Spandidos Publications style
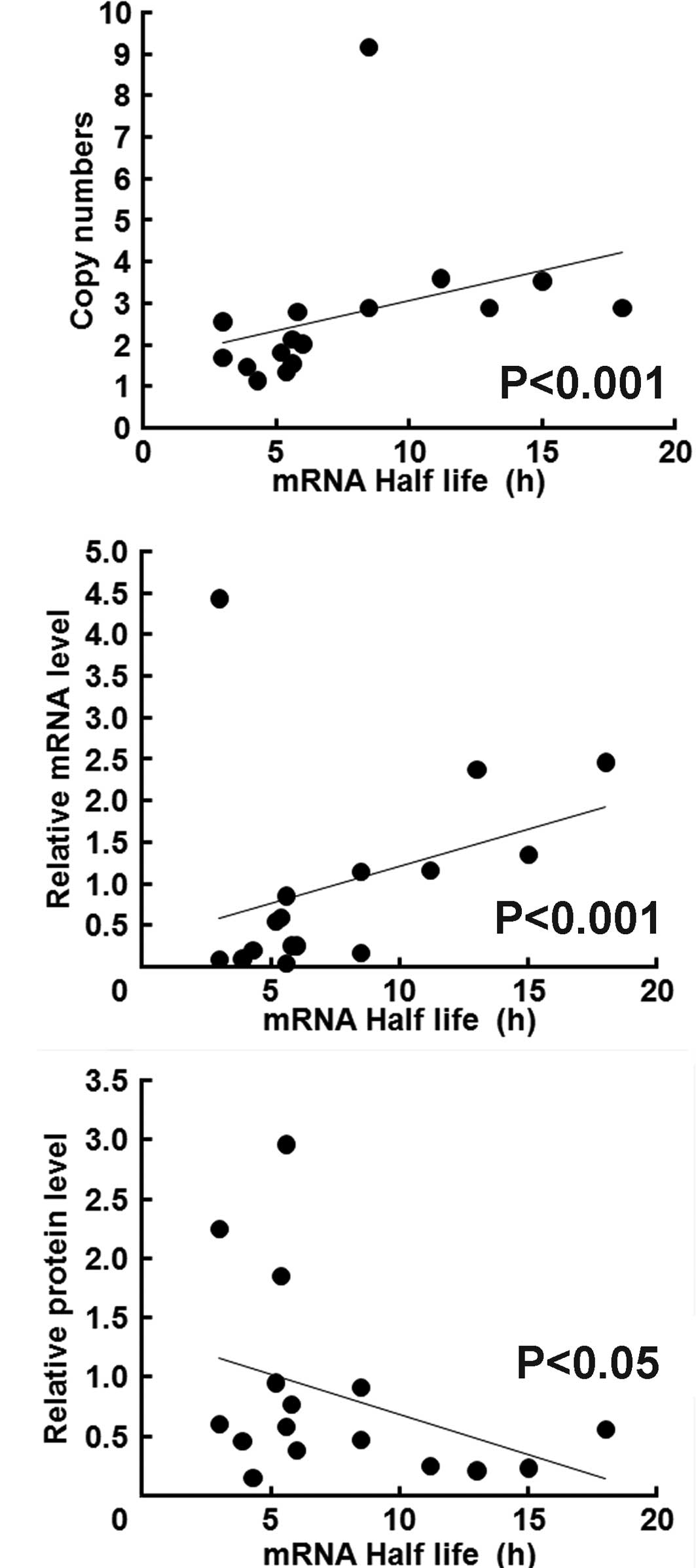
Nakazaki K, Kato Y, Taguchi T, Inayama Y, Ishiguro Y, Kondo N, Horiuchi C, Sakakibara A and Tsukuda M: Heterozygous mutation (G/G→G/A) at nt 2607 of the EGFR gene is closely associated with increases in EGFR copy number and mRNA half life, but impaired EGFR protein synthesis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck – implication for gefitinib efficacy. Oncol Lett 1: 1017-1020, 2010.
APA
Nakazaki, K., Kato, Y., Taguchi, T., Inayama, Y., Ishiguro, Y., Kondo, N. ... Tsukuda, M. (2010). Heterozygous mutation (G/G→G/A) at nt 2607 of the EGFR gene is closely associated with increases in EGFR copy number and mRNA half life, but impaired EGFR protein synthesis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck – implication for gefitinib efficacy. Oncology Letters, 1, 1017-1020. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2010.188
MLA
Nakazaki, K., Kato, Y., Taguchi, T., Inayama, Y., Ishiguro, Y., Kondo, N., Horiuchi, C., Sakakibara, A., Tsukuda, M."Heterozygous mutation (G/G→G/A) at nt 2607 of the EGFR gene is closely associated with increases in EGFR copy number and mRNA half life, but impaired EGFR protein synthesis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck – implication for gefitinib efficacy". Oncology Letters 1.6 (2010): 1017-1020.
Chicago
Nakazaki, K., Kato, Y., Taguchi, T., Inayama, Y., Ishiguro, Y., Kondo, N., Horiuchi, C., Sakakibara, A., Tsukuda, M."Heterozygous mutation (G/G→G/A) at nt 2607 of the EGFR gene is closely associated with increases in EGFR copy number and mRNA half life, but impaired EGFR protein synthesis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck – implication for gefitinib efficacy". Oncology Letters 1, no. 6 (2010): 1017-1020. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2010.188