Introduction
Liver transplantation, a surgical procedure used to
replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver allograft, is the
most commonly used technique for the treatment of liver failure and
end-stage liver disease (1,2). Due
to the limitations of this form of treatment, including a shortage
of donor organs, high technical difficulty and the requirement for
lifelong immunosuppression, cell therapy-based treatment strategies
have been developed (3,4). Terminally differentiated hepatocytes
exhibit powerful liver function of detoxification, metabolism and
synthesis. However, their availability and low expansion efficiency
in vitro are significant obstacles to hepatocyte
transplantation (5). Hepatic
progenitor cells (HPCs) are bipotential stem cells, which arise in
the liver and are capable of differentiation into either
hepatocytes or cholangiocytes, under the appropriate conditions.
Embryonic HPCs exhibit self-renewal and differentiation potential,
in addition to low immunogenicity, indicating that they may be a
useful alternative source of hepatocytes (6,7).
Although a number of researchers have reported that hepatic
progenitor cells are able to differentiate in vitro and
in vivo into hepatic cells with certain function, the
differentiation efficiency of these cells for use as a
transplantation substitute remains unclear (8,9).
Therefore, it is necessary to develop techniques to stably and
efficiently obtain mature functional hepatocytes from hepatic
progenitor cells.
5-azacytidine (5-azaC) is one of multiple DNA
methylase inhibitors that is able to reverse the methylation status
of a gene, and restore its expression (10), and is currently the only known
effective chemical compound with which to induce the
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) into myocardial
cells (11,12). Changes in DNA methylation status
affect the differentiation of stem cells (13,14).
The derivation of hepatic progenitor cells from embryonic fetal
liver cells is of value in the study of early human liver
organogenesis, as well as in the creation of an unlimited source of
donor cells for hepatocyte transplantation therapy (15). In the present study, it was
demonstrated that 5-azaC significantly increased the hepatic
differentiation of embryonic hepatic progenitor HP14.5 cells in the
hepatocyte induction medium. The present study assists in the
development of effective strategies to induce hepatic progenitor
cells differentiation and lays a foundation for the use of
progenitor cells as seed cells for liver transplantation in order
to treat disease resulting from liver injury.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and chemicals
HP14.5 cells were isolated from the livers of
embryonic mice at day 14.5 post coitus, and immortalized with SV40
large T antigen as described previously (16). HP14.5 cells were cultured in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Gibco Life Technologies,
Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum
(FBS, Gibco Life Technologies), 100 units/ml penicillin, and 100
μg/ml streptomycin at 37°C in 5% CO2. The hepatic
differentiation induction medium was composed of 0.1 μM
Dexmethesone (Dex)/10ng/ml Hepatic growth factor (HGF)/20 ng/ml
Fibroblast growth factor-4 (FGF4) and 2% horse serum (HS, Hyclone
Laboratories, Inc., Logan UT, USA) in DMEM. Unless indicated
otherwise, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St.
Louis, MO, USA).
Transfection of albumin promoter-driven
Gaussia luciferase (ALB-GLuc) reporter and Gaussia luciferase
reporter assay
HP14.5 cells were transfected with the pSEB-ALB-GLuc
reporter vector (17). To
construct pSEB-ALB-GLuc vector, the mouse ALB promoter gene was
amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and subcloned into
pSEB-GLuc retroviral vector to drive the expression of Gaussia
luciferase. Following 24 h of transfection, cells were replanted to
24-well plates and treated with 5-azaC at concentrations of 0, 0.1,
0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10 or 20 μmol/l, with or without hepatic
differentiation induction. Gaussia luciferase possesses a natural
secretory signal, which is secreted into the cell medium. Thus, at
the indicated time points, the medium was collected in order to
detect the activity of Gaussia luciferase, using a Gaussia
Luciferase Assay kit (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). Each
assay was performed in triplicate and three independent experiments
were conducted.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
(RT-q)PCR
As previously described (18), the total RNA from each of the
HP14.5 cell groups was extracted using the TRIzol (Invitrogen Life
Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) method. In order to generate cDNA
templates, 10 mcg of total RNA was reverse transcribed with random
hexamer pairs using Superscript II reverse transcriptase
(Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). PCR primers were
designed using the Primer3 program to amplify the gene of interest
(Table I). qPCR reactions were
conducted using a Bio-Rad protocol as follows: 94°Cfor 20 seconds,
55°C for 20 seconds, and 70°C for 20 seconds, for 40 cycles. Plates
were read after each cycle. Data were reported as the fold-change
with endogenous GAPDH normalization.
 | Table IRT-PCR primers (5′-3′). |
Table I
RT-PCR primers (5′-3′).
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|
| GAPDH |
GGCTGCCCAGAACATCAT |
CGGACACATTGGGGGTAG |
| DLK |
GCTGGGACGGGAAATTCT |
AACCCAGGTGTGCAGGAG |
| AFP |
ACGAGGAAAGCCCCTCAG |
GCCATTCCCTCACCACAG |
| ALB |
CCAGACATTCCCCAATGC |
CAAGTTCCGCCCTGTCAT |
| CK18 |
CTGGGCTCTGTGCGAACT |
ACAGAGCCACCCCAGACA |
| TAT |
ACCTTCAATCCCATCCGA |
TCCCGACTGGATAGGTAG |
| CYP7A1 |
GATTCTGATGCTGTCTTACTT |
CAATATCATTTAGTGGTGGC |
Western blot assay
Western blotting was performed as previously
described (18,19). Total proteins were extracted from
treated HP14.5 cells, which were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation
assay buffer with PMSF (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology,
Shanghai, China). Approximately 20 μg of total protein per
lane was electrophoretically separated on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide
gel (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) and then transferred to a
polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA).
The membrane was blocked with 5% non-fat milk in Tris-buffered
saline with Tween-20 (TBST; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at
room temperature for 1 h and incubated with rabbit anti-ALB
ployclonal antibody (1:200; cat. no. sc-50536; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) or mouse anti-β-actin
moloclonal antibody (1:200; cat. no sc-47778; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc.) antibodies at 4°C overnight. Following washing
with TBST, the membrane was probed with the appropriate secondary
antibody, conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA), at room temperature for 1 h.
Protein expression was visualized using enhanced Chemiluminescent
substrate (Kaiji, Nanjing, China) and exposed under the Syngene
GBox Imaging system (Syngene, Cambridge, UK).
Immunofluorescence Staining
Briefly, at 12 days following induction, cells were
fixed in ice-cold methanol for 15 min, permeabilized with 1% NP-40
and blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin. The cells were then
incubated with primary goat anti-Cytokeratin 18 (CK18; 1:100; cat.
no. sc-31700; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) or rabbit
anti-uridine diphosphategluc uronosyltransferase 1A (UGT1A)
polyclonal antibody (1:100; cat. no. sc-25847; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc.) at 4°C overnight, followed by probing with
DyLight 594- or 488-labelled secondary antibodies (Jackson
ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA, USA) at room
temperature for 30 min. Protein expression was examined under a
fluorescence microscope (Nikon Intensilight C-HGF1; Nikon, Tokyo,
Japan). Samples produced with control IgG were set up as negative
controls.
ICG uptake and release
Cells were cultured in 24-well plates. At 12 days
following treatment, cells were gently washed with PBS and
incubated in 0.5 ml of complete DMEM medium, supplemented with
1mg/ml freshly-prepared cardiogreen at 37°C for 1 h. DMEM medium
was then removed and the samples were gently washed several times
with PBS. Green-stained cells were counted as ICG-positive cells
under a microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti-S; Nikon). Cells were then
incubated in complete DMEM medium at 37°C for >6 h in order to
assess ICG release, using a microscope (16,19).
Ten nonoverlapping images were recorded.
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining
HP14.5 cells, cultured in 24-well plates, were
treated for 12 days. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for
10 min and then incubated in 0.5% periodic acid solution for 5 min.
Cells were then rinsed in ddH2O for 3 min, incubated
with Schiff’s reagent for 15 min and counter-stained with
hematoxylin solution for 2 min. Cells were subsequently thoroughly
rinsed with tap water. All steps were performed at room temperature
(16,19). Ten nonoverlapping visual fields
were recorded using a microscope, and cells stained a purple-red
color were counted as positive.
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± standard
deviation, and were calculated using SPSS 15.0 software (SPSS,
Inc., Chicago, IL USA). A two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for
statistical analysis. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
ALB-GLuc activity at various 5-azaC
concentrations in induced mouse HP14.5 cells
5-azaC, added at various concentrations to the
hepatocyte induction culture medium, induced the differentiation of
HP14.5 cells. ALB-GLuc is transcribed from the ALB promoter and
drives the luciferase reporter gene. Its activity indirectly
reflects the level of ALB expression in cells, providing a useful
means with which to detect hepatocyte maturation. At 6 days
following induction, ALB-GLuc readings were higher in the induced
group with 5-azaC than in the induced group without 5-azaC, and
exhibited a progressive increase with increasing induction time,
reaching a peak following induction for 9–12 days. It was shown
that 2 μmol/l 5-azaC was the optimal concentration for
hepatic induction (Fig. 1A).
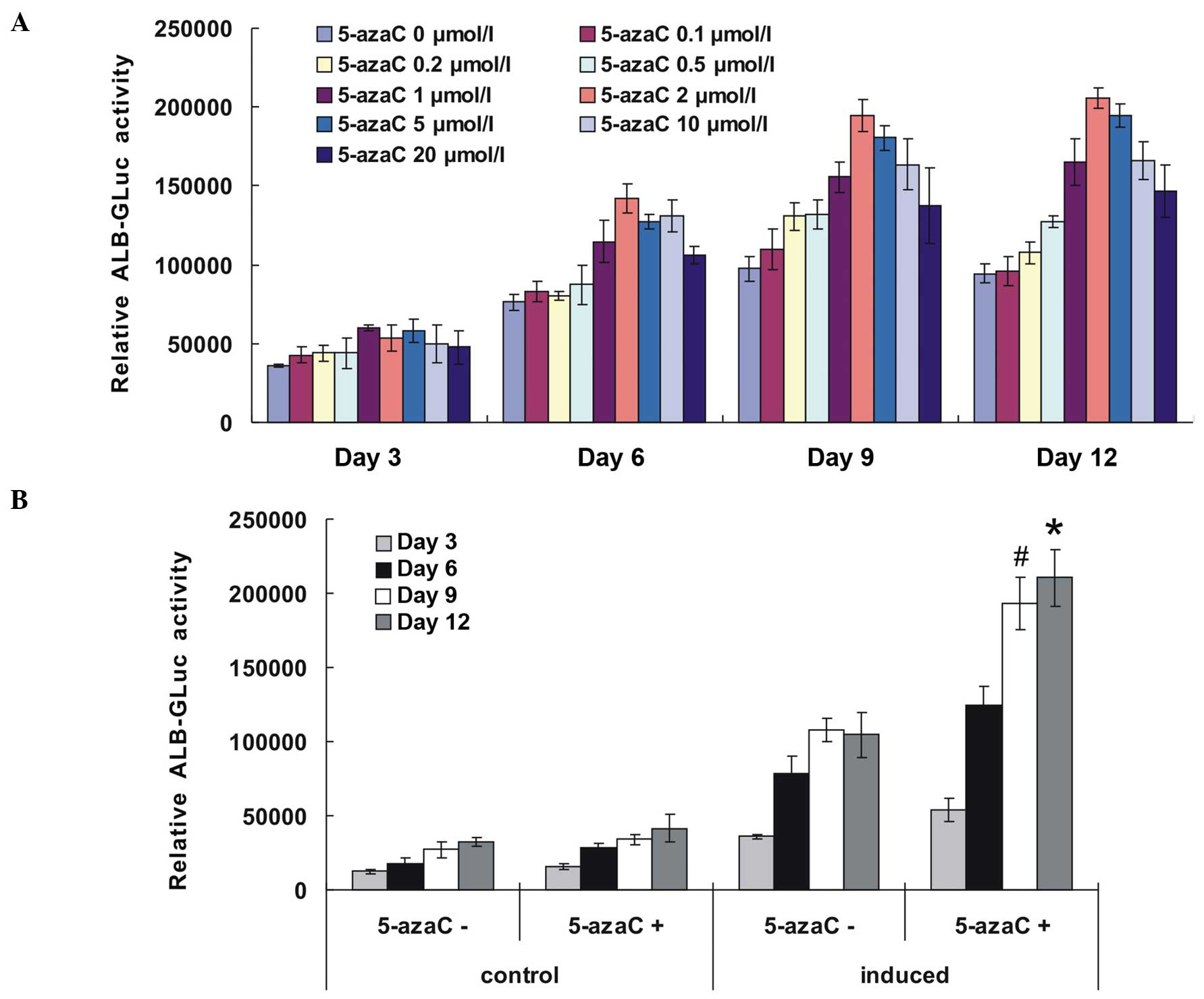 | Figure 15-azaC increased the ALB-GLuc
activity of induced HP14.5 cells. (A) Effect of various
concentrations of 5-azaC on ALB-GLuc activity in HP14.5 cells,
cultured in a hepatocyte induction medium. Cells were transfected
with pSEB-ALB-GLuc plasmid at 24 h prior to hepatic induction and
treated with 5-azaC at concentrations of 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5,
10 or 20 μmol/l, with hepatic differentiation induction. (B)
HP14.5 cells were treated with 2 μmol/l 5-azaC and
hepatocyte induction medium. ALB-GLuc activity of HP14.5 cells was
detected at 3, 6, 9 and 12 days following treatment.
#P<0.05, compared with the control group and
*P<0.05, compared with the group treated with induction medium
alone. 5-azaC, 5-azacytidine; ALB-GLuc, albumin promotor-driven
Gaussia luciferase. |
5-azaC enhances ALB-GLuc activity of
HP14.5 cells treated with hepatocyte induction culture medium
The ALB-GLuc activity using 2 μmol/l 5-azaC,
with or without hepatic induction culture medium was subsequently
detected. As shown in Fig. 1B, no
significant difference in ALB-GLuc activity was observed between
the group treated with 5-azaC alone and the control group. By
contrast, 5-azaC significantly increased the ALB-GLuc activity of
induced HP14.5 cells.
5-azaC increases the expression of
hepatic-associated marker genes of HP14.5 cells in association with
induction medium
qPCR results (Fig.
2A) showed that in the group treated with 5-azaC alone, the
expression of various hepatic-associated factors increased
slightly, although it was not significantly different compared with
that in the control group. Hepatic induction medium induced HP14.5
cells differentiation: The expression of DLK and α-fetoprotein
(AFP), which are characteristic markers of hepatic stem cells,
decreased significantly, while that of ALB, CK18, tyrosine
aminotransferase (TAT) and cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily A,
polypeptide 1(CYP7A1), which are mature hepatocyte markers,
increased significantly. ALB, CK18, TAT and CYP7A1 expression in
the induced group treated with 5-azaC, was higher than that of the
induced group without 5-azaC. Western blotting results were
consistent with these findings. 5-azaC treatment alone did not
affect the expression of ALB protein, while it enhanced the
expression of this protein in an induced environment (Fig. 2B). Immunofluorescence images
demonstrated expression of the mature hepatocyte markers, CK18 and
UGT1A, in cytoplasm, and no difference was detected between the
group treated with 5-azaC alone and the control group. By contrast,
the expression of these markers in the 5-azaC induced group was
significantly higher than that in the induced group without 5-azaC
(P=0.008597; Fig. 2C). Thus, the
results suggested that 5-azaC alone is insufficient to induce
hepatic progenitor cell differentiation. However, it does stimulate
hepatic maturation and differentiation within the appropriate
induced environment.
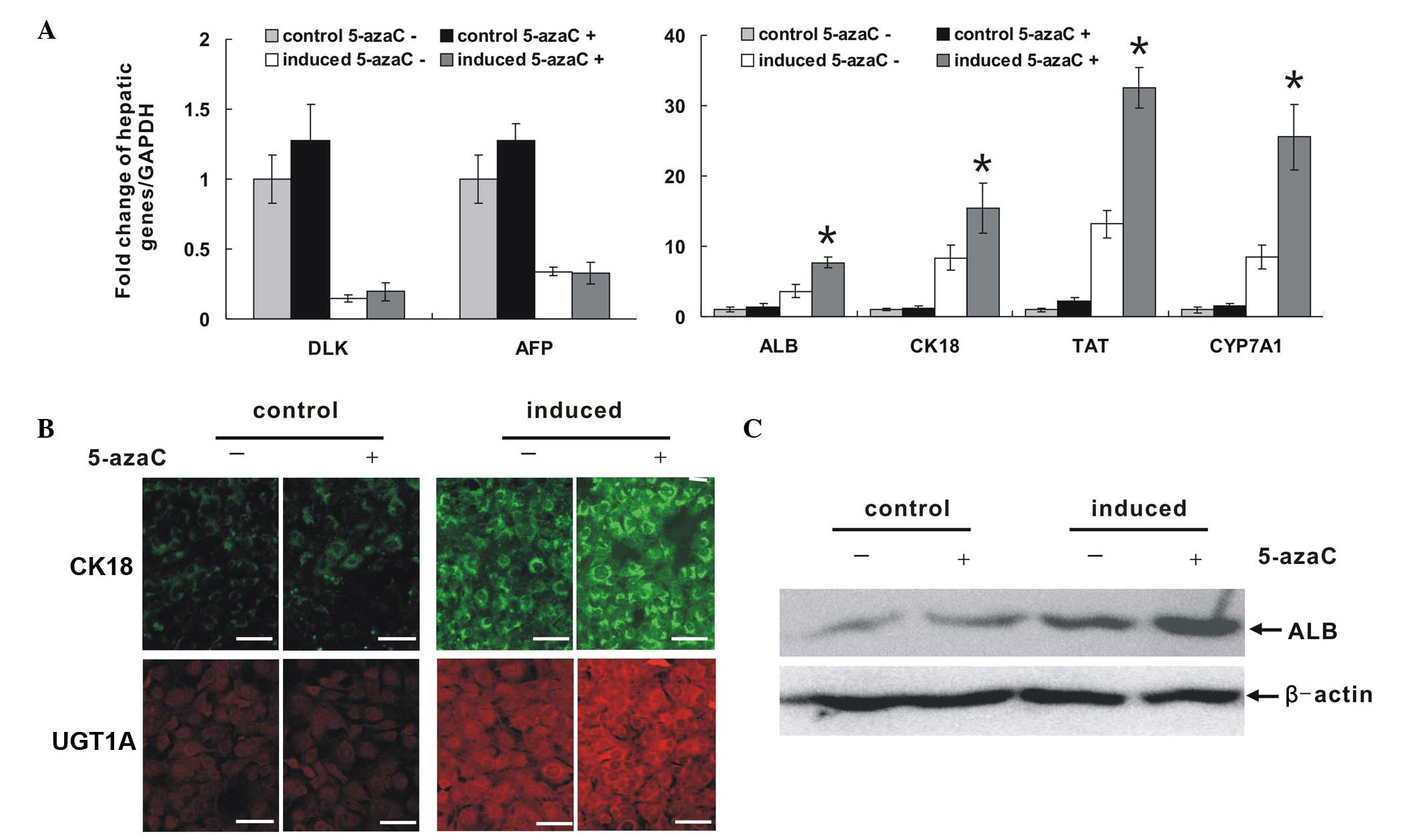 | Figure 25-azaC increased the expression of
hepatic-associated markers of induced HP14.5 cells. HP14.5 cells
were treated with 2 μmol/l 5-azaC alone, hepatocyte
induction medium alone, or a combination of the two, for 12 days.
Untreated cells were used as a control. (A) mRNA expression of
hepatic-associated marker genes, DLK, AFP, ALB, CK18, TAT and
CYP7A1. Total RNA of cells in the different groups was extracted
and reverse-transcribed into cDNA templates. The expression of
genes was detected by qPCR and the fold of change was normalized to
the expression GAPDH. qPCR results were confirmed in at least three
independent experiments *P<0.05, compared with
induction medium alone treated group. (B) Protein expression of
CK18 and UGT1A was detected using immunofluorescence staining.
Scale bar = 200 μm. (C) Expression of ALB was detected by
western blot analysis. Equal loading of the samples was confirmed
by β-actin. 5-azaC, 5-azacytidine; AFP, α-fetoprotein; ALB,
albumin; CK18, cytokeratin 18; TAT, tyrosine aminotransferase;
CYPA1, cytochrome p450, family 1, member A1; qPCR, quantitative
polymerase chain reaction; UGT1A, uridine
diphosphate-glucuronyltransferase 1A. |
5-azaC enhances the mature hepatic
function of HP14.5 cells in association with induction
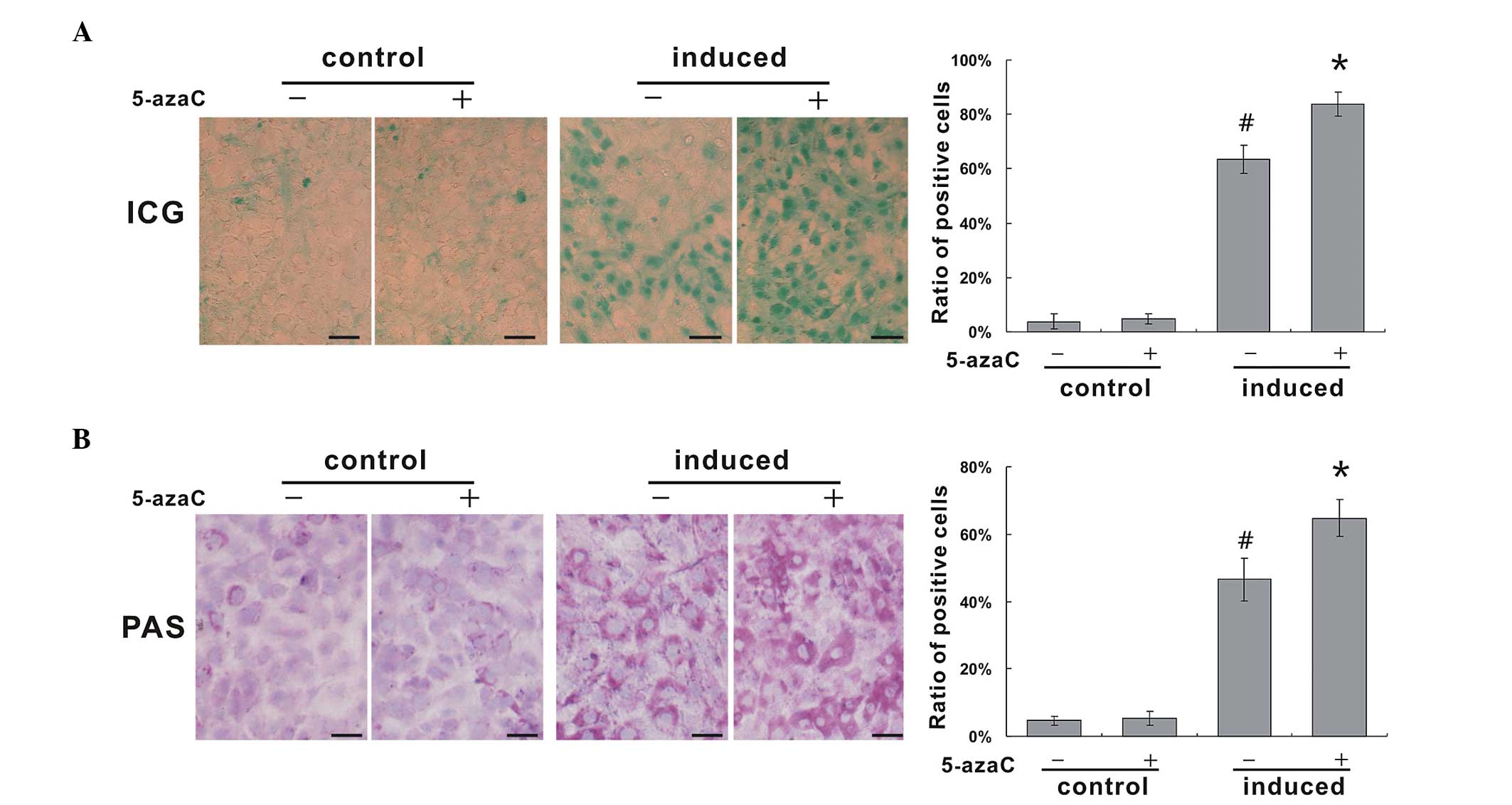
Mature hepatic cells are known to metabolize ICG,
and ICG uptake may therefore be used for the identification of
differentiated hepatocytes in vitro (20,21).
The ratios of ICG-positive cells to ICG-negative cells in the
non-induced control group and in the group treated with 5-azaC
alone, were 3.9±2.8% and 4.8±1.9%, respectively, and no significant
difference was detected between the two groups. Following 12 days
of induction, the ratio of ICG-positive to ICG-negative cells was
63.4±5.1%, which was significantly higher than that of the control
group, while it was significantly lower than the 5-azaC induced
group (83.9±4.5%; Fig. 3A).
Glycogen synthesis function is an important
indicator in the evaluation of hepatic differentiation. Synthetic
glycogen appears a purple-red color in the cytoplasm, upon PAS
staining (22). The ability of
HP14.5 cells to synthesize glycogen was weak, with a ratio of
PAS-positive to PAS-negative cells of 4.6±1.4%. Treatment with
5-azaC alone, did not significantly increase this ratio (5.3±2.1%).
At 12 days following induction, the ratio of PAS-positive to
PAS-negative HP14.5 cells increased to 46.6±6.3%, while the ratio
in the induced group treated with 5-azaC was 64.7±5.4%, which was
significantly higher than that in the induced group without 5-azaC.
There was widespread purple-red throughout the cytoplasm, which was
of a deeper color than that in the induced group (Fig. 3B). These results demonstrated that
5-azaC enhances the metabolic and synthetic function of HP14.5
cells in association with hepatocyte induction.
Discussion
Hepatic progenitor cells are a form of stem cell,
which are able to self-proliferate; differentiate into hepatocytes
and biliary epithelial cells, and participate in liver repair and
reconstruction. They may also be an important cell source for
hepatic cell transplantation (7,23,24).
Current research on hepatic stem cells remains at the theoretical
and experimental stage. Extrahepatic sources of hepatic stem cells,
including embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and bone
marrow MSCs are able to differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells
that express hepatocyte-specific genes or exhibit partial hepatic
cell function of regeneration in vivo (25,26).
However, the differentiation efficiency and substitution function
of these cells in vivo is far less than hepatic progenitor
cells from embryos (27,28). The process of differentiation of
stem cells into hepatocytes, includes bipotential hepatic
progenitor cells. Embryonic hepatic progenitor cells are precursor
cells, and may differentiate into hepatocytes or biliary epithelial
cells. The intermediate bipotential state is therefore required
during the differentiation of other types of stem cells into mature
hepatocytes (26,29,30).
Hepatocyte differentiation is periodically regulated
by different signals. In particular, the participation of
associated cytokines is required to facilitate stem cell
differentiation into hepatic endoderm (31-33).
At the hepatic progenitor cell stage, in which cells exhibit
bi-directional differentiation potential, the gene regulation
system sends different instructions to the cells, in order to
induce their differentiation into hepatocytes and biliary
epithelial cells, thus producing a unique hepatic tissue morphology
and function. It has been demonstrated that upregulating the
expression of differential-related genes may improve the
therapeutic efficacy of hepatic stem cells transplantation
(34,35). Therefore, stable and efficient
hepatocyte resources obtained from hepatic progenitor cells may
significantly improve the efficiency and biosafety profile of liver
cell transplantation.
5-azaC is a type of cytosine chemical analogue,
which is able to interfere with the physiological function of DNA
by embedding in this molecule in order to exert cytotoxic and
antitumor effects (10,36). 5-azaC has been used for the
treatment of breast cancer, colon cancer, melanoma and acute
myelogenous leukemia in clinical practice (37–39).
5-azaC also functions as a DNA methylation inhibitor. It combines
with the methylation enzyme and inactivates it, which leads to
hypomethylated DNA, thereby enhancing gene expression. In 1995,
Wakitani et al (40)
reported that 5-azaC induces the differentiation of bone marrow MSC
into cardiomyocytes. 5-azaC has been widely used in a variety of
directional stem cell induction. MSCs treated with 5-azaC in
vitro express cardiac-specific structural protein (atrial
natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide and α-/β-myosin
heavy chain) and myocardiocyte-specific transcription factors
(GATA4 and Nkx2.5/Csx), and partly improve myocardial systolic
ventricular pressure and tension following transplantation into
freezing damaged rat myocardium in vivo (41–43).
Furthermore, brief exposure to 5-azaC induces pig dermal fibroblast
reprogramming into insulin secreting cells (44). A high concentration (10
μmol/l) of 5-azaC has been reported to enhance the induction
of adipose-derived stem cell differentiation into myogenic
cardiogenic cells (45).
5-azaC mediated-inhibition of DNA methylation is
widespread rather than cell-specific. However, there are a number
of studies that have investigated the effect of 5-azaC on
hepatocyte differentiation and hepatic tumors. It has been reported
that 5-azaC inhibits HepG2 and Hep3B liver tumor cell
proliferation, induces apoptosis, and promotes their maturation and
differentiation (46). The present
study showed that 5-azaC exerts certain inducing differentiation
effects, when administered at a suitable concentration. However,
when treated with a high concentration condition of 5-azaC, the
ALB-GLuc activity of induced HP14.5 cells decreased. This
phenomenon may be due to higher doses of 5-azaC directly inhibiting
cell proliferation, and mediating cell cytotoxicity by embedding
into DNA and RNA (47,48). By contrast, lower doses of 5-azaC
primarily inhibit DNA methylation, resulting in the recovery of
gene normal expression (10,49,50).
Concomitantly, it was found that hepatic-associated markers of
HP14.5 cells treated with 5-azaC alone, did not increase
significantly, suggesting that DNA hypomethylation is not the only
factor that determines gene expression during the hepatic cell
differentiation process; the appropriate induced culture conditions
and the microenvironment also have an effect on transcriptional
control. Similarly, MSCs may be induced to differentiate into
cardiomyocytes by 5-azaC, although it is difficult to to obtain
functional beating myocardial cells (51). DLK and AFP proteins are markers of
hepatic stem cells (52,53). If 5-azaC promotes the maturational
differentiation of induced hepatic cells, the expression of these
stem cell markers should decrease. However, as 5-azaC could inhibit
DNA methylation, stem cell marker gene expression in the 5-azaC
induced group remained at the same level as that in the induced
group without 5-azaC treatment. The expression of CK18 and ALB,
which are markers of mature hepatocytes, was higher in the induced
group with 5-azaC than in the induced group without 5-azaC. It was
hypothesized that the different conformations of DNA cpG islands
may determine the extent of the effect of 5-azaC, which functions
primarily via modification of methylation (54,55).
This proposal requires further investigation.
In conclusion, The present study demonstrated that
5-azaC synergistically promotes the hepatic differentiation of
HP14.5 cells, significantly increases the expression of
hepatic-associated marker genes, and enhances the ICG metabolism
and glycogen synthesis function of these cells. The current study
provides a basis for the clinical application of hepatic progenitor
cells in liver disease. 5-azaC is known to induce differentiation
into myocardiocytes. The present study demonstrates that it is also
involved in the terminal maturation and differentiation of induced
hepatocytes, suggesting a wider role for this molecule as an
inducing agent.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81100309).
References
|
1
|
Samuel D, Colombo M, El-Serag H, Sobesky R
and Heaton N: Toward optimizing the indications for orthotopic
liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl.
17(Suppl 2): S6–S13. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adam R and Hoti E: Liver transplantation:
The current situation. Semin Liver Dis. 29:3–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oertel M: Fetal liver cell transplantation
as a potential alternative to whole liver transplantation? J
Gastroenterol. 46:953–965. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hughes RD, Mitry RR and Dhawan A: Current
status of hepatocyte transplantation. Transplantation. 93:342–347.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Haridass D, Narain N and Ott M: Hepatocyte
transplantation: Waiting for stem cells. Curr Opin Organ
Transplant. 13:627–632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sancho-Bru P, Najimi M, Caruso M, et al:
Stem and progenitor cells for liver repopulation: Can we
standardise the process from bench to bedside? Gut. 58:594–603.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kakinuma S, Nakauchi H and Watanabe M:
Hepatic stem/progenitor cells and stem-cell transplantation for the
treatment of liver disease. J Gastroenterol. 44:167–172. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sharma AD, Cantz T, Vogel A, et al: Murine
embryonic stem cell-derived hepatic progenitor cells engraft in
recipient livers with limited capacity of liver tissue formation.
Cell Transplant. 17:313–323. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tomiyama K, Miyazaki M, Nukui M, et al:
Limited contribution of cells of intact extrahepatic tissue origin
to hepatocyte regeneration in transplanted rat liver.
Transplantation. 83:624–630. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Venturelli S, Berger A, Weiland T, et al:
Differential induction of apoptosis and senescence by the DNA
methyltransferase inhibitors 5-azacytidine and
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in solid tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
12:2226–2236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kang PL, Chen CH, Chen SY, et al:
Nanosized collagen I molecules enhanced the differentiation of rat
mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes. J Biomed Mater Res A.
101:2808–2816. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moscoso I, Centeno A, López E, et al:
Differentiation ‘in vitro’ of primary and immortalized porcine
mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes for cell
transplantation. Transplant Proc. 37:481–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosca AM and Burlacu A: Effect of
5-azacytidine: Evidence for alteration of the multipotent ability
of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 20:1213–1221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
De Carvalho DD, You JS and Jones PA: DNA
methylation and cellular reprogramming. Trends Cell Biol.
20:609–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kamiya A, Gonzalez FJ and Nakauchi H:
Identification and differentiation of hepatic stem cells during
liver development. Front Biosci. 11:1302–1310. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bi Y, He Y, Huang JY, et al: Induced
maturation of hepatic progenitor cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 46:559–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bi Y, Huang J, He Y, et al: Wnt antagonist
SFRP3 inhibits the differentiation of mouse hepatic progenitor
cells. J Cell Biochem. 108:295–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bi Y, Gong M, He Y, Wei X, Chen J and Li
T: Adenovirus-mediated RAR-β over-expression enhances ATRA-induced
neuronal differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Med
Sci. 9:314–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He Y, Zhou JW, Xu L, Gong MJ, He TC and Bi
Y: Comparison of proliferation and differentiation potential
between mouse primary hepatocytes and embryonic hepatic progenitor
cells in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 32:476–484. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamada T, Yoshikawa M, Kanda S, et al: In
vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells into hepatocyte-like
cells identified by cellular uptake of indocyanine green. Stem
Cells. 20:146–154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshie S, Ito J, Shirasawa S, et al:
Establishment of novel detection system for embryonic stem
cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells based onnongenetic manipulation
with indocyanine green. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 18:12–20. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
König M, Bulik S and Holzhütter HG:
Quantifying the contribution of the liver to glucose homeostasis: A
detailed kinetic model of human hepatic glucose metabolism. PLoS
Comput Biol. 8:e10025772012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weiss TS, Lichtenauer M, Kirchner S, et
al: Hepatic progenitor cells from adult human livers for cell
transplantation. Gut. 57:1129–1138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sangan CB and Tosh D: Hepatic progenitor
cells. Cell Tissue Res. 342:131–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sokal EM: From hepatocytes to stem and
progenitor cells for liver regenerative medicine: Advances and
clinical perspectives. Cell Prolif. 44(Suppl 1): 39–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heo J, Factor VM, Uren T, et al: Hepatic
precursors derived from murine embryonic stem cells contribute to
regeneration of injured liver. Hepatology. 44:1478–1486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang W, Li W, Liu B, Wang P, Li W and
Zhang H: Efficient generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells
from human fetal hepatic progenitor cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol.
227:2051–2058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
You N, Liu W, Zhong X, Dou K and Tao K:
Possibility of the enhanced progression of fetal liver
stem/progenitor cells therapy for treating end-stage liver diseases
by regulating the notch signaling pathway. Arch Med Res.
43:585–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Q, Khoury M, Limmon G, Choolani M,
Chan JK and Chen J: Human fetal hepatic progenitor cells are
distinct from, but closely related to, hematopoietic
stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 31:1160–1169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Friedman JR and Kaestner KH: On the origin
of the liver. J Clin Invest. 121:4630–4633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du Z, Wei C, Yan J, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells overexpressing C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 improve
early liver regeneration of small-for-size liver grafts. Liver
Transpl. 19:215–225. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Haga S, Ozaki M, Inoue H, et al: The
survival pathways phospha-tidylinositol-3 kinase
(PI3-K)/phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1)/Akt
modulate liver regeneration through hepatocyte size rather than
proliferation. Hepatology. 49:204–214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kwon HJ, Won YS, Yoon YD, et al: Vitamin
D3 up-regulated protein 1 deficiency accelerates liver regeneration
after partial hepatectomy in mice. J Hepatol. 54:1168–1176. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Turner RA, Wauthier E, Lozoya O, et al:
Successful transplantation of human hepatic stem cells with
restricted localization to liver using hyaluronan grafts.
Hepatology. 57:775–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Lozoya OA, Wauthier E, Turner RA, et al:
Regulation of hepatic stem/progenitor phenotype by microenvironment
stiffness in hydrogel models of the human liver stem cell niche.
Biomaterials. 32:7389–7402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ding YB, Long CL, Liu XQ, et al:
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine leads to reduced embryo implantation and
reduced expression of DNA methyltransferasesand essential
endometrial genes. PLoS One. 7:e453642012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ghoshal K and Bai S: DNA
methyltransferases as targets for cancer therapy. Drugs Today
(Barc). 43:395–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Buckstein R, Yee K and Wells RA; Canadian
Consortium on Evidence-based Care in MDS: 5-Azacytidine in
myelodysplastic syndromes: A clinical practice guideline. Cancer
Treat Rev. 37:160–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Deng G, Kakar S, Okudiara K, Choi E,
Sleisenger MH and Kim YS: Unique methylation pattern of oncostatin
m receptor gene in cancers of colorectum and other digestive
organs. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1519–1526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wakitani S, Saito T and Caplan AI:
Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 18:1417–1426. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, et al:
Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro.
J Clin Invest. 103:697–705. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yeh HY, Liu BH and Hsu SH: The
calcium-dependent regulation of spheroid formation and
cardiomyogenic differentiation for MSCs on chitosan membranes.
Biomaterials. 33:8943–8954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Naeem N, Haneef K, Kabir N, Iqbal H,
Jamall S and Salim A: DNA methylation inhibitors, 5-azacytidine and
zebularine potentiate the transdifferentiation of rat bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Ther.
31:201–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pennarossa G, Maffei S, Campagnol M,
Rahman MM, Brevini TA and Gandolfi F: Reprogramming of pig dermal
fibroblast into insulin secreting cells by a brief exposure to
5-aza-cytidine. Stem Cell Rev. 10:31–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ravichandran R, Venugopal JR, Mueller M,
et al: Buckled structures and 5-azacytidine enhance cardiogenic
differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Nanomedicine (Lond).
8:1985–1997. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang XM, Wang X, Li J and Evers BM:
Effects of 5-azacytidine and butyrate on differentiation and
apoptosis of hepatic cancer cell lines. Ann Surg. 227:922–931.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo Y, Engelhardt M, Wider D, Abdelkarim M
and Lübbert M: Effects of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine on proliferation,
differentiation and p15/INK4b regulation of human hematopoietic
progenitor cells. Leukemia. 20:115–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhou Y and Lu Q: DNA methylation in T
cells from idiopathic lupus and drug-induced lupus patients.
Autoimmun Rev. 7:376–383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dhawan D, Ramos-Vara JA, Hahn NM, et al:
DNMT1: An emerging target in the treatment of invasive urinary
bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 31:1761–1769. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Stern-Straeter J, Bonaterra GA, Juritz S,
et al: Evaluation of the effects of different culture media on the
myogenic differentiation potential of adipose tissue- or bone
marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med.
33:160–170. 2014.
|
|
51
|
Ramesh B, Bishi DK, Rallapalli S, Arumugam
S, Cherian KM and Guhathakurta S: Ischemic cardiac tissue
conditioned media induced differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells into early stage cardiomyocytes. Cytotechnology. 64:563–575.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nishina H: hDlk-1: A cell surface marker
common to normal hepatic stem/progenitor cells and carcinomas. J
Biochem. 152:121–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kuhlmann WD and Peschke P: Hepatic
progenitor cells, stem cells, and AFP expression in models of liver
injury. Int J Exp Pathol. 87:343–359. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang J, Corsello TR and Ma Y: Stem cell
gene SALL4 suppresses transcription through recruitment of DNA
methyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 287:1996–2005. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Mi XB and Zeng FQ: Hypomethylation of
interleukin-4 and -6 promoters in T cells from systemic lupus
erythematosus patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:105–112. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|