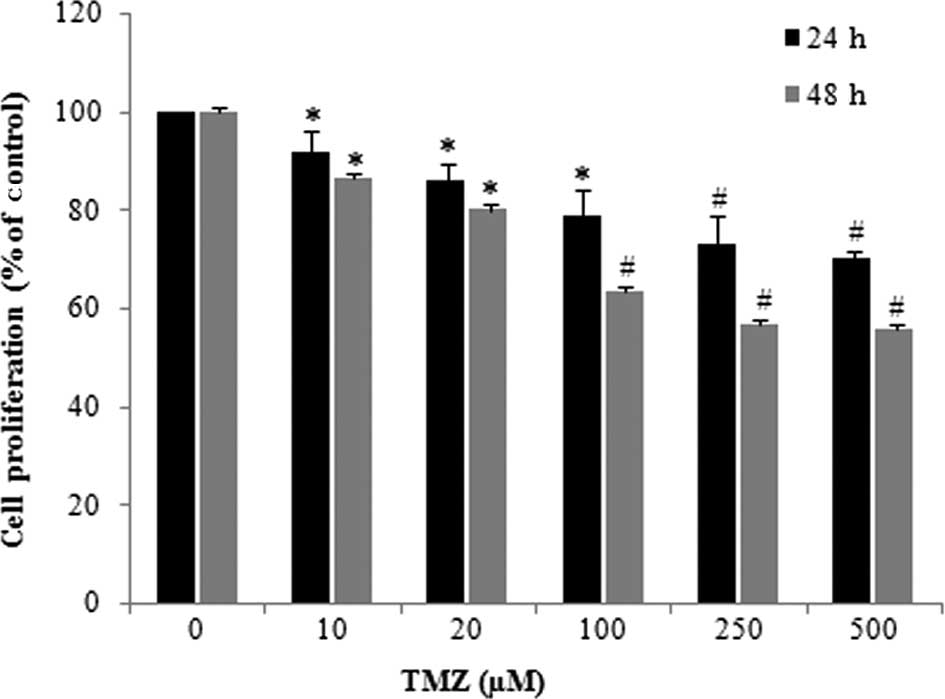
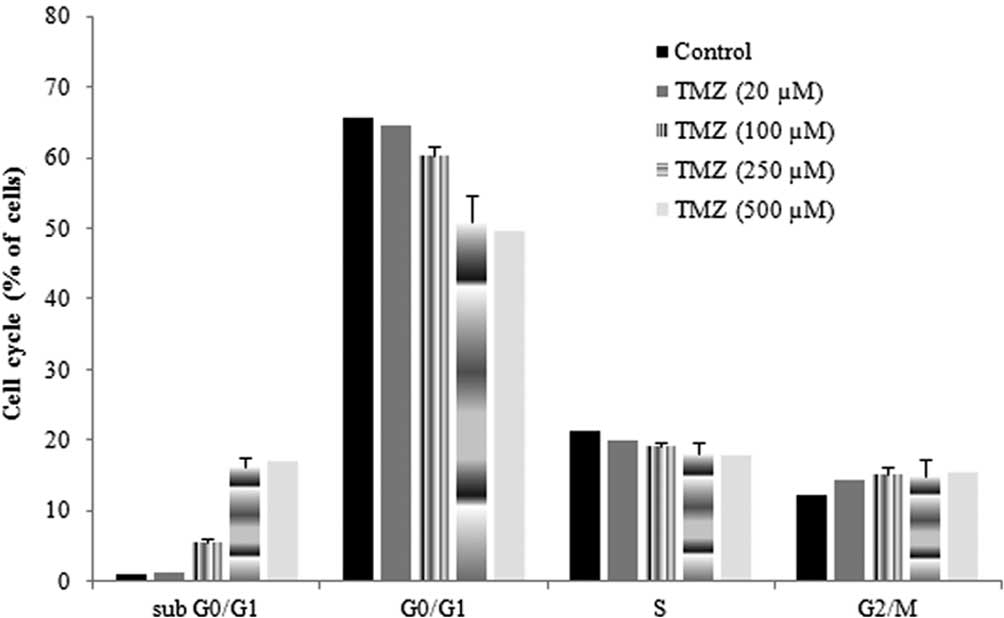
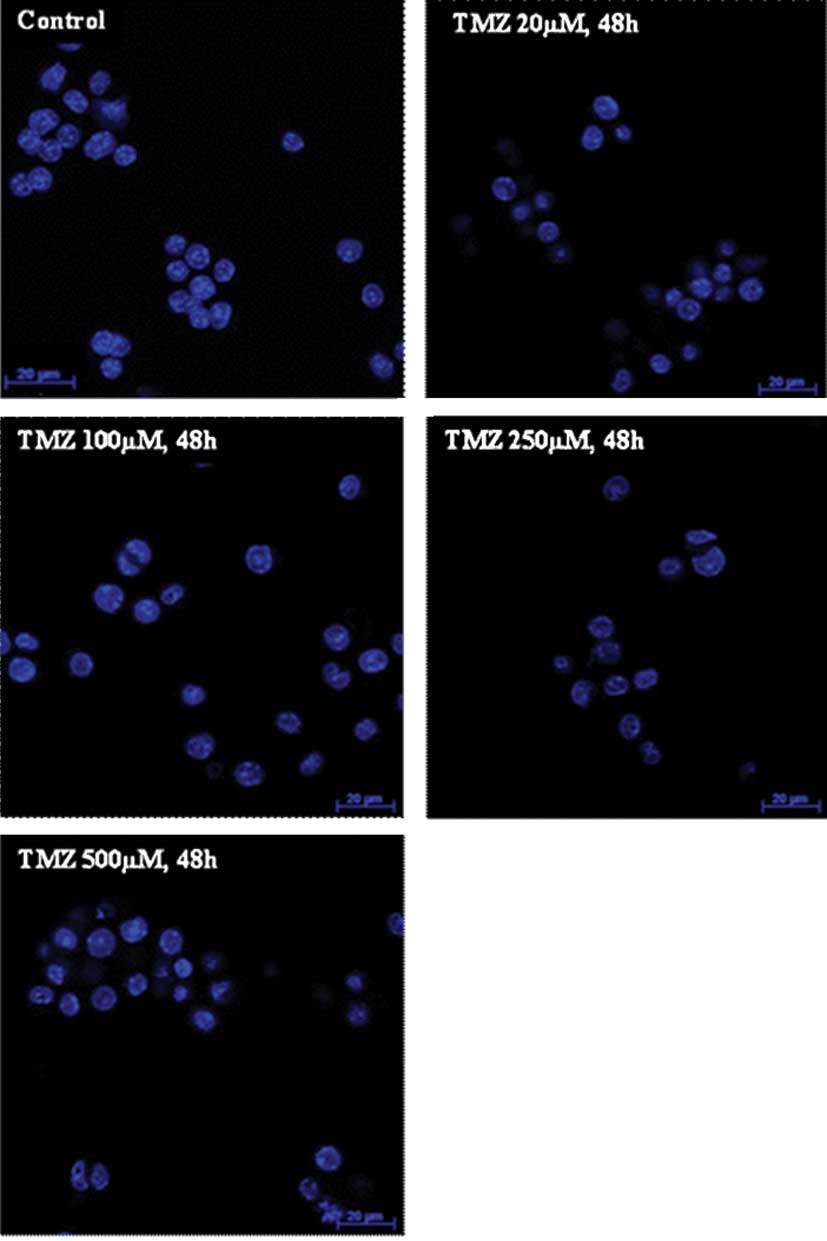
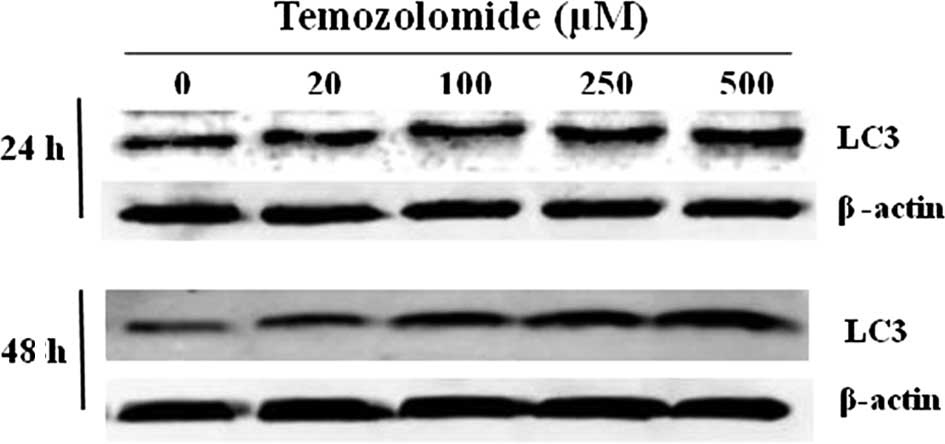
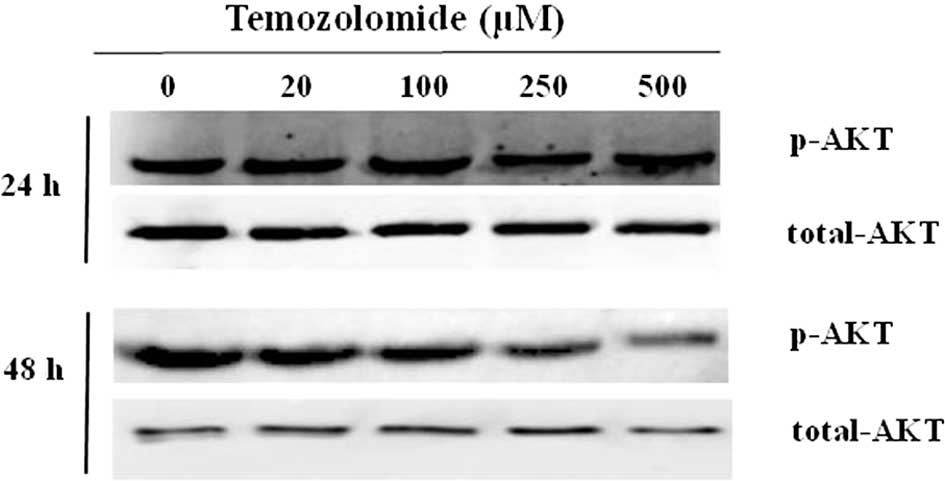
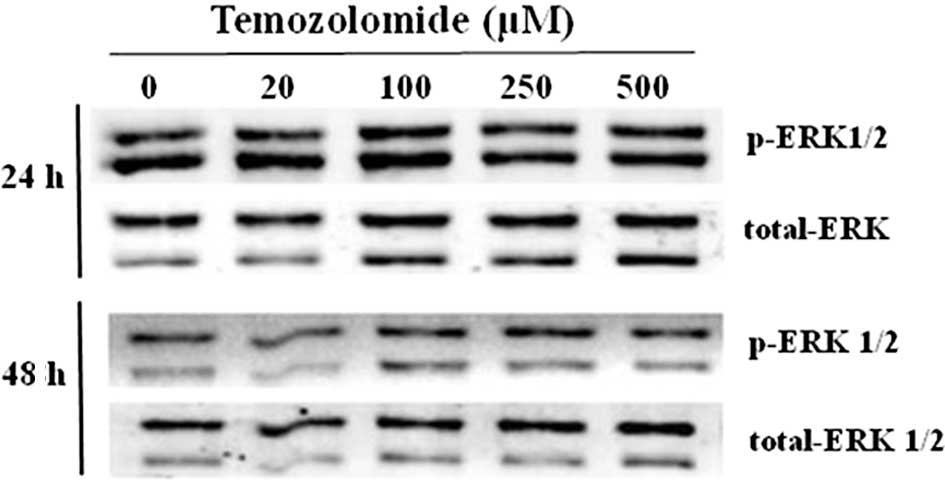
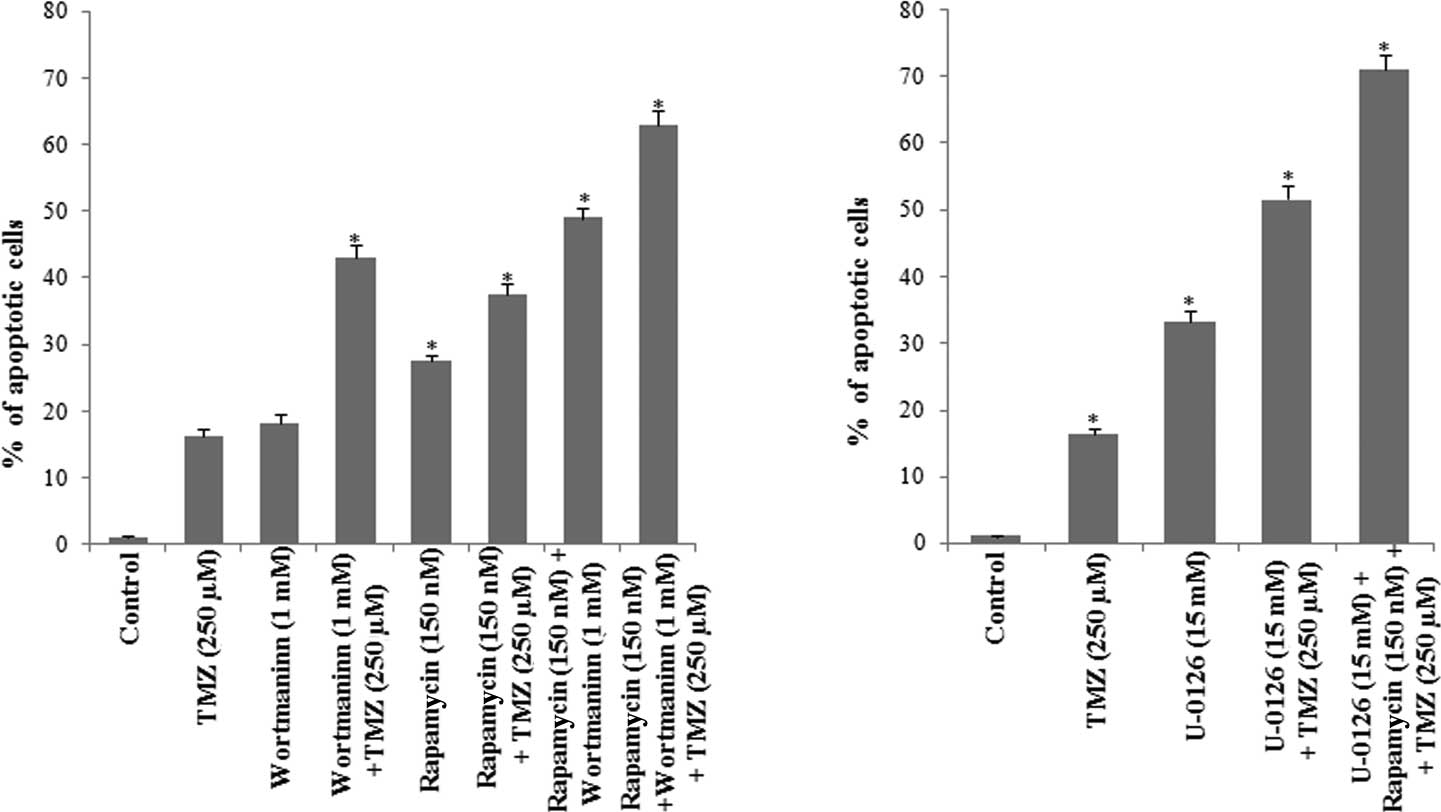
|
1
|
Schwartzbaum JA, Fisher JL, Aldape KD and
Wrensch M: Epidemiology and molecular pathology of glioma. Nat Clin
Pract Neurol. 2:494–503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Epidemiology and
etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 109:93–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
CBTRUS. Statistical Report: Primary Brain
Tumors in the United States, 2004—2006. Central Brain Tumor
Registry of the United States; pp. 1–65. 2010
|
|
4
|
Hadjipanayis CG and van Meir EG: Brain
cancer propagating cells: biology, genetics and targeted therapies.
Trends Mol Med. 15:519–530. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al:
Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO:
Abrogation of the Chk1-mediated G(2) checkpoint pathway potentiates
temozolomide-induced toxicity in a p53-independent manner in human
glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 61:5843–5849. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced
cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ.
11:448–457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hegi M, Diserens A, Gorlia T, et al: MGMT
gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N
Engl J Med. 352:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Keating AK, Kim GK, Jones AE, Donson AM,
Ware K, Mulcahy JM, Salzberg DB, Foreman NK, Liang X, Thorburn A
and Graham DK: Inhibition of Mer and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases
in astrocytoma cells leads to increased apoptosis and improved
chemosensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1298–1307. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akhavan D, Cloughesy TF and Mischel PS:
mTOR signaling in glioblastoma: lessons learned from bench to
bedside. Neuro Oncol. 12:882–889. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mrugala MM and Chamberlain MC: Mechanisms
of disease: temozolomide and glioblastoma – look to the future. Nat
Clin Pract Oncol. 5:476–486. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Hirose Y, Katayama M, Mirzoeva OK, Berger
MS and Pieper RO: Akt activation suppresses Chk2-mediated,
methylating agent-induced G2 arrest and protects from
temozolomide-induced mitotic catastrophe and cellular senescence.
Cancer Res. 65:4861–4869. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carmo A, Patricio I, Cruz MT, Carvalheiro
H and Lopes MC: CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes motility and proliferation of
glioma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:56–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Neves BM, Cruz MT, Francisco V, Goncalo M,
Figueiredo A, Duarte CB and Lopes MC: Differential modulation of
CXCR4 and CD40 protein levels by skin sensitizers and irritants in
the FSDC cell line. Toxicol Lett. 177:74–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD,
Shu H, Wen PY and Olson JJ: Exciting new advances in
neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA
Cancer J Clin. 60:166–193. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sathornsumetee S, Reardon DA, Desjardins
A, Quinn JA, Vredenburgh JJ and Rich JN: Molecularly targeted
therapy for malignant glioma. Cancer. 110:13–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Furnari F, Fenton T, Bachoo R, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma:genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes and Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gladson CL, Prayson RA and Liu WM: The
pathobiology of glioma tumors. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. 5:33–50.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hirose Y, Berger MS and Pieper RO: p53
effects both the duration of G2/M arrest and the fate of
temozolomide-treated human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res.
61:1957–1963. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Roos WP, Batista LF, Naumann SC, Wick W,
Weller M, Menck CF and Kaina B: Apoptosis in malignant glioma cells
triggered by the temozolomide-induced DNA lesion O6-methylguanine.
Oncogene. 26:186–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ogier-Denisy E and Codogno P: Autophagy: a
barrier or an adaptive response to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1603:113–128. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mariño G and López-Otín C: Autophagy:
molecular mechanisms, physiological functions and relevance in
human pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:1439–1454. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu J, Shao C, Chen F, Ng H and Chen Z:
Autophagy induced by valproic acid is associated with oxidative
stress in glioma cell lines. Neuro Oncol. 12:328–340. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thorburn A: Apoptosis and autophagy:
regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes.
Apoptosis. 13:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Katayama M, Kawaguchi T, Berger MS and
Pieper RO: DNA damaging agent-induced autophagy produces a
cytoprotective adenosine triphosphate surge in malignant glioma
cells. Cell Death Differ. 14:548–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lorente A, Mueller W, Urdangarín E, Lázcoz
P, Deimling A and Castresana JS: Detection of methylation in
promoter sequences by melting curve analysis-based semiquantitative
real time PCR. BMC Cancer. 8:61–75. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ronellenfitsch MW, Brucker DP, Burger MC,
Wolking S, Tritschler F, Rieger J, Wick W, Weller M and Steinbach
JP: Antagonism of the mammalian target of rapamycin selectively
mediates metabolic effects of epidermal growth factor receptor
inhibition and protects human malignant glioma cells
fromhypoxia-induced cell death. Brain. 13:1509–1522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Law BK: Rapamycin: an anti-cancer
immunosuppressant? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 56:47–60. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meloche S and Pouyssegur J: The ERK1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of
the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 26:3227–3239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tran SE, Holmstrom TH, Ahonen M, Kahari VM
and Eriksson JE: MAPK/ERK overrides the apoptotic signaling from
Fas, TNF, and TRAIL receptors. J Biol Chem. 276:16484–16490. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|