Introduction
Periodontal ligament (PDL) tissue, which originates
from cranial neural-crest-derived ectomesenchymal cells (1), is a specialized fibrous connective
tissue located between the cementum of the tooth root and the
alveolar bone (2). PDL serves a
role in anchoring teeth and maintaining the structural integrity of
the periodontium (2). Human PDL
cells (hPDLCs) form a heterogeneous mixture of cell types,
including fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts, epithelial
cells, vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and
certain types of neural cells (3).
The presence of multiple cell types has led to a hypothesis that
the PDL tissue may also contain stem cells that maintain PDL
homoeostasis and regenerate adjacent periodontal tissues. It has
been confirmed that multipotent stem cells of hPDLCs have the
ability to differentiate into osteoblastic/cementoblastic cells and
generate cementum/PDL-like tissue in vivo (4). Therefore, the application of hPDLCs
may be a promising therapeutic method for the reconstruction of
tissues damaged by periodontal diseases.
Hypoxia is commonly associated with pathologies
including tissue ischemia, inflammation and solid tumors (5–7).
Additionally, hypoxic microenvironments form in embryos, and adults
and often create specific niches which could regulate cellular
differentiation and multi-gene expression in verious cell types
(8). Furthermore, hypoxia has been
found to be a potent inducer of the expression of
osteogenesis/mineralization genes (9). Cells have the ability to modulate
their processes to adapt to specific hypoxic niches during
development and tissue maintenance or repair (8).
Cells respond to hypoxic microenvironment by
expressing a hypoxia-inducible heterodimeric transcription factor,
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), which serves an essential
role in sensing and responding to hypoxia-induced alterations in
the cellular environment (10,11).
HIF-1α regulates numerous hypoxia-responsive genes which are
involved in a variety of biological functions. Under normoxic
conditions, HIF-1α is targeted for proteasomal degradation by an
iron-containing prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzyme (12). By contrast, under hypoxic
conditions, HIF-1α evades hydroxylation and translocates to the
nucleus where it heterodimerizes with HIF-1β (13). Previous studies have demonstrated
that HIF-1α signaling pathway-mediated tissue hypoxia serves a
fundamental role in the regulation of stem/progenitor cell
recruitment, and the retention and differentiation of regenerating
tissues (14,15). It has also been demonstrated that
HIF-1α mediates the angiogenic, and osteogenic phases of bone
repair and regeneration, via genetic or pharmacological means
(10,16).
Deferoxamine (DFO) iron chelators can artificially
induce hypoxia by inhibiting PHD activity via chelation of iron in
the PHD active sites, which is required for PHD function, including
stabilization of HIF-1α expression (11,17).
Therefore, DFO has been extensively used as a hypoxia-mimetic agent
in normoxia and the effects are comparable to those resulting from
reduced atmospheric oxygen levels (17). Previous studies have demonstrated
that DFO directly triggers the differentiation of marrow stromal
cells (MSCs) (18), and increases
bone formation by stimulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis through
stabilization of HIF-1α expression (10).
Based on these observations, the influence of DFO on
hPDLCs was investigated and the preconditioning effect of DFO on
hPDLC osteogenic differentiation was evaluated. The results of the
present study may contribute to the efforts to design a cell
therapy for periodontal disease.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
All the participants of the present study signed
informed consent forms and the experimental protocol was approved
by the local Ethical Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of
Harbin Medical University (Harbin, China). All hPDLCs were derived
from PDL tissue which was obtained from a total of 10 clinically
healthy premolar teeth extracted for orthodontic reasons (two males
and three females aged 12–16 years) from April to June 2015 at The
Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University.
The extracted teeth were washed three times with PBS
Periodontal tissue was obtained from the middle third of the root
using a sterile scalpel. The tissue was cut with scissors into
small fragments following rinsing with growth media (α-Minimum
Essential Medium; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.,
Waltham, MA, USA) and placed in 25-cm2 culture flasks
containing Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine
serum (FBS; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, UT, USA), 4 mM
L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin.
Peridontal tissue was incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere
containing 5% carbon dioxide and 95% air. PDLCs were passaged until
they reached 80% confluence and the cells from the third to fifth
passages were used for the subsequent experiments.
For hypoxia treatment, hPDLCs were seeded on plates
and incubated with various concentrations (0, 5, 10 and 20 µM) of
DFO (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
Cell viability assay
The cell viability of hPDLCs was measured using an
MTT assay. hPDLCs were seeded in 96-well plates at an initial
density of 3.0×103 cells/well and cultured in DMEM with
10% FBS for 24 h. Subsequently, hPDLCs were starved overnight by
changing DMEM to a serum-free medium to compensate for the effect
of growth factors, and then incubated with 0, 5, 10 and 20 µM DFO
for 24, 48 or 72 h. At each time point, 20 µl MTT (0.5 mg/ml final
concentration; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) solution was added into
each well and hPDLCs were incubated at 37°C for 4 h. The
supernatants were subsequently removed and replaced with 150 µl
dimethyl sulfoxide (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 10 min to
solubilize the formazan. The absorbance was measured at a
wavelength of 490 nm with a microplate reader (Model 550; Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). A total of three
independent experiments were performed.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
To quantify the mRNA expression of HIF-1α,
runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx-2), osteopontin (OPN),
collagen type I (Col-1), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and
transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), confluent cells were
incubated with DFO (0, 5, 10 or 20 µM) for 2 days and total RNA was
isolated with TRIzol (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.),
according to the manufacturer's protocol. The cDNA was synthesized
from 1 µg total RNA using the PrimeScript™ RT Reagent kit (cat. no.
RR047A; Takara Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Dalian, China), according to
the manufacturer's protocol. The expression of HIF-1α was detected
using qPCR using SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ II (cat. no.
RR820A; Takara Biotechnology Co. Ltd.). The Mx3005P qPCR System
Thermal Cycler (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, USA) was
used according to the manufacturer's protocol. A total of 1 µl cDNA
was used as a template in a 25-µl reaction mixture. The mixture was
initially heated at 95°C for 30 sec followed by 40 cycles of
denaturation at 95°C for 5 sec and combined annealing/extension at
60°C for 30 sec. Quantities of the reaction products were
normalized to the β-actin reference gene. All reactions were run in
triplicate. The data was analyzed using the comparative threshold
cycle (2−∆∆Cq) method (19). The primer sequences used for all
qPCR reactions are listed in Table
I.
 | Table I.Primer sequences for quantitative
polymerase chain reaction. |
Table I.
Primer sequences for quantitative
polymerase chain reaction.
|
| Primer sequence
(5′-3′) |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|
| HIF-1α |
GTGTTATCTGTCGCTTTGAGTC |
CTGGCTGCTGTAATAATGTTCC |
| α-SMA |
CGGGACATCAAGGAGAAACT |
CCATCAGGCAACTCGTAACTC |
| TGF-β1 |
ACCTTGGGCACTGTTGAAGT |
CTCTGGGCTTGTTTCCTCAC |
| Runx2 |
TAGGCGCATTTCAGGTGCTT |
GGTGTGGTAGTGAGTGGTGG |
| OPN |
AGCAGCTTTACAACAAATACCCAG |
TTACTTGGAAGGGTCTGTGGG |
| Col-1 |
TGAACTTGTTGCTGAGGGC |
GCAGGCGTGATGGCTTAT |
| β-actin |
TTGCCGACAGGATGCAGAA |
CTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCACAT |
Wound healing assay
The scratch-wound assay was performed to determine
the effects of DFO on the migration of hPDLCs. The hPDLCs were
seeded into 6-well plates at an initial density of 5×105
cells/well and cultured to reach 80–90% confluence as a monolayer.
In order capture images of the corresponding locations at each
indicated time point, the outside surface of each well was marked
prior to the test. The surface of the cellular monolayer was then
gently and linearly scratched with a sterile pipette tip. Following
washing and removal of the detached cells, the plates were
incubated at 37°C with fresh medium containing 0, 5, 10 and 20 µM
DFO. Following 0, 24 and 48 h of incubation, phase contrast images
of the wounds were visualized under a light microscope (Eclipse
80i; Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and recorded using
NIS-Elements Basic Research software (Nikon Corporation). The
number of hPDLCs that migrated into the scratch area was counted to
quantify the cell migration rates. Experiments were independently
repeated three times.
Osteogenic induction
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of
7×104 cells/well. When confluent, the cells were treated
with 0, 5, 10 or 20 µM DFO for 2 days, and then changed to the
osteogenic medium DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 10 mM sodium
β-glycerophosphate, 100 nM dexamethasone and 50 mg/l ascorbic acid,
to induce mineralization. Osteogenic medium was replaced every 3
days.
Alkaline phosphatase activity
assay
Following 5 days of mineralization, ALP activity was
measured using a p-nitrophenol phosphate assay (ALP assay kit;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Shanghai, China), according to
the manufacturer's protocol. Initially, hPDLCs were washed three
times with PBS and lyzed with 0.1% Triton X-100. Subsequently, the
supernatant was collected into a 96-well plate, mixed with the
substrates and p-nitrophenol from the ALP assay kit and incubated
for 10 min at 37°C. Following the incubation, the absorbance of
p-nitrophenol was measured using a microplate reader at a
wavelength of 405 nm.
Immunofluorescence analysis
Immunofluorescence analysis of Col-1 in hPDLCs was
performed on the 5th day of osteogenic induction. Cells were fixed
in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 30 min. Following
rinsing with PBS, cells were incubated with 3% bovine serum albumin
(Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) for 1 h at room temperature
to bind nonspecific binding sites. Cells were then incubated
overnight at 4°C with a rabbit anti-human Col-I polyclonal primary
antibody (1:500; cat. no. ab34710; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). The
fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated goat polyclonal anti-rabbit
immunoglobulin G was used as the secondary antibody (1:160; cat.
no. ZF-0314; OriGene Technologies, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA) and
incubated with the membrane for 1 h at room temperature. Then, the
samples were incubated with DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 3
min at room temperature to allow for nucleus detection. Cell
staining was observed using a fluorescence microscope (Nikon
Corporation). Fluorescence quantification was achieved by comparing
the integrated optical density/pixel value of Col-1 between the DFO
group and the control group using ImageJ software (version 1.42q;
National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Alizarin red S (ARS) staining
Following induction of mineralization for 14 days,
mineral nodule formation was determined by 0.1% ARS staining (pH
4.2; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). For each experiment, human hPDLC
monolayers were washed twice with PBS and fixed with 95% ice-cold
ethanol for 10 min and rinsed twice with distilled water. Fixed
cells were stained with ARS for 30 min at room temperature and
washed with distilled water once more. ARS staining images were
captured using a phase-contrast microscope and calculated using the
Matlab image analysis software (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS
software for Windows (version 19.0.1; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
All experiments were performed in triplicate and results were
expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis
was performed by one-way analysis of variance followed by the
Dunnett's test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
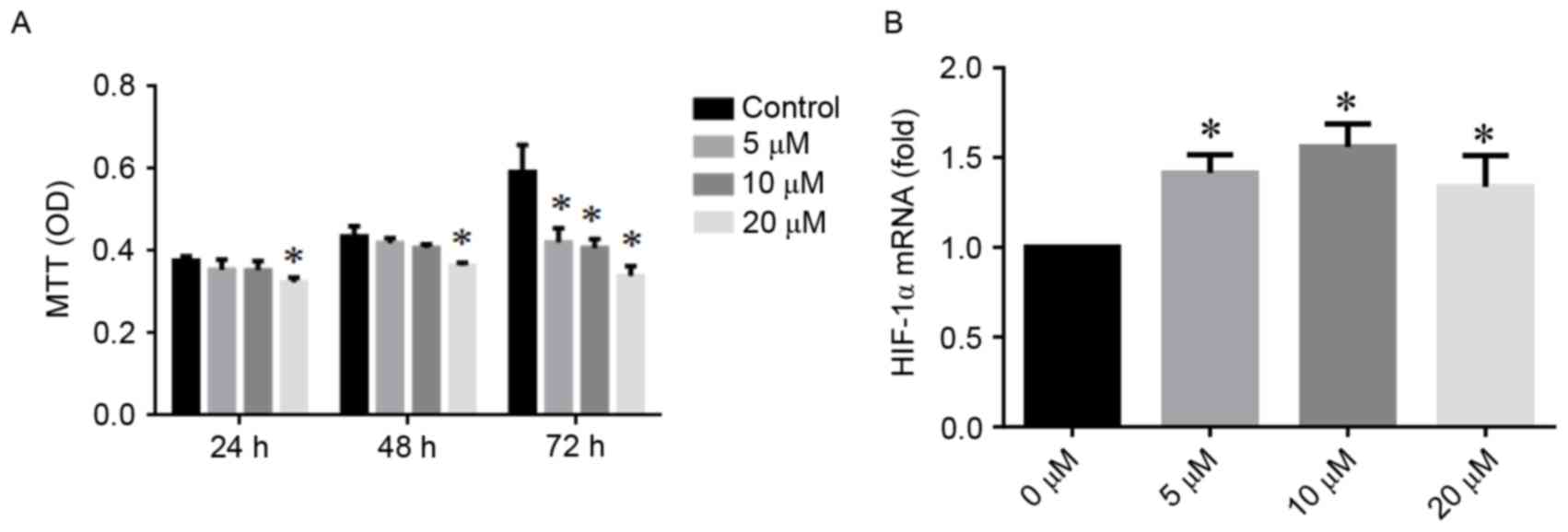
Effects of DFO on cell viability
MTT assays demonstrated a concentration-dependent
effect of DFO on hPDLC viability (Fig.
1A). Following a 48 h treatment, no significant difference was
observed between the 5 and 10 µM DFO groups compared with the
control group. At 72 h, the viability of hPDLCs decreased in all
DFO groups compared with the control group (all P<0.05). When
treated with high concentration of DFO (20 µM), the viability of
hPDLC significantly decreased as early as after 24 h.
DFO promotes the expression of HIF-1α
in hPDLCs
As presented in Fig.
1B, the expression of HIF-1α mRNA in hPDLCs was increased by
DFO. Compared with the control group, at the 48 h time point, the
expression levels of HIF-1α mRNA were increased 1.4-fold and
1.6-fold following incubation with 5 and 10 µM DFO, respectively
(both P<0.05).
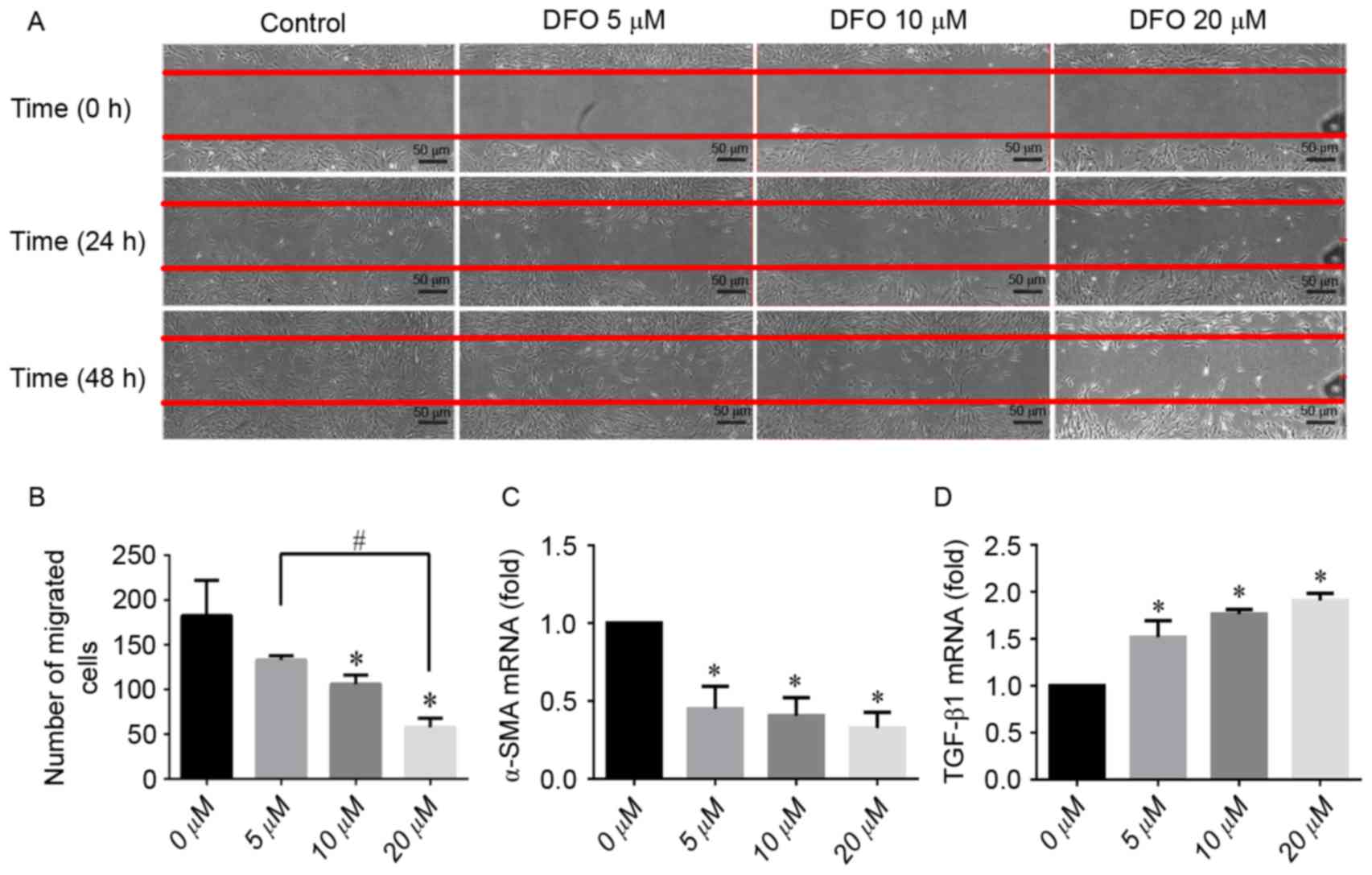
Scratch wound healing assay
The results of the scratch-wound assay are presented
in Fig. 2A. On the 2nd day DFO
demonstrated an inhibitory effect on hPDLC migration in a
concentration-dependent manner. There was no significant difference
in the number of cells that migrated into the wound area between
the low concentration (5 µM) DFO group and the control group
(Fig. 2B). In the 20-µM DFO group,
an increased amount of interspersed non-viable cells could be
observed under the light microscope, compared with the control
group. Subsequently, the α-SMA and TGF-β1 mRNA expression during
scratch wound healing was examined. Results from qPCR demonstrated
that DFO downregulated the expression of α-SMA (Fig. 2C). Contrastingly, the level of
TGF-β1 mRNA was upregulated by DFO in a concentration-dependent
manner (all P<0.05; Fig.
2D).
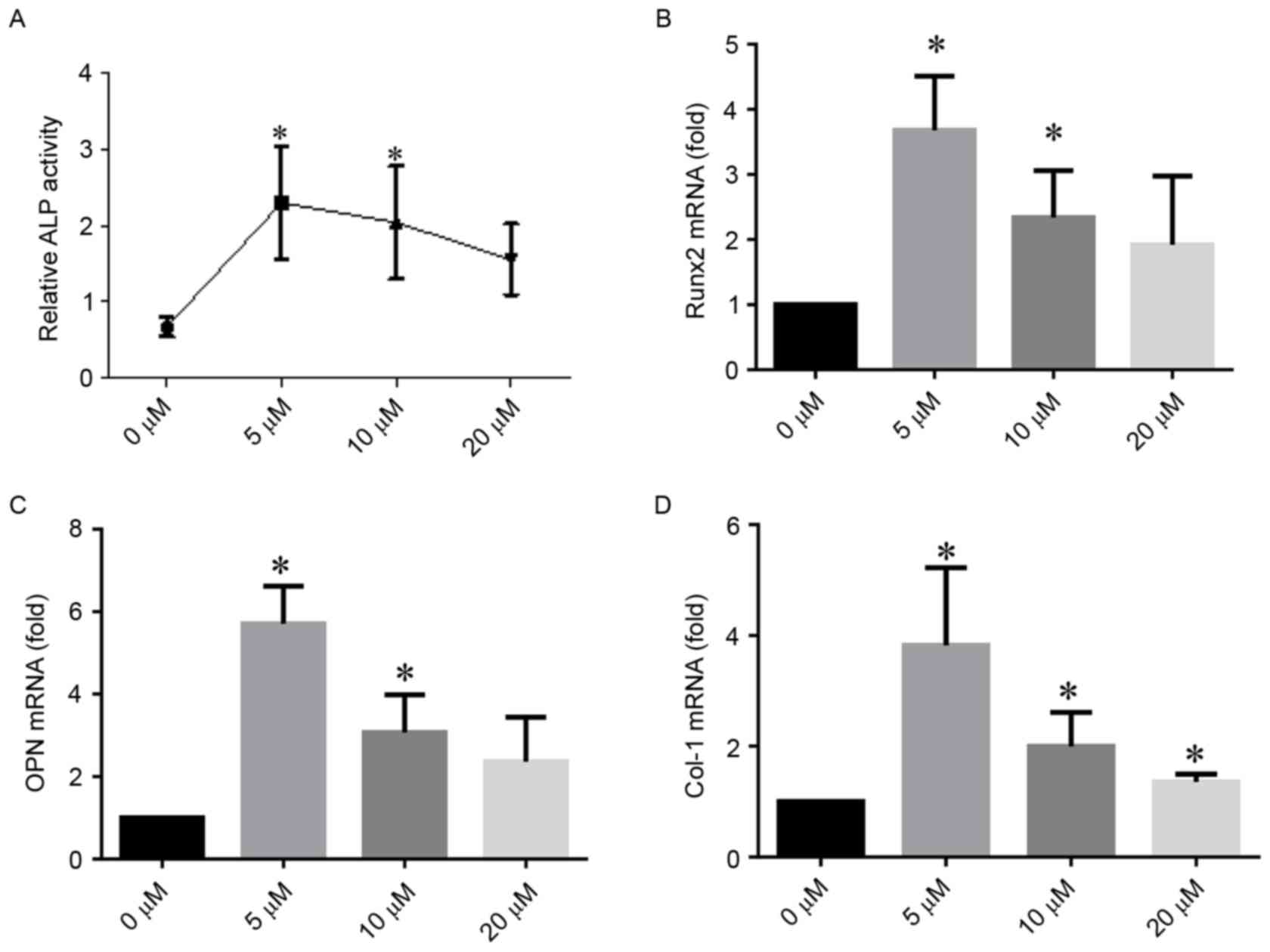
Effects of DFO on osteogenic
differentiation
ALP activity assay
ALP activity assays demonstrated that DFO
significantly promoted ALP activity in hPDLCs. Particularly, 5 µM
DFO demonstrated an increased activating potential compared with
the control group (P<0.05; Fig.
3A).
DFO induces the expression of
osteogenic-associated genes in vitro
qPCR demonstrated that DFO upregulated the mRNA
expression of hPDLC-osteogenic markers after 5 days of
mineralization (Fig. 3B-D).
Similarly to the results of the ALP assay, 5 µM DFO exhibited an
increased ability to stimulate osteogenic differentiation compared
with 10 µM DFO. Compared with the control group, the mRNA
expression of Runx2 increased to nearly 3.7- and 2.3-fold when
hPDLCs were treated with 5 and 10 µM DFO, respectively (Fig. 3B). The expression level of OPN
increased to >5- and 3-fold when treated with 5 and 10 µM DFO,
compared with the control group (Fig.
3C). The Col-1 expression quadrupled and doubled compared with
the control group when 5 and 10 µM DFO were applied, respectively
(Fig. 3D). The 20 µM treatment
with DFO also induced significant changes in Col-1 expression
(P<0.05).
DFO increases Col-1 synthesis in hPDLCs
Immunofluo-rescence staining for Col-1 demonstrated
a significant increase in staining intensity following treatment
with 5 and 10 µM DFO, compared with the control group (both
P<0.05; Fig. 4).
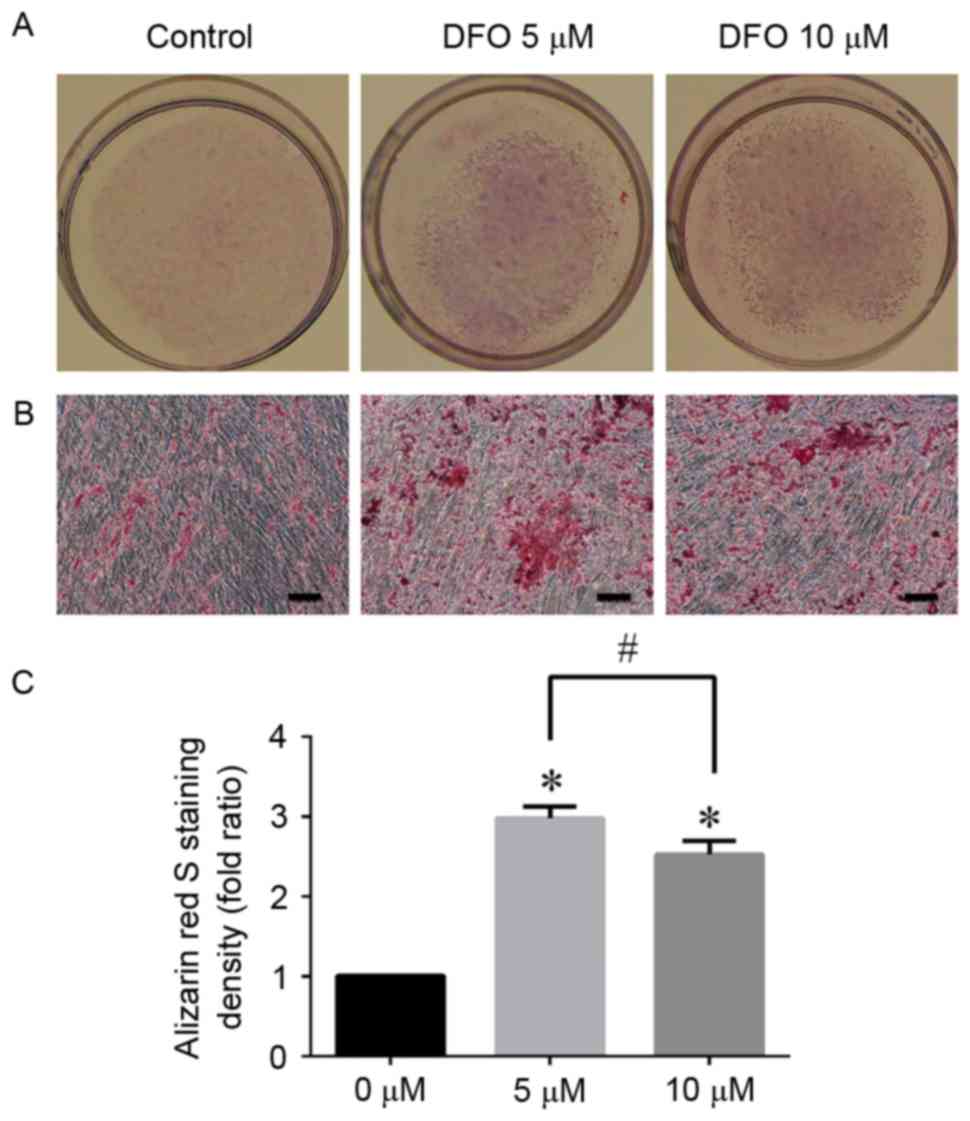
ARS staining
Mineralized nodule formation was analyzed using ARS
staining following 14 days of osteogenic induction (Fig. 5). The results were consistent with
the data obtained from the ALP activity assay and qPCR. There was
an increased calcium deposition in DFO groups compared with the
control group, and the intensity of ARS staining with 5 and 10 µM
DFO was increased 2.977 and 2.562-fold compared with the control
group, respectively. However, due to low cell viability, no
mineralization was observed when hPDLCs were treated with 20 µM DFO
(data not shown).
Discussion
Periodontitis is one of the most common inflammatory
diseases resulting from a complex interplay between bacterial
infection and host responses, and is characterized by destruction
of the attachment apparatus and the supporting bone of teeth
(20). Periodontitis is the most
prevalent cause of tooth loss and is difficult to heal (20). Searching for an effective method
for periodontium remodeling is an important part of the effort to
develop periodontitis therapeutic strategies.
PDL cells form a heterogeneous cell population and
have a potential to regenerate periodontal tissue under certain
conditions (4). Previous in
vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that under
hypoxic conditions the proportion of osteogenesis cells and their
differentiation potential are increased compared with under
normoxic conditions (9,21). In the present study, genetics-based
evidence that the DFO-induced hypoxia has the potency to induce
osteogenic differentiation in hPDLCs was presented.
Initially, the effect of DFO on human PDL cell
viability was investigated using the MTT method. It was
demonstrated that proliferation of hPDLCs was inhibited by DFO in a
concentration-dependent manner, while low concentrations of DFO
exhibited no apparent inhibitory effect on hPDLCs. One of the
reasons for the negative effect of DFO on hPDLC proliferation may
be associated with the removal of iron, which serves a role in
metabolic pathways. It has been previously suggested that through
chelating the intracellular iron pool, DFO can inhibit the activity
of ribonucleotide reductase, which is required for the synthesis of
deoxynucleotides and results in G1/S cell-cycle arrest (22).
The MTT results were consistent with those
previously reported in the literature. The results demonstrated
that DFO-induced hypoxia could downregulate the growth of
osteoblast through inhibition of Wnt signaling pathways via
activation of HIF-1α (23). The
proliferation of umbilical cord-derived human mesenchymal stem
cells is also significantly inhibited by DFO through influencing
the cell cycle, attenuating the intercellular signal transmission
and altering cell morphology/ultrastructure (24). Previous experimental in vivo
and in vitro research, as well as several initial clinical
trials, demonstrated that DFO could effectively inhibit certain
neoplasm growths and induce cell differentiation (25). Additionally, certain experiments
demonstrated that inhibition of growth is an important transition
point in the initiation of differentiation and mineralization of
proliferating cells (26). The
mechanism of DFO activity on PDL cells is complex and it is unclear
whether hPDLC proliferation inhibition is associated with
differentiation.
The migration of hPDLCs towards the site of injury
is necessary for periodontium healing. In the present study,
scratch-wound assays were performed to observe the effects of DFO
on the migration of hPDLCs. The results indicated that low
concentrations of DFO exhibited little inhibition on migration
within 48 h; however, the high concentration exhibited a
concentration-dependent inhibitory effect. In agreement with the
present study, a previous study reported that stress-fiber
formation was inhibited through cellular iron depletion mediated by
DFO, which could lead to inhibition of cellular migration (27). A previous study on the inhibitory
effect of DFO was also performed in the context of anticancer
treatments (28).
The mRNA expression of α-SMA and TGF-β1, which are
involved in scratch wound healing, was also examined. In wound
contraction, α-SMA serves a crucial role by increasing contractile
activity of stress fibers and the abundance of this protein is
positively associated with wound contraction efficiency in
vivo (29). The results from
qPCR demonstrated that the expression of α-SMA was downregulated by
DFO in a concentration-dependent manner, consistent with the wound
healing assay results. Downregulated expression of α-SMA may be
partly due to a low cellular oxygen tension in hPDLCs resulting
from upregulated expression of HIF-1α induced by DFO. Previous
studies have demonstrated that reduction of extra- and
intra-cellular tension leads to the removal of α-SMA from stress
fibers within h; under continued low stress, expression levels of
α-SMA are reduced (29,30). The results of the present study
were in agreement with previous evidence that dermal fibroblasts
exhibit low expression of α-SMA, and decreased migration and
proliferation under hypoxic conditions (31). In the future, DFO may serve a role
in the treatment of liver fibrosis by decreasing the expression of
α-SMA in hepatic stellate cells (32).
TGF-β1, which is highly expressed in the entirety of
periodontal ligament tissue, is a multifunctional cytokine that
regulates various cellular activities, including cell
differentiation, synthesis of extracellular matrix proteins and
wound repair (33,34). TGF-β1 induces α-SMA expression in
myofibroblasts and is a key regulator of type I collagen (25). In the present study, the expression
level of TGF-β1 in DFO-treated hPDLCs increased markedly, which is
consistent with the previous experiments demonstrating increased
levels of active and total TGF-β1 in response to hypoxic conditions
(30,35). α-SMA expression decreased in
hypoxic conditions, suggesting that hypoxia desensitized the
expression of α-SMA in the presence of TGF-β1. This phenomenon may
be in part due to concomitant downregulation of the expression of
the TGF-β1 receptor subunit, TGFβ-RII, possibly by a negative
TGF-β1 feedback loop (30). This
mechanism was proposed in a previous study, which indicated
significantly reduced expression of α-SMA and wound contraction
despite a high level of TGF-β1 when skin myofibroblasts were
cultured in hypoxic condition for 5 days (30). In addition, an increased level of
TGF-β1 could further increase the expression of HIF-1α (36) and stabilize hypoxia in hPDLCs. In
the future, thorough studies focused on this issue shall be
conducted.
Hard tissue regeneration is the most important part
in periodontium reconstruction. It is accepted that hPDLCs
demonstrate specific osteoblast-like properties, have osteogenic
characteristics (37), and can
differentiate into cementoblasts and osteoblasts, which are
necessary for cementum and alveolar bone formation, respectively.
The present study revealed that preconditioning of hPDLCs with DFO
could significantly stimulate ALP activity, upregulate the
expression of osteogenesis/cementogenesis-associated genes and
induce mineralization.
ALP, a membrane-associated enzyme, serves a key role
in connective tissue calcification and mineral deposition (38). Furthermore, ALP is also an early
marker for osteoblastic differentiation, and an indicator of the
presence of osteoblasts and new bone formation (39). HPDLCs exhibit increased ALP
activity compared with gingival fibroblasts, suggesting that hPDLCs
are crucial in the development of osteogenic characteristics
(38). In the present study, DFO
significantly increased ALP activity in hPDLCs and 5 µM DFO had the
most prominent effect.
Runx2, OPN and Col-1 are osteogenic-specific genes
in hPDLCs. Runx2, the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, is
described as the master regulator in the commitment of
osteoblastogenesis (40) and
regulates the expression of a number of genes associated with
osteoblasts (41). OPN produced by
osteoblasts at various stages of differentiation is one of the
vital non-collagenous bone matrix proteins. High OPN
calcium-binding potential can promote calcium adhesion, thus
influencing mineralization events (42). Col-1, an early marker of osteogenic
differentiation, is a major extracellular matrix component of
periodontal tissues that promotes osteoblast differentiation and
mineralization (43). The qPCR
conducted in the present study further demonstrated that DFO could
enhance osteogenic differentiation of hPDLCs by markedly
accelerating the expression of the osteogenic-specific genes.
To verify the role of DFO in the mineralization of
hPDLCs, a mineralization assay using ARS staining was performed. An
enhanced calcium deposition was observed in DFO groups compared
with the control group, indicating that DFO could promote the
mineralization propertied of hPDLCs.
From the qPCR and ARS staining results it was
inferred that 5 µM DFO is more efficient than 10 µM for
mineralization induction under normoxic condition. The adverse
effect of high DFO level on osteogenic ability was partly due to an
excessive depletion of iron in hPDLCs, which could also lead to
decreased cell viability. These results reinforce the previous
findings that osteogenesis is dependent on iron homeostasis in a
biphasic manner: Mild iron deficiency promotes osteogenesis, while
severe iron deficiency can inhibit this process (44). The results are further reinforced
by the evidence that a higher concentration of 20 µM DFO completely
abolished mineralization due to its toxicity on hPDLCs. Therefore,
it is vital to determine a suitable DFO concentration in order to
achieve the optimal osteogenic efficacy.
To conclude, the data gathered in the present study
indicate that by affecting osteogenic-associated factors, DFO could
enhance osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in hPDLCs.
These results provide a reference for further research on the
molecular mechanisms behind these processes. The results may also
have clinical implications since preconditioning of hPDLCs with DFO
may improve the efficacy of cell therapy and DFO is a promising
candidate for improving hard tissue regenerative potential in
periodontal disease. The mechanism underlying periodontal hard
tissue formation by hPDLCs treated with DFO in vivo remains
to be elucidated.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81570951) and the
Special Foundation for Sino-Russian Translational Medicine Research
Center of Harbin Medical University (grant no. CR201412).
References
|
1
|
Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, Bringas P Jr, Han
J, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP and Sucov HM: Fate of the
mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular
morphogenesis. Development. 127:1671–1679. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beertsen W, McCulloch Ca and Sodek J: The
periodontal ligament: A unique, multifunctional connective tissue.
Periodontol 2000. 13:20–40. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alvarez R, Lee HL, Wang CY and Hong C:
Characterization of the osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem
cells from human periodontal ligament based on cell surface
markers. Int J Oral Sci. 7:213–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM,
Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY and Shi S:
Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human
periodontal ligament. Lancet. 364:149–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1:
Oxygen homeostasis and disease pathophysiology. Trends Mol Med.
7:345–350. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia-a key regulatory factor
in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eltzschig HK and Carmeliet P: Hypoxia and
inflammation. N Engl J Med. 364:656–665. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simon MC and Keith B: The role of oxygen
availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:285–296. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ren H, Cao Y, Zhao Q, Li J, Zhou C, Liao
L, Jia M, Zhao Q, Cai H, Han ZC, et al: Proliferation and
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells under hypoxic
conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 347:12–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wan C, Gilbert SR, Wang Y, Cao X, Shen X,
Ramaswamy G, Jacobsen KA, Alaql ZS, Eberhardt AW, Gerstenfeld LC,
et al: Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 pathway
accelerates bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
686–691. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Mediator of
physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 88:1474–1480. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bruick RK and McKnight SL: A conserved
family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science.
294:1337–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ,
Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Levine JP
and Gurtner GC: Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic
gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med. 10:858–864.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao T, Zhang CP, Liu ZH, Wu LY, Huang X,
Wu HT, Xiong L, Wang X, Wang XM, Zhu LL and Fan M: Hypoxia-driven
proliferation of embryonic neural stem/progenitor cells-role of
hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1alpha. FEBS J.
275:1824–1834. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Wan C, Deng L, Liu X, Cao X,
Gilbert SR, Bouxsein ML, Faugere MC, Guldberg RE, Gerstenfeld LC,
et al: The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples
angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development. J Clin
Invest. 117:1616–1626. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hirsilä M, Koivunen P, Xu L, Seeley T,
Kivirikko KI and Myllyharju J: Effect of desferrioxamine and metals
on the hydroxylases in the oxygen sensing pathway. FASEB J.
19:1308–1310. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qu ZH, Zhang XL, Tang TT and Dai KR:
Promotion of osteogenesis through beta-catenin signaling by
desferrioxamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 370:332–337. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS and Johnson
NW: Periodontal diseases. Lancet. 366:1809–1820. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lennon DP, Edmison JM and Caplan AI:
Cultivation of rat marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in reduced
oxygen tension: Effects on in vitro and in vivo
osteochondrogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 187:345–355. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nurtjahja-Tjendraputra E, Fu D, Phang JM
and Richardson DR: Iron chelation regulates cyclin D1 expression
via the proteasome: A link to iron deficiency-mediated growth
suppression. Blood. 109:4045–4054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen D, Li Y, Zhou Z, Wu C, Xing Y, Zou X,
Tian W and Zhang C: HIF-1α inhibits Wnt signaling pathway by
activating Sost expression in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 8:e659402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeng HL, Zhong Q, Qin YL, Bu QQ, Han XA,
Jia HT and Liu HW: Hypoxia-mimetic agents inhibit proliferation and
alter the morphology of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal
stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 12:322011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Callens C, Coulon S, Naudin J,
Radford-Weiss I, Boissel N, Raffoux E, Wang PH, Agarwal S, Tamouza
H, Paubelle E, et al: Targeting iron homeostasis induces cellular
differentiation and synergizes with differentiating agents in acute
myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med. 207:731–750. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stein GS, Lian JB and Owen TA:
Relationship of cell growth to the regulation of tissue-specific
gene expression during osteoblast differentiation. FASEB J.
4:3111–3123. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun J, Zhang D, Zheng Y, Zhao Q, Zheng M,
Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR: Targeting the metastasis suppressor,
NDRG1, using novel iron chelators: Regulation of stress
fiber-mediated tumor cell migration via modulation of the
ROCK1/pMLC2 signaling pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 83:454–469. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Z, Zhang D, Yue F, Zheng M, Kovacevic
Z and Richardson DR: The iron chelators Dp44mT and DFO inhibit
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via up-regulation
of N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1). J Biol Chem.
287:17016–17028. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hinz B, Gabbiani G and Chaponnier C: The
NH2-terminal peptide of alpha-smooth muscle actin inhibits force
generation by the myofibroblast in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biol.
157:657–663. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Modarressi A, Pietramaggiori G, Godbout C,
Vigato E, Pittet B and Hinz B: Hypoxia impairs skin myofibroblast
differentiation and function. J Invest Dermatol. 130:2818–2827.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Faulknor RA, Olekson MA, Nativ NI,
Ghodbane M, Gray AJ and Berthiaume F: Mesenchymal stromal cells
reverse hypoxia-mediated suppression of α-smooth muscle actin
expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
458:8–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin H, Terai S and Sakaida I: The iron
chelator deferoxamine causes activated hepatic stellate cells to
become quiescent and to undergo apoptosis. J Gastroenterol.
42:475–484. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fujii S, Maeda H, Tomokiyo A, Monnouchi S,
Hori K, Wada N and Akamine A: Effects of TGF-β1 on the
proliferation and differentiation of human periodontal ligament
cells and a human periodontal ligament stem/progenitor cell line.
Cell Tissue Res. 342:233–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zimmerman KA, Graham LV, Pallero MA and
Murphy-Ullrich JE: Calreticulin regulates transforming growth
factor-β-stimulated extracellular matrix production. J Biol Chem.
288:14584–14598. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alizadeh N, Pepper MS, Modarressi A, Alfo
K, Schlaudraff K, Montandon D, Gabbiani G, Bochaton-Piallat ML and
Pittet B: Persistent ischemia impairs myofibroblast development in
wound granulation tissue: A new model of delayed wound healing.
Wound Repair Regen. 15:809–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McMahon S, Charbonneau M, Grandmont S,
Richard DE and Dubois CM: Transforming growth factor beta1 induces
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 stabilization through selective
inhibition of PHD2 expression. J Biol Chem. 281:24171–24181. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nagatomo K, Komaki M, Sekiya I, Sakaguchi
Y, Noguchi K, Oda S, Muneta T and Ishikawa I: Stem cell properties
of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 41:303–310.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Murakami Y, Kojima T, Nagasawa T,
Kobayashi H and Ishikawa I: Novel isolation of alkaline
phosphatase-positive subpopulation from periodontal ligament
fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 74:780–786. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu C, Zhou Y, Lin C, Chang J and Xiao Y:
Strontium-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with
improved osteogenic/cementogenic differentiation of periodontal
ligament cells for periodontal tissue engineering. Acta Biomater.
8:3805–3815. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vimalraj S, Arumugam B, Miranda PJ and
Selvamurugan N: Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in
osteoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 78:202–208. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jensen ED, Gopalakrishnan R and Westendorf
JJ: Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts. Biofactors.
36:25–32. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Elanagai R, Veeravarmal V and Nirmal RM:
Osteopontin expression in reactive lesions of gingiva. J Appl Oral
Sci. 23:26–32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mathews S, Bhonde R, Gupta PK and Totey S:
A novel tripolymer coating demonstrating the synergistic effect of
chitosan, collagen type 1 and hyaluronic acid on osteogenic
differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 414:270–276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao GY, Zhao LP, He YF, Li GF, Gao C, Li
K and Xu YJ: A comparison of the biological activities of human
osteoblast hFOB1.19 between iron excess and iron deficiency. Biol
Trace Elem Res. 150:487–495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|