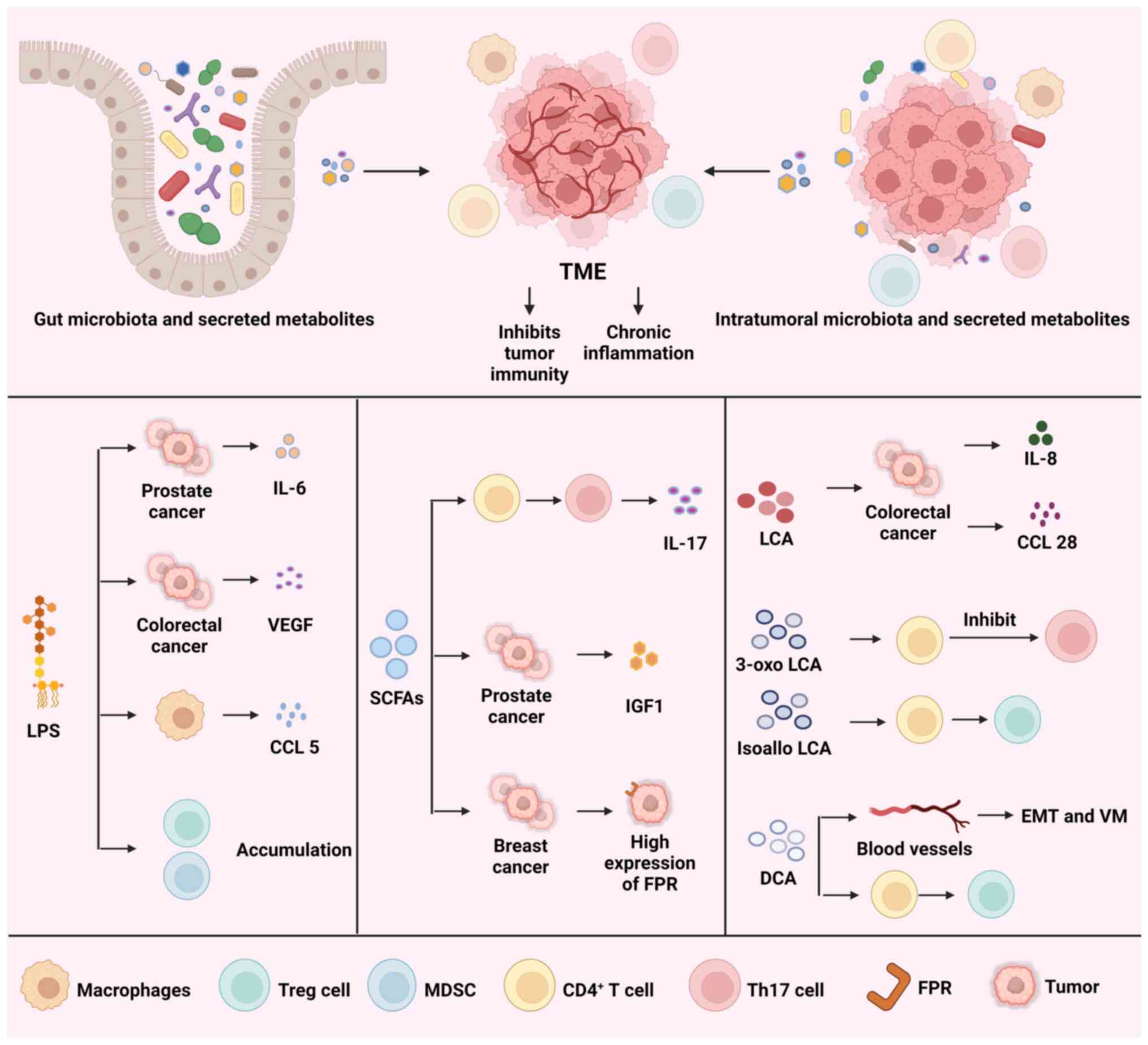
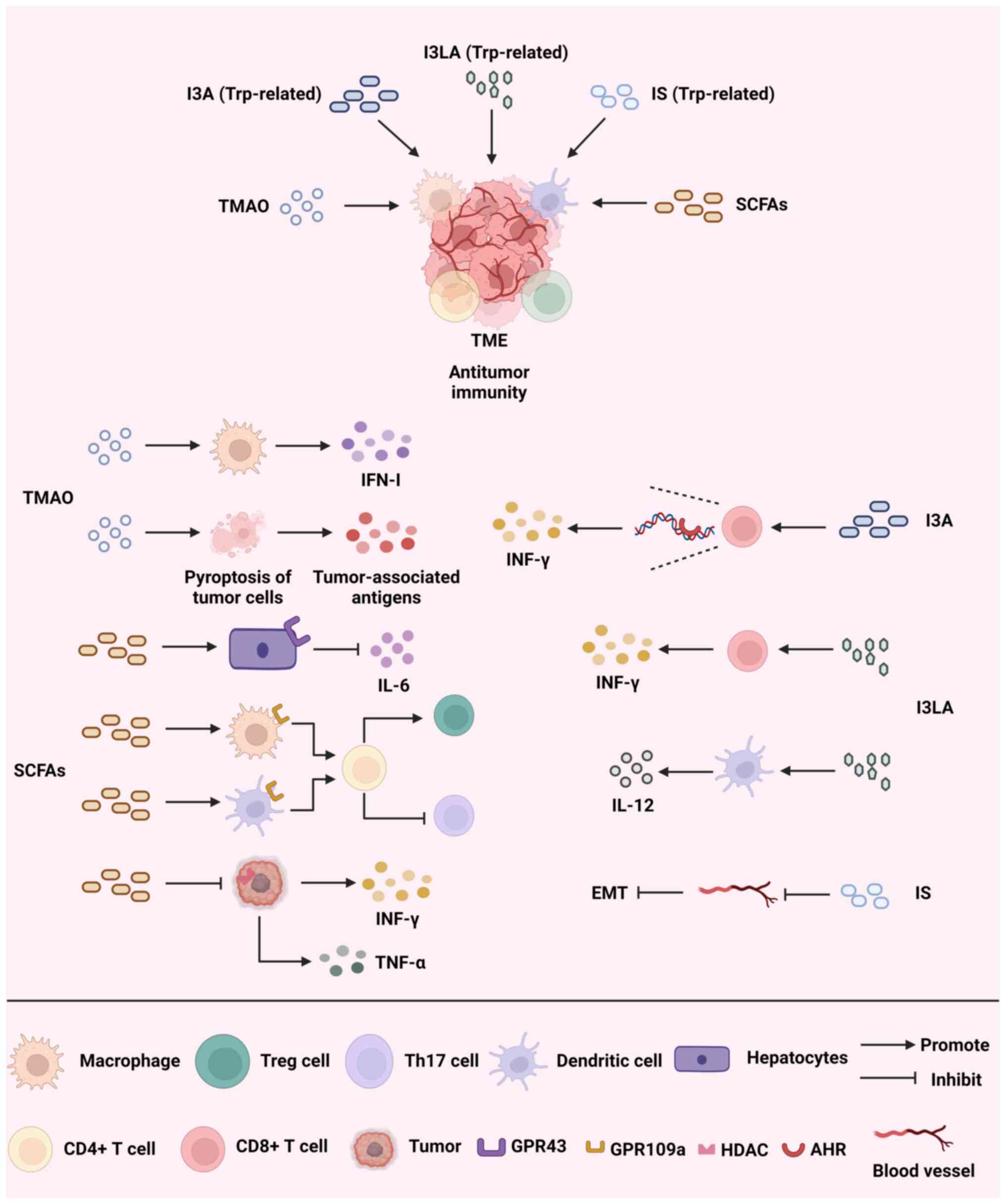
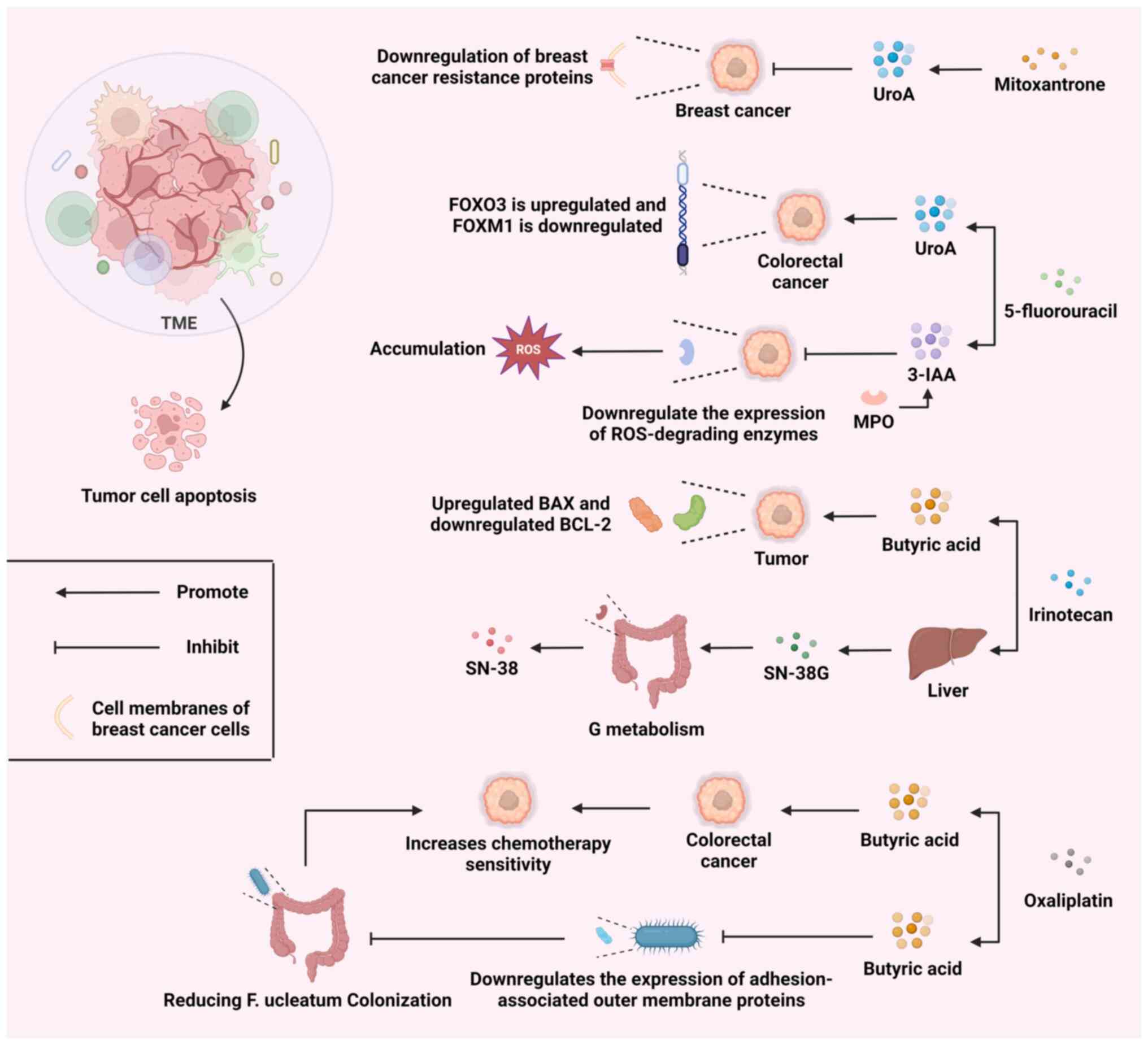
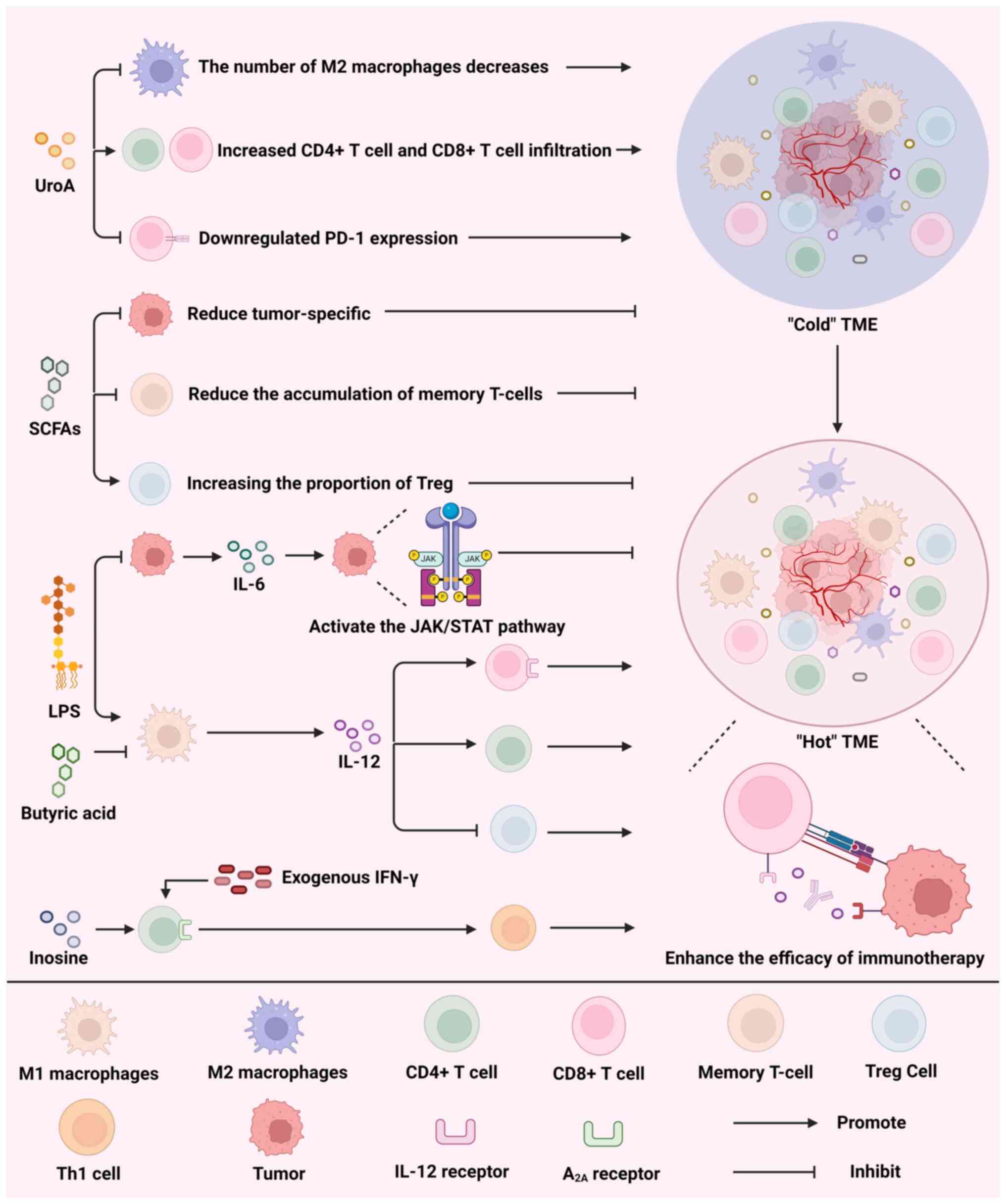
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Damelin M, Bankovich A, Bernstein J, Lucas
J, Chen L, Williams S, Park A, Aguilar J, Ernstoff E, Charati M, et
al: A PTK7-targeted antibody-drug conjugate reduces
tumor-initiating cells and induces sustained tumor regressions. Sci
Transl Med. 9:eaag26112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamada T, Togashi Y, Tay C, Ha D, Sasaki
A, Nakamura Y, Sato E, Fukuoka S, Tada Y, Tanaka A, et al: PD-1+
regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote
hyperprogression of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:9999–10008.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Srivastava S, Furlan SN, Jaeger-Ruckstuhl
CA, Sarvothama M, Berger C, Smythe KS, Garrison SM, Specht JM, Lee
SM, Amezquita RA, et al: Immunogenic chemotherapy enhances
recruitment of CAR-T cells to lung tumors and improves antitumor
efficacy when combined with checkpoint blockade. Cancer Cell.
39:193–208.e10. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhao Y, Li ZX, Zhu YJ, Fu J, Zhao XF,
Zhang YN, Wang S, Wu JM, Wang KT, Wu R, et al: Single-Cell
transcriptome analysis uncovers intratumoral heterogeneity and
underlying mechanisms for drug resistance in hepatobiliary tumor
organoids. Adv Sci (Weinh). 8:e20038972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He X, Smith SE, Chen S, Li H, Wu D,
Meneses-Giles PI, Wang Y, Hembree M, Yi K, Zhao X, et al:
Tumor-initiating stem cell shapes its microenvironment into an
immunosuppressive barrier and pro-tumorigenic niche. Cell Rep.
36:1096742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lam KC, Araya RE, Huang A, Chen Q, Di
Modica M, Rodrigues RR, Lopès A, Johnson SB, Schwarz B, Bohrnsen E,
et al: Microbiota triggers STING-type I IFN-dependent monocyte
reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
184:5338–5356.e21. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Routy B, Lenehan JG, Miller WH Jr, Jamal
R, Messaoudene M, Daisley BA, Hes C, Al KF, Martinez-Gili L,
Punčochář M, et al: Fecal microbiota transplantation plus anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in advanced melanoma: A phase I trial. Nat Med.
29:2121–2132. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schneider KM, Mohs A, Gui W, Galvez EJC,
Candels LS, Hoenicke L, Muthukumarasamy U, Holland CH, Elfers C,
Kilic K, et al: Imbalanced gut microbiota fuels hepatocellular
carcinoma development by shaping the hepatic inflammatory
microenvironment. Nat Commun. 13:39642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng R, Liu S, You W, Huang Y, Hu C, Gao
Y, Jia X, Li G, Xu Z and Chen Y: Gastric microbiome alterations are
associated with decreased CD8+ Tissue-Resident Memory T cells in
the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Res.
10:1224–1240. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu Y, Shi T, Lu X, Xu Z, Qu J, Zhang Z,
Shi G, Shen S, Hou Y, Chen Y and Wang T: Fungal-induced glycolysis
in macrophages promotes colon cancer by enhancing innate lymphoid
cell secretion of IL-22. EMBO J. 40:e1053202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Protopsaltis NJ, Liang W, Nudleman E and
Ferrara N: Interleukin-22 promotes tumor angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis. 22:311–323. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Briukhovetska D, Suarez-Gosalvez J, Voigt
C, Markota A, Giannou AD, Schübel M, Jobst J, Zhang T, Dörr J,
Märkl F, et al: T cell-derived interleukin-22 drives the expression
of CD155 by cancer cells to suppress NK cell function and promote
metastasis. Immunity. 56:143–161.e11. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Song X, Wei W, Zhong H, Dai J, Lan
Z, Li F, Yu X, Feng Q, Wang Z, et al: The microbiota continuum
along the female reproductive tract and its relation to
uterine-related diseases. Nat Commun. 8:8752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flemer B, Warren RD, Barrett MP, Cisek K,
Das A, Jeffery IB, Hurley E, O'Riordain M, Shanahan F and O'Toole
PW: The oral microbiota in colorectal cancer is distinctive and
predictive. Gut. 67:1454–1463. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Soto-Pantoja DR, Gaber M, Arnone AA,
Bronson SM, Cruz-Diaz N, Wilson AS, Clear KYJ, Ramirez MU, Kucera
GL, Levine EA, et al: Diet alters entero-mammary signaling to
regulate the breast microbiome and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
81:3890–3904. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Dwyer DN, Ashley SL, Gurczynski SJ, Xia
M, Wilke C, Falkowski NR, Norman KC, Arnold KB, Huffnagle GB,
Salisbury ML, et al: Lung microbiota contribute to pulmonary
inflammation and disease progression in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 199:1127–1138. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sipos A, Ujlaki G, Mikó E, Maka E, Szabó
J, Uray K, Krasznai Z and Bai P: The role of the microbiome in
ovarian cancer: Mechanistic insights into oncobiosis and to
bacterial metabolite signaling. Mol Med. 27:332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma C, Han M, Heinrich B, Fu Q, Zhang Q,
Sandhu M, Agdashian D, Terabe M, Berzofsky JA, Fako V, et al: Gut
microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via
NKT cells. Science. 360:eaan59312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Imai S, Ooki T, Murata-Kamiya N, Komura D,
Tahmina K, Wu W, Takahashi-Kanemitsu A, Knight CT, Kunita A, Suzuki
N, et al: Helicobacter pylori CagA elicits BRCAness to induce
genome instability that may underlie bacterial gastric
carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 29:941–958.e10. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bell HN, Rebernick RJ, Goyert J, Singhal
R, Kuljanin M, Kerk SA, Huang W, Das NK, Andren A, Solanki S, et
al: Reuterin in the healthy gut microbiome suppresses colorectal
cancer growth through altering redox balance. Cancer Cell.
40:185–200.e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Zhu X, Li K, Liu G, Wu R, Zhang Y, Wang S,
Xu M, Lu L and Li P: Microbial metabolite butyrate promotes
anti-PD-1 antitumor efficacy by modulating T cell receptor
signaling of cytotoxic CD8 T cell. Gut Microbes. 15:22491432023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang SS, Xie YL, Xiao XY, Kang ZR, Lin
XL, Zhang L, Li CS, Qian Y, Xu PP, Leng XX, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum-derived succinic acid induces tumor resistance to
immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Cell Host Microbe.
31:781–797.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Behary J, Amorim N, Jiang XT, Raposo A,
Gong L, McGovern E, Ibrahim R, Chu F, Stephens C, Jebeili H, et al:
Gut microbiota impact on the peripheral immune response in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Nat Commun. 12:1872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Høgh RI, Møller SH, Jepsen SD, Mellergaard
M, Lund A, Pejtersen M, Fitzner E, Andresen L and Skov S:
Metabolism of short-chain fatty acid propionate induces surface
expression of NKG2D ligands on cancer cells. FASEB J.
34:15531–15546. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun K, Xu R, Ma F, Yang N, Li Y, Sun X,
Jin P, Kang W, Jia L, Xiong J, et al: scRNA-seq of gastric tumor
shows complex intercellular interaction with an alternative T cell
exhaustion trajectory. Nat Commun. 13:49432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leader AM, Grout JA, Maier BB, Nabet BY,
Park MD, Tabachnikova A, Chang C, Walker L, Lansky A, Le Berichel
J, et al: Single-cell analysis of human non-small cell lung cancer
lesions refines tumor classification and patient stratification.
Cancer Cell. 39:1594–1609.e12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Lee HY, Zhao X, Han J, Su Y, Sun
Q, Shao J, Ge J, Zhao Y, Bai X, et al: Interleukin-17D regulates
group 3 innate lymphoid cell function through its receptor CD93.
Immunity. 54:673–686.e4. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu L, Jin Y, Zhao X, Tang K, Zhao Y, Tong
L, Yu X, Xiong K, Luo C, Zhu J, et al: Tumor aerobic glycolysis
confers immune evasion through modulating sensitivity to T
cell-mediated bystander killing via TNF-α. Cell Metab.
35:1580–1596.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Brown TP and Ganapathy V: Lactate/GPR81
signaling and proton motive force in cancer: Role in angiogenesis,
immune escape, nutrition, and Warburg phenomenon. Pharmacol Ther.
206:1074512020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tang T, Huang X, Lu M, Zhang G, Han X and
Liang T: Transcriptional control of pancreatic cancer
immunosuppression by metabolic enzyme CD73 in a tumor-autonomous
and -autocrine manner. Nat Commun. 14:33642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bell HN, Huber AK, Singhal R, Korimerla N,
Rebernick RJ, Kumar R, El-Derany MO, Sajjakulnukit P, Das NK, Kerk
SA, et al: Microenvironmental ammonia enhances T cell exhaustion in
colorectal cancer. Cell Metab. 35:134–149.e6. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Shi Q, Wang J, Zhou M, Zheng R, Zhang X
and Liu B: Gut Lactobacillus contribute to the progression of
breast cancer by affecting the antitumor activities of immune cells
in the TME of tumor-bearing mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 124(Pt B):
1110392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nejman D, Livyatan I, Fuks G, Gavert N,
Zwang Y, Geller LT, Rotter-Maskowitz A, Weiser R, Mallel G, Gigi E,
et al: The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor
type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science. 368:973–980. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song W, Tiruthani K, Wang Y, Shen L, Hu M,
Dorosheva O, Qiu K, Kinghorn KA, Liu R and Huang L: Trapping of
lipopolysaccharide to promote immunotherapy against colorectal
cancer and attenuate liver metastasis. Adv Mater. 30:e18050072018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu CH, Chen Z, Chen K, Liao FT, Chung CE,
Liu X, Lin YC, Keohavong P, Leikauf GD and Di YP:
Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated chronic inflammation promotes tobacco
carcinogen-induced lung cancer and determines the efficacy of
immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 81:144–157. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Zhong W, Wu K, Long Z, Zhou X, Zhong C,
Wang S, Lai H, Guo Y, Lv D, Lu J and Mao X: Gut dysbiosis promotes
prostate cancer progression and docetaxel resistance via activating
NF-κB-IL6-STAT3 axis. Microbiome. 10:942022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhu G, Huang Q, Huang Y, Zheng W, Hua J,
Yang S, Zhuang J, Wang J and Ye J: Lipopolysaccharide increases the
release of VEGF-C that enhances cell motility and promotes
lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis through the
TLR4-NF-κB/JNK pathways in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
7:73711–73724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu C, Yao Z, Wang J, Zhang W, Yang Y,
Zhang Y, Qu X, Zhu Y, Zou J, Peng S, et al: Macrophage-derived CCL5
facilitates immune escape of colorectal cancer cells via the
p65/STAT3-CSN5-PD-L1 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 27:1765–1781.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Medhat A and
Spector I: Short-chain fatty acids in cancer pathogenesis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 42:677–698. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brennan CA, Clay SL, Lavoie SL, Bae S,
Lang JK, Fonseca-Pereira D, Rosinski KG, Ou N, Glickman JN and
Garrett WS: Fusobacterium nucleatum drives a pro-inflammatory
intestinal microenvironment through metabolite receptor-dependent
modulation of IL-17 expression. Gut Microbes. 13:19877802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matsushita M, Fujita K, Hayashi T, Kayama
H, Motooka D, Hase H, Jingushi K, Yamamichi G, Yumiba S, Tomiyama
E, et al: Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote
prostate cancer growth via IGF1 signaling. Cancer Res.
81:4014–4026. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meiser J, Schuster A, Pietzke M, Vande
Voorde J, Athineos D, Oizel K, Burgos-Barragan G, Wit N, Dhayade S,
Morton JP, et al: Increased formate overflow is a hallmark of
oxidative cancer. Nat Commun. 9:13682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hennequart M, Pilley SE, Labuschagne CF,
Coomes J, Mervant L, Driscoll PC, Legrave NM, Lee Y, Kreuzaler P,
Macintyre B, et al: ALDH1L2 regulation of formate,
formyl-methionine, and ROS controls cancer cell migration and
metastasis. Cell Rep. 42:1125622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ternes D, Tsenkova M, Pozdeev VI, Meyers
M, Koncina E, Atatri S, Schmitz M, Karta J, Schmoetten M, Heinken
A, et al: The gut microbial metabolite formate exacerbates
colorectal cancer progression. Nat Metab. 4:458–475. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim M, Vogtmann E, Ahlquist DA, Devens ME,
Kisiel JB, Taylor WR, White BA, Hale VL, Sung J, Chia N, et al:
Fecal metabolomic signatures in colorectal adenoma patients are
associated with gut microbiota and early events of colorectal
cancer pathogenesis. mBio. 11:e03186–19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Petrick JL, Florio AA, Koshiol J, Pfeiffer
RM, Yang B, Yu K, Chen CJ, Yang HI, Lee MH and McGlynn KA:
Prediagnostic concentrations of circulating bile acids and
hepatocellular carcinoma risk: REVEAL-HBV and HCV studies. Int J
Cancer. 147:2743–2753. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Funabashi M, Grove TL, Wang M, Varma Y,
McFadden ME, Brown LC, Guo C, Higginbottom S, Almo SC and Fischbach
MA: A metabolic pathway for bile acid dehydroxylation by the gut
microbiome. Nature. 582:566–570. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun L, Zhang Y, Cai J, Rimal B, Rocha ER,
Coleman JP, Zhang C, Nichols RG, Luo Y, Kim B, et al: Bile salt
hydrolase in non-enterotoxigenic Bacteroides potentiates colorectal
cancer. Nat Commun. 14:7552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Song X, An Y, Chen D, Zhang W, Wu X, Li C,
Wang S, Dong W, Wang B, Liu T, et al: Microbial metabolite
deoxycholic acid promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation in
intestinal carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 113:459–477. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Nguyen TT, Lian S, Ung TT, Xia Y, Han JY
and Jung YD: Lithocholic acid stimulates IL-8 expression in human
colorectal cancer cells via activation of Erk1/2 MAPK and
suppression of STAT3 activity. J Cell Biochem. 118:2958–2967. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee YS, Choi I, Ning Y, Kim NY,
Khatchadourian V, Yang D, Chung HK, Choi D, LaBonte MJ, Ladner RD,
et al: Interleukin-8 and its receptor CXCR2 in the tumour
microenvironment promote colon cancer growth, progression and
metastasis. Br J Cancer. 106:1833–1841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fang ZZ, Zhang D, Cao YF, Xie C, Lu D, Sun
DX, Tanaka N, Jiang C, Chen Q, Chen Y, et al: Irinotecan
(CPT-11)-induced elevation of bile acids potentiates suppression of
IL-10 expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 291:21–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Liu Q, Yang C, Wang S, Shi D, Wei C, Song
J, Lin X, Dou R, Bai J, Xiang Z, et al: Wnt5a-induced M2
polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via IL-10 promotes
colorectal cancer progression. Cell Commun Signal. 18:512020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hang S, Paik D, Yao L, Kim E, Trinath J,
Lu J, Ha S, Nelson BN, Kelly SP, Wu L, et al: Bile acid metabolites
control TH17 and Treg cell differentiation. Nature. 576:143–148.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang N, Yang J, Han W, Han M, Liu X, Jiang
L, Cao H, Jing M, Sun T and Xu J: Identifying distinctive tissue
and fecal microbial signatures and the tumor-promoting effects of
deoxycholic acid on breast cancer. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
12:10299052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Riquelme E, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Montiel M,
Zoltan M, Dong W, Quesada P, Sahin I, Chandra V, San Lucas A, et
al: Tumor microbiome diversity and composition influence pancreatic
cancer outcomes. Cell. 178:795–806.e12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L,
Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, Prieto PA, Vicente D, Hoffman
K, Wei SC, et al: Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 359:97–103. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Huang J, Zheng X, Kang W, Hao H, Mao Y,
Zhang H, Chen Y, Tan Y, He Y, Zhao W and Yin Y: Metagenomic and
metabolomic analyses reveal synergistic effects of fecal microbiota
transplantation and anti-PD-1 therapy on treating colorectal
cancer. Front Immunol. 13:8749222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Davar D, Dzutsev AK, McCulloch JA,
Rodrigues RR, Chauvin JM, Morrison RM, Deblasio RN, Menna C, Ding
Q, Pagliano O, et al: Fecal microbiota transplant overcomes
resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. Science.
371:595–602. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Joachim L, Göttert S, Sax A, Steiger K,
Neuhaus K, Heinrich P, Fan K, Orberg ET, Kleigrewe K, Ruland J, et
al: The microbial metabolite desaminotyrosine enhances T-cell
priming and cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
EBioMedicine. 97:1048342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Green BL, Myojin Y, Ma C, Ruf B, Ma L,
Zhang Q, Rosato U, Qi J, Revsine M, Wabitsch S and Bauer K:
Immunosuppressive CD29+ Treg accumulation in the liver in mice on
checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Gut. 73:509–520. 2024.
|
|
63
|
Klement JD, Paschall AV, Redd PS, Ibrahim
ML, Lu C, Yang D, Celis E, Abrams SI, Ozato K and Liu K: An
osteopontin/CD44 immune checkpoint controls CD8+ T cell activation
and tumor immune evasion. J Clin Invest. 128:5549–5560. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Thomas MS and Fernandez ML: Trimethylamine
N-Oxide (TMAO), diet and cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler
Rep. 23:122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wu Y, Rong X, Pan M, Wang T, Yang H, Chen
X, Xiao Z and Zhao C: Integrated analysis reveals the gut microbial
metabolite TMAO promotes inflammatory hepatocellular carcinoma by
upregulating POSTN. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8401712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mirji G, Worth A, Bhat SA, El Sayed M,
Kannan T, Goldman AR, Tang HY, Liu Q, Auslander N, Dang CV, et al:
The microbiome-derived metabolite TMAO drives immune activation and
boosts responses to immune checkpoint blockade in pancreatic
cancer. Sci Immunol. 7:eabn07042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jalandra R, Dalal N, Yadav AK, Verma D,
Sharma M, Singh R, Khosla A, Kumar A and Solanki PR: Emerging role
of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) in colorectal cancer. Appl
Microbiol Biotechnol. 105:7651–7660. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Luo Z, Yu X, Wang C, Zhao H, Wang X and
Guan X: Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes oxidative stress and lipid
accumulation in macrophage foam cells via the Nrf2/ABCA1 pathway. J
Physiol Biochem. 80:67–79. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Baldominos P, Barbera-Mourelle A, Barreiro
O, Huang Y, Wight A, Cho JW, Zhao X, Estivill G, Adam I, Sanchez X,
et al: Quiescent cancer cells resist T cell attack by forming an
immunosuppressive niche. Cell. 185:1694–1708.e19. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Wang H, Rong X, Zhao G, Zhou Y, Xiao Y, Ma
D, Jin X, Wu Y, Yan Y, Yang H, et al: The microbial metabolite
trimethylamine N-oxide promotes antitumor immunity in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Metab. 34:581–594.e8. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang S, Dai H, Lu Y, Li R, Gao C and Pan
S: Trimethylamine N-Oxide promotes cell proliferation and
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. J Immunol Res. 2022:70438562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Roberts AB, Gu X, Buffa JA, Hurd AG, Wang
Z, Zhu W, Gupta N, Skye SM, Cody DB, Levison BS, et al: Development
of a gut microbe-targeted nonlethal therapeutic to inhibit
thrombosis potential. Nat Med. 24:1407–1417. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta
N, Wang Z, Li L, Fu X, Wu Y, Mehrabian M, et al: Gut microbial
metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis
risk. Cell. 165:111–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li Z, Wu Z, Yan J, Liu H, Liu Q, Deng Y,
Ou C and Chen M: Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine
N-oxide induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Lab Invest.
99:346–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Peng L, Li ZR, Green RS, Holzman IR and
Lin J: Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating
tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein
kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Nutr. 139:1619–1625. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang SL, Mao YQ, Zhang ZY, Li ZM, Kong
CY, Chen HL, Cai PR, Han B, Ye T and Wang LS: Pectin supplement
significantly enhanced the anti-PD-1 efficacy in tumor-bearing mice
humanized with gut microbiota from patients with colorectal cancer.
Theranostics. 11:4155–4170. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yao Y, Cai X, Fei W, Ye Y, Zhao M and
Zheng C: The role of short-chain fatty acids in immunity,
inflammation and metabolism. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:1–12. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Song Q, Zhang X, Liu W, Wei H, Liang W,
Zhou Y, Ding Y, Ji F, Ho-Kwan Cheung A, Wong N and Yu J:
Bifidobacterium pseudolongum-generated acetate suppresses
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 79:1352–1365. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bindels LB, Porporato P, Dewulf EM, Verrax
J, Neyrinck AM, Martin JC, Scott KP, Buc Calderon P, Feron O,
Muccioli GG, et al: Gut microbiota-derived propionate reduces
cancer cell proliferation in the liver. Br J Cancer. 107:1337–1344.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Thirunavukkarasan M, Wang C, Rao A, Hind
T, Teo YR, Siddiquee AA, Goghari MAI, Kumar AP and Herr DR:
Short-chain fatty acid receptors inhibit invasive phenotypes in
breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e01863342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Singh N, Gurav A, Sivaprakasam S, Brady E,
Padia R, Shi H, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, Manicassamy S, Munn DH, et
al: Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal
metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and
carcinogenesis. Immunity. 40:128–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lavoie S, Chun E, Bae S, Brennan CA,
Gallini Comeau CA, Lang JK, Michaud M, Hoveyda HR, Fraser GL,
Fuller MH, et al: Expression of free fatty acid receptor 2 by
dendritic cells prevents their expression of interleukin 27 and is
required for maintenance of mucosal barrier and immune response
against colorectal tumors in mice. Gastroenterology.
158:1359–1372.e9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ramaiah MJ, Tangutur AD and Manyam RR:
Epigenetic modulation and understanding of HDAC inhibitors in
cancer therapy. Life Sci. 277:1195042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shanmugam G, Rakshit S and Sarkar K: HDAC
inhibitors: Targets for tumor therapy, immune modulation and lung
diseases. Transl Oncol. 16:1013122022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Li X, Su X, Liu R, Pan Y, Fang J, Cao L,
Feng C, Shang Q, Chen Y, Shao C and Shi Y: HDAC inhibition
potentiates antitumor activity of macrophages and enhances
anti-PD-L1-mediated tumor suppression. Oncogene. 40:1836–1850.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Luu M, Riester Z, Baldrich A, Reichardt N,
Yuille S, Busetti A, Klein M, Wempe A, Leister H, Raifer H, et al:
Microbial short-chain fatty acids modulate CD8+ T cell responses
and improve adoptive immunotherapy for cancer. Nat Commun.
12:40772021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
87
|
Dupraz L, Magniez A, Rolhion N, Richard
ML, Da Costa G, Touch S, Mayeur C, Planchais J, Agus A, Danne C, et
al: Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulate IL-17
production by mouse and human intestinal γδ T cells. Cell Rep.
36:1093322021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Zhang H, Du M, Yang Q and Zhu MJ: Butyrate
suppresses murine mast cell proliferation and cytokine production
through inhibiting histone deacetylase. J Nutr Biochem. 27:299–306.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Qiao P, Zhang C, Yu J, Shao S, Zhang J,
Fang H, Chen J, Luo Y, Zhi D, Li Q, et al: Quinolinic acid, a
tryptophan metabolite of the skin microbiota, negatively regulates
NLRP3 inflammasome through AhR in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol.
142:2184–2193.e6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Fang Z, Pan T, Li L, Wang H, Zhu J, Zhang
H, Zhao J, Chen W and Lu W: Bifidobacterium longum mediated
tryptophan metabolism to improve atopic dermatitis via the gut-skin
axis. Gut Microbes. 14:20447232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sehgal R, Ilha M, Vaittinen M, Kaminska D,
Männistö V, Kärjä V, Tuomainen M, Hanhineva K, Romeo S, Pajukanta
P, et al: Indole-3-Propionic acid, a Gut-Derived tryptophan
metabolite, associates with hepatic fibrosis. Nutrients.
13:35092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cheng Y, Jin UH, Allred CD, Jayaraman A,
Chapkin RS and Safe S: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity of
tryptophan metabolites in young adult mouse colonocytes. Drug Metab
Dispos. 43:1536–1543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Bender MJ, McPherson AC, Phelps CM, Pandey
SP, Laughlin CR, Shapira JH, Medina Sanchez L, Rana M, Richie TG,
Mims TS, et al: Dietary tryptophan metabolite released by
intratumoral Lactobacillus reuteri facilitates immune checkpoint
inhibitor treatment. Cell. 186:1846–1862.e26. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Hezaveh K, Shinde RS, Klötgen A, Halaby
MJ, Lamorte S, Ciudad MT, Quevedo R, Neufeld L, Liu ZQ, Jin R, et
al: Tryptophan-derived microbial metabolites activate the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in tumor-associated macrophages to suppress
antitumor immunity. Immunity. 55:324–340.e8. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Zhang Q, Zhao Q, Li T, Lu L, Wang F, Zhang
H, Liu Z, Ma H, Zhu Q, Wang J, et al: Lactobacillus
plantarum-derived indole-3-lactic acid ameliorates colorectal
tumorigenesis via epigenetic regulation of CD8+ T cell immunity.
Cell Metab. 35:943–960.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Garris CS, Arlauckas SP, Kohler RH, Trefny
MP, Garren S, Piot C, Engblom C, Pfirschke C, Siwicki M,
Gungabeesoon J, et al: Successful Anti-PD-1 cancer immunotherapy
requires T cell-dendritic cell crosstalk involving the cytokines
IFN-γ and IL-12. Immunity. 49:1148–1161.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Sári Z, Mikó E, Kovács T, Boratkó A,
Ujlaki G, Jankó L, Kiss B, Uray K and Bai P: Indoxylsulfate, a
metabolite of the microbiome, has cytostatic effects in breast
cancer via activation of AHR and PXR receptors and induction of
oxidative stress. Cancers (Basel). 12:29152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Sharma MD, Pacholczyk R, Shi H, Berrong
ZJ, Zakharia Y, Greco A, Chang CS, Eathiraj S, Kennedy E, Cash T,
et al: Inhibition of the BTK-IDO-mTOR axis promotes differentiation
of monocyte-lineage dendritic cells and enhances antitumor T cell
immunity. Immunity. 54:2354–2371.e8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Campesato LF, Budhu S, Tchaicha J, Weng
CH, Gigoux M, Cohen IJ, Redmond D, Mangarin L, Pourpe S, Liu C, et
al: Blockade of the AHR restricts a Treg-macrophage suppressive
axis induced by L-Kynurenine. Nat Commun. 11:40112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Liu H, Xu X, Wang J, Wang W, Ma C, Sun T
and Shao Q: Clinical study on different doses and fractionated
radiotherapies for multiple brain metastases of non-EGFR mutant
lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Palliat Med. 9:2003–2012. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu Z, Huang L, Wang H, Shi Z, Huang Y,
Liang L, Wang R and Hu K: Predicting nomogram for severe oral
mucositis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma during
intensity-modulated radiation therapy: A retrospective cohort
study. Curr Oncol. 30:219–232. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Guo H, Chou WC, Lai Y, Liang K, Tam JW,
Brickey WJ, Chen L, Montgomery ND, Li X, Bohannon LM, et al:
Multi-omics analyses of radiation survivors identify
radioprotective microbes and metabolites. Science.
370:eaay90972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhang Y, Yan T, Mo W, Song B, Zhang Y,
Geng F, Hu Z, Yu D and Zhang S: Altered bile acid metabolism in
skin tissues in response to ionizing radiation: deoxycholic acid
(DCA) as a novel treatment for radiogenic skin injury. Int J Radiat
Biol. 100:87–98. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Han JX, Tao ZH, Wang JL, Zhang L, Yu CY,
Kang ZR, Xie Y, Li J, Lu S, Cui Y, et al: Microbiota-derived
tryptophan catabolites mediate the chemopreventive effects of
statins on colorectal cancer. Nat Microbiol. 8:919–933. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Deng B, Yang B, Chen J, Wang S, Zhang W,
Guo Y, Han Y, Li H, Dang Y, Yuan Y, et al: Gallic acid induces
T-helper-1-like Treg cells and strengthens immune checkpoint
blockade efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0040372022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
Li K, Xiao Y, Bian J, Han L, He C, El-Omar
E, Gong L and Wang M: Ameliorative effects of gut microbial
metabolite urolithin a on pancreatic diseases. Nutrients.
14:25492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
González-Sarrías A, Miguel V, Merino G,
Lucas R, Morales JC, Tomás-Barberán F, Alvarez AI and Espín JC: The
gut microbiota ellagic acid-derived metabolite urolithin A and its
sulfate conjugate are substrates for the drug efflux transporter
breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2/BCRP). J Agric Food Chem.
61:4352–4359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Ghosh S, Singh R, Vanwinkle ZM, Guo H,
Vemula PK, Goel A, Haribabu B and Jala VR: Microbial metabolite
restricts 5-fluorouracil-resistant colonic tumor progression by
sensitizing drug transporters via regulation of FOXO3-FOXM1 axis.
Theranostics. 12:5574–5595. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhang Y, Jiang L, Su P, Yu T, Ma Z, Liu Y
and Yu J: Urolithin A suppresses tumor progression and induces
autophagy in gastric cancer via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Drug Dev
Res. 84:172–184. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Blouin JM, Penot G, Collinet M, Nacfer M,
Forest C, Laurent-Puig P, Coumoul X, Barouki R, Benelli C and
Bortoli S: Butyrate elicits a metabolic switch in human colon
cancer cells by targeting the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Int J
Cancer. 128:2591–2601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Yuksel B, Deveci Ozkan A, Aydın D and
Betts Z: Evaluation of the antioxidative and genotoxic effects of
sodium butyrate on breast cancer cells. Saudi J Biol Sci.
29:1394–1401. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhao ZH, Wang ZX, Zhou D, Han Y, Ma F, Hu
Z, Xin FZ, Liu XL, Ren TY, Zhang F, et al: Sodium butyrate
supplementation inhibits hepatic steatosis by stimulating liver
kinase B1 and insulin-induced gene. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.
12:857–871. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Encarnação JC, Pires AS, Amaral RA,
Gonçalves TJ, Laranjo M, Casalta-Lopes JE, Gonçalves AC,
Sarmento-Ribeiro AB, Abrantes AM and Botelho MF: Butyrate, a
dietary fiber derivative that improves irinotecan effect in colon
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 56:183–192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Shuwen H, Yangyanqiu W, Jian C, Boyang H,
Gong C and Jing Z: Synergistic effect of sodium butyrate and
oxaliplatin on colorectal cancer. Transl Oncol. 27:1015982023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170:548–563.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Chen L, Zhao R, Kang Z, Cao Z, Liu N, Shen
J, Wang C, Pan F, Zhou X, Liu Z, et al: Delivery of short chain
fatty acid butyrate to overcome Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced
chemoresistance. J Control Release. 363:43–56. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Tintelnot J, Xu Y, Lesker TR, Schönlein M,
Konczalla L, Giannou A D, Pelcza r P, Kylies D, Puelles VG,
Bielecka AA, et al: Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences
chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 615:168–174.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Colbert LE, El Alam MB, Wang R, Karpinets
T, Lo D, Lynn EJ, Harris TA, Elnaggar JH, Yoshida-Court K, Tomasic
K, et al: Tumor-resident Lactobacillus iners confer chemoradiation
resistance through lactate-induced metabolic rewiring. Cancer Cell.
41:1945–1962.e11. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Chang TK, Yin TC, Su WC, Tsai HL, Huang
CW, Chen YC, Li CC, Chen PJ, Ma CJ, Chuang KH, et al: A Pilot Study
of Silymarin as Supplementation to reduce toxicities in metastatic
colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line FOLFIRI Plus
Bevacizumab. Oncol Res. 28:801–809. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Yang W, Chang L, Guo Q, Chen J, Yu W and
Zhang W: Programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitors in the
treatment of digestive system tumors in Chinese population: An
observational study of effectiveness and safety. Ann Palliat Med.
10:9015–9024. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Renga G, Nunzi E, Pariano M, Puccetti M,
Bellet MM, Pieraccini G, D'Onofrio F, Santarelli I, Stincardini C,
Aversa F, et al: Optimizing therapeutic outcomes of immune
checkpoint blockade by a microbial tryptophan metabolite. J
Immunother Cancer. 10:e0037252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Lu C, Liu Z, Klement JD, Yang D, Merting
AD, Poschel D, Albers T, Waller JL, Shi H and Liu K: WDR5-H3K4me3
epigenetic axis regulates OPN expression to compensate PD-L1
function to promote pancreatic cancer immune escape. J Immunother
Cancer. 9:e0026242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wang J, Ge J, Wang Y, Xiong F, Guo J,
Jiang X, Zhang L, Deng X, Gong Z, Zhang S, et al: EBV miRNAs BART11
and BART17-3p promote immune escape through the enhancer-mediated
transcription of PD-L1. Nat Commun. 13:8662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lainé A, Labiad O, Hernandez-Vargas H,
This S, Sanlaville A, Léon S, Dalle S, Sheppard D, Travis MA,
Paidassi H and Marie JC: Regulatory T cells promote cancer
immune-escape through integrin αvβ8-mediated TGF-β activation. Nat
Commun. 12:62282021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Peng S, Wang R, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zhong L, Li
K, Nishiyama A, Arai S, Yano S and Wang W: EGFR-TKI resistance
promotes immune escape in lung cancer via increased PD-L1
expression. Mol Cancer. 18:1652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Mehra S, Garrido VT, Dosch AR, Lamichhane
P, Srinivasan S, Singh SP, Zhou Z, De Castro Silva I, Joshi C, Ban
Y, et al: Remodeling of stromal immune microenvironment by
urolithin a improves survival with immune checkpoint blockade in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res Commun. 3:1224–1236. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Coutzac C, Jouniaux JM, Paci A, Schmidt J,
Mallardo D, Seck A, Asvatourian V, Cassard L, Saulnier P, Lacroix
L, et al: Systemic short chain fatty acids limit antitumor effect
of CTLA-4 blockade in hosts with cancer. Nat Commun. 11:21682020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Lv B, Wang Y, Ma D, Cheng W, Liu J, Yong
T, Chen H and Wang C: Immunotherapy: Reshape the tumor immune
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 13:8441422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu
J, Zhang B, Meng Q, Yu X and Shi S: Crosstalk between
cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor
microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer.
20:1312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Korbecki J, Kojder K, Simińska D,
Bohatyrewicz R, Gutowska I, Chlubek D and Baranowska-Bosiacka I: CC
Chemokines in a Tumor: A Review of Pro-Cancer and Anti-Cancer
Properties of the Ligands of Receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:84122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Hennessy M, Wahba A, Felix K, Cabrera M,
Segura MG, Kundra V, Ravoori MK, Stewart J, Kleinerman ES, Jensen
VB, et al: Bempegaldesleukin (BEMPEG; NKTR-214) efficacy as a
single agent and in combination with checkpoint-inhibitor therapy
in mouse models of osteosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 148:1928–1937. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Rosen DB, Kvarnhammar AM, Laufer B, Knappe
T, Karlsson JJ, Hong E, Lee YC, Thakar D, Zúñiga LA, Bang K, et al:
TransCon IL-2 β/γ: A novel long-acting prodrug with sustained
release of an IL-2Rβ/γ-selective IL-2 variant with improved
pharmacokinetics and potent activation of cytotoxic immune cells
for the treatment of cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0049912022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Naing A, Papadopoulos KP, Autio KA, Ott
PA, Patel MR, Wong DJ, Falchook GS, Pant S, Whiteside M, Rasco DR,
et al: Safety, antitumor activity, and immune activation of
pegylated recombinant human interleukin-10 (AM0010) in patients
with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 34:3562–3569. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Taniguchi Y, Kurokawa Y, Hagi T, Takahashi
T, Miyazaki Y, Tanaka K, Makino T, Yamasaki M, Nakajima K, Mori M
and Doki Y: Methylprednisolone inhibits tumor growth and peritoneal
seeding induced by surgical stress and post-operative
complications. Ann Surg Oncol. 26:2831–2838. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Hailemichael Y, Johnson DH, Abdel-Wahab N,
Foo WC, Bentebibel SE, Daher M, Haymaker C, Wani K, Saberian C,
Ogata D, et al: Interleukin-6 blockade abrogates immunotherapy
toxicity and promotes tumor immunity. Cancer Cell. 40:509–523.e6.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Xue D, Moon B, Liao J, Guo J, Zou Z, Han
Y, Cao S, Wang Y, Fu YX and Peng H: A tumor-specific pro-IL-12
activates preexisting cytotoxic T cells to control established
tumors. Sci Immunol. 7:eabi68992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Agliardi G, Liuzzi AR, Hotblack A, De Feo
D, Núñez N, Stowe CL, Friebel E, Nannini F, Rindlisbacher L,
Roberts TA, et al: Intratumoral IL-12 delivery empowers CAR-T cell
immunotherapy in a pre-clinical model of glioblastoma. Nat Commun.
12:4442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Chang PV, Hao L, Offermanns S and
Medzhitov R: The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal
macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:2247–2252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Mager LF, Burkhard R, Pett N, Cooke NCA,
Brown K, Ramay H, Paik S, Stagg J, Groves RA, Gallo M, et al:
Microbiome-derived inosine modulates response to checkpoint
inhibitor immunotherapy. Science. 369:1481–1489. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
O'Keefe SJ: Diet, microorganisms and their
metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:691–706. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Niekamp P and Kim CH: Microbial metabolite
dysbiosis and colorectal cancer. Gut Liver. 17:190–203. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Wu X, Wu Y, He L, Wu L, Wang X and Liu Z:
Effects of the intestinal microbial metabolite butyrate on the
development of colorectal cancer. J Cancer. 9:2510–2517. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka K, Marano L, Merola
E, Roviello F and Połom K: Sodium butyrate in both prevention and
supportive treatment of colorectal cancer. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 12:10238062022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Zhao H, Wang D, Zhang Z, Xian J and Bai X:
Effect of gut microbiota-derived metabolites on immune checkpoint
inhibitor therapy: Enemy or friend? Molecules. 27:47992022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|