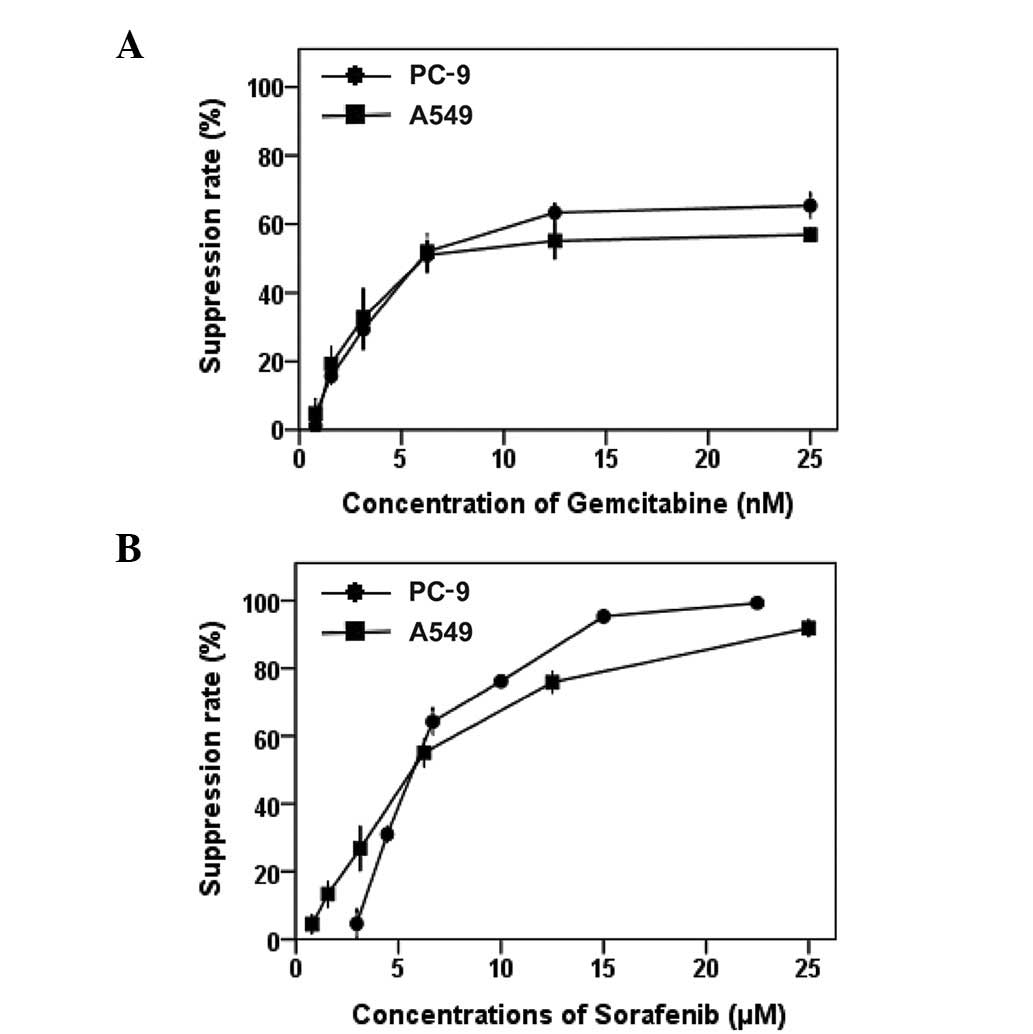
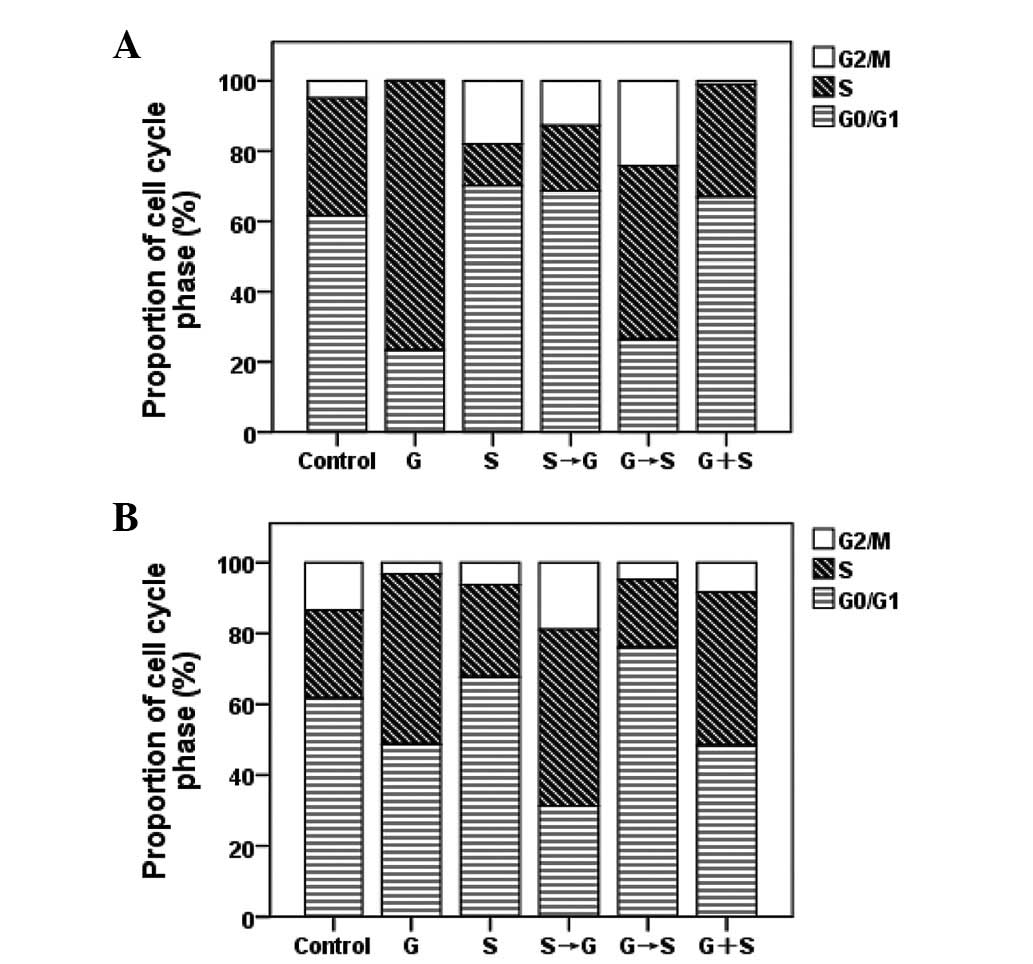
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al:
Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al:
Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Masago K, Fujita S, Togashi Y, et al:
Clinicopathologic factors affecting the progression-free survival
of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after
gefitinib therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. 12:56–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, et al: KRAS
mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to
gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2:e172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Gazdar AF: Activating and resistance
mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical
response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene. 28:S24–S31.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Rodenhuis S, Slebos RJ, Boot AJ, et al:
Incidence and possible clinical significance of K-ras oncogene
activation in adenocarcinoma of the human lung. Cancer Res.
48:5738–5741. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Mitsudomi T, Kosaka T, Endoh H, et al:
Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene predict
prolonged survival after gefitinib treatment in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer with postoperative recurrence. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2513–2520. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, et al:
Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to
gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5764–5769. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Toi M, Matsumoto T and Bando H: Vascular
endothelial growth factor:its prognostic, predictive, and
therapeutic implications. Lancet Oncol. 2:667–673. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM and Cortes JE:
Biology of platelet-derived growth factor and its involvement in
disease. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 81:1241–1257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wu E, Palmer N, Tian Z, et al:
Comprehensive dissection of PDGF-PDGFR signaling pathways in PDGFR
genetically defined cells. PLoS One. 3:e37942008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Erber R, Thurnher A, Katsen AD, et al:
Combined inhibition of VEGF and PDGF signaling enforces tumor
vessel regression by interfering with pericyte-mediated endothelial
cell survival mechanisms. FASEB J. 18:338–340. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Shikada Y, Yonemitsu Y, Koga T, et al:
Platelet-derived growth factor-AA is an essential and autocrine
regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cancer Res. 65:7241–7248. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Busund
LT and Bremnes RM: Co-expression of PDGF-B and VEGFR-3 strongly
correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor survival in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 21:223–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Kanaloupiti D, et
al: Assessment of somatic k-Ras mutations as a mechanism associated
with resistance to EGFR-targeted agents: a systematic review and
meta-analysis of studies in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and
colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 9:962–972. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Rodenhuis S, van de Wetering ML, Mooi WJ,
Evers SG, van Zandwijk N and Bos JL: Mutational activation of the
K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of
the lung. N Engl J Med. 317:929–935. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Lopez-Chavez A, Carter CA and Giaccone G:
The role of KRAS mutations in resistance to EGFR inhibition in the
treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 10:1305–1314.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets
the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Dal Lago L, D’Hondt V and Awada A:
Selected combination therapy with sorafenib: a review of clinical
data and perspectives in advanced solid tumors. Oncologist.
13:845–858. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Blumenschein GR Jr, Gatzemeier U, Fossella
F, et al: Phase II, multicenter, uncontrolled trial of single-agent
sorafenib in patients with relapsed or refractory, advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:4274–4280. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Dy GK, Hillman SL, Rowland KM Jr, et al
North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study N0326: A front-line
window of opportunity phase 2 study of sorafenib in patients with
advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: North Central Cancer Treatment
Group Study N0326. Cancer. 116:5686–5693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Carter CA, Chen C, Brink C, et al:
Sorafenib is efficacious and tolerated in combination with
cytotoxic or cytostatic agents in preclinical models of human
non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
59:183–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Scagliotti G, Novello S, von Pawel J, et
al: Phase III study of carboplatin and paclitaxel alone or with
sorafenib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1835–1842. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Paz-Ares LG, Biesma B, Heigener D, et al:
Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
gemcitabine/cisplatin alone or with sorafenib for the first-line
treatment of advanced, nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 30:3084–3092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Plastaras JP, Kim SH, Liu YY, et al: Cell
cycle dependent and schedule-dependent antitumor effects of
sorafenib combined with radiation. Cancer Res. 67:9443–9454. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Takezawa K, Okamoto I, Yonesaka K,
Hatashita E, Yamada Y, Fukuoka M and Nakagawa K: Sorafenib inhibits
non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by targeting B-RAF in KRAS
wild-type cells and C-RAF in KRAS mutant cells. Cancer Res.
69:6515–6521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Mahaffey CM, Davies AM, Lara PN Jr, et al:
Schedule-dependent apoptosis in K-ras mutant non-small-cell lung
cancer cell lines treated with docetaxel and erlotinib: rationale
for pharmacodynamic separation. Clin Lung Cancer. 8:548–553. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Cheng H, An SJ, Zhang XC, et al: In vitro
sequence-dependent synergism between paclitaxel and gefitinib in
human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
67:637–646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Dougherty DW and Friedberg JW: Gemcitabine
and other new cytotoxic drugs: will any find their way into primary
therapy? Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 5:148–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Strumberg D, Clark JW, Awada A, et al:
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary antitumor activity of
sorafenib: a review of four phase I trials in patients with
advanced refractory solid tumors. Oncologist. 12:426–437. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Rajeswaran A, Trojan A, Burnand B and
Giannelli M: Efficacy and side effects of cisplatin- and
carboplatin-based doublet chemotherapeutic regimens versus
non-platinum-based doublet chemotherapeutic regimens as first line
treatment of meta-static non-small cell lung carcinoma: a
systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Lung Cancer.
59:1–11. 2008.
|
|
36.
|
Maemondo M: Timing the change of
chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
39:1316–1319. 2012.(in Japanese).
|
|
37.
|
Ayoola A, Barochia A, Belani K and Belani
CP: Primary and acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer:
an update. Cancer Invest. 30:433–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Petrelli A and Giordano S: From single- to
multi-target drugs in cancer therapy: when aspecificity becomes an
advantage. Curr Med Chem. 15:422–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Pasqualetti G, Ricciardi S, Mey V, Del
Tacca M and Danesi R: Synergistic cytotoxicity, inhibition of
signal transduction pathways and pharmacogenetics of sorafenib and
gemcitabine in human NSCLC cell lines. Lung Cancer. 74:197–205.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Zhang XH, Shin JY, Kim JO, Oh JE, Yoon SA,
Jung CK and Kang JH: Synergistic antitumor efficacy of sequentially
combined paclitaxel with sorafenib in vitro and in vivo NSCLC
models harboring KRAS or BRAF mutations. Cancer Lett. 322:213–222.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Ulivi P, Arienti C, Zoli W, et al: In
vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy of docetaxel and sorafenib
combination in human pancreatic cancer cells. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 10:600–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Torres K and Horwitz SB: Mechanisms of
taxol-induced cell death are concentration dependent. Cancer Res.
58:3620–3626. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Li QL, Gu FM, Wang Z, et al: Activation of
PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathway through a PDGFRβ-dependent feedback loop
is involved in rapamycin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
PLoS One. 7:e333792012.
|