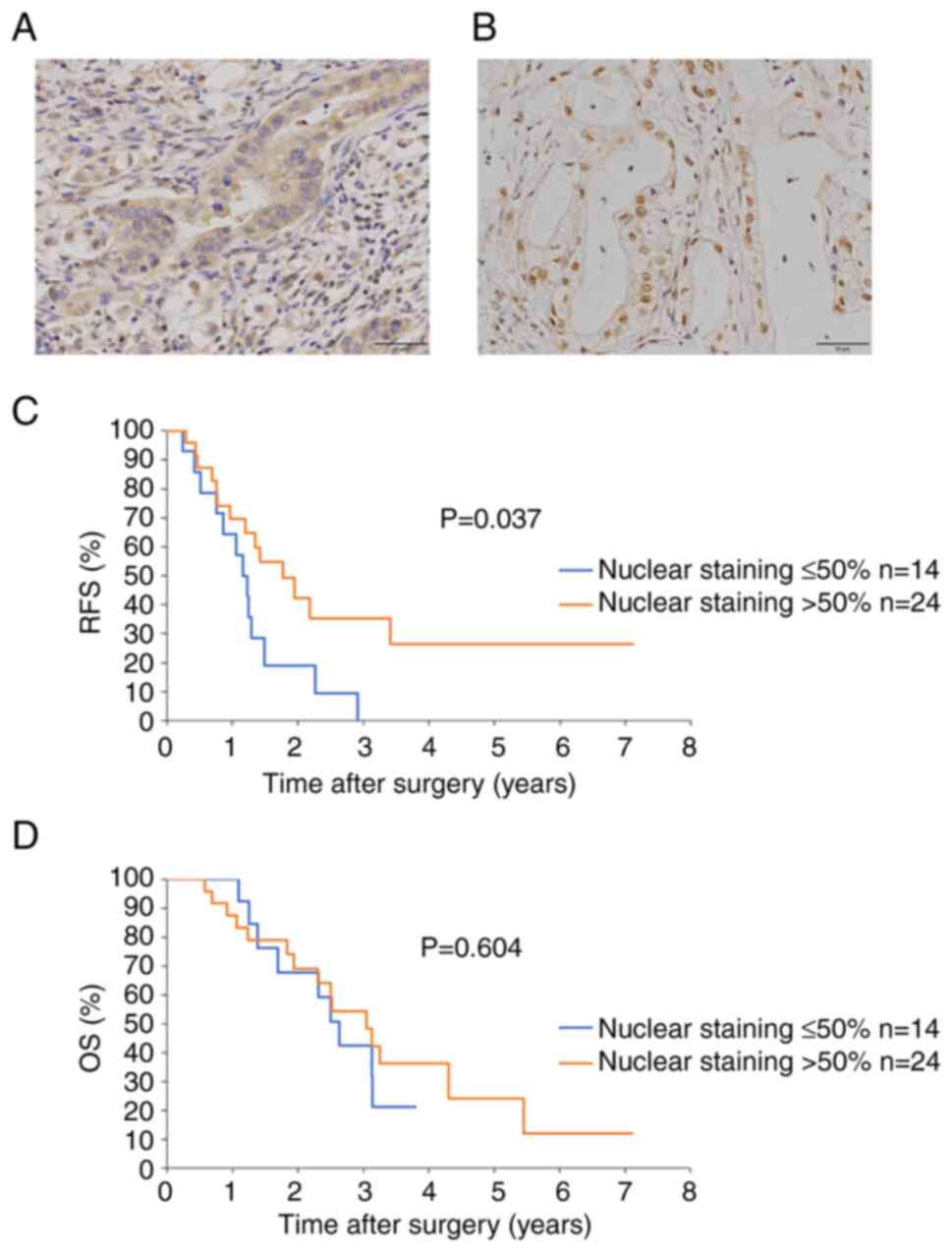
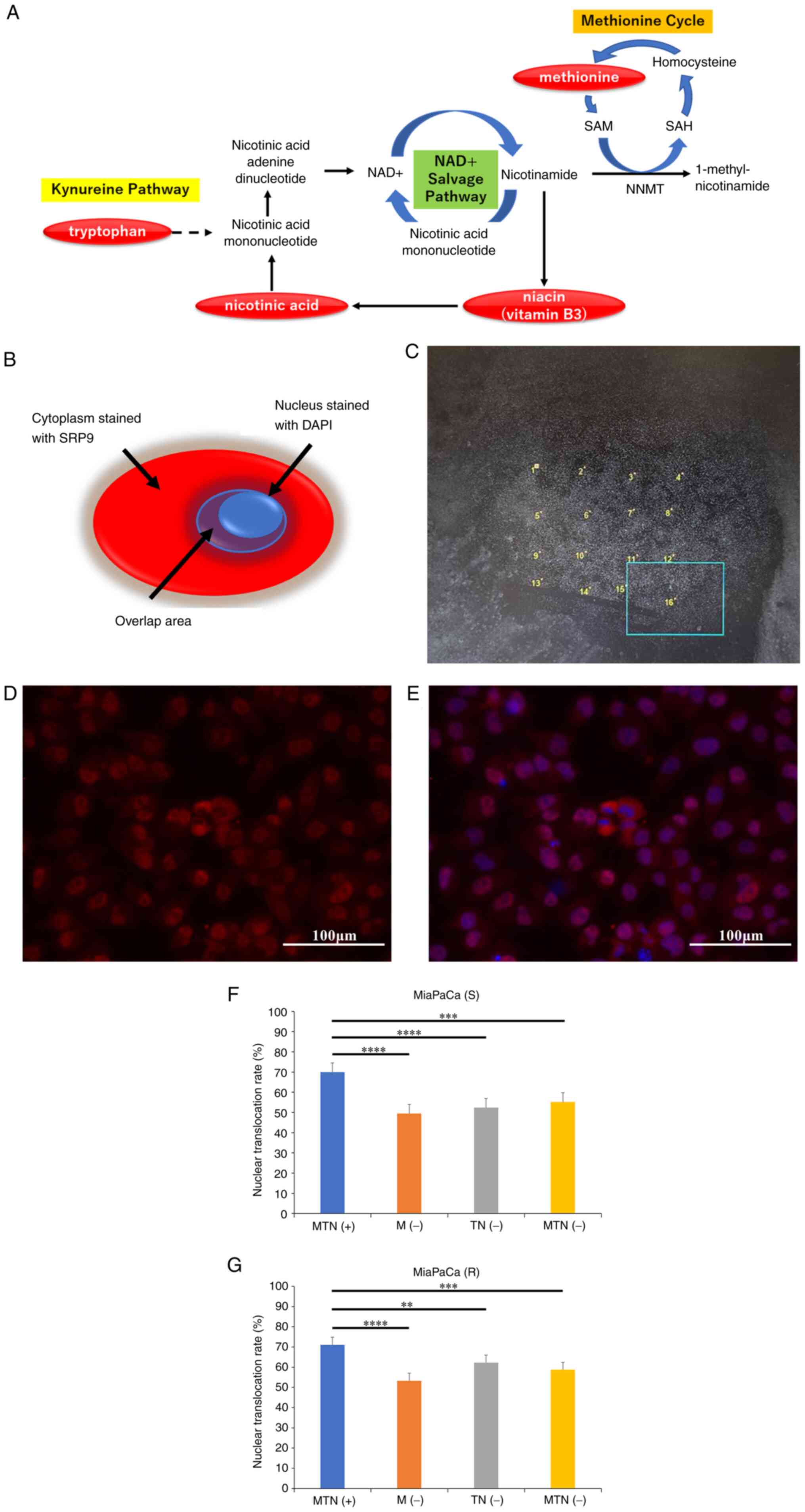
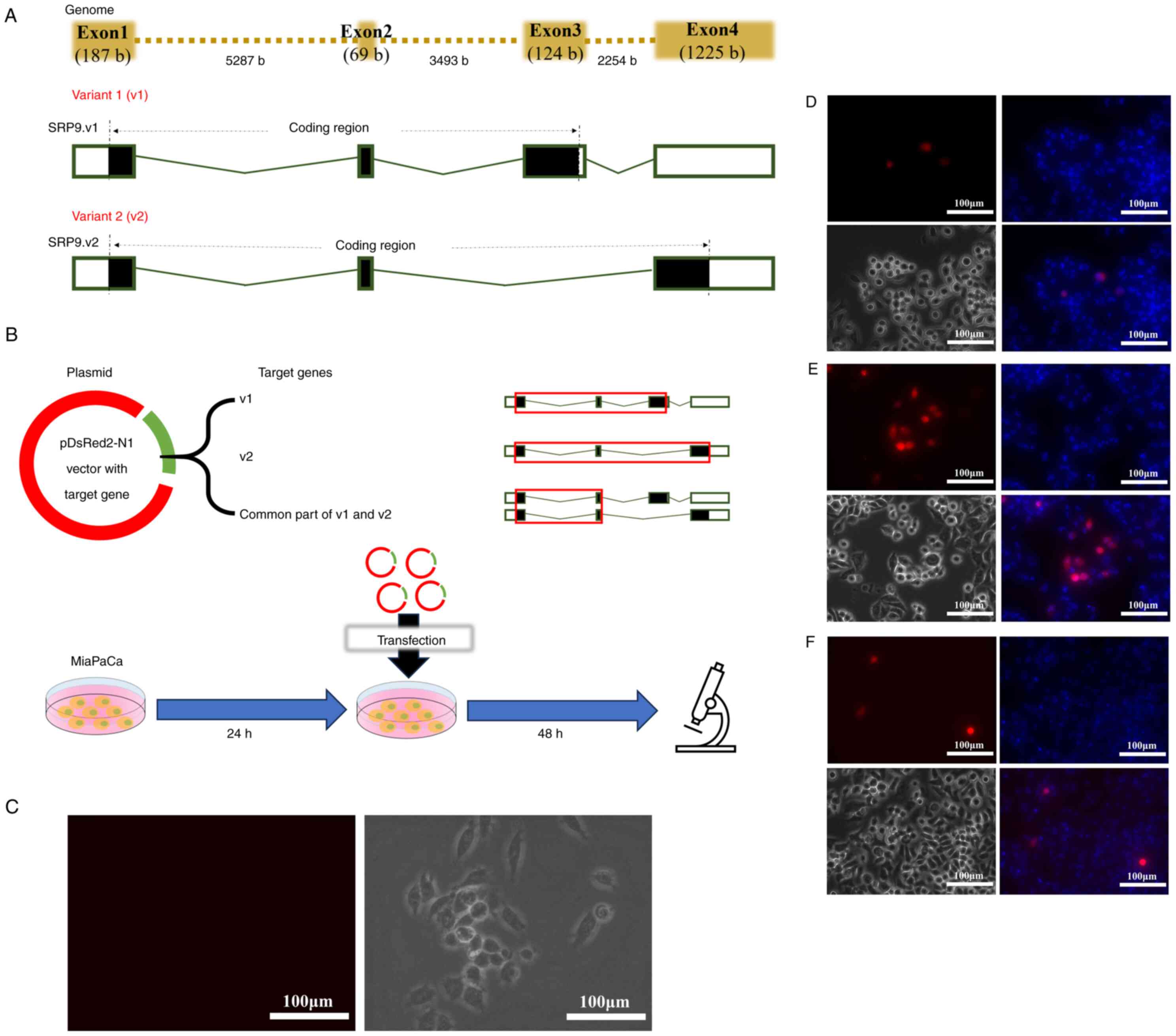
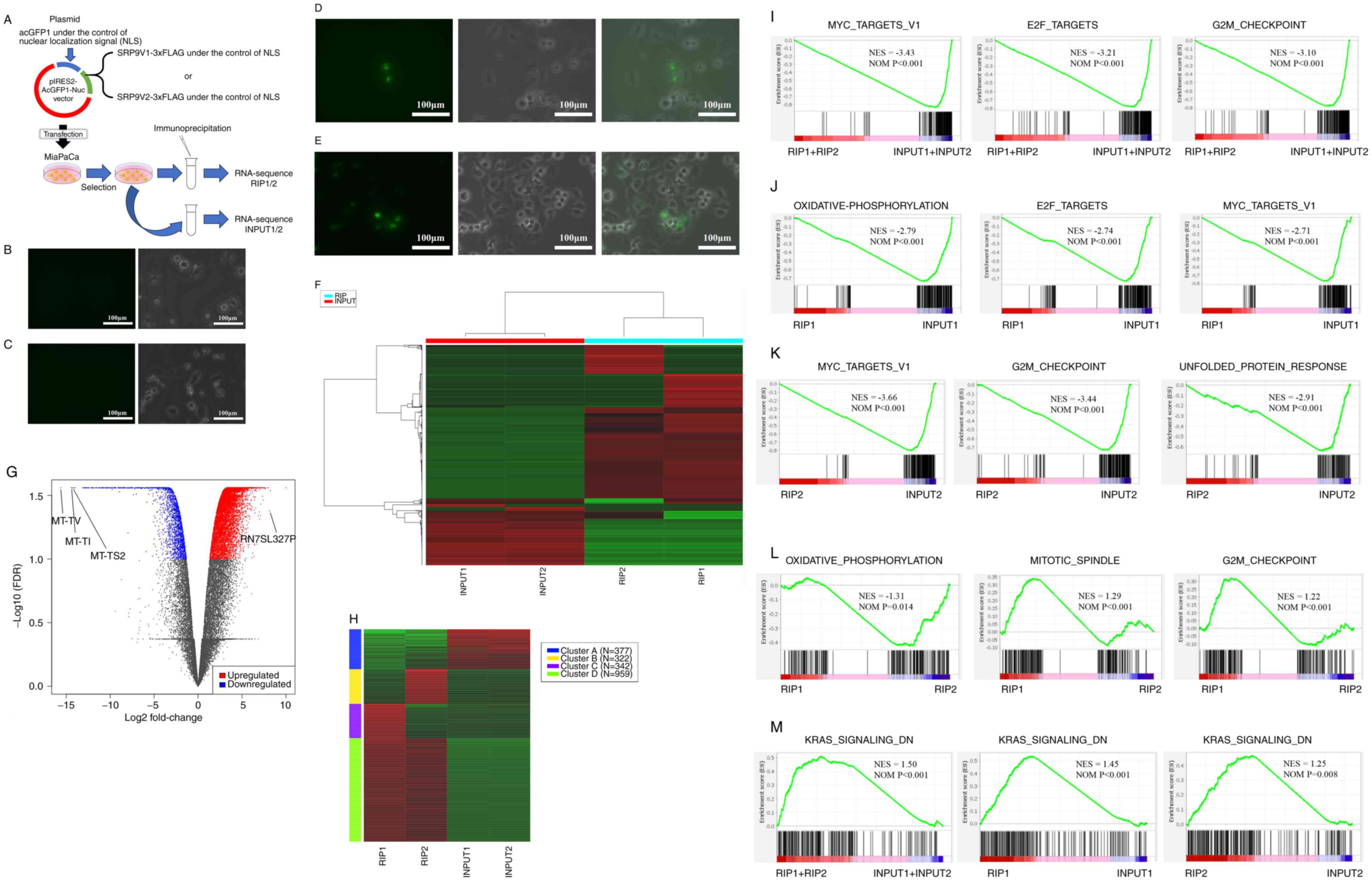
|
1
|
Kellogg MK, Tikhonova EB and Karamyshev
AL: Signal recognition particle in human diseases. Front Genet.
13:8980832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Erdogan G, Trabulus DC, Talu CK and Guven
M: Investigation of SRP9 protein expression in breast cancer. Mol
Biol Rep. 49:531–537. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rho JH, Qin S, Wang JY and Roehrl MH:
Proteomic expression analysis of surgical human colorectal cancer
tissues: Up-regulation of PSB7, PRDX1, and SRP9 and hypoxic
adaptation in cancer. J Proteome Res. 7:2959–2972. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang M, Peng Y, Yang Z, Zhang H, Xu C,
Liu L, Zhao Q, Wu J, Wang H and Liu J: DAB2IP down-regulates
HSP90AA1 to inhibit the malignant biological behaviors of
colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 22:5612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hessel EV, de Wit M, Wolterink-Donselaar
IG, Karst H, de Graaff E, van Lith HA, de Bruijn E, de Sonnaville
S, Verbeek NE, Lindhout D, et al: Identification of Srp9 as a
febrile seizure susceptibility gene. Ann Clin Transl Neurol.
1:239–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bovia F, Fornallaz M, Leffers H and Strub
K: The SRP9/14 subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) is
present in more than 20-fold excess over SRP in primate cells and
exists primarily free but also in complex with small cytoplasmic
Alu RNAs. Mol Biol Cell. 6:471–484. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berger A, Ivanova E, Gareau C, Scherrer A,
Mazroui R and Strub K: Direct binding of the Alu binding protein
dimer SRP9/14 to 40S ribosomal subunits promotes stress granule
formation and is regulated by Alu RNA. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:11203–11217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nabet BY, Qiu Y, Shabason JE, Wu TJ, Yoon
T, Kim BC, Benci JL, DeMichele AM, Tchou J, Marcotrigiano J and
Minn AJ: Exosome RNA unshielding couples stromal activation to
pattern recognition receptor signaling in cancer. Cell. 170:352–366
e13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sugimura T, Birnbaum SM, Winitz M and
Greenstein JP: Quantitative nutritional studies with water-soluble,
chemically defined diets. VIII. The forced feeding of diets each
lacking in one essential amino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys.
81:448–455. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaiser P: Methionine dependence of cancer.
Biomolecules. 10:5682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Yip LY, Lee JHJ, Wu Z, Chew HY,
Chong PKW, Teo CC, Ang HY, Peh KLE, Yuan J, et al: Methionine is a
metabolic dependency of tumor-initiating cells. Nat Med.
25:825–837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao X, Sanderson SM, Dai Z, Reid MA,
Cooper DE, Lu M, Richie JP Jr, Ciccarella A, Calcagnotto A, Mikhael
PG, et al: Dietary methionine influences therapy in mouse cancer
models and alters human metabolism. Nature. 572:397–401. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bian Y, Li W, Kremer DM, Sajjakulnukit P,
Li S, Crespo J, Nwosu ZC, Zhang L, Czerwonka A, Pawłowska A, et al:
Cancer SLC43A2 alters T cell methionine metabolism and histone
methylation. Nature. 585:277–282. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tatekawa S, Ofusa K, Chijimatsu R,
Vecchione A, Tamari K, Ogawa K and Ishii H: Methylosystem for
cancer sieging strategy. Cancers (Basel). 13:50882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kilgour MK, MacPherson S, Zacharias LG,
Ellis AE, Sheldon RD, Liu EY, Keyes S, Pauly B, Carleton G, Allard
B, et al: 1-Methylnicotinamide is an immune regulatory metabolite
in human ovarian cancer. Sci Adv. 7:eabe11742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pellagatti A, Armstrong RN, Steeples V,
Sharma E, Repapi E, Singh S, Sanchi A, Radujkovic A, Horn P,
Dolatshad H, et al: Impact of spliceosome mutations on RNA splicing
in myelodysplasia: Dysregulated genes/pathways and clinical
associations. Blood. 132:1225–1240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Figg JW, Barajas JM and Obeng EA:
Therapeutic approaches targeting splicing factor mutations in
myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Opin
Hematol. 28:73–79. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang E, Pineda JMB, Kim WJ, Chen S,
Bourcier J, Stahl M, Hogg SJ, Bewersdorf JP, Han C, Singer ME, et
al: Modulation of RNA splicing enhances response to BCL2 inhibition
in leukemia. Cancer Cell. 41:164–180 e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Rahman MA, Lin KT, Bradley RK, Abdel-Wahab
O and Krainer AR: Recurrent SRSF2 mutations in MDS affect both
splicing and NMD. Genes Dev. 34:413–427. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang Q, Zhao J, Zhang W, Chen D and Wang
Y: Aberrant alternative splicing in breast cancer. J Mol Cell Biol.
11:920–929. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nanjo S, Wu W, Karachaliou N, Blakely CM,
Suzuki J, Chou YT, Ali SM, Kerr DL, Olivas VR, Shue J, et al:
Deficiency of the splicing factor RBM10 limits EGFR inhibitor
response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. J Clin Invest.
132:e1450992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wan L, Lin KT, Rahman MA, Ishigami Y, Wang
Z, Jensen MA, Wilkinson JE, Park Y, Tuveson DA and Krainer AR:
Splicing Factor SRSF1 promotes pancreatitis and KRASG12D-mediated
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 13:1678–1695. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tan C, Cao J, Chen L, Xi X, Wang S, Zhu Y,
Yang L, Ma L, Wang D, Yin J, et al: Noncoding RNAs serve as
diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clin Chem. 65:905–915. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson LR, Lee DY, Eacret JS, Ye D, June
CH and Minn AJ: The immunostimulatory RNA RN7SL1 enables CAR-T
cells to enhance autonomous and endogenous immune function. Cell.
184:4981–4995 e14. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie X, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yu H, Li G,
Ruan Z, Li F, Wang X and Zhang J: Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase
enhances resistance to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells
through inhibition of the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway. Oncotarget.
7:45837–45848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Novak Kujundzic R, Prpic M, Dakovic N,
Dabelić N, Tomljanović M, Mojzeš A, Fröbe A and Trošelj KG:
Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase in acquisition of stem cell
properties and therapy resistance in cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
22:56812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rodrigues F, van Hemert M, Steensma HY,
Corte-Real M and Leao C: Red fluorescent protein (DsRed) as a
reporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 183:3791–3794.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kimura A, Toda Y, Matsumoto Y, Yamamoto H,
Yahiro K, Shimada E, Kanahori M, Oyama R, Fukushima S, Nakagawa M,
et al: Nuclear β-catenin translocation plays a key role in
osteoblast differentiation of giant cell tumor of bone. Sci Rep.
12:134382022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Larsson SC, Giovannucci E and Wolk A:
Methionine and vitamin B6 intake and risk of pancreatic cancer: A
prospective study of Swedish women and men. Gastroenterology.
132:113–118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei DH and Mao QQ: Vitamin B6, vitamin B12
and methionine and risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Nutr
J. 19:1112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kellogg MK, Miller SC, Tikhonova EB and
Karamyshev AL: SRPassing Co-translational Targeting: The role of
the signal recognition particle in protein targeting and mRNA
protection. Int J Mol Sci. 22:62842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ala M: Target c-Myc to treat pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 23:34–50. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peng YP, Zhu Y, Yin LD, Zhang JJ, Wei JS,
Liu X, Liu XC, Gao WT, Jiang KR and Miao Y: PEG10 overexpression
induced by E2F-1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:302017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oshi M, Patel A, Le L, Tokumaru Y, Yan L,
Matsuyama R, Endo I and Takabe K: G2M checkpoint pathway alone is
associated with drug response and survival among cell
proliferation-related pathways in pancreatic cancer. Am J Cancer
Res. 11:3070–3084. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ashton TM, McKenna WG, Kunz-Schughart LA
and Higgins GS: Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in
cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2482–2490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Long D, Chen K, Yang Y and Tian X:
Unfolded protein response activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress
in pancreatic cancer: Potential therapeutical target. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 26:1689–1696. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Luo J: KRAS mutation in pancreatic cancer.
Semin Oncol. 48:10–18. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brierley J, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. Wiley Blackwell;
Hoboken, NJ: 2017
|