Introduction
Although there is usually no mature fatty tissue
within the thyroid gland, fat-containing thyroid lesions have been
reported (1). Fat-containing thyroid
lesions may be classified into two groups, namely neoplastic and
non-neoplastic lesions. Thyrolipoma, also referred to as
lipoadenoma, is the most common fat-containing lesion of the
thyroid gland; it is considered to be a variant of follicular
adenoma and is characterized by the presence of mature adipose
cells interspersed throughout the follicular adenoma (2). Moreover, a few cases of papillary
carcinoma and follicular carcinoma with adipose cells have been
reported (1). Non-neoplastic
fat-containing thyroid lesions include amyloid goiter and Hashimoto
thyroiditis (1,3).
Albeit extremely rare, diffuse mature adipose cell
infiltration of the normal thyroid gland has been previously
reported, referred to as thyrolipomatosis or diffuse lipomatosis of
the thyroid gland (2). To the best
of our knowledge, only 11 cases have been documented in the
literature to date (2,4–8). We
herein describe an additional case of thyrolipomatosis and review
the fat-containing thyroid lesions.
Case report
A 68-year-old Japanese woman with a past history of
diabetes mellitus and angina pectoris presented at the Kusatsu
General Hospital in August 2016 with a neck mass that had been
noticed ~7 years earlier. A computed tomography scan revealed
diffuse thyroid gland enlargement, compressing the trachea, with
multiple calcifications in the bilateral lobes. The serum
thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine (FT4) levels were
within the normal range (0.63 µIU/ml, range 0.4–4.0 µIU/ml; and
1.01 ng/dl, range 0.8–1.7 ng/dl, respectively), but the free
triiodothyronine (FT3) level was mildly decreased (1.84 pg/ml,
range 2.2–4.1 pg/ml). Total thyroidectomy was performed.
The postoperative course was uneventful and the
patient has been free from tumor recurrence and metastasis during
the 3 months of medical follow-up.
The formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue blocks
of the resected thyroid specimens were cut into 3-µm sections,
deparaffinized and rehydrated. Each section was stained with
hematoxylin and eosin.
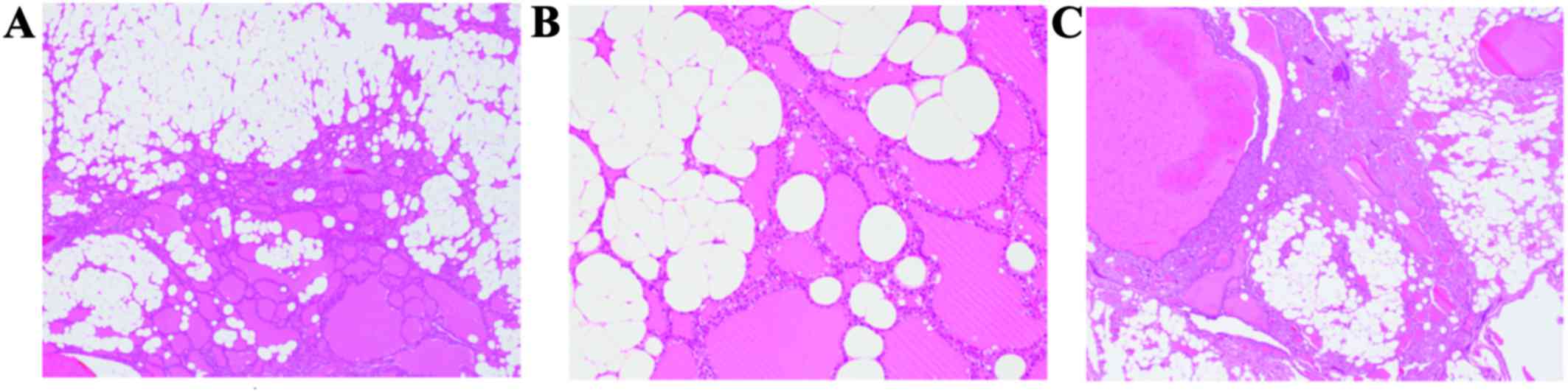
Histopathological examination of the thyroid gland
revealed that mature fatty tissue was diffusely distributed
throughout the gland (Fig. 1A).
Capsular formation was not observed, and the follicular cells had
small round nuclei without nucleoli (Fig. 1B). Nuclear grooves or intranuclear
cytoplasmic inclusions were not observed. Hyperplastic follicles
were noted, and mature fatty cells were also present among the
hyperplastic follicles (Fig. 1C).
Focal stromal sclerosis and calcifications were identified. Amyloid
deposition and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration were not
observed.
Based on these findings, thyrolipomatosis was
diagnosed.
Discussion
In this report, we describe what is, to the best of
our knowledge, the 12th case of thyrolipomatosis documented to
date. Ge et al summarized the clinicopathological
characteristics of 10 cases of thyrolipomatosis (2). According to their review, the median
age of the patients was 42 years (range, 11–76 years) and the
gender distribution was almost equal. The common complaint was
diffuse or nodular goiter, with or without compression symptoms.
The patients usually presented with little change in thyroid
function (2). The
clinicopathological characteristics of the present case were
consistent with those of previously reported cases.
The characteristic pathological feature of
thyrolipomatosis is the presence of diffuse mature adipose cell
infiltration among the non-neoplastic thyroid follicles. Although
no fibrous capsule formation has been reported, stromal fibrosis
and lymphocytic infiltration may be occasionally observed (2). Ge et al classified
fat-containing thyroid lesions into three categories: i) Nodular
pattern (thyrolipoma), ii) diffuse pattern (the adipose tissue is
diffusely distributed throughout the thyroid gland, the thyroid
gland is composed of unremarkable follicles, and fat infiltration
is also present in adenomatous nodules), and iii) combined nodular
and diffuse pattern (presence of thyrolipoma, with diffuse fatty
infiltration also noted in the thyroid tissue surrounding the
thyrolipoma) (2). In the present
case, fatty infiltration was observed throughout the bilateral
lobes of the thyroid, and it was also present in the hyperplastic
thyroid nodules, without follicular adenoma. Therefore, this case
exhibits the diffuse pattern (thyrolipomatosis) according to the
classification proposed by Ge et al (2).
The mechanism underlying fatty infiltration of the
thyroid gland remains unclear. A hypothesis involving a metaplastic
process has been suggested. Fatty tissue may be derived from
metaplasis of stromal fibroblasts, possibly in response to chronic
tissue hypoxia or senile involution (1,2,9). However, the detailed mechanism has not
been elucidated; therefore, additional studies are required to
determine the mechanism underlying the occurrence of this rare
lesion.
Neoplastic as well as non-neoplastic thyroid lesions
may contain mature fatty tissue. The fat-containing thyroid lesions
are summarized in Table I. The
neoplastic lesions comprise thyrolipoma, papillary carcinoma and
follicular carcinoma, whereas the non-neoplastic lesions include
adenomatous nodule, thyrolipomatosis, amyloid goiter,
dyshormonogenetic goiter and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (1). Thyrolipomatosis must be differentiated
from the other abovementioned lesions. Thyrolipoma is the most
common fat-containing lesion of the thyroid gland (1). The characteristic histopathological
feature is the presence of mature fatty tissue in the follicular
adenoma and a fibrous capsule is present around the tumor (1,2). Amyloid
goiter is also a relatively common fat-containing non-neoplastic
thyroid lesion (3). The presence of
amyloid among the non-neoplastic thyroid follicles is
characteristic of this condition, and special staining may help
with the differential diagnosis. Papillary carcinoma and follicular
carcinoma with mature fatty tissue have a characteristic
carcinomatous component; therefore, the diagnosis may not be
difficult (1). Furthermore,
lipid-rich follicular neoplasms, in which intracellular lipid is
present in the cytoplasm of the neoplastic follicular cells, must
be differentiated from thyrolipomatosis (1,2).
 | Table I.Summary of fat-containing lesions of
the thyroid gland. |
Table I.
Summary of fat-containing lesions of
the thyroid gland.
| Neoplastic | Non-neoplastic |
|---|
| Thyrolipoma | Amyloid goiter |
| Papillary
carcinoma | Adenomatous
nodule |
| Follicular
carcinoma | Thyrolipomatosis |
|
| Dyshormonogenetic
goiter |
|
| Lymphocytic
thyroiditis |
In conclusion, the present report describes the 12th
case of thyrolipomatosis documented to date. Albeit rare, fatty
infiltration may occur in various neoplastic and non-neoplastic
thyroid lesions. Therefore, the abovementioned lesions must be
considered in the differential diagnosis of thyrolipomatosis.
References
|
1
|
Gnepp DR, Ogorzalek JM and Heffess CS:
Fat-containing lesions of the thyroid gland. Am J Surg Pathol.
13:605–612. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ge Y, Luna MA, Cowan DF, Truong LD and
Ayala AG: Thyrolipoma and thyrolipomatosis: 5 case reports and
historical review of the literature. Ann Diagn Pathol. 13:384–389.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Himmetoglu C, Yamak S and Tezel GG:
Diffuse fatty infiltration in amyloid goiter. Pathol Int.
57:449–453. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chesky VE, Dreese WC and Hellwig CA:
Adenolipomatosis of the thyroid: A new type of goiter. Surgery.
34:38–45. 1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asirwatham JE, Barcos M and Shimaoka K:
Hamartomatous adiposity of thyroid gland. J Med. 10:197–206.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simha MR and Doctor VM: Adenolipomatosis
of the thyroid gland. Indian J Cancer. 20:215–217. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arslan A, Alíç B, Uzunlar AK, Büyükbayram
H and Sari I: Diffuse lipomatosis of thyroid gland. Auris Nasus
Larynx. 26:213–215. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sanuvada RV, Chowhan AK, Rukmangadha N,
Patnayak R, Yootla M and Amancharla LY: Thyrolipomatosis: An
inquisitive rare entity. Gland Surg. 3:E6–E9. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schröder S and Böcker W: Lipomatous
lesions of the thyroid gland: A review. Appl Pathol. 3:140–149.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|