Introduction
The liver, one of the largest organs in the human
body, serves a vital role in the metabolism of carbohydrates,
lipids and proteins, the regulation of immune responses, and the
clearance of toxins and pathogens (1,2). The
liver is frequently exposed to various insults, which may cause
cell swelling, degeneration, necrosis, apoptosis, hepatic fibrosis
and dysfunction. As the fifth most common cause of mortality
following heart disease, stroke, lung disease and cancer (3), the rates of liver disease, unlike
other major causes of mortality, are increasing (4). However, the available synthetic
drugs, including interferon and corticosteroids, are expensive and
may present the risk of adverse effects (5). Therefore, treating liver disease with
alternative medicine seems attractive, as a number of medicinal
plants, which have been traditionally used for centuries, are
accessible and appear to exhibit decreased toxicity (6). Ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1) is one of the
primary active ingredients in ginseng, and possesses the potential
to protect cardiovascular and nervous system activity, as well as
anti-tumor, anti-fatigue and anti-aging capabilities (7–9).
Komatsu et al (10)
demonstrated that Rg1 protected against lipopolysaccharide- and
galactosamine-induced hepatic damage. Additionally, Cao et
al (11) reported that Rg1
reduced concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibition
of cytokine secretion and lymphocyte infiltration. Pretreatment
with Rg1 protected mice from IR-induced liver injury by reducing
hepatocellular apoptosis and inhibiting inflammatory responses
(12). The present study aimed to
investigate the effect and underlying mechanism of Rg1 on carbon
tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced acute liver injury in
vitro and in vivo, and to provide the theoretical
foundation of the clinical application of Rg1 in acute liver
injury.
Liver injury is a common pathological state in
various types of liver disease; severe or persistent liver damage
is the basis of hepatic failure (13). CCl4 is a
commonly-applied chemical substance which may induce acute and
chronic liver injury in animal models. It is well known that
following activation by cytochrome P450 metabolism in the liver,
CCl4 generates numerous free radicals and reactive
oxygen species which cause oxidative stress. These species cause
membrane lipid peroxidation and bind protein macromolecules through
covalent linkage, ultimately leading to interference with protein
function, the destruction of cell membrane structure, increased
permeability of the cell membrane, leakage of liver enzymes and
liver cell death (14,15).
Nuclear factor (NF)-κB, a transcription factor known
to regulate inflammatory responses in a number of cell types
(16), was demonstrated to be
involved in a variety of types of liver injuries (17–21).
Liu et al (9) observed that
Rg1 inhibited NF-κB activity to protect against
H2O2-induced cell death in rat adrenal
pheochromocytoma PC12 cells; additionally, the study of Tao et
al (12) demonstrated that
pretreatment with Rg1 protected mice from ionizing
radiation-induced liver injury by reducing hepatocellular apoptosis
and inhibiting inflammatory responses, in part via the NF-κB
signaling pathway. However, the effect of Rg1 on
CCl4-induced acute liver injury and its mechanism,
including the association between Rg1 and NF-κB, have not been
systematically studied. The present study demonstrated that
pretreatment with Rg1 may protect against CCl4-induced
acute liver injury in vivo and in vitro, and the
protective effect was associated with inhibition of the NF-κB
signaling pathway to restore the anti-oxidative defense system. A
reduction in elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate
aminotransferase (AST) levels was observed, as well as the
inhibition of lipid peroxidation expressed as enhancement in
superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and a decrease in
malondialdehyde (MDA) expression. Attenuation of inflammatory
responses expressed as a decrease in serum tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 levels was also observed.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Rg1 (C42H72O14) was
obtained from Shanghai YaJi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai,
China; cat. no. MUST-11041201); CCl4 was purchased from
Shanghai ShenXiang Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China;
cat. no. 20090510); minimum essential medium with Earle's balanced
salts (MEM-EBSS) was purchased from Gibco (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA); fetal bovine serum (FBS) was
from Hangzhou Evergreen Biological Material Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou,
China); penicillin and streptomycin were from North China
Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shijiazhuang, China); dimethyl sulfoxide
(DMSO) was from Beijing YiLi Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Beijing,
China); NF-κB p65 antibody (rabbit anti-mouse) was from
Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany; cat. no.
SAB4502609); bicinchoninic acid protein concentration assay kit was
from Beijing Biosynthesis Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China);
NF-κB electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) kit (cat. no.
20148) was from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; biotin-labeled
NF-κB probes (oligonucleotide sequences:
3′-TCAACTCCCCTGAAAGGGTCCG-5′ and 5′-AGTTGAGGGGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′) were
purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Co., Ltd.
(Shanghai, China); TNF-α (cat. no. MTA000B) and IL-6 (cat. no.
M6000B) ELISA kits were from R&D Systems, Inc. (Minneapolis,
MN, USA); and ALT (cat. no. C009-3), AST (cat. no. C010-3), SOD
(cat. no. A001-2), and MDA (cat. no. A003-1) kits were from Nanjing
JianCheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China).
CCl4 injury mouse
model
A CCl4-induced acute liver injury model
of mice was established as described by Li et al (22). Male Kunming mice (20±2 g; n=60)
were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Anhui Medical
University [animal license no. SCXK (Anhui) 2011–002; Hefei,
China]. The facilities and the protocol for these experiments were
consistent with the regulations of animal use for biomedical
experiments as issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of
China and were also approved by the animal ethics committee of
Bengbu Medical College (Bengbu, China). The mice were kept in the
dark and had free access to standard chow and water. Following 3
days of adaptive feedings, the 60 mice were randomly divided into
five groups: i) Control group [olive oil (Hong Rui Men; Jiangxi
Hongrui Oil Food Co. Ltd., Nanchang, China), 0.1 ml/10 g body
weight]; ii) model group (CCl4, 0.1 ml/10 g body
weight), iii) low Rg1 group (Rg1, 10 mg/kg body weight;
CCl4 0.1 ml/10 g body weight), iv) middle Rg1 group
(Rg1, 20 mg/kg; CCl4 0.1 ml/10 g body weight), v) high
Rg1 group (Rg1, 40 mg/kg; CCl4 0.1 ml/10 g body weight).
Oral doses of Rg1 were administered once a day for 7 days and all
groups, except the control group, were intraperitoneally injected
with 0.1% CCl4 in olive oil (v/v) 2 h subsequent to the
last dose of Rg1 in order to induce acute liver injury, while the
mice in control group were injected with an equal volume of olive
oil. All mice were fasted and had free access to water overnight.
The blood was obtained from the orbital sinus, centrifuged at 268.3
× g for 5 min at 37°C and prepared for ALT and AST content
detection. The liver was rapidly removed subsequent to the mice
being sacrificed, and was rinsed three times with saline to remove
blood. The left lobe of the liver was prepared for hematoxylin and
eosin (H&E) staining and the right lobe of the liver for SOD,
MDA, TNF-α and IL-6 content detection.
Isolation and purification of Kupffer
cells
Following intraperitoneal injection with
CCl4 olive oil solution into mice for 1 h, Kupffer cells
from each group of animals were collected (n=4). Hepatic perfusion
and digestion was performed according to the method described by
Fukada et al (23).
Following intraperitoneal injection with CCl4 olive oil
solution into the mouse for 1 h, the mouse was anesthetized with
chloral hydrate (5% chloral hydrate, 0.1 ml/10 g body weight) and
the abdomen opened to confirm the location of the portal vein. The
portal vein was cannulated with a 22 G catheter, ~1 cm away from
the hepatic portal with 0.8-cm insertion and an arterial clamp. The
liver was perfused with the first infusion, composed of NaCl (137
mmol/l), KCl (2.68 mmol/l),
Na2HPO4·12H2O (0.7 mmol/l), HEPES
(10 mmol/l), glucose (10 mmol/l), EDTA-Na2 (0.5 mmol/l)
and heparin (2,000 U/l), pH 7.4, until the liver volume had
expanded to ~2X the original volume and a slight white color was
observed. The inferior vena cava was subsequently cut. Finger
pressure was applied to the segments, and they were intermittently
opened to enlarge and retract the liver alternately following liver
retraction. When the liver had turned white, with 15 min
reperfusion, the liver was removed to a sterile petri dish
(reserving the portal vein catheterization). Perfusion of the liver
was continued with the second infusion, composed of NaCl (137
mmol/l), KCl (2.68 mmol/l),
Na2HPO4·12H2O (0.7 mmol/l), HEPES
(10 mmol/l), glucose (10 mmol/l), CaCl2 (5 mmol/l) and
collagenase IV (0.05%), pH 7.4, for ~15 min, until the liver became
soft and structural collapse was observed. Liver cells were
scattered to form a cell suspension using stirring and percussion
with a dropper.
For the isolation of Kupffer cells, the method
described by Fukada et al (23) and Smedsrød and Pertoft (24) in 1985 was employed and improved.
The cell suspension was subjected to low-speed centrifugation (16.7
× g for 3 min at 4°C) and the supernatant was removed prior to the
precipitate being resuspended in 10 ml PBS. Subsequently, 15 ml 50%
Percoll liquid (Shanghai Xinyu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai,
China) was added into a new tube and 20 ml 25% Percoll liquid was
carefully added along the tube wall, followed by 10 ml cell
suspension. Following centrifugation at 268.3 × g for 15 min at
4°C, four apparent partitions were observed: From top to bottom
these were cell debris, non-parenchymal cells enriched in
endothelial cells, Kupffer cells and red cells, which precipitated
at the bottom of the tube. The Kupffer cells were collected, ~15
ml, and were diluted with 15 ml PBS. Following centrifugation at
268.3 × g for 10 min at 4°C, the precipitate was resuspended in
culture medium.
Subsequently, purification of Kupffer cells was
performed; the survival rate of the cells was >90% as observed
with Trypan blue staining (3 min at 4°C). The cells were counted
and the concentration adjusted to 2×106/ml, and 1 ml
cell suspension/well was seeded on 12-well culture plates.
Following incubation for 2 h at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5%
CO2 in air, the cells were gently washed with fresh
culture medium, and the adherent cells were considered to be
Kupffer cells. Cell culture was continued, with the medium being
changed every 2–3 days.
H&E staining of liver tissue
The left lobe of the removed liver was fixed in
neutral formalin, paraffin-embedded and sliced. A 2.0×2.0×0.3 cm
block of tissue was selected from the same site of each mouse,
washed with saline and placed in 10% neutral formalin buffer at
37°C. Following dehydration, the blocks were wax embedded, sliced
into 5-µm sections, dewaxed, H&E stained for 5 min at 37°C,
dehydrated, and mounted in neutral balsam. The tissues were
observed using an optical microscope in the Department of Pathology
at the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College and
images of morphological changes were captured using a light
microscope (magnification, ×100).
Determination of serum ALT and AST
content
The blood obtained from the orbital sinus was
centrifuged at 1,341.6 × g at 4°C for 10 min and the serum content
of ALT and AST was measured in accordance with the manufacturer's
protocol of the ALT and AST activity kits.
Determination of liver SOD and MDA
content
The right liver lobes of the sacrificed mice were
cut and weighed and 400 mg liver tissue was combined with saline
(1:9 v/v) and crushed on ice using a glass homogenizer. The
homogenized solutions were centrifuged at 1,341.6 × g at 4°C for 15
min, and the resulting 10% liver homogenate supernatants were
measured for SOD and MDA content in accordance with the
manufacturer's protocol for the kits.
Determination of liver TNF-α, IL-6
levels using ELISA
The remainder of the right lobes of the livers were
cut and weighed, and 400 mg was combined with saline (1:9 v/v) and
crushed on ice using a glass homogenizer. The homogenates were
centrifuged at 1,341.6 × g at 4°C for 15 min, and the optical
density of the supernatant was detected at 450 nm and compared to
the TNF-α or IL-6 standard curve in accordance with the
manufacturer's protocol for the kit.
LO2 cell culture
LO2 human normal liver cells, donated by
the College of Pharmacy, Sun Yat-sen University, were maintained in
MEM-EBSS containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C
in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. The cells were
trypsinized and diluted to 5×104 cells/ml in the
logarithmic phase prior to the experiment.
CCl4 injury cell model
The viability of LO2 cells incubated with
CCl4 or Rg1 was measured by MTT assay. A total of
5×103 cells/well were seeded into 96-well plates for 24
h and then increasing concentrations of CCl4 in normal
saline (2.5, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mM) were added for 3 h. Each group
was plated in triplicate and normal saline was used as control
group. For Rg1 treatment, 0.1, 1 and 10 µM Rg1 was added to
LO2 cells. After 21 h, 20 mM CCl4 (the most
appropriate concentration from the liver cell injury model) was
added and incubated for a further 3 h. An NF-κB inhibitor [caffeic
acid phenethyl ester (CAPE); 25 µM for 2 h] was additionally
assessed. Subsequently, 20 µl MTT (Shanghai Gefan Biotechnology
Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China; 5 mg/ml) was added to each well for a
further 4 h, the supernatants were carefully discarded and 150 µl
DMSO was added to each well in order to dissolve the crystals. The
absorbance at 570 nm was measured and the cell viability was
calculated as follows: Survival rate=(absorbance of treated
group-absorbance of blank group)/(absorbance of control
group-absorbance of blank group).
Determination of cell AST, ALT levels,
SOD activity and MDA content
A total of 5×104 LO2
cells/well were seeded into 24-well plates and incubated at 37°C
for 24 h. Treatment with Rg1 at 0.1, 1 and 10 µM was performed for
21 h, and 20 mM CCl4 was added for a further 3 h. The
supernatant was collected, and AST and ALT expression levels, SOD
activity and MDA, content were measured according to the
manufacturer's protocols.
Determination of cell NF-κB activity
using EMSA
The NF-κB activity in LO2 and Kupffer
cells was detected by EMSA as described by Li et al
(25). The nuclear proteins were
incubated in 1X binding buffer (50 ng/µl poly
(deoxyinosinic-deoxycytidylic), 0.05% NP-40, 5 mM MgCl2,
50 mM KCl, 2.5% glycerol, and ultra-pure H2O at room
temperature for 10 min, and the biotin-labeled NF-κB probe was
added for a further 20 min. All reactions were electrophoresed on a
6% polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a positively charged nylon
membrane and UV cross-linked to fix the DNA. The bands were
visualized by Amersham ECL™ Plus Detection kit (GE
Healthcare Bio-Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA).
Western blotting
Cells were harvested using lysis buffer [20 mM
Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton
X-100, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM
Na3VO4, 1 mM β-glycerophosphate and 1:1,000
protease inhibitors]. Protein concentration was determined using
the BCA kit then 25 µg total protein from each sample was analyzed
by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane followed
by immunoblotting. The membranes were probed with antibodies
against p65 (1:1,000) and β-actin (A1978; 1:8,000; Sigma-Aldrich;
Merck KGaA) and the antibodies were blocked with the primary
antibody dilution (Bi Yun Tian Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai,
China), at 4°C overnight. Then the membranes were probed by goat
anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG antibody HRP conjugate secondary
antibodies for p65 (1:2,000) and β-actin (BL003A; 1:10,000;
Biosharp, Hefei, China) at room temperature for 1 h. Immunopositive
bands were visualized by Amersham ECL™ Plus Western
Blotting Detection kit (RPN2232; GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences,
Pittsburgh, PA, USA). The expression of p65 and β-actin as detected
by western blotting were analyzed by Image J software version 1.48
(National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) as was the
density of western blotting.
Statistical analysis
Data were processed using SPSS software (version 16;
SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results are expressed as the
mean ± standard error of the mean. Two-group comparisons were
analyzed using an unpaired Student's t test. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All
analyses were plotted using SigmaPlot version 10.0 (Jandel
Scientific, San Rafael, CA, USA).
Results
Protective effect of Rg1 on acute
CCl4-induced liver injury models
In order to characterize the function of Rg1 in
acute CCl4-induced liver injury in mice, histopathology
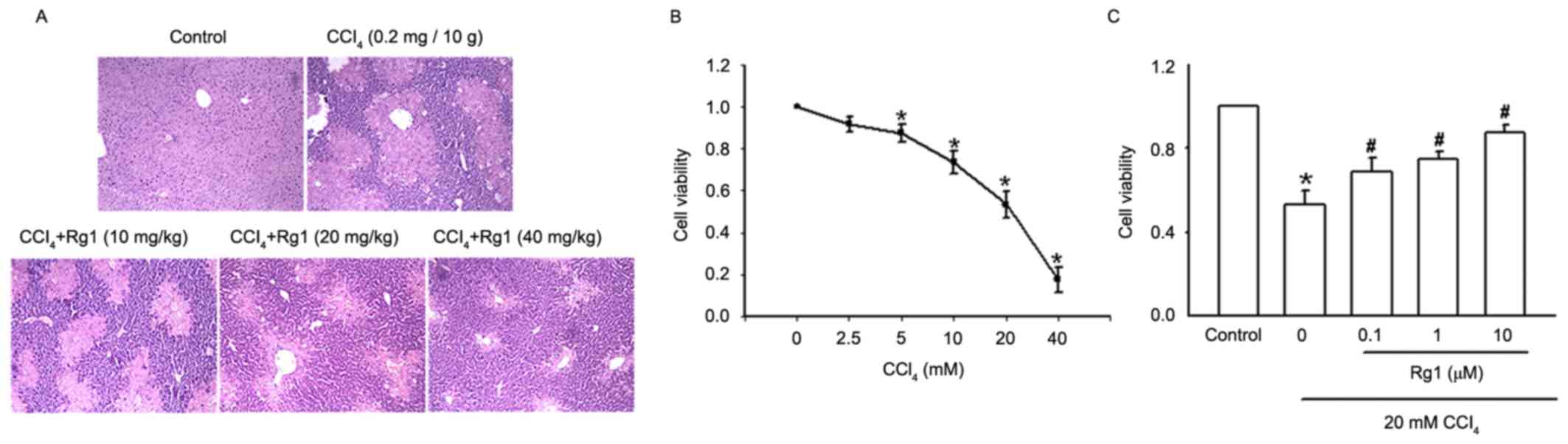
of liver tissues was performed using H&E staining (Fig. 1A). The control group exhibited
normal liver morphology and intact lobular architecture, neat
hepatic cords, clear boundaries of liver cells and round and
well-defined nuclei in the absence of inflammatory cell
infiltration. In the liver of the CCl4-treated mouse
presented in the second panel, normal liver tissue structure
disappeared and lobular structure was disrupted, inflammatory cell
infiltration was observed at lobular and portal areas, including
disordered hepatic cords, and significant swelling of liver cells
suggested high levels of necrosis. However, with the addition of
Rg1, particularly for the higher dose group, liver cell
degeneration and necrosis was markedly reduced, a clearer lobular
structure and neatly arranged liver cells were observed, and the
inflammatory cell infiltration was also reduced.
The effect of Rg1 on acute CCl4-induced
liver injury in LO2 cells was also investigated
(Fig. 1B and C). Increasing
concentrations of CCl4 (2.5–40 mM) were added to
LO2 cells for 3 h, and the effect of CCl4
cytotoxicity on LO2 cells was detected by MTT assay. As
presented in Fig. 1B, CCl4 led to
an apparent concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability. The
cell survival rates with 2.5 and 20 mM CCl4 were 91.23
and 53.39%, respectively. When the 40 mM CCl4 cells were
observed under the microscope, the survival rate was 20.12%. A
concentration of 20 mM CCl4 was used for the following
CCl4-induced LO2 cell injury model.
The addition of Rg1 at a range of concentrations
(0.1–10 µM) to LO2 cells for 21 h prior to exposure to
20 mM CCl4, and detection of cell viability by MTT
assay, demonstrated that incubation with CCl4 alone for
3 h decreased cell viability to 53.08%; the addition of Rg1
markedly improved cell viability in a concentration-dependent
manner. The cell survival rate of the 0.1 µM Rg1 group was 66.67%
and the 10 µM group reached 84.69% (Fig. 1C).
Effect of Rg1 on ALT and AST levels in
acute CCl4-induced liver injury models
The serum contents of ALT and AST presented in
Table I demonstrated that,
compared with levels of ALT and AST in the control group
(34.54±5.63 and 75.76±7.64 U/l, respectively), the expression
levels of ALT and AST in CCl4-treated mice significantly
increased (89.90±8.18 and 182.20±8.33 U/l, respectively;
P<0.05). However, oral administration of Rg1 gradually reduced
the serum levels of ALT and AST; particularly in the high-dose
group (40 mg/kg), the serum ALT expression level reduced to
50.88±10.85 U/l and the AST expression level reduced to 100.64±8.53
U/l.
 | Table I.Effects of Rg1 on the serum levels of
ALT and AST in mice with acute liver injury induced by CCl4 (mean ±
standard error of the mean; n=8). |
Table I.
Effects of Rg1 on the serum levels of
ALT and AST in mice with acute liver injury induced by CCl4 (mean ±
standard error of the mean; n=8).
| Groups | Rg1 dose,
mg/kg | ALT, U/l | AST, U/l |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
34.54±5.63 |
75.76±7.64 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
89.90±8.18a |
182.20±8.33a |
| Rg1 (low) | 10 |
80.81±5.46 |
169.02±7.60b |
| Rg1 (middle) | 20 |
67.25±9.21b |
148.77±5.45b |
| Rg1 (high) | 40 |
50.88±10.85b |
100.64±8.53b |
ALT and AST levels in the cell culture supernatant
of CCl4-treated LO2 cells were assessed
following pretreatment with increasing concentrations of Rg1
(0.1–10 µM). Consistent with the results of ALT and AST expression
levels in vivo, 20 mM CCl4 caused a significant increase
in the levels of ALT and AST, while pretreatment with Rg1 decreased
ALT and AST expression levels in a concentration-dependent manner
(Table II).
 | Table II.Effects of Rg1 on ALT and AST levels
in supernatants of CCl4-treated LO2 cells
(mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8). |
Table II.
Effects of Rg1 on ALT and AST levels
in supernatants of CCl4-treated LO2 cells
(mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8).
| Groups | Rg1 dose,
mg/kg | ALT, U/l | AST, U/l |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
19.35±4.82 |
25.88±6.54 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
85.88±7.55a |
128.36±9.03a |
| Rg1 (low) | 0.1 |
78.14±6.60 |
116.04±7.91b |
| Rg1 (middle) | 1 |
52.33±8.37b |
70.07±4.96b |
| Rg1 (high) | 10 |
32.49±7.15b |
36.50±6.8b |
Effect of Rg1 on SOD activity and MDA
content in acute CCl4-induced liver injury models
In order to investigate the effect of Rg1 on SOD
activity and MDA content in acute CCl4-induced liver
injury in mice, 10% liver homogenate supernatants of the different
treatment groups were prepared, and the results presented in
Table III demonstrated that SOD
activity in mice that were intraperitoneally injected with
CCl4 was decreased (113.21±11.31 U/mg) compared with
control group (212.31±5.65 U/mg); however, pretreatment with Rg1
caused a dose-dependent enhancement of SOD activity. By contrast,
the MDA expression level was increased in CCl4-treated
mice (8.78±0.62 nmol/mg) compared with the control group (3.42±0.88
nmol/mg), while pretreatment with Rg1 caused a dose-dependent
reduction in the MDA expression level.
 | Table III.Effects of Rg1 on the activity of SOD
and concentration of MDA in liver homogenates of
CCl4-treated mice (mean ± standard error of the mean;
n=8). |
Table III.
Effects of Rg1 on the activity of SOD
and concentration of MDA in liver homogenates of
CCl4-treated mice (mean ± standard error of the mean;
n=8).
| Groups | Rg1 dose,
mg/kg | SOD, U/mgprot | MDA,
nmol/mgprot |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
212.31±5.65 |
3.42±0.88 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
113.21±11.31a |
8.78±0.62a |
| Rg1 (low) | 10 |
128.14±11.50b |
8.35±0.73 |
| Rg1 (middle) | 20 |
145.61±8.27b |
7.18±0.94b |
| Rg1 (high) | 40 |
185.20±11.25b |
4.86±0.92b |
SOD activity and MDA content in the cell culture
supernatants of the CCl4-induced LO2 cell
injury and Rg1 treatment groups were also examined (Table IV). CCl4 inhibited SOD
activity and increased the MDA expression levels of LO2
cells; however, Rg1 alleviated the inhibited SOD activity and
reduced the increased MDA level, which was consistent with the
results of SOD activity and MDA content experiments in
vivo.
 | Table IV.Effects of Rg1 on SOD activity and
MDA concentration in supernatants from LO2 cells treated
with CCl4 (mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8). |
Table IV.
Effects of Rg1 on SOD activity and
MDA concentration in supernatants from LO2 cells treated
with CCl4 (mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8).
| Groups | Rg1 concentration,
µM | SOD, U/mgprot | MDA,
nmol/mgprot |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
5.24±0.353 |
0.71±0.12 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
2.01±0.246a |
1.85±0.24a |
| Rg1 (low) | 0.1 |
2.21±0.26 |
1.66±0.16 |
| Rg1 (middle) | 1 |
4.17±0.33b |
1.24±0.19b |
| Rg1 (high) | 10 |
4.85±0.27b |
0.88±0.12b |
Effect of Rg1 on NF-κB activity in
acute CCl4-induced liver injury models
Liver Kupffer cells serve a role as a barrier to
liver injury. In order to investigate whether NF-κB is involved in
the protective effect of Rg1 in acute CCl4-induced liver
injury in mice, liver Kupffer cells were isolated from the
different treatment groups. NF-κB p65 protein expression was
determined using western blotting and NF-kB binding activity using
EMSA analysis. The results of the western blotting demonstrated
that NF-κB p65 protein expression was significantly increased in
the CCl4 model group, although pretreatment with Rg1
(10–40 mg/kg) reduced the protein expression of p65 in a
dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2A).
Additionally, the results of the EMSA analysis demonstrated that
CCl4 (0.2 mg/10 g) used alone enhanced NF-kB binding
activity, however, pretreatment with Rg1 alleviated the enhanced
NF-kB binding in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2B).
 | Figure 2.Expression and binding activity of
NF-κB in the Kupffer cells of mice with CCl4-induced
liver injury and CCl4-treated LO2 cells. (A)
Representative images of NF-κB P65 protein expression assessed by
western blotting in Kupffer cells isolated from mice treated with
CCl4 and/or Rg1 (n=4). (B) Representative image of NF-κB
binding activity assessed by EMSA in the Kupffer cells of acute
liver injury mice pretreated with Rg1 (n=4). Lane 1, control group;
lane 2, CCl4 group; lane 3, CCl4 + Rg1 (10
mg/kg); lane 4, CCl4 + Rg1 (20 mg/kg); lane 5,
CCl4 + Rg1 (40 mg/kg). (C) The function of the NF-κB
inhibitor CAPE (25 µM, 2 h) in CCl4-treated
LO2 cells was assessed by MTT assay. The data are
expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n=3). (D)
Representative images of NF-κB P65 protein expression assessed by
western-blotting in lysates from LO2 cells treatment
with CCl4 (n=3). (E) Representative images of NF-κB P65
protein expression assessed by western-blotting in lysates from
LO2 cells treatment with 10 µM Rg1 (n=3). (F)
Representative image of NF-κB binding activity assessed by EMSA in
CCl4-treated LO2 cells (n=3). Lane 1, probe
without nucleoprotein; lane 2 control group; lane 3, Rg1 (0.1 µM);
lane 4, Rg1 (1 µM); lane 5, Rg1 (10 µM); lane 6, CCl4
group; lane 7, CCl4 + Rg1 (0.1 µM); lane 8,
CCl4 + Rg1 (1 µM); lane 9, CCl4 + Rg1 (10
µM); lane 10, CAPE (25 µM); +, positive control (20 ng/ml tumor
necrosis factor-α stimulation for 30 min); -, negative control
(untreated LO2 cells). *P<0.05 vs. control group,
#P<0.05 vs. CCl4 group. CAPE, caffeic acid
phenethyl ester; Rg1, ginsenoside Rg1; CCl4, carbon
tetrachloride; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kB; EMSA, electrophoretic
mobility shift assay. |
NF-κB function in the protective effect of Rg1 on
acute CCl4-induced liver injury was further confirmed
in vitro. CAPE, an inhibitor of NF-κB, was used and its role
observed on CCl4-induced LO2 cell injury. The
results of the MTT assay presented in Fig. 2C demonstrated that exposure of
LO2 cells to 20 mM CCl4 for 3 h inhibited
cell growth, and CAPE (25 µM, 2 h) attenuated this cell growth
inhibition. P65 expression in LO2 cells treated with
CCl4 alone or in combination with Rg1 was observed by
western blotting. When treated with 20 mM CCl4 for 15
min, there was no significant alteration in p65 expression;
however, when the incubation time was prolonged to 30 or 60 min,
the expression level increased, and 10 µM Rg1 alleviated the
increased p65 expression (Fig. 2D and
E). The present results were also confirmed by EMSA assay. Rg1
(0.1–10 µM) used alone did not affect NF-κB binding activity;
however, it significantly alleviated the enhanced binding of NF-κB
when used in combination with CCl4; the NF-κB inhibitor
CAPE served a comparable role and inhibited CCl4-induced
NF-κB binding (Fig. 2F).
Mechanism of NF-κB in Rg1 protective
effect on acute CCl4-induced liver injury models
The results presented in Table IV demonstrated that pretreatment
with Rg1 alleviated the inhibited SOD activity and reduced MDA
expression level in CCl4-induced LO2 cell
injury. Inhibition of NF-κB activity by CAPE demonstrated
comparable results: CCl4 inhibited SOD activity and
increased the MDA expression level compared with the control group;
however, using 25 µM CAPE for 2 h enhanced the inhibited SOD
activity and reduced the MDA expression level (Table V). The expression levels of TNF-α
and IL-6 in 10% liver homogenate supernatants of the different
treatment groups of mice were measured by ELISA, and it was
observed that CCl4 injection led to an increase in the
serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6; however, pretreatment with Rg1
reduced this increase in a dose-dependent manner (Table VI).
 | Table V.Effects of CAPE on SOD activity and
MDA concentration in supernatants from LO2 cells treated
with CCl4 (mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8). |
Table V.
Effects of CAPE on SOD activity and
MDA concentration in supernatants from LO2 cells treated
with CCl4 (mean ± standard error of the mean; n=8).
| Groups | CAPE concentration,
µM | SOD, U/mgprot | MDA,
nmol/mgprot |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
5.24±0.353 |
0.71±0.12 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
2.01±0.246a |
1.85±0.24a |
| CAPE | 25 |
4.96±0.31b |
0.95±0.27b |
 | Table VI.Effects of Rg1 on serum levels of
TNF-α and IL-6 in CCl4-induced liver injury in mice. |
Table VI.
Effects of Rg1 on serum levels of
TNF-α and IL-6 in CCl4-induced liver injury in mice.
| Groups | Rg1 concentration,
µM | TNF-α, pg/ml | IL-6, pg/ml |
|---|
| Control | 0 |
18.42±3.57 |
23.66±5.32 |
| CCl4
model | 0 |
823.45±7.43a |
97.30±13.09a |
| Rg1 (low) | 10 |
81.39±14.75 |
96.20±10.53 |
| Rg1 (middle) | 20 |
68.56±11.17b |
78.75±7.17b |
| Rg1 (high) | 40 |
39.22±7.06b |
48.75±9.54b |
It is well known that NF-κB expression and activity
in liver Kupffer cells may be modulated by TNF-α, IL-6 and other
cytokines, and NF-κB may, in turn, activate these inflammatory
regulators (26,27). The results of the present study,
displayed in Fig. 2A and B,
demonstrated that CCl4 increased NF-κB p65 protein
expression and enhanced NF-kB binding activity, while pretreatment
with Rg1 reduced p65 protein expression and alleviated the enhanced
NF-κB binding. Therefore, Rg1 protected CCl4-induced
liver injury, by directly alleviating the inhibition of SOD
activity and reducing MDA, and possibly by inhibiting NF-κB
activity, thereby further alleviating the inhibited SOD activity
and reducing MDA, TNF-α and IL-6 expression levels.
Discussion
The present study demonstrated that pretreatment
with Rg1 protected the liver from CCl4-induced acute
injury in cell culture and animal experimental systems. It was
observed that pretreatment with Rg1 attenuated the pathological
damage to liver tissues in vivo and LO2 cell
death in vitro. The indicative enzymes of liver cell damage,
serum transaminases ALT and AST, were markedly increased in the
CCl4 treatment model group and decreased in the Rg1
pretreatment group. Further investigations into the antioxidant
properties of Rg1 in acute CCl4-induced liver injury
demonstrated that SOD activity was inhibited in the CCl4
treatment group, and recovered in the Rg1 pretreatment group; MDA
level was increased by treatment with CCl4 and
attenuated by pretreatment with Rg1. Inflammatory cytokines TNF-α
and IL-6, which were enhanced by CCl4 treatment, were
attenuated in the Rg1 pretreatment group. Rg1 inhibited p65
expression and NF-κB activity in vivo and in vitro,
and NF-κB inhibitor CAPE, which was observed to exhibit comparable
effects, enhanced SOD activity, reduced MDA level and promoted
LO2 cell survival. As NF-κB serves a role in the
activation of inflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that Rg1
protected CCl4-induced liver injury by directly
alleviating the inhibition of SOD activity and reducing MDA, and
additionally by inhibiting NF-κB activity, thereby further
alleviating the inhibited SOD activity and reducing MDA, TNF-α and
IL-6 expression levels.
As a common pathological state of various types of
liver disease, liver injury may be caused by ischemia, viral
infection, autoimmune disorders and various xenobiotic substances,
including alcohol, drugs and toxins (28). The present study used a
CCl4-induced acute liver injury model, and this type of
liver injury model is widely used in hepatoprotective drug
screening (29,30). The characteristics of the acute
liver injury induced by CCl4 are liver dysfunction and
cell morphology deterioration (31); therefore, alterations in
histopathology and liver function were investigated, and it was
observed that pretreatment with Rg1 attenuated the pathological
damage to liver tissues and LO2 cell death. In addition,
increased levels of ALT and AST expression caused by
CCl4 in animal experimental systems and cell culture,
which are direct hepatic functional indicators and have been
demonstrated to correlate with the severity of liver injury
(32), were markedly reduced by
pretreatment with Rg1. The results of the present study
demonstrated that pretreatment with Rg1 decreased hepatic
dysfunction and cell morphology deterioration induced by
CCl4.
Oxidative stress is considered to serve an important
role in the development of CCl4-induced acute liver
injury (33,34). When CCl4 enters the
liver and is activated by cytochrome P450 metabolism, it generates
various free radicals and reactive oxygen species for oxidative
stress and causes membrane lipid peroxidation (14,15).
The activity of SOD, an effective metalloenzyme which catalyzes the
dismutation of superoxide anions into H2O2
and O2 (35–37), was markedly increased compared with
the injury group. The studies of Zhang et al (31) and Li C (22), demonstrated that the expression
level of MDA was associated with CCl4-induced acute
liver injury in mice; increased expression of MDA, a lipid
peroxidative product of cell membranes (38), was prevented by pretreatment with
Rg1 in the present study. The hepatoprotective effect of Rg1 may be
partly due to attenuation of oxidative stress and inhibition of
lipid peroxidation.
Kupffer cells, as tissue macrophages, reside within
the liver sinusoid and serve a role in homeostatic liver
regeneration and protection (39–41).
Activated Kupffer cells mediate the hepatic inflammation process by
releasing a wide range of cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6
(42). A previous study reported
that NF-κB is sensitive to redox status in abnormal physiological
conditions, including CCl4-induced acute liver injury
(43). Additionally, the study of
Tao et al (12)
demonstrated that pretreatment with Rg1 inhibited the inflammatory
response and protected the mouse liver against ischemia-reperfusion
injury, partly through the NF-κB signaling pathway. The present
study demonstrated that pretreatment with Rg1 inhibited NF-κB
activity and p65 expression in Kupffer cells and reduced the serum
levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in acute CCl4-induced liver
injury in mice. As NF-κB expression and activity in liver Kupffer
cells may be modulated by TNF-α, IL-6 and other cytokines, and
NF-κB may, in turn, activate these inflammatory regulators, it is
hypothesized that the protective effect of Rg1 on
CCl4-induced liver injury was partly involved in the
attenuation of inflammatory responses expressed as a reduction of
serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels via the NF-κB signaling pathway.
NF-κB was first identified as a transcription factor
in 1986 by Sen and Baltimore (44). In an inactive state, NF-κB is
sequestered in the cytoplasm as a heterotrimer consisting of p50,
p65, and inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) subunits. On activation, IκBα
undergoes phosphorylation and ubiquitination-dependent degradation
leading to p65 nuclear translocation and binding to a specific
consensus sequence in the DNA, which results in gene transcription.
The nuclear translocation of NF-κB leads to gene expression of
prostaglandin G/H synthase 2, inducible nitric oxide synthase,
chemokines, adhesion molecules, matrix metalloproteinases and
various pro-inflammatory cytokines (45,46).
These released inflammatory factors subsequently activate further
amplification of NF-κB activity in a regulatory cycle. As a result,
the oxidative stress in injury liver activates NF-κB, triggering
expression of oxidative stress-responsive genes, which ultimately
leads to liver cell necrosis and apoptosis (47–49).
The present study demonstrated that Rg1 inhibited p65 expression
and NF-κB activity, in vivo and in vitro. The NF-κB
inhibitor CAPE, which was confirmed to exhibit a similar effect
compared with Rg1, enhanced SOD activity and reduced the MDA
expression level in addition to promoting LO2 cell
survival. Therefore, the possible underlying mechanisms of the
beneficial effect of Rg1 may be attributed to an attenuation of the
inflammatory response and oxidative stress in
CCl4-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of
NF-κB.
In conclusion, the present study reveals the
potential clinical value of Rg1, and demonstrates that pretreatment
with Rg1 may protect against CCl4-induced acute
hepatotoxicity in vivo and in vitro, via inhibition
of NF-κB activity to restore the anti-oxidative defense system and
downregulate pro-inflammatory signaling pathways.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of Anhui (grant no. 1508085QH151), the
Natural Science Foundation of the Provincial Education Department
of Anhui (grant no. KJ2015A147), the National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant no. 81001457) and the Foundation of
Bengbu Medical College (grant nos. Byycxz1422 and Byky1407ZD).
References
|
1
|
Protzer U, Maini MK and Knolle PA: Living
in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat Rev Immunol. 12:201–213.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duarte S, Baber J, Fujii T and Coito AJ:
Matrix metalloproteinases in liver injury, repair and fibrosis.
Matrix Biol. 44–46:147–156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bengmark S: Curcumin an atoxic antioxidant
and natural NFkappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, lipooxygenase, and
inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor: A shield against acute
and chronic diseases. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 30:45–51. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Williams R: Global challenges in liver
disease. Hepatology. 44:521–526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stickel F and Schuppan D: Herbal medicine
in the treatment of liver diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 39:293–304.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ghosh N, Ghosh R, Mandal V and Mandal S:
Recent advances in herbal medicine for treatment of liver diseases.
Pharm Biol. 49:970–988. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Attele AS, Wu JA and Yuan CS: Ginseng
pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem
Pharmacol. 58:1685–1693. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li QF, Shi SL, Liu QR, Tang J, Song J and
Liang Y: Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg1, cinnamic acid, and
tanshinone IIA in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells: Nuclear matrix
downregulation and cytoplasmic trafficking of nucleophosmin. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1918–1929. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Q, Kou JP and Yu BY: Ginsenoside Rg1
protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells
via inhibiting NF-κB activation. Neurochem Int. 58:119–125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Komatsu K, Tanaka H, Nakagawa D and
Kawashima K: Effect of notoginseng extracts and their components on
lipopolysaccharide and galactosamine mixture-induced impaired
hepatic function in mice. Yakugaku Zasshi. 132:831–836. 2012.(In
Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao L, Zou Y, Zhu J, Fan X and Li J:
Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice
through inhibition of cytokine secretion and lymphocyte
infiltration. Mol Cell Biochem. 380:203–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tao T, Chen F, Bo L, Xie Q, Yi W, Zou Y,
Hu B, Li J and Deng X: Ginsenoside Rg1 protects mouse liver against
ischemia-reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory and
anti-apoptosis properties. J Surg Res. 191:231–238. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hines IN and Wheeler MD: Recent advances
in alcoholic liver disease III. Role of the innate immune response
in alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
287:G310–G314. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
LeSage GD, Benedetti A, Glaser S, Marucci
L, Tretjak Z, Caligiuri A, Rodgers R, Phinizy JL, Baiocchi L,
Francis H, et al: Acute carbon tetrachloride feeding selectively
damages large, but not small, cholangiocytes from normal rat liver.
Hepatology. 29:307–319. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shiga A, Kakamu S, Sugiyama Y, Shibata M,
Makino E and Enomoto M: Acute toxicity of pierisin-1, a cytotoxic
protein from Pieris rapae, in mouse and rat. J Toxicol Sci.
31:123–137. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harada N, Iimuro Y, Nitta T, Yoshida M,
Uchinami H, Nishio T, Hatano E, Yamamoto N, Yamamoto Y and Yamaoka
Y: Inactivation of the small GTPase Rac1 protects the liver from
ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Surgery. 134:480–491. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Son G, Iimuro Y, Seki E, Hirano T, Kaneda
Y and Fujimoto J: Selective inactivation of NF-kappaB in the liver
using NF-kappaB decoy suppresses CCl4-induced liver injury and
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G631–G639.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suetsugu H, Iimuro Y, Uehara T, Nishio T,
Harada N, Yoshida M, Hatano E, Son G, Fujimoto J and Yamaoka Y:
Nuclear factor {kappa}B inactivation in the rat liver ameliorates
short term total warm ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Gut.
54:835–842. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Veal N, Hsieh CL, Xiong S, Mato JM, Lu S
and Tsukamoto H: Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
TNF-alpha promoter activity by S-adenosylmethionine and
5′-methylthioadenosine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
287:G352–G362. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Uesugi T, Froh M, Arteel GE, Bradford BU,
Gäbele E, Wheeler MD and Thurman RG: Delivery of IkappaB
superrepressor gene with adenovirus reduces early alcohol-induced
liver injury in rats. Hepatology. 34:1149–1157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Yi LT, Geng D, Han YY and Weng LJ:
Hepatoprotective effect of ethanol extract from Berchemia lineate
against CCL4-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice. Pharm Biol.
53:767–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fukada H, Yamashina S, Izumi K, Komatsu M,
Tanaka K, Ikejima K and Watanabe S: Suppression of autophagy
sensitizes kupffer cells to endotoxin. Hepatol Res. 42:1112–1118.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smedsrød B and Pertoft H: Preparation of
pure hepatocytes and reticuloendothelial cells in high yield from a
single rat liver by means of Percoll centrifugation and selective
adherence. J Leukoc Biol. 38:213–230. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li L, Wang Y, Qi B, Yuan D, Dong S, Guo D,
Zhang C and Yu M: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion
and migration by ginsenoside Rg1 via the inhibition of
NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:1779–1786.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kunsch C and Medford RM: Oxidative stress
as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ Res.
85:753–766. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parola M and Robino G: Oxidative
stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 35:297–306.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, Adachi M and
Nagata S: Essential roles of the Fas ligand in the development of
hepatitis. Nat Med. 3:409–413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Streetz KL, Wüstefeld T, Klein C, Manns MP
and Trautwein C: Mediators of inflammation and acute phase response
in the liver. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 47:661–673.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Masuda Y: Learning toxicology from carbon
tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Yakugaku Zasshi. 126:885–899.
2006.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang F, Wang X, Qiu X, Wang J, Fang H,
Wang Z, Sun Y and Xia Z: The protective effect of Esculentoside A
on experimental acute liver injury in mice. PLoS One.
9:e1131072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ozer J, Ratner M, Shaw M, Bailey W and
Schomaker S: The current state of serum biomarkers of
hepatotoxicity. Toxicology. 245:194–205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun F, Hamagawa E, Tsutsui C, Ono Y, Ogiri
Y and Kojo S: Evaluation of oxidative stress during apoptosis and
necrosis caused by carbon tetrachloride in rat liver. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1535:186–191. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weber LW, Boll M and Stampfl A:
Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: Carbon
tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol.
33:105–136. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Osuna C and Gitto E:
Actions of melatonin in the reduction of oxidative stress. A
review. J Biomed Sci. 7:444–458. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng N, Ren N, Gao H, Lei X, Zheng J and
Cao W: Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Schisandra
chinensis pollen extract on CCl4-induced acute liver damage in
mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 55:234–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ai G, Liu Q, Hua W, Huang Z and Wang D:
Hepatoprotective evaluation of the total flavonoids extracted from
flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic: In vitro and in vivo
studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:794–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Montanari RM, Barbosa LC, Demuner AJ,
Silva CJ, Andrade NJ, Ismail FM and Barbosa MC: Exposure to
Anacardiaceae volatile oils and their constituents induces lipid
peroxidation within food-borne bacteria cells. Molecules.
17:9728–9740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tsutsui H and Nishiguchi S: Importance of
Kupffer cells in the development of acute liver injuries in mice.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:7711–7730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meijer C, Wiezer MJ, Diehl AM, Schouten
HJ, Schouten HJ, Meijer S, van Rooijen N, van Lambalgen AA,
Dijkstra CD and van Leeuwen PA: Kupffer cell depletion by
CI2MDP-liposomes alters hepatic cytokine expression and delays
liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Liver. 20:66–77.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Seki E, Tsutsui H, Iimuro Y, Naka T, Son
G, Akira S, Kishimoto T, Nakanishi K and Fujimoto J: Contribution
of Toll-like receptor/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling
to murine liver regeneration. Hepatology. 41:443–450. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Akamatsu K, Yamasaki Y, Nishikawa M,
Takakura Y and Hashida M: Synthesis and pharmacological activity of
a novel water-soluble hepatocyte-specific polymeric prodrug of
prostaglandin E(1) using lactosylated poly(L-glutamic hydrazide) as
a carrier. Biochem Pharmacol. 62:1531–1536. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ko JH and Lim KT: Glycoprotein isolated
from Ulmus davidiana NAKAI protects against carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver injury in the mouse. J Pharmacol Sci.
101:205–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sen R and Baltimore D: Inducibility of
kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a
posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 47:921–928. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baeuerle PA and Baichwal VR: NF-kappa B as
a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory
molecules. Adv Immunol. 65:111–137. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nanji AA, Jokelainen K, Rahemtulla A, Miao
L, Fogt F, Matsumoto H, Tahan SR and Su GL: Activation of nuclear
factor kappa B and cytokine imbalance in experimental alcoholic
liver disease in the rat. Hepatology. 30:934–943. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tacchini L, Pogliaghi G, Radice L, Anzon E
and Bernelli-Zazzera A: Differential activation of heat-shock and
oxidation-specific stress genes in chemically induced oxidative
stress. Biochem J. 309:453–459. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim WH, Hong F, Jaruga B, Hu Z, Fan S,
Liang TJ and Gao B: Additive activation of hepatic NF-kappaB by
ethanol and hepatitis B protein X (HBX) or HCV core protein:
involvement of TNF-alpha receptor 1-independent and -dependent
mechanisms. FASEB J. 15:2551–2553. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Lucca FL, Serrano SV, Souza LR and
Watanabe MA: Activation of RNA-dependent protein kinase and nuclear
factor-kB by regulatory RNA from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
macrophages: Implications for cytokine production. Eur J Pharmacol.
450:85–89. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|