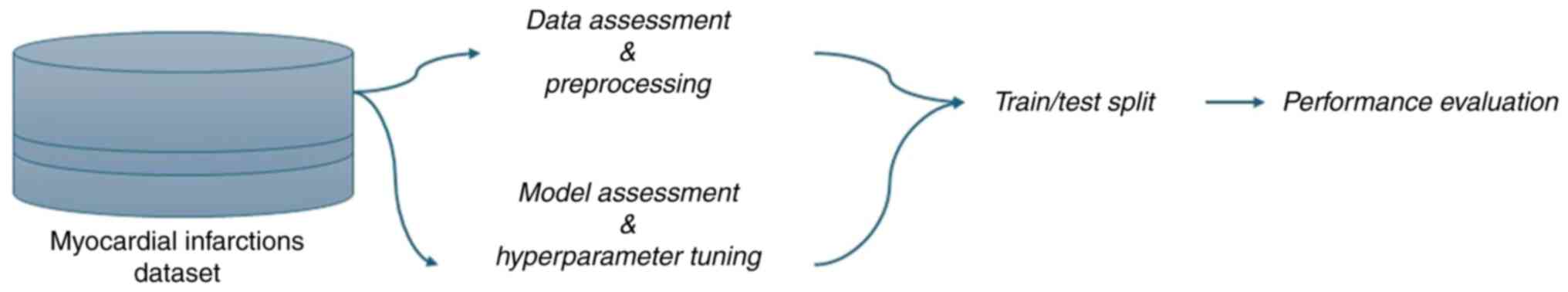
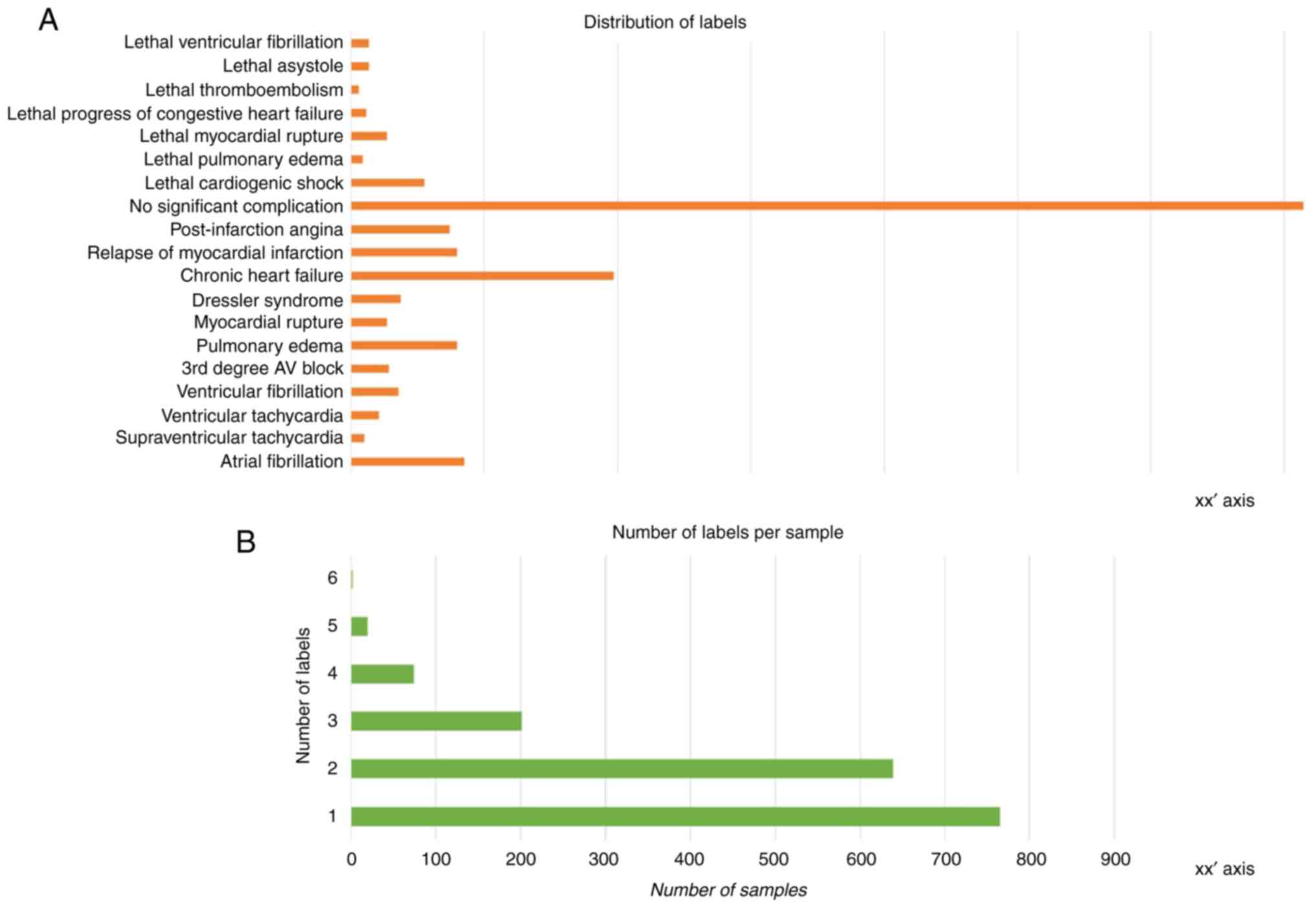
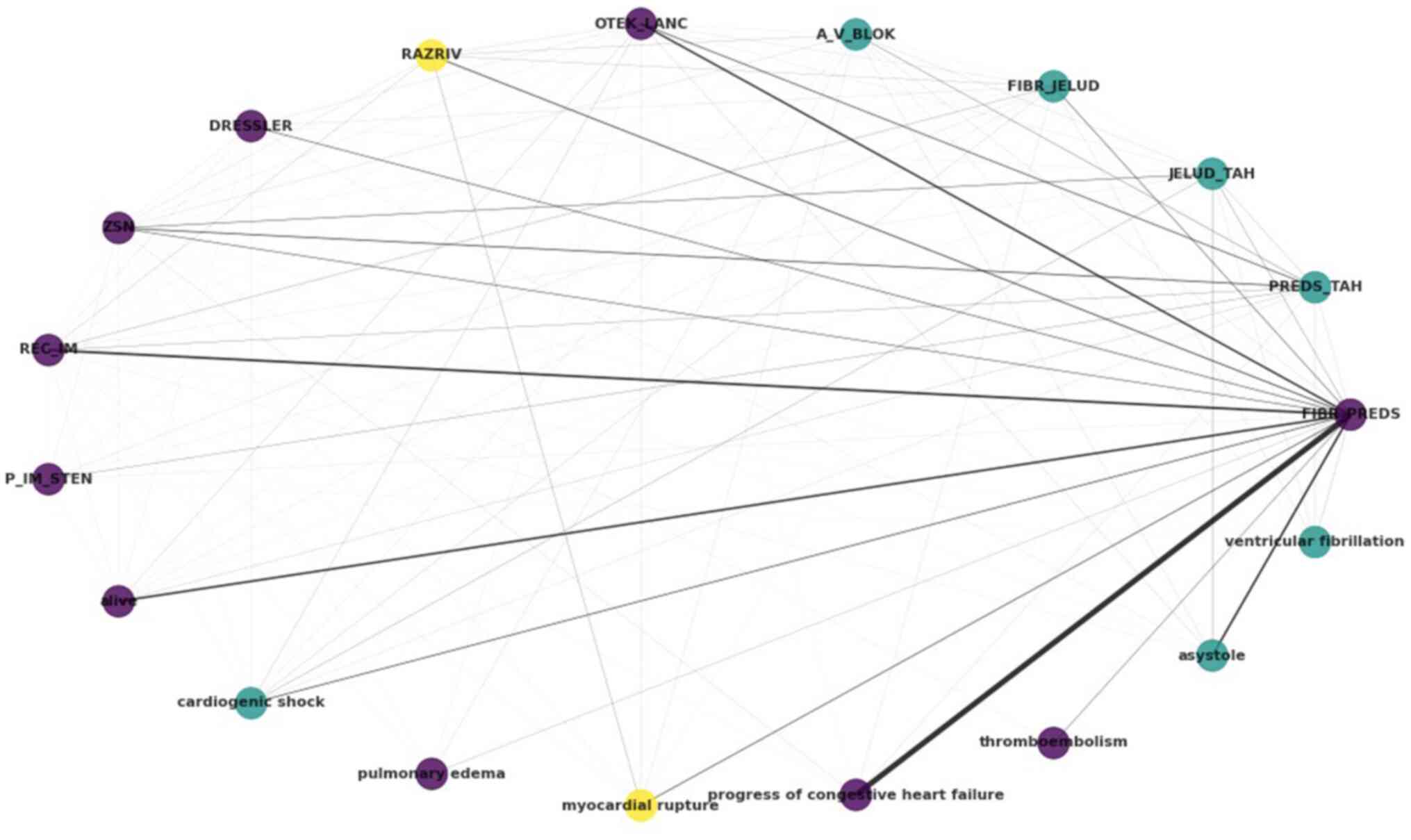
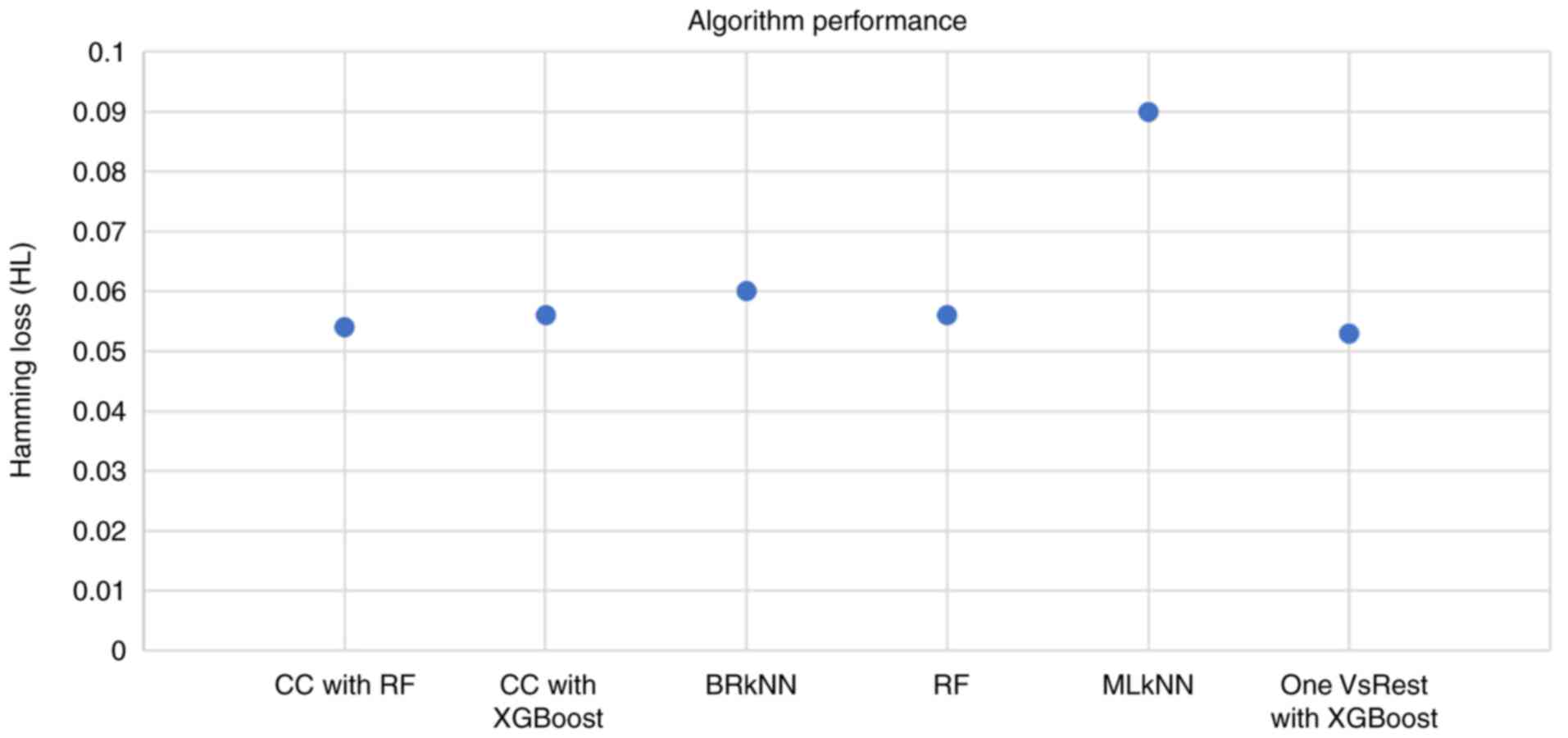
|
1
|
Anderson JR: Machine learning: an
artificial intelligence approach. Elsevier Science, 1983.
|
|
2
|
Russell S and Norvig P: Artificial
intelligence: A modern approach. 3rd edition. Prentice-Hall, Upper
Saddle River, 2010.
|
|
3
|
Somani P and Kaur G: A review on
supervised learning algorithms. Int J Adv Sci Technol.
29:2551–2559. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Singh P: Supervised machine learning. In:
Learn PySpark: Build Python-based Machine Learning and Deep
Learning Models. Singh P (ed). Apress, Berkeley, CA, pp117-159,
2019.
|
|
5
|
Gentleman R and Carey VJ: Unsupervised
machine learning. In: Bioconductor Case Studies. Hahne F, Huber W,
Gentleman R and Falcon S (eds). Springer New York, New York, NY,
pp137-157, 2008.
|
|
6
|
Hady MFA and Schwenker F: Semi-supervised
Learning. In: Handbook on Neural Information Processing. Bianchini
M, Maggini M and Jain LC (eds). Intelligent Systems Reference
Library. Vol. 49. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp215-239,
2013.
|
|
7
|
Sutton RS and Barto AG: Reinforcement
learning: An introduction. MIT Press, 2018.
|
|
8
|
Lee D, Seo H and Jung MW: Neural basis of
reinforcement learning and decision making. Annu Rev Neurosci.
35:287–308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Czarnul P, Proficz J and Krzywaniak A:
Energy-aware high-performance computing: Survey of state-of-the-art
tools, techniques, and environments. Sci Program.
2019(8348791)2019.
|
|
10
|
Mascetti L, Arsuaga Rios M, Bocchi E,
Vicente JC, Cheong BCK, Castro D, Collet J, Contescu C, Labrador
HG, Iven J, et al: CERN disk storage services: Report from last
data taking, evolution and future outlook towards Exabyte-scale
storage. EPJ Web Conf. 245(04038)2020.
|
|
11
|
Amin R, Vadlamudi S and Rahaman MM:
Opportunities and challenges of data migration in cloud. Eng Int.
9:41–50. 2021.
|
|
12
|
Dash S, Shakyawar SK, Sharma M and Kaushik
S: Big data in healthcare: Management, analysis and future
prospects. J Big Data. 6(54)2019.
|
|
13
|
Wachter RM: Chapter 11. Other
complications of healthcare. In: Understanding Patient Safety, 2e.
The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York, NY, 2012.
|
|
14
|
Ghosheh GO, Alamad B, Yang KW, Syed F,
Hayat N, Iqbal I, Al Kindi F, Al Junaibi S, Al Safi M, Ali R, et
al: Clinical prediction system of complications among patients with
COVID-19: A development and validation retrospective multicentre
study during first wave of the pandemic. Intell Based Med.
6(100065)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
van Smeden M, Reitsma JB, Riley RD,
Collins GS and Moons KG: Clinical prediction models: Diagnosis
versus prognosis. J Clin Epidemiol. 132:142–145. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
de Souza FSH, Hojo-Souza NS, dos Santos
EB, da Silva CM and Guidoni DL: Predicting the disease outcome in
COVID-19 positive patients through machine learning: A
retrospective cohort study with Brazilian data. medRxiv:
2020.2006.2026.20140764, 2020.
|
|
17
|
Ezzoddin M, Nasiri H and Dorrigiv M:
Diagnosis of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images using deep
neural network and LightGBM. IEEE, 2022.
|
|
18
|
Pathak Y, Shukla PK, Tiwari A, Stalin S
and Singh S: Deep transfer learning-based classification model for
COVID-19 disease. IRBM. 43:87–92. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yuan B: Towards a clinical efficacy
evaluation system adapted for personalized medicine. Pharmgenomics
Pers Med. 14:487–496. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kotsiantis SB, Zaharakis ID and Pintelas
PE: Machine learning: A review of classification and combining
techniques. Artif Intell Rev. 26:159–190. 2006.
|
|
21
|
Wei Y, Xia W, Huang J, Ni B, dong J, Zhao
Y and Yan S: CNN: Single-label to multi-label. ArXiv:
abs/1406.5726, 2014.
|
|
22
|
Soofi AA and Awan A: Classification
techniques in machine learning: Applications and issues. J Basic
Appl Sci. 13:459–465. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Tsoumakas G and Katakis I: Multi-label
classification: An overview. Int J Data Warehous Min. 3:1–13.
2009.
|
|
24
|
Herrera F, Charte F, Rivera AJ and del
Jesus MJ: Multilabel classification. In: Multilabel Classification:
Problem Analysis, Metrics and Techniques. Herrera F, Charte F,
Rivera AJ and del Jesus MJ (eds). Springer International
Publishing, Cham, pp17-31, 2016.
|
|
25
|
Sun Y, Wong AKC and Kamel MS:
Classification of imbalanced data: A review. Int J Pattern Recognit
Artif Intell. 23:687–719. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Tarekegn AN, Giacobini M and Michalak K: A
review of methods for imbalanced multi-label classification.
Pattern Recognit. 118(107965)2021.
|
|
27
|
Charte F, Rivera AJ, del Jesus MJ and
Herrera F: Dealing with difficult minority labels in imbalanced
mutilabel data sets. Neurocomputing. 326-327:39–53. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Charte F, Rivera A, del Jesus MJ and
Herrera F: A first approach to deal with imbalance in multi-label
datasets. In: Pan JS, Polycarpou MM, Woźniak M, de Carvalho ACPLF,
Quintián H and Corchado E (eds). Hybrid Artificial Intelligent
Systems. HAIS 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 8073.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp150-160, 2013.
|
|
29
|
Huang Y, Giledereli B, Köksal A, Ozgur A
and Ozkirimli E: Balancing methods for multi-label text
classification with long-tailed class distribution. arXiv:
2109.04712, 2021.
|
|
30
|
Giraldo Forero AF, Jaramillo-Garzón J,
Ruiz-Muñoz J and Castellanos-Dominguez G: Managing Imbalanced Data
Sets in Multi-label Problems: A Case Study with the SMOTE
Algorithm. In: Ruiz-Shulcloper J, Sanniti di Baja G (eds). Progress
in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and
Applications. CIARP 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol.
8258. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp334-342, 2013.
|
|
31
|
Tahir MA, Kittler J and Bouridane A:
Multilabel classification using heterogeneous ensemble of
multi-label classifiers. Pattern Recognit Lett. 33:513–523.
2012.
|
|
32
|
Cao P, Liu X, Zhao D and Zaiane O: Cost
sensitive ranking support vector machine for multi-label data
learning. In: Abraham A, Haqiq A, Alimi A, Mezzour G, Rokbani N and
Muda A (eds). Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on
Hybrid Intelligent Systems (HIS 2016). HIS 2016. Advances in
Intelligent Systems and Computing. Vol. 552. Springer, Cham,
pp244-255, 2017.
|
|
33
|
Saleh M and Ambrose JA: Understanding
myocardial infarction. F1000Res. 7(1378)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
World Health Organization: Cardiovascular
diseases, 2022.
|
|
35
|
Badimon L and Vilahur G: Thrombosis
formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J Intern
Med. 276:618–632. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Asada Y, Yamashita A, Sato Y and
Hatakeyama K: Thrombus formation and propagation in the onset of
cardiovascular events. J Atheroscler Thromb. 25:653–664.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shavadia JS, Chen AY, Fanaroff AC, de
Lemos JA, Kontos MC and Wang TY: Intensive care utilization in
stable patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
treated with rapid reperfusion. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 12:709–717.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Abrignani MG, Dominguez LJ, Biondo G, Di
Girolamo A, Novo G, Barbagallo M, Braschi A, Braschi G and Novo S:
In-hospital complications of acute myocardial infarction in
hypertensive subjects. Am J Hypertens. 18:165–170. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Malla RR and Sayami A: In hospital
complications and mortality of patients of inferior wall myocardial
infarction with right ventricular infarction. JNMA J Nepal Med
Assoc. 46:99–102. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Babaev A, Frederick PD, Pasta DJ, Every N,
Sichrovsky T and Hochman JS: NRMI Investigators. Trends in
management and outcomes of patients with acute myocardial
infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. JAMA. 294:448–454.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Golovenkin SE, Gorban A, Mirkes E, Shulman
VA, Rossiev DA, Shesternya PA, Nikulina SY, Orlova YV and Dorrer
MG: Myocardial infarction complications Database. Journal,
2020.
|
|
42
|
Yang J and Leskovec J: Defining and
evaluating network communities based on ground-truth. Knowl Inf
Syst. 42:181–213. 2015.
|
|
43
|
Huang SJ and Zhou ZH: Multi-label learning
by exploiting label correlations locally. Proc AAAI Conf Artif
Intell. 26:949–955. 2021.
|
|
44
|
Chakravarty A, Sarkar T, Ghosh N,
Sethuraman R and Sheet D: Learning decision ensemble using a graph
neural network for comorbidity aware chest radiograph screening.
Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020:1234–1237.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Szymański P, Kajdanowicz T and Kersting K:
How is a data-driven approach better than random choice in label
space division for multi-label classification? Entropy.
18(282)2016.
|
|
46
|
Blondel VD, Guillaume JL, Lambiotte R and
Lefebvre E: Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat
Mech. 2008(P10008)2008.
|
|
47
|
Hagberg A, Swart PJ and Chult DA:
Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX,
2008.
|
|
48
|
Goutte C and Gaussier E: A probabilistic
interpretation of precision, recall and F-score, with implication
for evaluation. In: Losada DE, Fernández-Luna JM (eds). Advances in
Information Retrieval. ECIR 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science. Vol. 3408. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp345-359,
2005.
|
|
49
|
Qin T: Machine learning basics. In: Dual
Learning. Qin T (ed). Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp11-23,
2020.
|
|
50
|
Sorower MS: A literature survey on
algorithms for multi-label learning. Oregon State University,
Corvallis, 2010.
|
|
51
|
Wu J, Chen XY, Zhang H, Xiong LD, Lei H
and Deng SH: Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning
models based on bayesian optimizationb. J Electron Sci Technol.
17:26–40. 2019.
|
|
52
|
Liashchynskyi P and Liashchynskyi P: Grid
search, random search, genetic algorithm: A big comparison for NAS.
arXiv: 1912.06059, 2019.
|
|
53
|
Feurer M and Hutter F: Hyperparameter
optimization. In: Automated Machine Learning: Methods, Systems,
Challenges. Hutter F, Kotthoff L and Vanschoren J (eds). Springer
International Publishing, Cham, pp3-33, 2019.
|
|
54
|
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A,
Michel V and Thirion B: Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J
Mach Learn Res. 12:2825–2830. 2011.
|
|
55
|
Chen T and Guestrin C: XGBoost: A scalable
tree boosting system. KDD ‘16: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD
International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining,
pp785-794, 2016.
|
|
56
|
Mason L, Baxter J, Bartlett P and Frean M:
Boosting algorithms as gradient descent. Adv Neural Inf Process
Syst. 12:1999.
|
|
57
|
Boehmke B and Greenwell B: Hands-on
Machine Learning with R. Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, NY,
pp221-246, 2019.
|
|
58
|
Medar R, Rajpurohit VS and Rashmi B:
Impact of training and testing data splits on accuracy of time
series forecasting in machine learning. In: 2017 International
Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation
(ICCUBEA). IEEE, pp1-6. 2017.
|
|
59
|
Sarker IH: Machine learning: Algorithms,
real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput Sci.
2(160)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Nti I, Nyarko-Boateng O and Aning J:
Performance of machine learning algorithms with different K values
in K-fold cross-validation. Int J Inf Technol and Comp Sci.
6:61–71. 2021.
|
|
61
|
Refaeilzadeh P, Tang L and Liu H:
Cross-validation. In: Encyclopedia of Database Systems. Liu L and
ÖZsu MT (eds). Springer US, Boston, MA, pp532-538, 2009.
|
|
62
|
Sechidis K, Tsoumakas G and Vlahavas I: On
the Stratification of Multi-label. Data. In: Gunopulos D, Hofmann
T, Malerba D and Vazirgiannis M (eds). Machine Learning and
Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2011. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science. Vol. 6913. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg,
pp145-458, 2011.
|
|
63
|
Szymański P and Kajdanowicz T: A network
perspective on stratification of multi-label data. Proc Mach Learn
Res. 74:22–35. 2017.
|
|
64
|
Li W, Liu Y, Liu W, Tang ZR, Dong S, Li W,
Zhang K, Xu C, Hu Z, Wang H, et al: Machine learning-based
prediction of lymph node metastasis among osteosarcoma patients.
Front Oncol. 12(797103)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Tang Z, Wong HS and Yu Z:
Privacy-preserving federated learning with domain adaptation for
multi-disease ocular disease recognition. IEEE J Biomed Health
Inform. 28:3219–3227. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Chawla NV: Data mining for imbalanced
datasets: An overview. In: Maimon O, Rokach L (eds). Data Mining
and Knowledge Discovery Handbook. Springer, Boston, MA, pp853-867,
2005.
|
|
67
|
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO and
Kegelmeyer WP: SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J
Artif Intell Res. 16:321–357. 2002.
|