Introduction
Primary malignant melanoma of the esophagus (PMME)
accounts for only 0.1 to 0.3% of all esophageal neoplasms (1–3), and the
prognosis is extremely poor because of early hematogenous and
lymphatic metastases. Standard treatment strategies and clear
guidelines have not been established for PMME, much less for
recurrent disease. There have been major recent advances in the
management of metastatic melanoma, including immune checkpoint
inhibitors, such as anti-programmed death-1 (anti-PD-1) and
anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. In particular, targeting the PD-1 pathway
in patients with metastatic melanoma has demonstrated a substantial
clinical benefit (4,5). However, there are currently no reports
on the use of the anti-PD-1 antibody, nivolumab, followed by
radiotherapy in patients with recurrent PMME. Here, we report a
case of PMME that recurred in the lymph node (LN) around the celiac
axis after thoracoscopic esophagectomy, which was treated with
multidisciplinary therapy with dacarbazine, monoclonal antibodies
directed against negative regulators such as PD-1, hypofractionated
radiotherapy and laparoscopic lymphadenectomy.
Case report
A 60-year-old Japanese man who presented with a
chief complaint of dysphagia to solid foods was diagnosed with PMME
in the lower esophagus. Because the patient had a prior history of
right upper lobectomy for lung cancer, he underwent
mediastinoscope-assisted subtotal esophagectomy with two-field LN
dissection and gastric tube reconstruction via the mediastinal
route. Evaluation of the resected specimen demonstrated that the
tumor invaded the muscularis propria (pT2), and two nodal
involvements were detected in the LNs along the left gastric artery
(pN1). The UICC pathological staging for his PMME was IIA, T2, pN1,
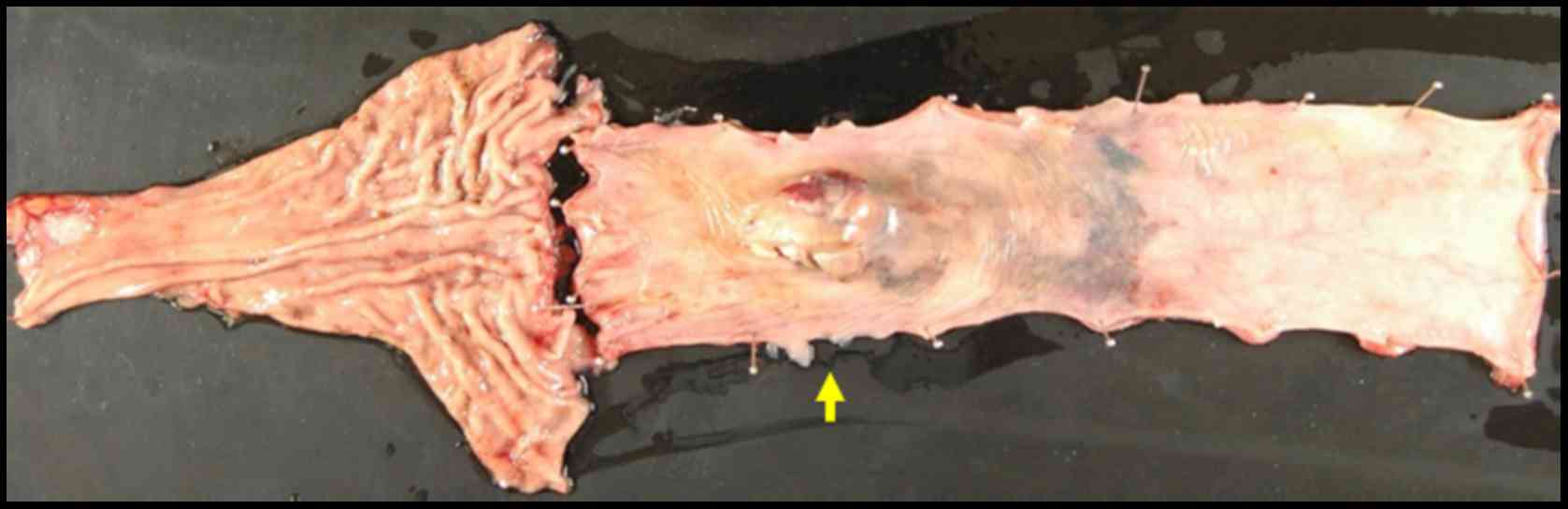
pM0. The resected specimen showed an elevated polypoid tumor 85×55
mm in size (Fig. 1).
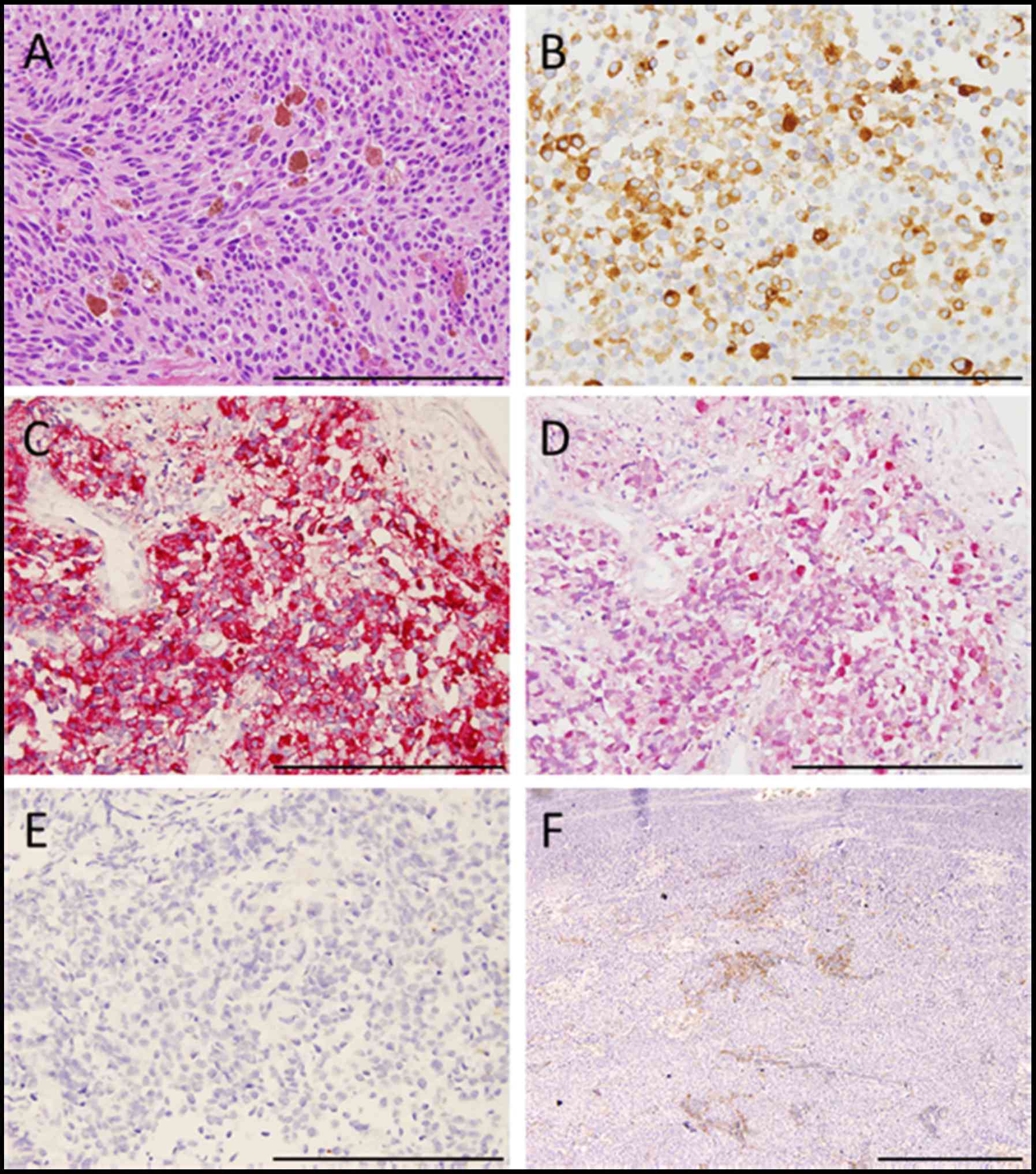
Histopathologically, tumor cells consisted of malignant large tumor
cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, and contained few
melanin granules on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining
(Fig. 2A). Subsequent
immunohistology revealed that the tumor cells were positive for
melan-A (Fig. 2B), HMB-45 (Fig. 2C), and S-100 (Fig. 2D) and negative for cytokeratin
markers, AE1/AE3 (Fig. 2E),
resulting in a diagnosis of PMME. Further analysis revealed a
membranous staining pattern for programmed death ligand 1(PD-L1)
(Fig. 2F). The percentage of PD-L1
positive tumor cells within resected specimen was ~10% (anti-PD-L1
antibody; clone 28-8; ab205921; Abcam). No BRAF mutations were
detected by direct sequencing analysis. Paclitaxel and S-1, an oral
dihydropyrimidine-dehydrogenase-inhibitory fluoropyrimidine, were
administered for 2 months as adjuvant therapy based on the results
of a histoculture drug response assay (HDRA), which is a clinically
practical in vitro drug-response assay for identifying
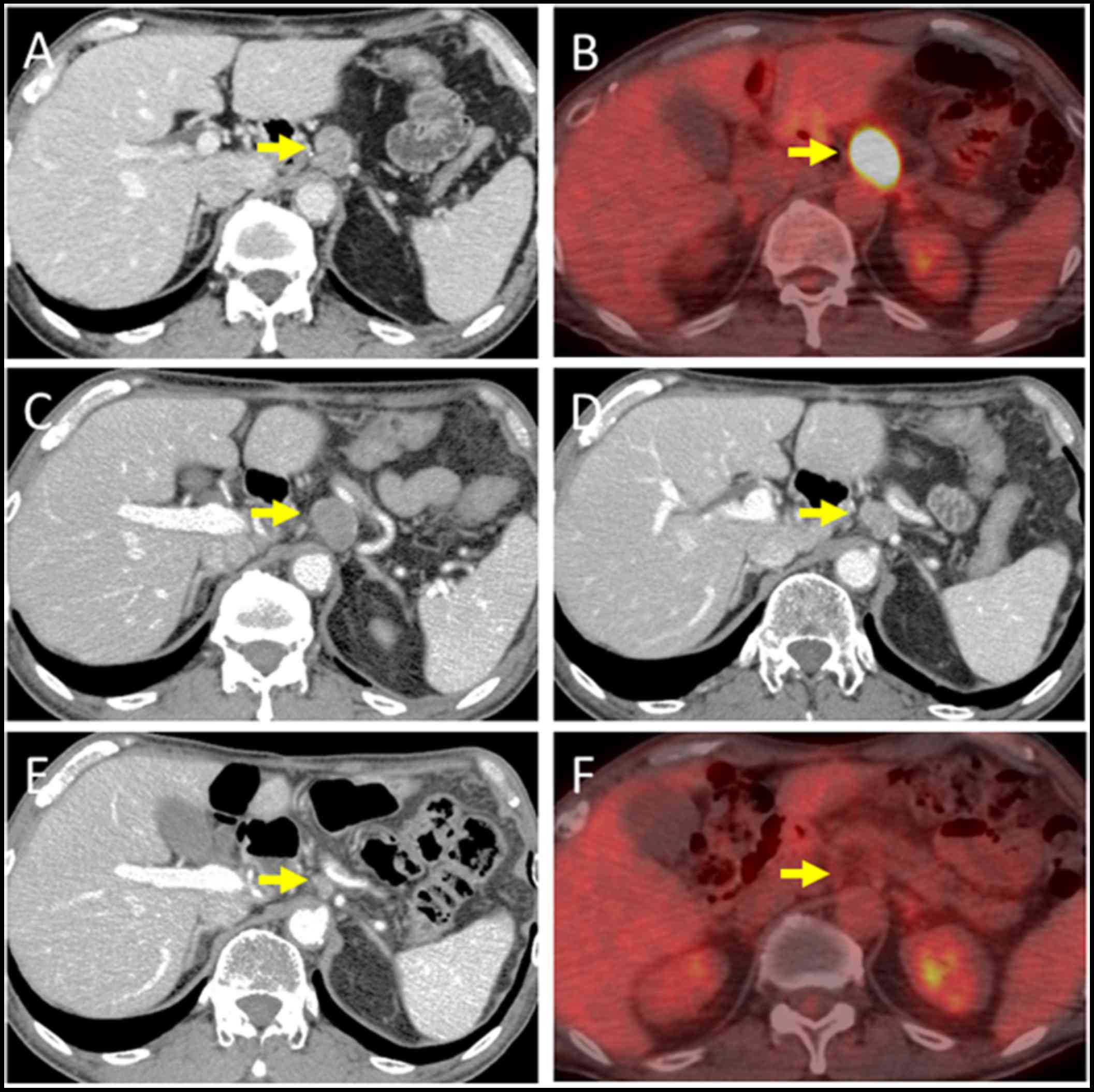
optimal anticancer agents. Eight months after surgery, computed
tomography (CT) revealed a 19-mm-diameter, oval-shaped mass in the
LN around the celiac axis (Fig. 3A),
and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission
tomography/CT (FDG-PET/CT) showed intense FDG uptake in the lesion
(Fig. 3B). No abnormal uptake was
found at any other site of the body. Thus, based on imaging study
findings, we diagnosed recurrence of disease in the LN around the
celiac axis. The level of 5-S-CD was 12.6 nmol/l (reference value,
1.5–8 nmol/l) at the time of diagnosis of recurrent disease.
Although there was only one site of recurrence, we first initiated
nonoperative management because of a high rate of relapse. The
patient received the first treatment session with dacarbazine
(1,000 mg/m2, day 1) and interferon β (300 units/day,
days 1–10); no substantial adverse effects were observed. CT
performed after 4 courses after chemotherapy revealed progressive
disease (PD) of the metastatic LN lesion according to response
evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST) (Fig. 3C). Second, nivolumab, an anti-PD-1
antibody, was administered at a dose of 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks.
After 8 treatment courses, CT revealed a partial response (PR) of
the LN lesion (Fig. 3D); however,
after 4 more treatment courses, CT revealed PD of the LN lesion.
During the first courses of nivolumab treatment, hyperthyroidism
was observed, and predonizoron and potassium iodide were used to
treat hyperthyroidism. Third, hypofractionated radiotherapy (RT)
(4,000 cGy divided in 8 fractions) was targeted at the metastatic
LN and resulted in a PR (Fig. 3E and
F); no substantial adverse effects were observed. Fourth,
ipilimumab, an anti-CTLA-4 antibody, was given at a dose of 3
mg/kg. After initial administration of ipilimumab, grade 3
peripheral neuropathy [defined by National Cancer Institute Common
Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE), version 4.0]
was recognized; thereafter, ipilimumab was not administered.
Eighteen months after treatment for the metastatic LN, the LN
decreased in size, and there were no other signs of metastasis to
other organs. The patient then underwent laparoscopic celiac axis
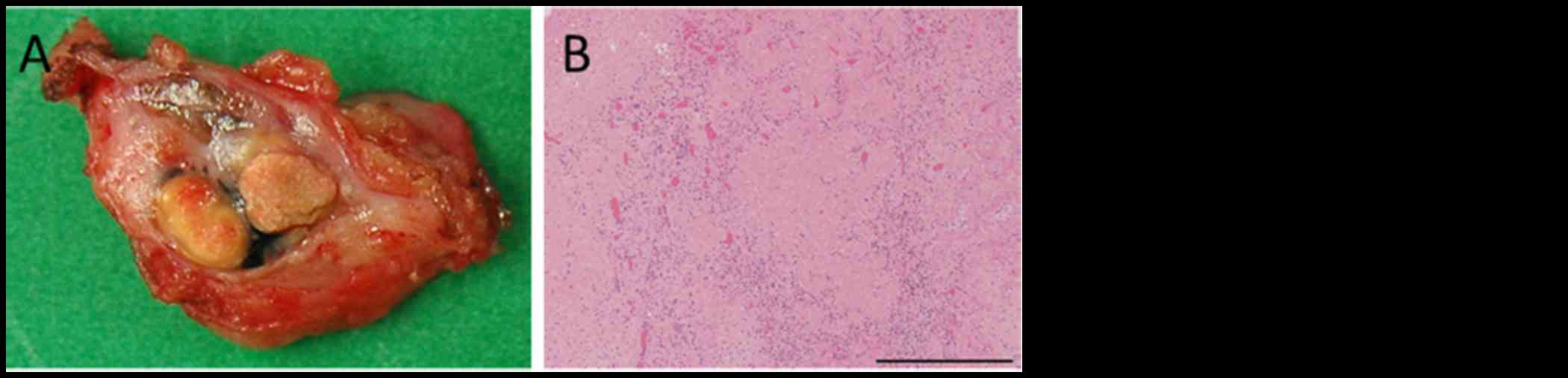
lymphadenectomy, and had no post-operative complications.
Pathologic examination of the surgical specimens identified no
viable melanoma cells (Fig. 4A and
B). Eight months after surgery, he is free from evidence of
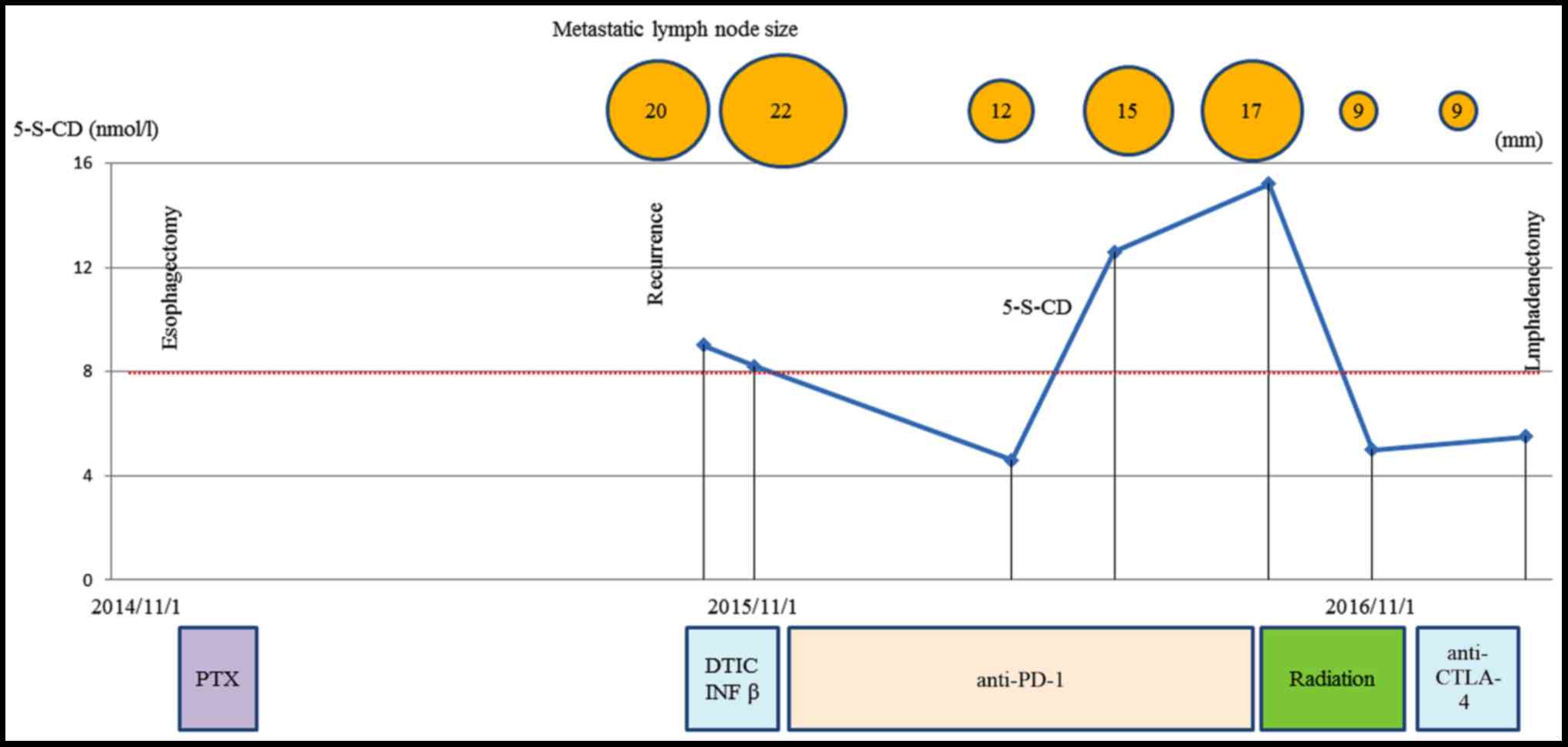
local and distant disease recurrence (Fig. 4C). shows the clinical course and
changes in the tumor marker 5-S-CD and in tumor size is shown in
Fig. 5. Written informed consent was
obtained from the patient.
Discussion
Metastatic melanoma is particularly difficult to
cure because it shows resistance to therapies. An abdominal LN
metastasis was detected 8 months after surgery, although the
present case received adjuvant therapy for the prevention of cancer
recurrence. Despite recent advances in melanoma treatment,
interferon alpha is the only therapy currently licensed for the
adjuvant treatment of melanoma, with documented success in
improving recurrence-free survival and, to a lesser extent, overall
survival (OS) (6). Therefore,
adjuvant treatment based on the results of HDRA, which was
developed as an in vitro drug-response assay for choosing
anticancer agents (7), was given.
The tumor inhibition rates of chemotherapy agents evaluated by the
HDRA were found to be predictive of the response of various types
of cancer to chemotherapy (8–10).
Conventionally, a cytotoxic agent such as dacarbazine has been used
for metastatic malignant melanoma. However, it is hard to say that
dacarbazine has a high response rate. Inhibition of the PD-1
pathway by nivolumab improves OS compared with dacarbazine in
advanced melanoma (5). Primary
anorectal (11) and lung (12) malignant melanomas successfully
treated with nivolumab were reported; however, to the best of our
knowledge, this is the first case report regarding the
administration of anti-PD-1 antibody followed by definitive
hypofractionated RT for recurrent PMME. We administered dacarbazine
as first-line therapy; however, we considered that dacarbazine
therapy was not effective, and we started nivolumab as a
second-line therapy. Nivolumab markedly reduced the tumor size. In
this case, PD-L1 expression in tumor cells supported a response to
nivolumab. Although malignant melanoma is generally considered to
be radioresistant, hypofractionated RT led to a favorable outcome.
Preclinical evidence suggests that PD-1 blockade may interact with
RT to improve local tumor control in melanoma (13) and survival in glioma (14) in a variety of radiation dose and
fractionation schema in breast cancer (15). Furthermore, Park et al
reported that PD-1 blockade or deficiency can synergize with local
radiotherapy to induce tumor-specific CD8-positive T-cell immunity
(16). Only 3 clinical studies
reported to date have focused on the relationship between anti-PD-1
antibody and RT. A retrospective cohort study reported that control
of distant brain metastases and OS may be improved with anti-PD-1
antibody therapy and stereotactic RT compared with RT and/or
surgery alone. Control of distant brain metastases and OS were not
affected by the timing of anti-PD-1 antibody administration before,
during or after stereotactic RT (17). A case series reported that
neoadjuvant treatment for stage III/IV melanoma with anti-PD-1
antibody and hypofractionated RT had substantial clinical benefit
without significant toxicity (18).
A case report showed an abscopal effect, a rare phenomenon of tumor
regression at a site distant from the primary site of radiotherapy
(19), when radiotherapy was added
to ongoing anti-CTLA-4 antibody therapy in a patient with melanoma
(20). Prospective clinical studies
of RT and anti-PD-1 antibody therapy in patients with melanoma and
other malignancies are warranted. Anti-CTLA4 antibody therapy was
additionally performed, although anti-PD-1 antibody therapy and RT
have resulted in a PR. PMME is an extremely difficult malignancy
because of early hematogenous and lymphatic metastases. Therefore,
we did not intend to perform lymphadenectomy at first, and
performed anti-CTLA4 antibody therapy to obtain complete response.
However, severe peripheral neuropathy was recognized at the initial
dose, and we determined to perform lymphadenectomy. The limitation
of this case study is that we have not been able to show if
anti-PD1 antibody was effective against PMME. Total remission was
achieved rather after radiotherapy, however, we think that not only
radiotherapy but also multidisciplinary therapy including anti-PD-1
antibody therapy were effective for PMME in this case because
malignant melanoma is generally considered to be radioresistant,
and there are some reports about synergic effect of RT and
anti-PD-1 antibody (13–18).
In conclusion, we report the first case of recurrent
PMME to be treated with combinations of chemotherapy,
immunotherapy, RT and laparoscopic lymphadenectomy. This finding
indicates that the combination of cytotoxic and molecular-targeted
chemotherapy and RT may be suitable for select patients with
metastatic PMME. Additional studies are needed to establish the
usefulness of anti-PD-1antibody therapy for metastatic PMME.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
PMME
|
primary malignant melanoma of the
esophagus
|
|
PD-1
|
programmed death 1
|
|
CTLA-4
|
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated
antigen 4
|
|
PD-L1
|
programmed death ligand 1
|
|
CT
|
computed tomography
|
|
PD
|
progressive disease
|
|
RECIST
|
response evaluation criteria in solid
tumors
|
|
PR
|
partial response
|
|
RT
|
radiotherapy
|
|
OS
|
overall survival
|
References
|
1
|
Makuuchi H, Takubo K, Yanagisawa A and
Yamamoto S: Esophageal malignant melanoma: Analysis of 134 cases
collected by the Japan Esophageal Society. Esophagus. 12:158–169.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Terada T: A clinicopathologic study of
esophageal 860 benign and malignant lesions in 910 cases of
consecutive esophageal biopsies. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:191–198.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sabanathan S, Eng J and Pradhan GN:
Primary malignant melanoma of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol.
84:1475–1481. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weber JS, D'Angelo SP, Minor D, Hodi FS,
Gutzmer R, Neyns B, Hoeller C, Khushalani NI, Miller WH Jr, Lao CD,
et al: Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced
melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate
037): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 16:375–384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, Dutriaux C,
Maio M, Mortier L, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, McNeil C,
Kalinka-Warzocha E, et al: Nivolumab in previously untreated
melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 372:320–330. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mocellin S, Pasquali S, Rossi CR and Nitti
D: Interferon alpha adjuvant therapy in patients with high-risk
melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:493–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Furukawa T, Kubota T, Watanabe M, Takahara
T, Yamaguchi H, Takeuchi T, Kase S, Kodaira S, Ishibiki K, Kitajima
M, et al: High in vitro-in vivo correlation of drug response using
sponge-gel-supported three-dimensional histoculture and the MTT end
point. Int J Cancer. 51:489–498. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Furukawa T, Kubota T and Hoffman RM:
Clinical applications of the histoculture drug response assay. Clin
Cancer Res. 1:305–311. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kubota T, Sasano N, Abe O, et al:
Potential of the histoculture drug-response assay to contribute to
cancer patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 1:1537–1543.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fujita Y, Hiramatsu M, Kawai M, Nishimura
H, Miyamoto A and Tanigawa N: Histoculture drug response assay
predicts the postoperative prognosis of patients with esophageal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 21:499–505. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tokuhara K, Nakatani K, Tanimura H,
Yoshioka K, Kiyohara T and Kon M: A first reported case of
metastatic anorectal amelanotic melanoma with a marked response to
anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep.
31:188–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hirai I, Tanese K, Obata S and Funakoshi
T: A case of primary malignant melanoma of the lung responded to
anti-PD-1 antibody therapy. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
33:1–3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liang H, Deng L, Chmura S, Burnette B,
Liadis N, Darga T, Beckett MA, Lingen MW, Witt M, Weichselbaum RR,
et al: Radiation-induced equilibrium is a balance between tumor
cell proliferation and T cell–mediated killing. J Immunol.
190:5874–5881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng J, See AP, Phallen J, et al:
Anti-PD-1 blockade and stereotactic radiation produce long-term
survival in mice with intracranial gliomas. International Journal
of Radiation Oncol Biol Phys. 86:343–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Verbrugge I, Hagekyriakou J, Sharp LL,
Galli M, West A, McLaughlin NM, Duret H, Yagita H, Johnstone RW,
Smyth MJ, et al: Radiotherapy increases the permissiveness of
established mammary tumors to rejection by immunomodulatory
antibodies. Cancer Res. 72:3163–3174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park SS, Dong H, Liu X, Harrington SM,
Krco CJ, Grams MP, Mansfield AS, Furutani KM, Olivier KR and Kwon
ED: PD-1 restrains radiotherapy-induced abscopal effect. Cancer
Immunol Res. 3:610–619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ahmed KA, Stallworth DG, Kim Y, Johnstone
PAS, Harrison LB, Caudell JJ, Yu HHM, Etame AB, Weber JS and Gibney
GT: Clinical outcomes of melanoma brain metastases treated with
stereotactic radiation and anti-PD-1 therapy. Ann Oncol.
27:434–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alevizakos M, Ollila DW, Chera BS, Dodd
LG, Kish JB and Moschos SJ: Combined modality neoadjuvant treatment
for stage III/IV melanoma with PD-1 blockade plus radiation: A case
series. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 10:12–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mole R: Whole body
irradiation-Radiobiology or medicine? Br J Radiol. 26:234–241.
1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Postow MA, Callahan MK, Barker CA, Yamada
Y, Yuan J, Kitano S, Mu Z, Rasalan T, Adamow M, Ritter E, et al:
Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 366:925–931. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|