMT through targeting HBP1. Cancer Med. 7:2485–2503. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Bian Z, Ji W, Xu B, Huo Z, Huang H, Huang
J, Jiao J, Shao J and Zhang X: Noncoding RNAs involved in the STAT3
pathway in glioma. Cancer Cell Int. 21:4452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Tse J, Pierce T, Carli ALE, Alorro MG,
Thiem S, Marcusson EG, Ernst M and Buchert M: Onco-miR-21 promotes
Stat3-dependent gastric cancer progression. Cancers (Basel).
14:2642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Yue X, Zhao Y, Zhang C, Li J, Liu Z, Liu J
and Hu W: Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes EMT through
STAT3-dependent miR-21 induction. Oncotarget. 7:3777–3790. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
134
|
Lu YF, Zhang L, Waye MM, Fu WM and Zhang
JF: MiR-218 mediates tumorigenesis and metastasis: Perspectives and
implications. Exp Cell Res. 334:173–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Li YJ, Zhang W, Xia H, Zhang BS, Chen P,
Zhao YL and Li J: miR-218 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting Robo1 and Ecop in lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Future Oncol. 13:2571–2582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Shi ZM, Wang L, Shen H, Jiang CF, Ge X, Li
DM, Wen YY, Sun HR, Pan MH, Li W, et al: Downregulation of miR-218
contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling.
Oncogene. 36:2577–2588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Jiang Z, Song Q, Zeng R, Li J, Li J, Lin
X, Chen X, Zhang J and Zheng Y: MicroRNA-218 inhibits EMT,
migration and invasion by targeting SFMBT1 and DCUN1D1 in cervical
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:45622–45636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zhang L, Li J, Wang Q, Meng G, Lv X, Zhou
H, Li W and Zhang J: The relationship between microRNAs and the
STAT3-related signaling pathway in cancer. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177198692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Li Z, Qian R, Zhang J and Shi X:
MiR-218-5p targets LHFPL3 to regulate proliferation, migration, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions of human glioma cells. Biosci
Rep. 39:BSR201808792019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Lun W, Wu X, Deng Q and Zhi F: MiR-218
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in
colorectal cancer via targeting CTGF. Cancer Cell Int. 18:832018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Wang G, Fu Y, Liu G, Ye Y and Zhang X:
miR-218 inhibits proliferation, migration, and EMT of gastric
cancer cells by targeting WASF3. Oncol Res. 25:355–364. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Mathew LK, Huangyang P, Mucaj V, Lee SS,
Skuli N, Eisinger-Mathason TS, Biju K, Li B, Venneti S, Lal P, et
al: Feedback circuitry between miR-218 repression and RTK
activation in glioblastoma. Sci Signal. 8:ra422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Mattick JS, Amaral PP, Carninci P,
Carpenter S, Chang HY, Chen LL, Chen R, Dean C, Dinger ME,
Fitzgerald KA, et al: Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions,
challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:430–447.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Shen D, Peng H, Xia C, Deng Z, Tong X,
Wang G and Qian K: The role of long non-coding RNAs in
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related signaling pathways in
prostate cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 9:9390702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Rahbar Farzam O, Najafi S, Amini M, Rahimi
Z, Dabbaghipour R, Zohdi O, Asemani Shahgoli G, Baradaran B and
Akbari B: Interplay of miRNAs and lncRNAs in STAT3 signaling
pathway in colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int.
24:162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Liu S, Li W, Liang L, Zhou Y and Li Y: The
regulatory relationship between transcription factor STAT3 and
noncoding RNA. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 29:42024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Orouei S,
Zarrin V, Rahmani Moghadam E, Zabolian A, Mohammadi S, Hushmandi K,
Gharehaghajlou Y, Makvandi P, et al: STAT3 pathway in gastric
cancer: Signaling, therapeutic targeting and future prospects.
Biology (Basel). 9:1262020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Knutsen E, Harris AL and Perander M:
Expression and functions of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and isoforms
in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 126:551–561. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
150
|
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Hanley SJB,
Kobayashi N, Todo Y and Watari H: Long Non-coding RNA NEAT1: A
novel target for diagnosis and therapy in human tumors. Front
Genet. 9:4712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Yang X, Qu S, Wang L, Zhang H, Yang Z,
Wang J, Dai B, Tao K, Shang R, Liu Z, et al: PTBP3 splicing factor
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by destroying the splicing
balance of NEAT1 and pre-miR-612. Oncogene. 37:6399–6413. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Wang H and Zheng G: LncRNA NEAT1 promotes
proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition process in TGF-β2-stimulated lens epithelial cells
through regulating the miR-486-5p/SMAD4 axis. Cancer Cell Int.
20:5292020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Chen Q, Cai J, Wang Q, Wang Y, Liu M, Yang
J, Zhou J, Kang C, Li M and Jiang C: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1,
regulated by the EGFR pathway, contributes to glioblastoma
progression through the WNT/β-catenin pathway by scaffolding EZH2.
Clin Cancer Res. 24:684–695. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Chen Y, Li J, Xiao JK, Xiao L, Xu BW and
Li C: The lncRNA NEAT1 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-483
to upregulate STAT3 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 21:902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Xu D, Ihira K,
Konno Y, Kobayashi N, Todo Y and Watari H: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1
drives aggressive endometrial cancer progression via
miR-361-regulated networks involving STAT3 and tumor
microenvironment-related genes. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Xia D, Yao R, Zhou P, Wang C, Xia Y and Xu
S: LncRNA NEAT1 reversed the hindering effects of miR-495-3p/STAT3
axis and miR-211/PI3K/AKT axis on sepsis-relevant inflammation. Mol
Immunol. 117:168–179. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Esmaeili M and Taheri M:
H19 lncRNA: Roles in tumorigenesis. Biomed Pharmacother.
123:1097742020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Hashemi M, Moosavi MS, Abed HM, Dehghani
M, Aalipour M, Heydari EA, Behroozaghdam M, Entezari M,
Salimimoghadam S, Gunduz ES, et al: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)
H19 in human cancer: From proliferation and metastasis to therapy.
Pharmacol Res. 184:1064182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Liu SJ, Dang HX, Lim DA, Feng FY and Maher
CA: Long noncoding RNAs in cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
21:446–460. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chen X, Li Y, Zuo C, Zhang K, Lei X, Wang
J, Yang Y, Zhang J, Ma K, Wang S, et al: Long non-coding RNA H19
regulates glioma cell growth and metastasis via miR-200a-mediated
CDK6 and ZEB1 expression. Front Oncol. 11:7576502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zhao Y, Feng C, Li Y, Ma Y and Cai R:
LncRNA H19 promotes lung cancer proliferation and metastasis by
inhibiting miR-200a function. Mol Cell Biochem. 460:1–8. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Luo M, Li Z, Wang W, Zeng Y, Liu Z and Qiu
J: Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by
associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer
Lett. 333:213–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Xu JX, Yang Y, Zhang X and Luan XP:
MicroRNA-29b promotes cell sensitivity to temozolomide by targeting
STAT3 in glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:1922–1931.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Fang JH, Zheng ZY, Liu JY, Xie C, Zhang ZJ
and Zhuang SM: Regulatory role of the MicroRNA-29b-IL-6 signaling
in the formation of vascular mimicry. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
8:90–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Liu L and Lu S: lncRNA H19 promotes
viability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung
adenocarcinoma cells by targeting miR-29b-3p and modifying STAT3.
Int J Oncol. 54:929–941. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Wang F, Rong L, Zhang Z, Li M, Ma L, Ma Y,
Xie X, Tian X and Yang Y: LncRNA H19-derived miR-675-3p promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in human pancreatic
cancer cells by targeting the STAT3 pathway. J Cancer.
11:4771–4782. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Sasaki N, Hirano K, Shichi Y, Gomi F,
Yoshimura H, Matsushita A, Toyoda M and Ishiwata T: Gp130-mediated
STAT3 activation contributes to the aggressiveness of pancreatic
cancer through H19 long non-coding RNA expression. Cancers (Basel).
14:20552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Wu J, Zhang J, Shen B, Yin K, Xu J, Gao W
and Zhang L: Long noncoding RNA lncTCF7, induced by IL-6/STAT3
transactivation, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:1162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Li J, Jiang ZZ, Li YY, Tang WT, Yin J and
Long XP: LncRNA CHRF promotes TGF-β1 induced EMT in alveolar
epithelial cells by inhibiting miR-146a up-regulating L1CAM
expression. Exp Lung Res. 47:198–209. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Tan WX, Sun G, Shangguan MY, Gui Z, Bao Y,
Li YF and Jia ZH: Novel role of lncRNA CHRF in cisplatin resistance
of ovarian cancer is mediated by miR-10b induced EMT and STAT3
signaling. Sci Rep. 10:147682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Gong H, Tao Y, Xiao S, Li X, Fang K, Wen
J, He P and Zeng M: LncRNA KIAA0087 suppresses the progression of
osteosarcoma by mediating the SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Exp Mol Med. 55:831–843. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Harsij A, Hussen BM,
Taheri M and Sharifi G: A review on the role of CASC11 in cancers.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:11311992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Huang H, Fan X, Zhang X, Xie Y and Ji Z:
LncRNA CARLo-7 facilitates proliferation, migration, invasion, and
EMT of bladder cancer cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin and
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. Transl Androl Urol. 9:2251–2261.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Han Y, Chen M, Wang A and Fan X:
STAT3-induced upregulation of lncRNA CASC11 promotes the cell
migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma by epigenetically silencing PTEN and
activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
508:472–479. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Cheng Z, Guo J, Chen L, Luo N, Yang W and
Qu X: A long noncoding RNA AB073614 promotes tumorigenesis and
predicts poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
6:25381–25389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Zeng S, Liu S, Feng J, Gao J and Xue F:
Upregulation of lncRNA AB073614 functions as a predictor of
epithelial ovarian cancer prognosis and promotes tumor growth in
vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biomark. 24:421–428. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Guo LY, Qin CF, Zou HX, Song MY, Gong ML
and Chen C: LncRNA AB073614 promotes the proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by repressing RBM5. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:2374–2379. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Hu L, Lv QL, Chen SH, Sun B, Qu Q, Cheng
L, Guo Y, Zhou HH and Fan L: Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA
AB073614 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with glioma. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 13:4332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Li J, Wang YM and Song YL: Knockdown of
long noncoding RNA AB073614 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and
migration via affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3997–4002. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wang Y, Kuang H, Xue J, Liao L, Yin F and
Zhou X: LncRNA AB073614 regulates proliferation and metastasis of
colorectal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 93:1230–1237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Xue J, Liao L, Yin F, Kuang H, Zhou X and
Wang Y: LncRNA AB073614 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of colorectal cancer cells via regulating the JAK/STAT3 pathway.
Cancer Biomark. 21:849–858. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Zhao F, Tan F, Tang L, Du Z, Chen X, Yang
Y, Zhou G and Yuan C: Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 and
DLGAP1-AS2: Two novel oncogenes in multiple cancers. Curr Med Chem.
30:2822–2834. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Lin Y, Jian Z, Jin H, Wei X, Zou X, Guan R
and Huang J: Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 facilitates
tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma via the feedback loop of
miR-26a/b-5p/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 11:342020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Zheng X, Hu H and Li S: High expression of
lncRNA PVT1 promotes invasion by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in esophageal cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:2357–2362. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Zhang X, Feng W, Zhang J, Ge L, Zhang Y,
Jiang X, Peng W, Wang D, Gong A and Xu M: Long non-coding RNA PVT1
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TGF-β/Smad
pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 40:1093–1102.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Wang L, Xiao B, Yu T, Gong L, Wang Y,
Zhang X, Zou Q and Zuo Q: lncRNA PVT1 promotes the migration of
gastric cancer by functioning as ceRNA of miR-30a and regulating
Snail. J Cell Physiol. 236:536–548. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Chang Z, Cui J and Song Y: Long noncoding
RNA PVT1 promotes EMT via mediating microRNA-186 targeting of
Twist1 in prostate cancer. Gene. 654:36–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Zhou Y, Xu S, Xia H, Gao Z, Huang R, Tang
E and Jiang X: Long noncoding RNA FEZF1-AS1 in human cancers. Clin
Chim Acta. 497:20–26. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Wang H, Wu Y, Wang Z, Chen Y, Mo J, Guan
W, Zhang Y and Yao H: The LncRNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes tumor
proliferation in colon cancer by regulating the mitochondrial
protein PCK2. Oncol Res. 29:201–215. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Zhang G, Yang W, Li D, Li X, Huang J,
Huang R and Luo J: lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes migration, invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinoblastoma cells by
targeting miR-1236-3p. Mol Med Rep. 22:3635–3644. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
He R, Zhang FH and Shen N: LncRNA
FEZF1-AS1 enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through
suppressing E-cadherin and regulating WNT pathway in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC). Biomed Pharmacother. 95:331–338. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Zhao X, Cheng Z and Wang J: Long noncoding
RNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in
ovarian cancer by activation of JAK-STAT3 pathway. Med Sci Monit.
24:8088–8095. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Bian Z, Zhang J, Li M, Feng Y, Wang X,
Zhang J, Yao S, Jin G, Du J, Han W, et al: LncRNA-FEZF1-AS1
promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by
regulating PKM2 signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4808–4819. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Wang YD, Sun XJ, Yin JJ, Yin M, Wang W,
Nie ZQ and Xu J: Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes cell
invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:134–141. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Shang BQ, Li ML, Quan HY, Hou PF, Li ZW,
Chu SF, Zheng JN and Bai J: Functional roles of circular RNAs
during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer.
18:1382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Wei X, Shi Y, Dai Z, Wang P, Meng X and
Yin B: Underlying metastasis mechanism and clinical application of
exosomal circular RNA in tumors (review). Int J Oncol. 58:289–297.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Sharma AR, Banerjee S, Bhattacharya M,
Saha A, Lee SS and Chakraborty C: Recent progress of circular RNAs
in different types of human cancer: Technological landscape,
clinical opportunities and challenges (review). Int J Oncol.
60:562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Liu CX and Chen LL: Circular RNAs:
Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell.
185:2016–2034. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Xue C, Li G, Zheng Q, Gu X, Bao Z, Lu J
and Li L: The functional roles of the circRNA/Wnt axis in cancer.
Mol Cancer. 21:1082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Long F, Lin Z, Li L, Ma M, Lu Z, Jing L,
Li X and Lin C: Comprehensive landscape and future perspectives of
circular RNAs in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 20:262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Kristensen LS, Jakobsen T, Hager H and
Kjems J: The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 19:188–206. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y and
Gu C: Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in
cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 19:910–928. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Chen S, Chen C, Hu Y, Song G and Shen X:
The diverse roles of circular RNAs in pancreatic cancer. Pharmacol
Ther. 226:1078692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Song J, Liu Q, Han L, Song T, Huang S,
Zhang X, He Q, Liang C, Zhu S and Xiong B:
Hsa_circ_0009092/miR-665/NLK signaling axis suppresses colorectal
cancer progression via recruiting TAMs in the tumor
microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:3192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Wu M, Sun T and Xing L: Circ_0004913
inhibits cell growth, metastasis, and glycolysis by absorbing
miR-184 to regulate HAMP in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 38:708–719. 2023.
|
|
206
|
Li G, Kong J, Dong S, Niu H, Wu S and Sun
W: Circular BANP knockdown inhibits the malignant progression of
residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency
ablation. Chin Med J (Engl). 135:1578–1587. 2022.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
He SL, Zhao X and Yi SJ: CircAHNAK
upregulates EIF2B5 expression to inhibit the progression of ovarian
cancer by modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 43:941–955. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y and
Fu X: Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer.
19:1452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Beebe JD, Liu JY and Zhang JT: Two decades
of research in discovery of anticancer drugs targeting STAT3, how
close are we? Pharmacol Ther. 191:74–91. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Turkson J, Ryan D, Kim JS, Zhang Y, Chen
Z, Haura E, Laudano A, Sebti S, Hamilton AD and Jove R:
Phosphotyrosyl peptides block Stat3-mediated DNA binding activity,
gene regulation, and cell transformation. J Biol Chem.
276:45443–45455. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Turkson J, Kim JS, Zhang S, Yuan J, Huang
M, Glenn M, Haura E, Sebti S, Hamilton AD and Jove R: Novel
peptidomimetic inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 dimerization and biological activity. Mol Cancer
Ther. 3:261–269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Auzenne EJ, Klostergaard J, Mandal PK,
Liao WS, Lu Z, Gao F, Bast RC Jr, Robertson FM and McMurray JS: A
phosphopeptide mimetic prodrug targeting the SH2 domain of Stat3
inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Exp Ther Oncol.
10:155–162. 2012.
|
|
213
|
Wong ALA, Hirpara JL, Pervaiz S, Eu JQ,
Sethi G and Goh BC: Do STAT3 inhibitors have potential in the
future for cancer therapy? Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 26:883–887.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Redell MS, Ruiz MJ, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB
and Tweardy DJ: Stat3 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia:
Ligand-dependent and -independent activation and induction of
apoptosis by a novel small-molecule Stat3 inhibitor. Blood.
117:5701–5709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Peng HY, Wang L, Das JK, Kumar A, Ballard
DJ, Ren Y, Xiong X, de Figueiredo P, Yang JM and Song J: Control of
CD4+ T cells to restrain inflammatory diseases via
eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:4152023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
216
|
Bharadwaj U, Eckols TK, Xu X, Kasembeli
MM, Chen Y, Adachi M, Song Y, Mo Q, Lai SY and Tweardy DJ:
Small-molecule inhibition of STAT3 in radioresistant head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:26307–26330. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Genini D, Brambilla L, Laurini E, Merulla
J, Civenni G, Pandit S, D'Antuono R, Perez L, Levy DE, Pricl S, et
al: Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by a SH2 domain-targeting
STAT3 inhibitor leads to metabolic synthetic lethality in cancer
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E4924–E4933. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Kim MJ, Nam HJ, Kim HP, Han SW, Im SA, Kim
TY, Oh DY and Bang YJ: OPB-31121, a novel small molecular
inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an
antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
335:145–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Hayakawa F, Sugimoto K, Harada Y,
Hashimoto N, Ohi N, Kurahashi S and Naoe T: A novel STAT inhibitor,
OPB-31121, has a significant antitumor effect on leukemia with
STAT-addictive oncokinases. Blood Cancer J. 3:e1662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Brambilla L, Genini D, Laurini E, Merulla
J, Perez L, Fermeglia M, Carbone GM, Pricl S and Catapano CV:
Hitting the right spot: Mechanism of action of OPB-31121, a novel
and potent inhibitor of the signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol Oncol. 9:1194–1206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Crooke ST, Baker BF, Crooke RM and Liang
XH: Antisense technology: An overview and prospectus. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 20:427–453. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Odate S, Veschi V, Yan S, Lam N, Woessner
R and Thiele CJ: Inhibition of STAT3 with the generation 2.5
antisense oligonucleotide, azd9150, decreases neuroblastoma
tumorigenicity and increases Chemosensitivity. Clin Cancer Res.
23:1771–1784. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
223
|
Reilley MJ, McCoon P, Cook C, Lyne P,
Kurzrock R, Kim Y, Woessner R, Younes A, Nemunaitis J, Fowler N, et
al: STAT3 antisense oligonucleotide AZD9150 in a subset of patients
with heavily pretreated lymphoma: Results of a phase 1b trial. J
Immunother Cancer. 6:1192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Roschewski M, Patel MR, Reagan PM, Saba
NS, Collins GP, Arkenau HT, de Vos S, Nuttall B, Acar M, Burke K,
et al: Phase I study of acalabrutinib plus danvatirsen (AZD9150) in
relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma including
circulating tumor DNA biomarker assessment. Clin Cancer Res.
29:3301–3312. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Cascone T, Kar G, Spicer JD,
García-Campelo R, Weder W, Daniel DB, Spigel DR, Hussein M,
Mazieres J, Oliveira J, et al: Neoadjuvant durvalumab alone or
combined with novel immuno-oncology agents in resectable lung
cancer: The phase II NeoCOAST platform trial. Cancer Discov.
13:2394–2411. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Shastri A, Choudhary G, Teixeira M,
Gordon-Mitchell S, Ramachandra N, Bernard L, Bhattacharyya S, Lopez
R, Pradhan K, Giricz O, et al: Antisense STAT3 inhibitor decreases
viability of myelodysplastic and leukemic stem cells. J Clin
Invest. 128:5479–5488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Proia TA, Singh M, Woessner R, Carnevalli
L, Bommakanti G, Magiera L, Srinivasan S, Grosskurth S, Collins M,
Womack C, et al: STAT3 antisense oligonucleotide remodels the
suppressive tumor microenvironment to enhance immune activation in
combination with anti-PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res. 26:6335–6349. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Leong PL, Andrews GA, Johnson DE, Dyer KF,
Xi S, Mai JC, Robbins PD, Gadiparthi S, Burke NA, Watkins SF and
Grandis JR: Targeted inhibition of Stat3 with a decoy
oligonucleotide abrogates head and neck cancer cell growth. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4138–4143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Xi S, Gooding WE and Grandis JR: In vivo
antitumor efficacy of STAT3 blockade using a transcription factor
decoy approach: Implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene.
24:970–979. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Zhang X, Zhang J, Wang L, Wei H and Tian
Z: Therapeutic effects of STAT3 decoy oligodeoxynucleotide on human
lung cancer in xenograft mice. BMC Cancer. 7:1492007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Sen M, Thomas SM, Kim S, Yeh JI, Ferris
RL, Johnson JT, Duvvuri U, Lee J, Sahu N, Joyce S, et al:
First-in-human trial of a STAT3 decoy oligonucleotide in head and
neck tumors: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Discov.
2:694–705. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Njatcha C, Farooqui M, Kornberg A, Johnson
DE, Grandis JR and Siegfried JM: STAT3 cyclic decoy demonstrates
robust antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer
Ther. 17:1917–1926. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Zhang Q, Hossain DMS, Duttagupta P,
Moreira D, Zhao X, Won H, Buettner R, Nechaev S, Majka M, Zhang B,
et al: Serum-resistant CpG-STAT3 decoy for targeting survival and
immune checkpoint signaling in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
127:1687–1700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Pettersson M and Crews CM: PROteolysis
targeting chimeras (PROTACs)-past, present and future. Drug Discov
Today Technol. 31:15–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Békés M, Langley DR and Crews CM: PROTAC
targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 21:181–200. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Bai L, Zhou H, Xu R, Zhao Y, Chinnaswamy
K, McEachern D, Chen J, Yang CY, Liu Z, Wang M, et al: A potent and
selective small-molecule degrader of STAT3 achieves complete tumor
regression in vivo. Cancer Cell. 36:498–511.e17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
237
|
Jin J, Wu Y, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Zhou YD, Liu S,
Sun Q, Yang G, Lin J, Nagle DG, et al: Small-molecule PROTAC
mediates targeted protein degradation to treat STAT3-dependent
epithelial cancer. JCI Insight. 7:e1606062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Shih PC, Naganuma M, Tsuji G, Demizu Y and
Naito M: Development of decoy oligonucleotide-warheaded chimeric
molecules targeting STAT3. Bioorg Med Chem. 95:1175072023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
He X, Weng Z and Zou Y: Progress in the
controllability technology of PROTAC. Eur J Med Chem.
265:1160962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto
T: Targeting interleukin-6 signaling in clinic. Immunity.
50:1007–1023. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Shen P, Wang Y, Jia X, Xu P, Qin L, Feng
X, Li Z and Qiu Z: Dual-target Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors:
Comprehensive review on the JAK-based strategies for treating solid
or hematological malignancies and immune-related diseases. Eur J
Med Chem. 239:1145512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Liang D, Wang Q, Zhang W, Tang H, Song C,
Yan Z, Liang Y and Wang H: JAK/STAT in leukemia: A clinical update.
Mol Cancer. 23:252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Plimack ER, Lorusso PM, McCoon P, Tang W,
Krebs AD, Curt G and Eckhardt SG: AZD1480: A phase I study of a
novel JAK2 inhibitor in solid tumors. Oncologist. 18:819–820. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Deisseroth A, Ko CW, Nie L, Zirkelbach JF,
Zhao L, Bullock J, Mehrotra N, Del Valle P, Saber H, Sheth C, et
al: FDA approval: Siltuximab for the treatment of patients with
multicentric Castleman disease. Clin Cancer Res. 21:950–954. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Rossi JF, Lu ZY, Jourdan M and Klein B:
Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target. Clin Cancer Res.
21:1248–1257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Dorff TB, Goldman B, Pinski JK, Mack PC,
Lara PN Jr, Van Veldhuizen PJ Jr, Quinn DI, Vogelzang NJ, Thompson
IM Jr and Hussain MH; Clinical and correlative results of SWOG
S0354: A phase II trial of CNTO328 (siltuximab), a monoclonal
antibody against interleukin-6, in chemotherapy-pretreated patients
with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:3028–3034. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Angevin E, Tabernero J, Elez E, Cohen SJ,
Bahleda R, van Laethem JL, Ottensmeier C, Lopez-Martin JA, Clive S,
Joly F, et al: A phase I/II, multiple-dose, dose-escalation study
of siltuximab, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, in
patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2192–2204.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Fizazi K, De Bono JS, Flechon A,
Heidenreich A, Voog E, Davis NB, Qi M, Bandekar R, Vermeulen JT,
Cornfeld M and Hudes GR: Randomised phase II study of siltuximab
(CNTO 328), an anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody, in combination with
mitoxantrone/prednisone versus mitoxantrone/prednisone alone in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer.
48:85–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
249
|
Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M,
Kang YK, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S and Hong DS: Phase
I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice
weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
35:180–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
250
|
Liu S, Wang L, Li Y, Cui Y, Wang Y and Liu
C: Long non-coding RNA CHRF promotes proliferation and mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in prostate cancer cell line PC3 requiring
up-regulating microRNA-10b. Biol Chem. 400:1035–1045. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Li Y and Xu X: The long noncoding RNA
cardiac hypertrophy-related factor plays oncogenic roles in
hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating microRNA-211. J Cell
Biochem. 120:13361–13371. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Tao Y, Han T, Zhang T, Ma C and Sun C:
LncRNA CHRF-induced miR-489 loss promotes metastasis of colorectal
cancer via TWIST1/EMT signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 8:36410–36422.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Gong J, Wang Y and Shu C: LncRNA CHRF
promotes cell invasion and migration via EMT in gastric cancer. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:1168–1176. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|