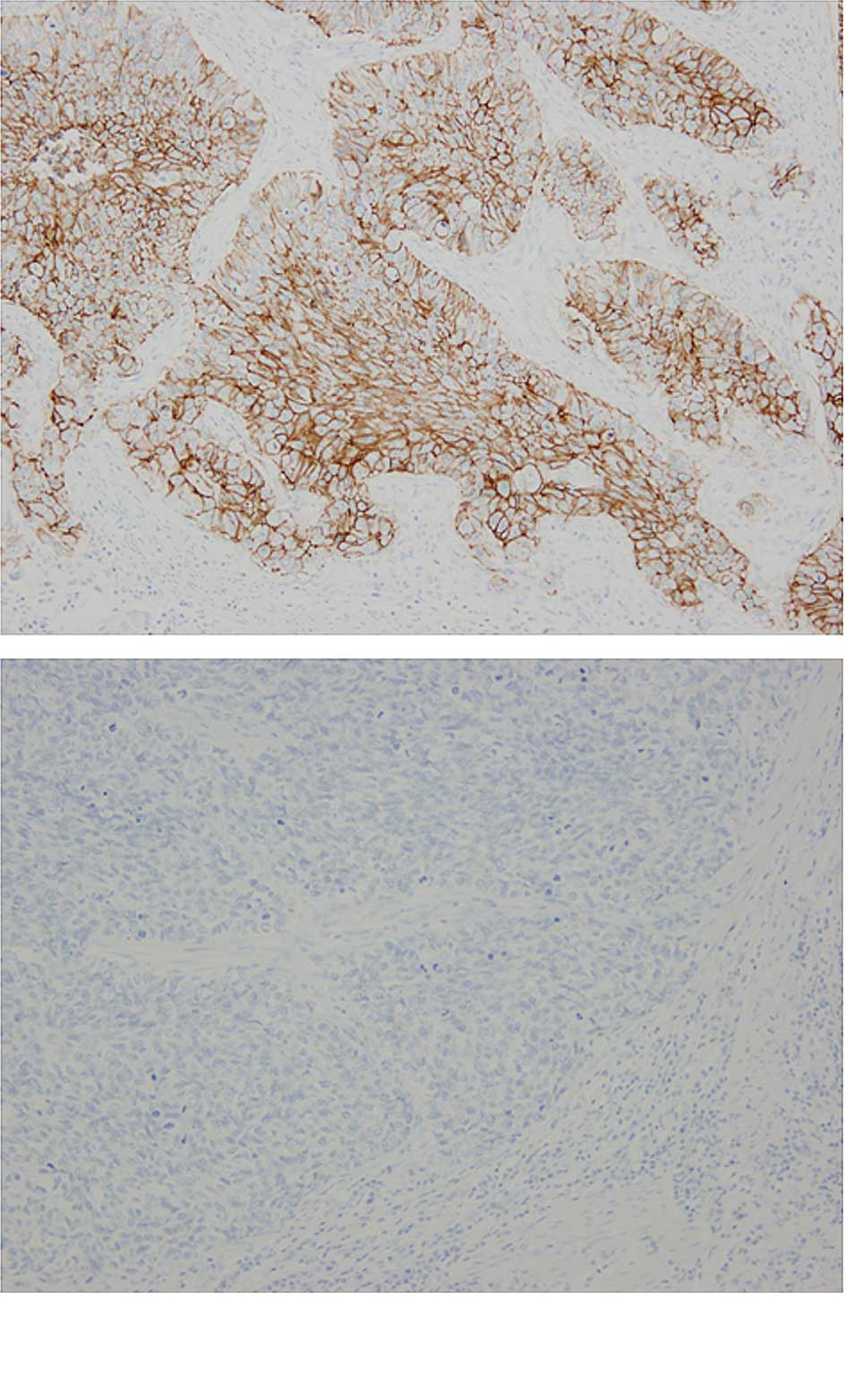
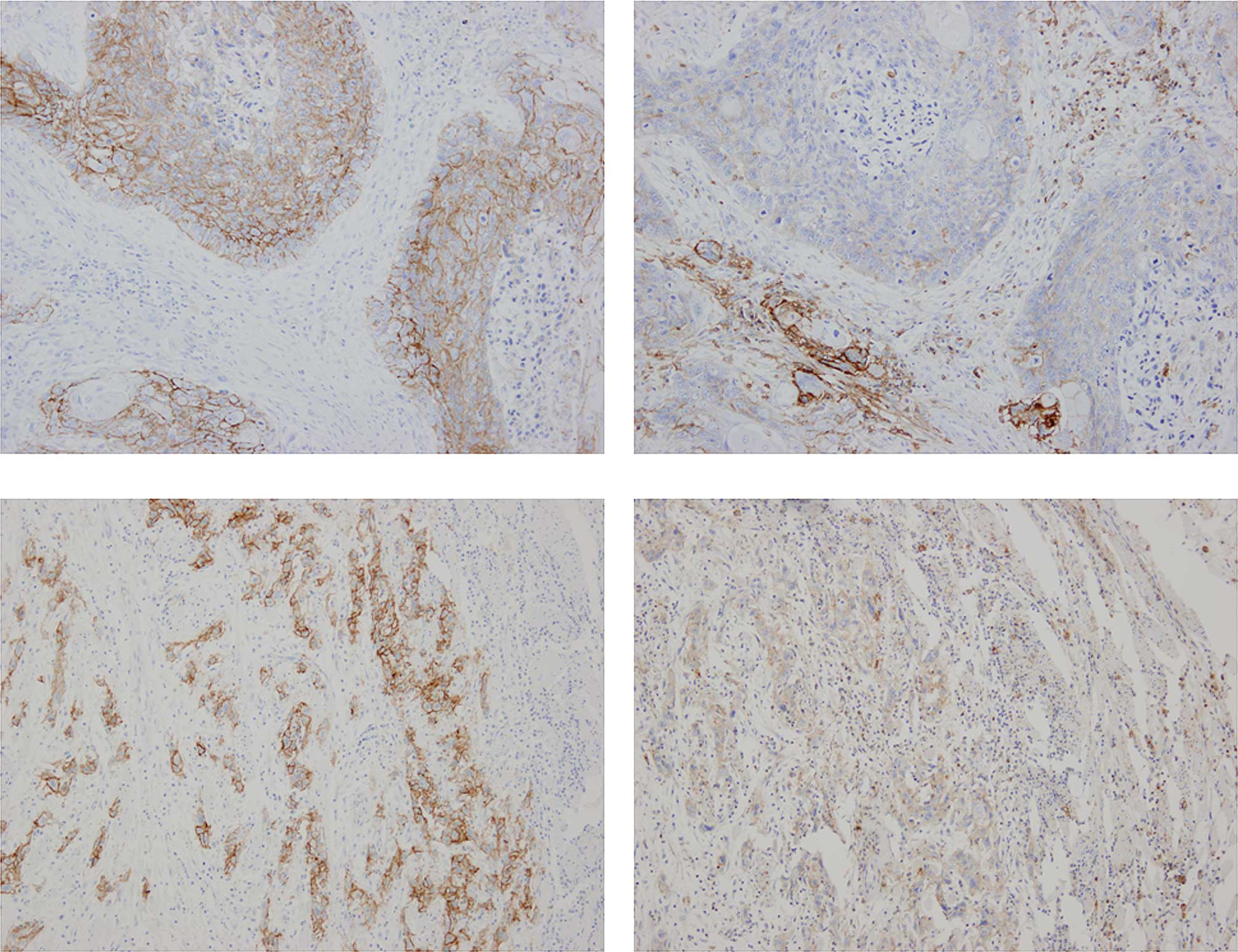
|
1
|
Parkin DM and Bray F: Evaluation of data
quality in the cancer registry: principles and methods Part II.
Completeness. Eur J Cancer. 45:756–764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lyons AJ and Jones J: Cell adhesion
molecules, the extracellular matrix and oral squamous carcinoma.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 36:671–679. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rautava J, Soukka T, Inki P,
Leimola-Virtanen R, Saloniemi I, Happonen RP and Heikinheimo K:
CD44v6 in developing, dysplastic and malignant oral epithelia. Oral
Oncol. 39:373–379. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Naor D, Wallach-Dayan SB, Zahalka MA and
Sionov RV: Involvement of CD44, a molecule with a thousand faces,
in cancer dissemination. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:260–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van Weering DH, Baas PD and Bos JL: A
PCR-based method for the analysis of human CD44 splice products.
PCR Methods Appl. 3:100–106. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iida N and Bourguignon LY: New CD44 splice
variants associated with human breast cancers. J Cell Physiol.
162:127–133. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuniyasu H, Oue N, Tsutsumi M, Tahara E
and Yasui W: Heparan sulfate enhances invasion by human colon
carcinoma cell lines through expression of CD44 variant exon 3.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:4067–4072. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pirinen R, Hirvikoski P, Bohm J,
Kellokoski J, Moisio K, Viren M, Johansson R, Hollmen S and Kosma
VM: Reduced expression of CD44v3 variant isoform is associated with
unfavorable outcome in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
31:1088–1095. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuhn S, Koch M, Nubel T, Ladwein M,
Antolovic D, Klingbeil P, Hildebrand D, Moldenhauer G, Langbein L,
Franke WW, Weitz J and Zoller M: A complex of EpCAM, claudin-7,
CD44 variant isoforms, and tetraspanins promotes colorectal cancer
progression. Mol Cancer Res. 5:553–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mizera-Nyczak E, Dyszkiewicz W, Heider KH
and Zeromski J: Isoform expression of CD44 adhesion molecules,
Bcl-2, p53 and Ki-67 proteins in lung cancer. Tumour Biol.
22:45–53. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iida N and Bourguignon LY: Coexpression of
CD44 variant (v10/ex14) and CD44S in human mammary epithelial cells
promotes tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol. 171:152–160. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koyama S, Maruyama T and Adachi S:
Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and CD44 splicing
variants sharing exons 6 and 9 on gastric and esophageal
carcinomas: a two-color flow-cytometric analysis. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 125:47–54. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gotoda T, Matsumura Y, Kondo H, Ono H,
Kanamoto A, Kato H, Watanabe H, Tachimori Y, Nakanishi Y and
Kakizoe T: Expression of CD44 variants and prognosis in oesophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Gut. 46:14–19. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li DM, Li SS, Zhang YH, Zhang HJ, Gao DL
and Wang YX: Expression of human chorionic gonadotropin, CD44v6 and
CD44v4/5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:7401–7404. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gunthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S,
Zoller M, Haussmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H and Herrlich P:
A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to
rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 65:13–24. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seiter S, Arch R, Reber S, Komitowski D,
Hofmann M, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Matzku S and Zoller M: Prevention
of tumor metastasis formation by anti-variant CD44. J Exp Med.
177:443–455. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Van Hal NL, van Dongen GA, Stigter-van
Walsum M, Snow GB and Brakenhoff RH: Characterization of CD44v6
isoforms in head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
82:837–845. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanke M, Fujii M, Kameyama K, Kanzaki J,
Tokumaru Y, Imanishi Y, Tomita T and Matsumura Y:
Clinicopathological significance of expression of CD44 variants in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res.
91:410–415. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heider KH, Sproll M, Susani S, Patzelt E,
Beaumier P, Ostermann E, Ahorn H and Adolf GR: Characterization of
a high-affinity monoclonal antibody specific for CD44v6 as
candidate for immunotherapy of squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 43:245–253. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simon JC, Heider KH, Dietrich A, Wuttig C,
Schopf E, Adolf GR, Ponta H and Herrlich P: Expression of CD44
isoforms in human skin cancer. Eur J Cancer. 32A:1394–1400. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ekici S, Cerwinka WH, Duncan R, Gomez P,
Civantos F, Soloway MS and Lokeshwar VB: Comparison of the
prognostic potential of hyaluronic acid, hyaluronidase (HYAL-1),
CD44v6 and microvessel density for prostate cancer. Int J Cancer.
112:121–129. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sonobe S, Miyamoto H, Nobukawa B, Izumi H,
Futagawa T, Ishikawa N, Yamazaki A, Uekusa T, Abe H and Suda K:
Prognostic value of CD44 isoform expression in thymic epithelial
neoplasms. Cancer. 103:2015–2022. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaufmann M, Heider KH, Sinn HP, von
Minckwitz G, Ponta H and Herrlich P: CD44 variant exon epitopes in
primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet. 345:615–619.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lipponen P, Aaltoma S, Kosma VM, Ala-Opas
M and Eskelinen M: Expression of CD44 standard and variant-v6
proteins in transitional cell bladder tumours and their relation to
prognosis during a long-term follow-up. J Pathol. 186:157–164.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heider KH, Kuthan H, Stehle G and Munzert
G: CD44v6: a target for antibody-based cancer therapy. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 53:567–579. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stroomer JW, Roos JC, Sproll M, Quak JJ,
Heider KH, Wilhelm BJ, Castelijns JA, Meyer R, Kwakkelstein MO,
Snow GB, Adolf GR and van Dongen GA: Safety and biodistribution of
99mTechnetium-labeled anti-CD44v6 monoclonal antibody BIWA 1 in
head and neck cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 6:3046–3055.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Riechelmann H, Sauter A, Golze W, Hanft G,
Schroen C, Hoermann K, Erhardt T and Gronau S: Phase I trial with
the CD44v6-targeting immunoconjugate bivatuzumab mertansine in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 44:823–829. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Orian-Rousseau V, Chen L, Sleeman JP,
Herrlich P and Ponta H: CD44 is required for two consecutive steps
in HGF/c-Met signaling. Genes Dev. 16:3074–3086. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tremmel M, Matzke A, Albrecht I, Laib AM,
Olaku V, Ballmer-Hofer K, Christofori G, Heroult M, Augustin HG,
Ponta H and Orian-Rousseau V: A CD44v6 peptide reveals a role of
CD44 in VEGFR-2 signaling and angiogenesis. Blood. 114:5236–5244.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|