|
1
|
Hashimoto S, Kawamura J, Yamamoto T,
Kinoshita A, Segawa Y, Harada Y and Suenaga T: Transient myoclonic
state with asterixis in elderly patients: A new syndrome? J Neurol
Sci. 109:132–139. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
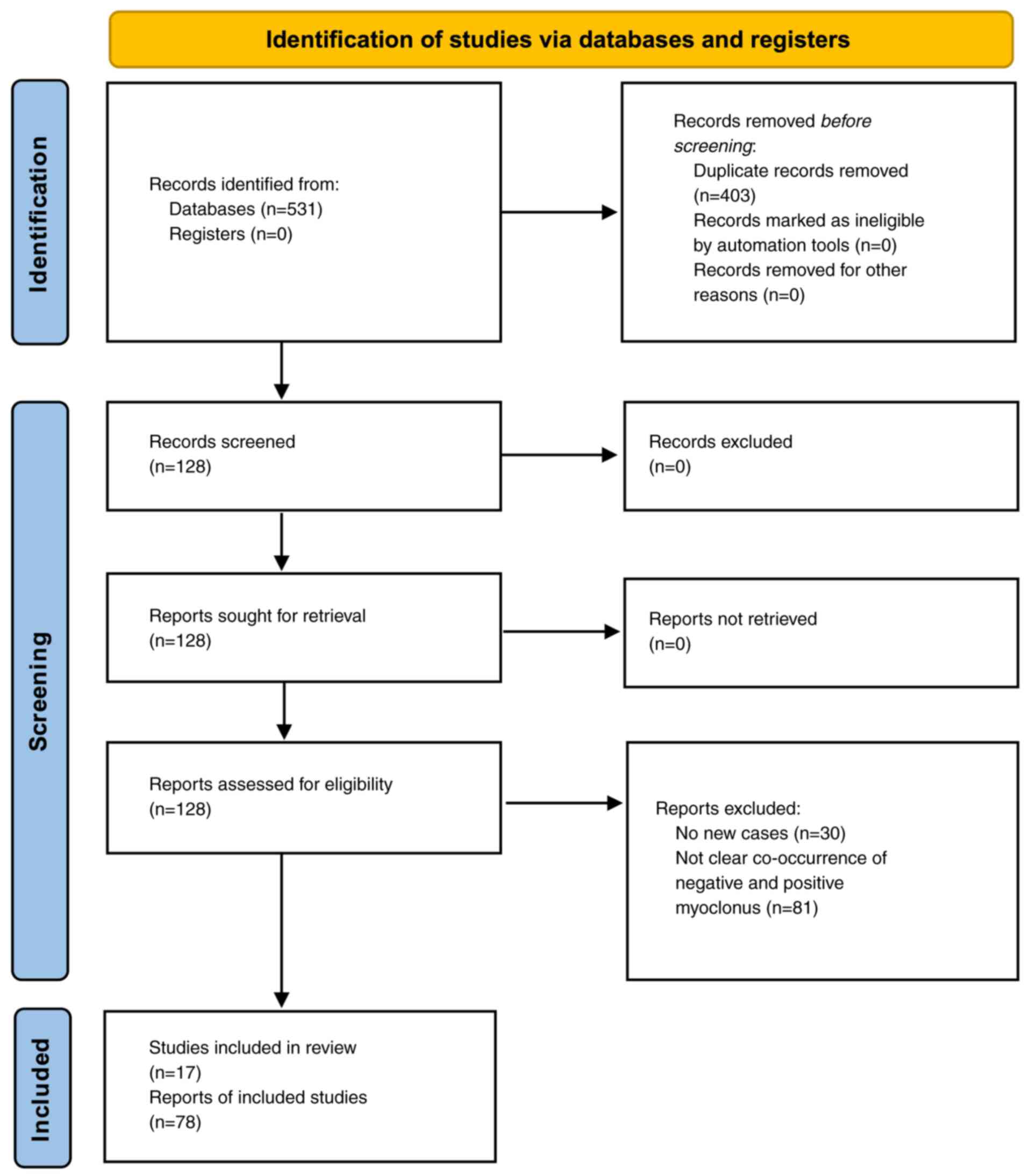
2
|
Mizutani T, Ida M, Egarashi O, Daida H and
Shiozawa R: Recurrent myoclonus associated with Epstein-Barr virus
infection in an elderly patient. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 26:1042–1046.
1986.PubMed/NCBI(In Japanese).
|
|
3
|
Doden T, Sato H and Hashimoto T: Clinical
characteristics and etiology of transient myoclonic state in the
elderly. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 139:192–198. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shibasaki H and Hallett M:
Electrophysiological studies of myoclonus. Muscle Nerve.
31:157–174. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Thomas B and Frucht SJ: Myoclonus: An
update. Curr Opin Neurol. 37:421–425. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kojovic M, Cordivari C and Bhatia K:
Myoclonic disorders: A practical approach for diagnosis and
treatment. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 4:47–62. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hiraga A, Kamitsukasa I and Kuwabara S:
Isolated transient myoclonus in the elderly: An under-recognized
condition? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 117:51–54. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Harada T, Yamasato K, Nakanishi T and
Nakai M: In-hospital onset of transient myoclonic state in older
adults: A case report. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med.
11(004254)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
De Vries E, Schoonvelde M and Schumacher
G: No longer lost in translation: Evidence that google translate
works for comparative bag-of-words text applications. Polit Anal.
26:417–430. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ma LL, Wang YY, Yang ZH, Huang D, Weng H
and Zeng XT: Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools
for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which
is better? Mil Med Res. 7(7)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Negoro K, Fukusako T, Tsuda N, Nogaki H
and Morimatsu M: Clinical analysis of benign transient
shuddering-like involuntary movement in elderly people. Rinsho
Shinkeigaku. 34:1153–1156. 1994.PubMed/NCBI(In Japanese).
|
|
13
|
Fujihara K, Iwato K and Ohta M: Transient
involuntary shuddering movement in the aged. Neurol Med (Tokyo).
43(90)1995.
|
|
14
|
Hirata K, Kawamoto M, Takatsuka K,
Yoshikawa N and Kawamura J: Transient myoclonic state with
asterixis: A case report. Neurol Med (Tokyo). 46:53–56. 1997.
|
|
15
|
Iijima M, Osawa M and Iwata M: Transient
myoclonus-like involuntary movements in an elderly patient: A case
report. Neurol Med (Tokyo). 46:413–416. 1997.
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto A: Elevated serum amyloid A
protein in senile transient myoclonus. Neurol Med (Tokyo).
47(546)1997.
|
|
17
|
Kohono Y, Hayashi A, Ishii A, Hoshino S
and Shoji S: Two cases of benign transient shivering-like
involuntary movements. JMDD. 8:109–113. 1998.
|
|
18
|
Okuma Y, Komine M, Shimo Y, Miwa H and
Mizuno Y: Transient myoclonic state in elderly patients; clinical
and physiological study. Rinsho Nouha. 41:780–785. 1999.(In
Japanese).
|
|
19
|
Kawakami T: Transient myoclonic state with
asterixis. Neurol Med (Tokyo). 66:117–121. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Hitomi T, Ikeda A, Inouchi M, Imamura H,
Nakagawa T, Fumuro T, Matsumoto R and Takahashi R: Transient
myoclonic state with asterixis: Primary motor cortex
hyperexcitability is correlated with myoclonus. Intern Med.
50:2303–2309. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sethi NK: Isolated transient myoclonus in
the elderly-cortical vs subcortical. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
122(137)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Umemura A, Oeda T and Sawada H: Transient
myoclonic state with asterixis presenting as persistent
hyperperfusion on single-photon emission computed tomography: A
case report. Neurol Clin Neurosci. 3:101–102. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Tsuchiyama M, Yuasa R, Matsuura M and
Tomoda K: Transient myoclonic state with asterixis in elderly
patients. 2 cases of (Hashimoto). Rōka to shikkan (Ageing and
diseases). 8:1644–1646. 1995.https://jglobal.jst.go.jp/en/detail?JGLOBAL_ID=200902147153567053.
|
|
24
|
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P,
Ruiz I, Roberts EA, Janecek E, Domecq C and Greenblatt DJ: A method
for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 30:239–245. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hiraga A and Kuwabara S: Reply to letter
to the Editor: Isolated transient myoclonus in the elderly. Clin
Neurol Neurosurg. 120(142)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ugawa Y, Shimpo T and Mannen T:
Physiological analysis of asterixis: Silent period locked
averaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 52:89–93. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mima T, Nagamine T, Ikeda A, Yazawa S,
Kimura J and Shibasaki H: Pathogenesis of cortical myoclonus
studied by magnetoencephalography. Ann Neurol. 43:598–607.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lüders H: The effect of aging on the wave
form of the somatosensory cortical evoked potential.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 29:450–460. 1970.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tanosaki M, Ozaki I, Shimamura H, Baba M
and Matsunaga M: Effects of aging on central conduction in
somatosensory evoked potentials: Evaluation of onset versus peak
methods. Clin Neurophysiol. 110:2094–2103. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kanosue K, Zhang YH, Yanase-Fujiwara M and
Hosono T: Hypothalamic network for thermoregulatory shivering. Am J
Physiol. 267:R275–R282. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rissanen SM, Hyppönen J, Silvennoinen K,
Säisänen L, Karjalainen PA, Mervaala E and Kälviäinen R: Wearable
monitoring of positive and negative myoclonus in progressive
myoclonic epilepsy type 1. Clin Neurophysiol. 132:2464–2472.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chandarana M, Saraf U, Divya KP, Krishnan
S and Kishore A: Myoclonus-a review. Ann Indian Acad Neurol.
24:327–338. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Riva A, D’Onofrio G, Ferlazzo E,
Pascarella A, Pasini E, Franceschetti S, Panzica F, Canafoglia L,
Vignoli A, Coppola A, et al: Myoclonus: Differential diagnosis and
current management. Epilepsia Open. 9:486–500. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cantarín-Extremera V, Jiménez-Legido M,
Aguilera-Albesa S, Hedrera-Fernández A, Arrabal-Fernández L,
Gorría-Redondo N, Martí-Carrera I, Yoldi-Pedtri ME, Sagaseta-De
Ilúrdoz M and González-Gutiérrez-Solana L: Opsoclonus-myoclonus
syndrome: Clinical characteristics, therapeutic considerations, and
prognostic factors in a Spanish paediatric cohort. Neurologia (Engl
Ed): July 8, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
35
|
Rissardo JP, Fornari Caprara AL, Bhal N,
Repudi R, Zlatin L and Walker IM: Drug-induced myoclonus: A
systematic review. Medicina (Kaunas). 61(131)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shibasaki H: Neurophysiological
classification of myoclonus. Neurophysiol Clin. 36:267–269.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kakigi R and Shibasaki H: Generator
mechanisms of giant somatosensory evoked potentials in cortical
reflex myoclonus. Brain. 110:1359–1373. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hallett M, Chadwick D and Marsden CD:
Cortical reflex myoclonus. Neurology. 29:1107–1125. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Caraballo RH, Capovilla G, Vigevano F,
Beccaria F, Specchio N and Fejerman N: The spectrum of benign
myoclonus of early infancy: Clinical and neurophysiologic features
in 102 patients. Epilepsia. 50:1176–1183. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Capovilla G: Shaking body attacks: A new
type of benign non-epileptic attack in infancy. Epileptic Disord.
13:140–144. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Capovilla G, Montagnini A, Peruzzi C and
Beccaria F: Head atonic attacks: A new type of benign non-epileptic
attack in infancy strongly mimicking epilepsy. Epileptic Disord.
15:44–48. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Menozzi E, Balint B, Latorre A, Valente
EM, Rothwell JC and Bhatia KP: Twenty years on: Myoclonus-dystonia
and ε-sarcoglycan-neurodevelopment, channel, and signaling
dysfunction. Mov Disord. 34:1588–1601. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shibasaki H: Electrophysiological studies
of myoclonus. Muscle Nerve. 23:321–335. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|